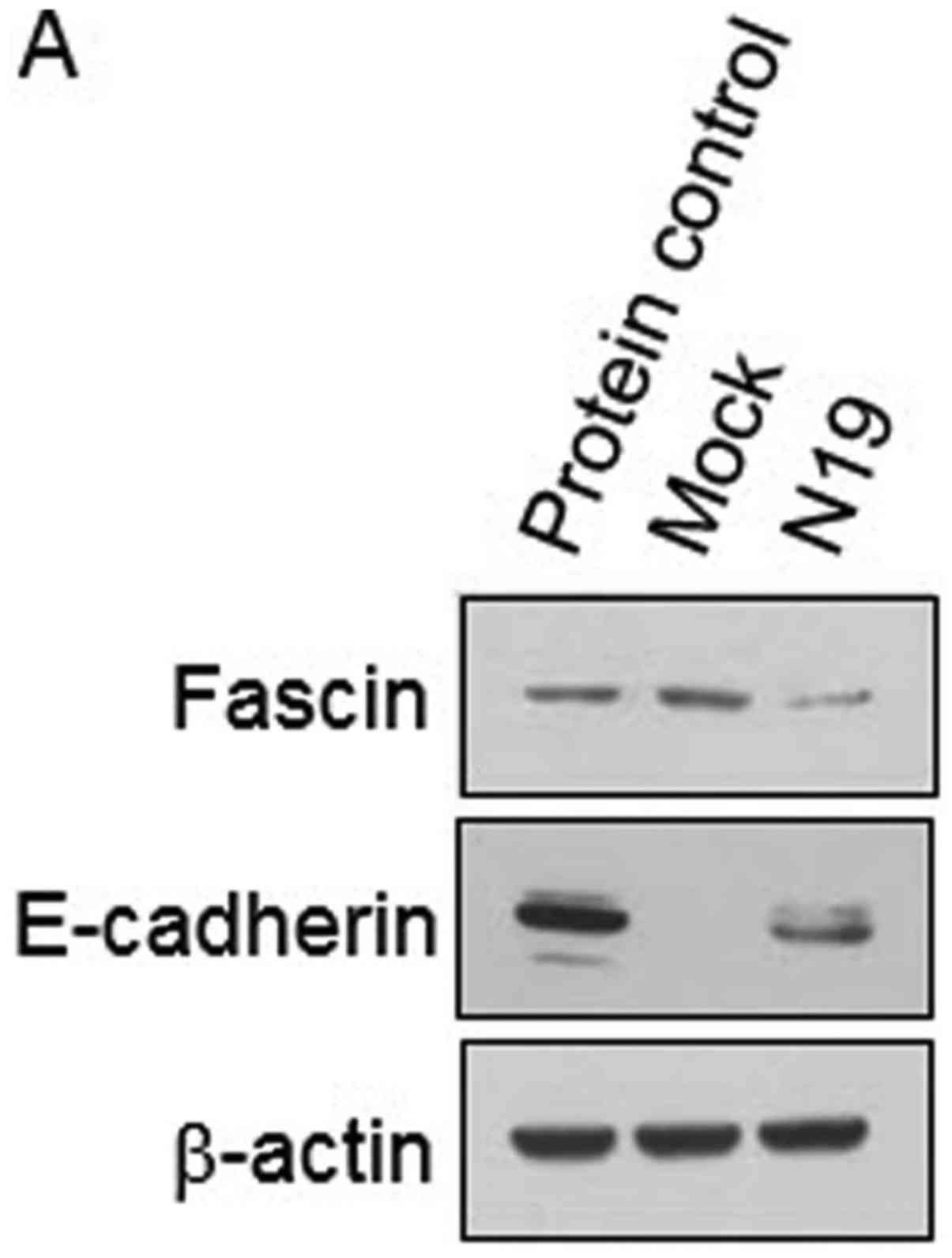
|
1
|
Guan X: Cancer metastases: Challenges and
opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:402–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eddy RJ, Weidmann MD, Sharma VP and
Condeelis JS: Tumor cell invadopodia: Invasive protrusions that
orchestrate metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 27:595–607. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA and
Weinberg RA: EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:128–134. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gould CM and Courtneidge SA: Regulation of
invadopodia by the tumor microenvironment. Cell Adh Migr.
8:226–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li A, Dawson JC, Forero-Vargas M, Spence
HJ, Yu X, König I, Anderson K and Machesky LM: The actin-bundling
protein fascin stabilizes actin in invadopodia and potentiates
protrusive invasion. Curr Biol. 20:339–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim EJ, Che ZM, Park YJ, Hwang YS, Kim KY,
Jung DW, Jeon NK, Choi YW, Lee EJ and Kim J: Morphogenesis and
biological significance of spindle cell transformation in a spindle
cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 275:61–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Toth M, Sohail A and Fridman R: Assessment
of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) by gelatin zymography. Methods Mol
Biol. 878:121–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hwang YS, Park KK and Chung WY: Stromal
transforming growth factor-beta 1 is crucial for reinforcing the
invasive potential of low invasive cancer. Arch Oral Biol.
