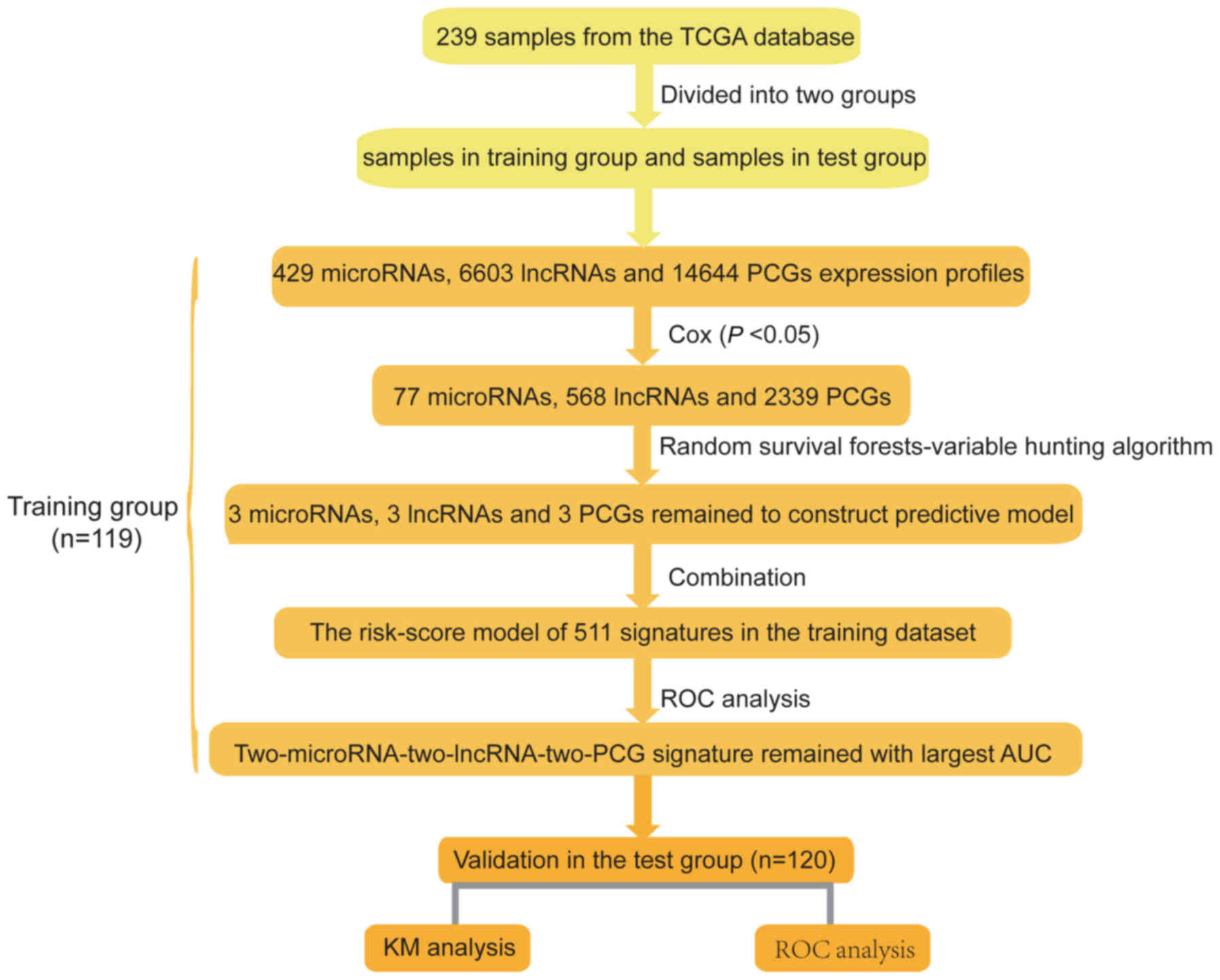
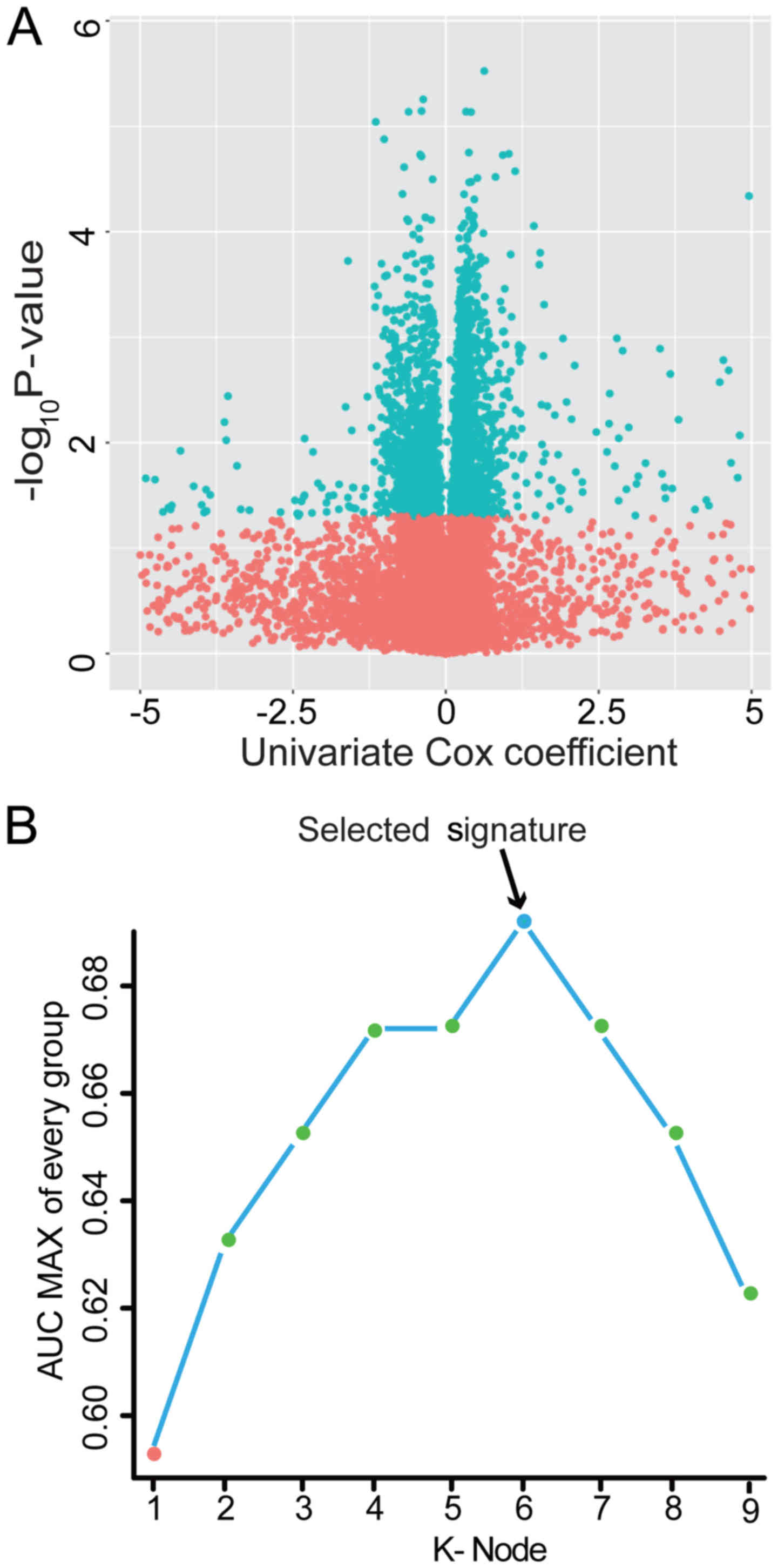
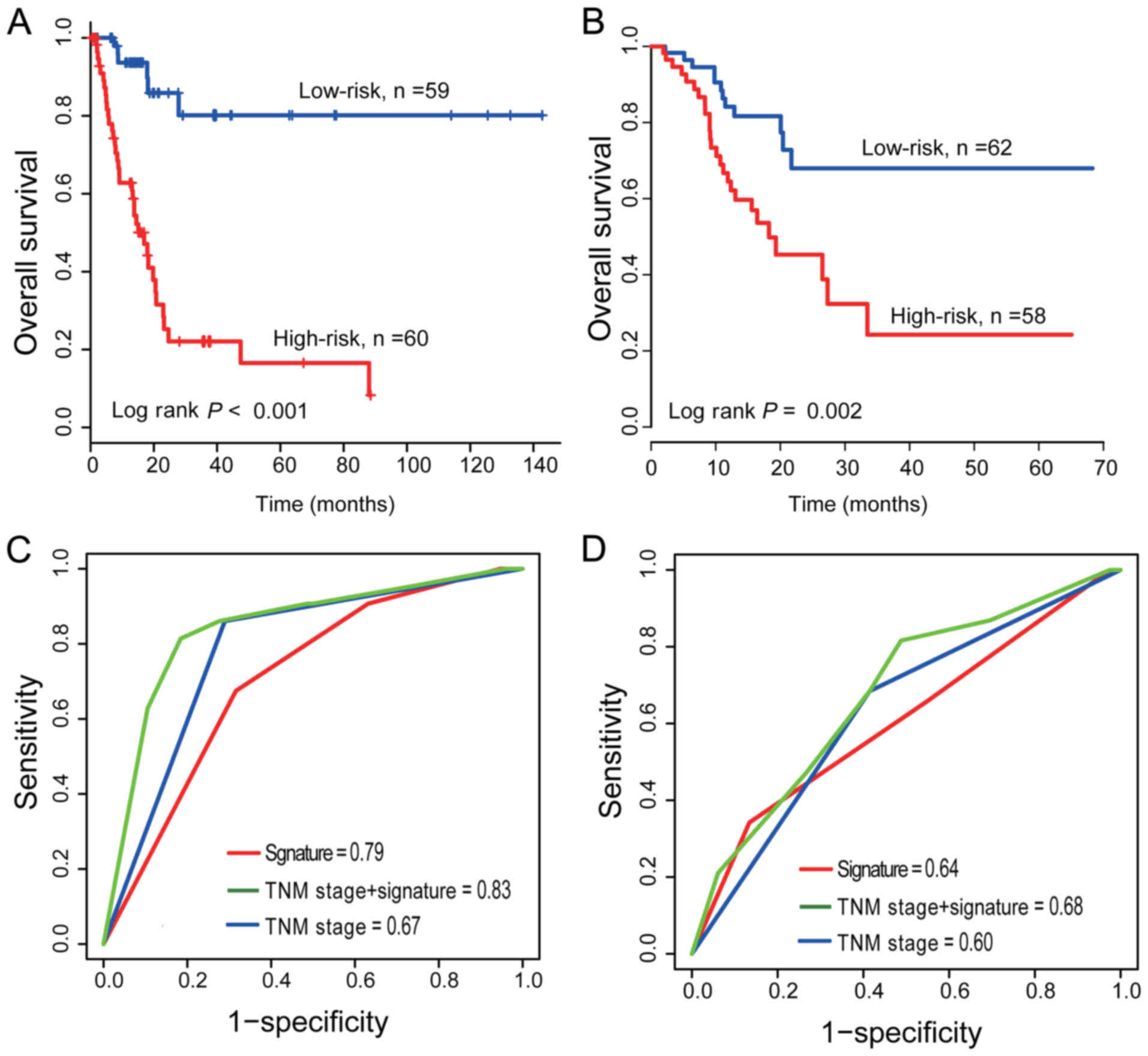
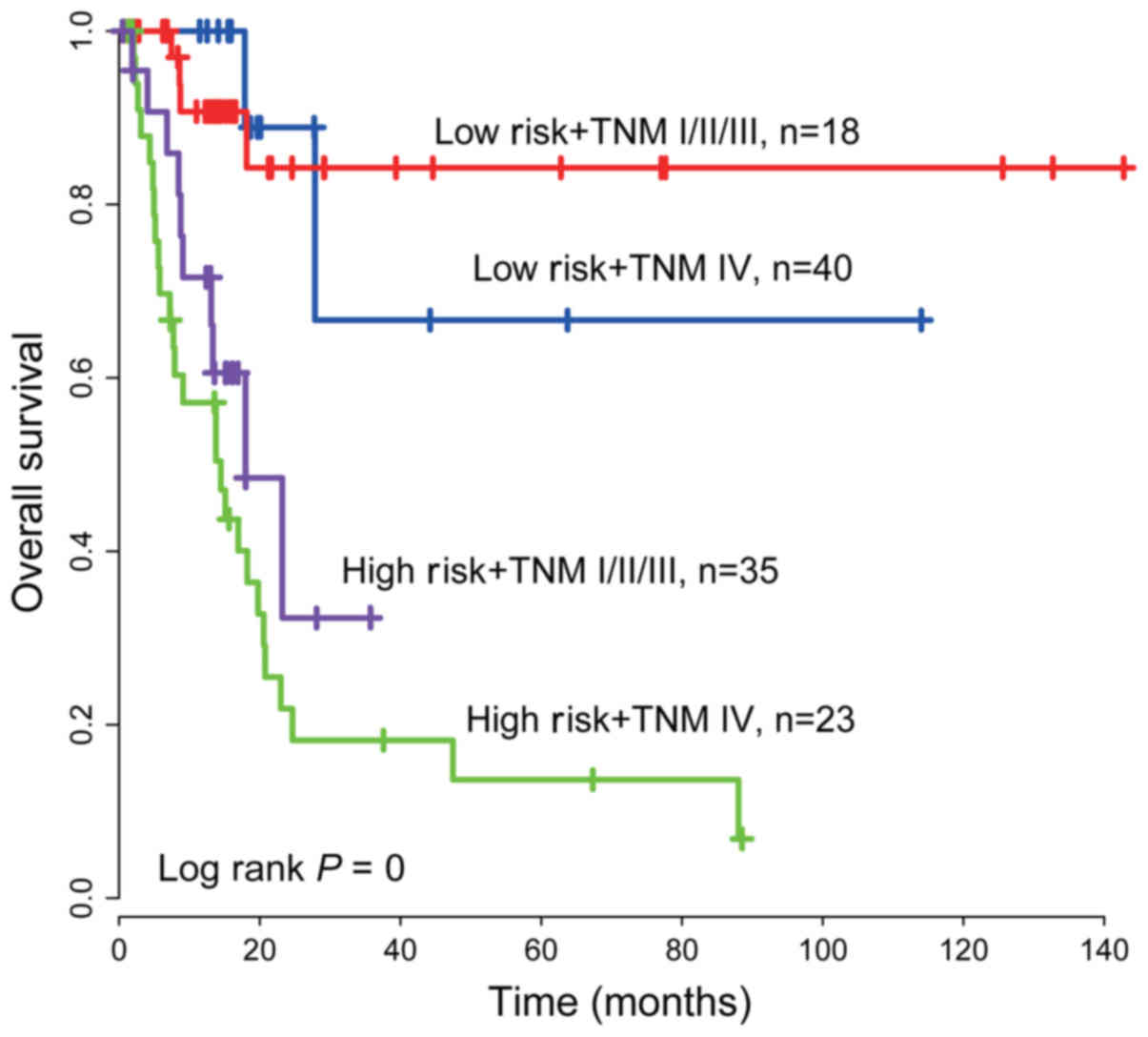
|
1
|
Clark PE, Spiess PE, Agarwal N, Bangs R,
Boorjian SA, Buyyounouski MK, Efstathiou JA, Flaig TW, Friedlander
T, Greenberg RE, et al: NCCN Guidelines Insights: Bladder cancer,
version 2.2016. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 14:1213–1224. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Solomon JP and Hansel DE: Prognostic
factors in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: Histologic and
molecular correlates. Adv Anat Pathol. 22:102–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dykes IM and Emanueli C: Transcriptional
and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA.
Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 15:177–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Petrovic N, Ergun S and Isenovic ER:
Levels of microRNA heterogeneity in cancer biology. Mol Diagn Ther.
21:511–523. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adams BD, Parsons C, Walker L, Zhang WC
and Slack FJ: Targeting noncoding RNAs in disease. J Clin Invest.
127:761–771. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo JC, Li CQ, Wang QY, Zhao JM, Ding JY,
Li EM and Xu LY: Protein-coding genes combined with long non-coding
RNAs predict prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
patients as a novel clinical multi-dimensional signature. Mol
Biosyst. 12:3467–3477. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo JC, Wu Y, Chen Y, Pan F, Wu ZY, Zhang
JS, Wu JY, Xu XE, Zhao JM, Li EM, et al: Protein-coding genes
combined with long noncoding RNA as a novel transcriptome molecular
staging model to predict the survival of patients with esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 38:42018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shang C, Guo Y, Zhang H and Xue YX: Long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR is a prognostic biomarker and inhibits
chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in bladder transitional cell
carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 77:507–513. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Y, Lu W, Xu J, Shi Y, Zhang H and Xia
D: Prognostic value of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer
patients. Tumour Biol. 37:897–903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M, Lioudmer P,
Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Miller K, Kilic E, Erbersdobler A, Weikert
S, et al: miRNA profiling identifies candidate mirnas for bladder
cancer diagnosis and clinical outcome. J Mol Diagn. 15:695–705.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang S, Li Q, Wang K, Dai Y, Yang J, Xue
S, Han F, Zhang Q, Liu J and Wu W: Decreased expression of
microRNA-31 associates with aggressive tumor progression and poor
prognosis in patients with bladder cancer. Clin Transl Oncol.