59:687–694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bowden ET, Coopman PJ and Mueller SC:
Invadopodia: Unique methods for measurement of extracellular matrix
degradation in vitro. Methods Cell Biol. 63:613–627. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hwang YS, Park KK, Cha IH, Kim J and Chung
WY: Role of insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding protein-3 in
invadopodia formation and the growth of oral squamous cell
carcinoma in athymic nude mice. Head Neck. 34:1329–1339. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hodge JC, Bub J, Kaul S, Kajdacsy-Balla A
and Lindholm PF: Requirement of RhoA activity for increased nuclear
factor kappaB activity and PC-3 human prostate cancer cell
invasion. Cancer Res. 63:1359–1364. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Struckhoff AP, Rana MK and Worthylake RA:
RhoA can lead the way in tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1915–1926. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bremnes RM, Dønnem T, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli
K, Andersen S, Sirera R, Camps C, Marinez I and Busund LT: The role
of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: Emphasis on
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Oncol. 6:209–217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shiga K, Hara M, Nagasaki T, Sato T,
Takahashi H and Takeyama H: Cancer-associated fibroblasts: Their
characteristics and their roles in tumor growth. Cancers.
7:2443–2458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Wever O and Mareel M: Role of tissue
stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol. 200:429–447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Jia Z, Kong J, Zhang F, Fang S, Li
X, Li W, Yang X, Luo Y, Lin B, et al: Carcinoma-associated
fibroblasts lead the invasion of salivary gland adenoid cystic
carcinoma cells by creating an invasive track. PLoS One.
11:e01502472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen S, Niu Y, Yeh S and Chang C: BM-MSCs
promote prostate cancer progression via the conversion of normal
fibroblasts to cancer-associated fibroblasts. Int J Oncol.
47:719–727. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taniwaki K, Fukamachi H, Komori K, Ohtake
Y, Nonaka T, Sakamoto T, Shiomi T, Okada Y, Itoh T, Itohara S, et
al: Stroma-derived matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 promotes
membrane type 1-MMP-dependent tumor growth in mice. Cancer Res.
67:4311–4319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
van Beers EH and Nederlof PM: Array-CGH
and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 8:2102006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Al-Alwan M, Olabi S, Ghebeh H, Barhoush E,
Tulbah A, Al-Tweigeri T, Ajarim D and Adra C: Fascin is a key
regulator of breast cancer invasion that acts via the modification
of metastasis-associated molecules. PLoS One. 6:e273392011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang FK, Han S, Xing B, Huang J, Liu B,
Bordeleau F, Reinhart-King CA, Zhang JJ and Huang XY: Targeted
inhibition of fascin function blocks tumour invasion and metastatic
colonization. Nat Commun. 6:74652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Min KW, Chae SW, Kim DH, Do SI, Kim K, Lee
HJ, Sohn JH, Pyo JS, Kim DH, Oh SJ, et al: Fascin expression
predicts an aggressive clinical course in patients with advanced
breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 10:121–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Darnel AD, Behmoaram E, Vollmer RT, Corcos
J, Bijian K, Sircar K, Su J, Jiao J, Alaoui-Jamali MA and Bismar
TA: Fascin regulates prostate cancer cell invasion and is
associated with metastasis and biochemical failure in prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1376–1383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang CQ, Tang CH, Chang HT, Li XN, Zhao
YM, Su CM, Hu GN, Zhang T, Sun XX, Zeng Y, et al: Fascin-1 as a
novel diagnostic marker of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Med. 5:1983–1988. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takikita M, Hu N, Shou JZ, Giffen C, Wang
QH, Wang C, Hewitt SM and Taylor PR: Fascin and CK4 as biomarkers
for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 31:945–952.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li L, Cao F, Liu B, Luo X, Ma X and Hu Z:
TGF-β induces fascin expression in gastric cancer via
phosphorylation of smad3 linker area. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1890–1896.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun J, He H, Pillai S, Xiong Y, Challa S,
Xu L, Chellappan S and Yang S: GATA3 transcription factor abrogates
Smad4 transcription factor-mediated fascin overexpression,
invadopodium formation, and breast cancer cell invasion. J Biol
Chem. 288:36971–36982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ghebeh H, Al-Khaldi S, Olabi S, Al-Dhfyan
A, Al-Mohanna F, Barnawi R, Tulbah A, Al-Tweigeri T, Ajarim D and
Al-Alwan M: Fascin is involved in the chemotherapeutic resistance
of breast cancer cells predominantly via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Br J
Cancer. 111:1552–1561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hashimoto Y, Loftis DW and Adams JC:
Fascin-1 promoter activity is regulated by CREB and the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in human carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
4:e51302009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Langhans SA: Three-dimensional in vitro
cell culture models in drug discovery and drug repositioning. Front
Pharmacol. 9:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|