15:849–854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Xue S, Dai Y, Yang J, Chen Z, Fang
X, Zhou W, Wu W and Li Q: Reduced expression of microRNA-100
confers unfavorable prognosis in patients with bladder cancer.
Diagn Pathol. 7:1592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Villadsen SB, Bramsen JB, Ostenfeld MS,
Wiklund ED, Fristrup N, Gao S, Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Borre M,
Ørntoft TF, et al: The miR-143/-145 cluster regulates plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:366–374.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bao Z, Zhang W and Dong D: A potential
prognostic lncRNA signature for predicting survival in patients
with bladder urothelial carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:10485–10497. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou H, Tang K, Xiao H, Zeng J, Guan W,
Guo X, Xu H and Ye Z: A panel of eight-miRNA signature as a
potential biomarker for predicting survival in bladder cancer. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang X, Du L, Duan W, Wang R, Yan K, Wang
L, Li J, Zheng G, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al: Serum microRNA expression
signatures as novel noninvasive biomarkers for prediction and
prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
7:36733–36742. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mitra AP, Pagliarulo V, Yang D, Waldman
FM, Datar RH, Skinner DG, Groshen S and Cote RJ: Generation of a
concise gene panel for outcome prediction in urinary bladder
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:3929–3937. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Taylor J, Eustace A, Irlam JJ,
Denley H, Hoskin PJ, Alsner J, Buffa FM, Harris AL, Choudhury A, et
al: A gene signature for selecting benefit from hypoxia
modification of radiotherapy for high-risk bladder cancer patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:4761–4768. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu J, Li Y, Lu J, Pan T, Ding N, Wang Z,
Shao T, Zhang J, Wang L and Li X: The mRNA related ceRNA-ceRNA
landscape and significance across 20 major cancer types. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43:8169–8182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Chen Z, Tian L, Zhou C, He MY, Gao
Y, Wang S, Zhou F, Shi S, Feng X, et al: LncRNA profile study
reveals a three-lncRNA signature associated with the survival of
patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gut.
63:1700–1710. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou M, Guo M, He D, Wang X, Cui Y, Yang
H, Hao D and Sun J: A potential signature of eight long non-coding
RNAs predicts survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
J Transl Med. 13:2312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo JC, Xie YM, Ran LQ, Cao HH, Sun C, Wu
JY, Wu ZY, Liao LD, Zhao WJ, Fang WK, et al: L1CAM drives
oncogenicity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by stimulation
of ezrin transcription. J Mol Med. 95:1355–1368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tse LA, Dai J, Chen M, Liu Y, Zhang H,
Wong TW, Leung CC, Kromhout H, Meijer E, Liu S, et al: Prediction
models and risk assessment for silicosis using a retrospective
cohort study among workers exposed to silica in China. Sci Rep.
5:110592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heagerty PJ, Lumley T and Pepe MS:
Time-dependent ROC curves for censored survival data and a
diagnostic marker. Biometrics. 56:337–344. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP and
Pauler FM: Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA
transcription. BMC Biol. 11:592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:7–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang XQ, Sun S, Lam KF, Kiang KM, Pu JK,
Ho AS, Lui WM, Fung CF, Wong TS and Leung GK: A long non-coding RNA
signature in glioblastoma multiforme predicts survival. Neurobiol
Dis. 58:123–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wan J, Wu W, Che Y, Kang N and Zhang R:
Insights into the potential use of microRNAs as a novel class of
biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 29:412–420. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Geng Q, Fan T, Zhang B, Wang W, Xu Y and
Hu H: Five microRNAs in plasma as novel biomarkers for screening of
early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Respir Res. 15:1492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hauptman N and Glavac D: Long non-coding
RNA in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:4655–4669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du Z, Fei T, Verhaak RG, Su Z, Zhang Y,
Brown M, Chen Y and Liu XS: Integrative genomic analyses reveal
clinically relevant long noncoding RNAs in human cancer. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 20:908–913. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheetham SW, Gruhl F, Mattick JS and
Dinger ME: Long noncoding RNAs and the genetics of cancer. Br J
Cancer. 108:2419–2425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peterson JM, Wei Z and Wong GW: CTRP8 and
CTRP9B are novel proteins that hetero-oligomerize with C1q/TNF
family members. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 388:360–365. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen Y and Su Z: Reveal genes functionally
associated with ACADS by a network study. Gene. 569:294–302. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|