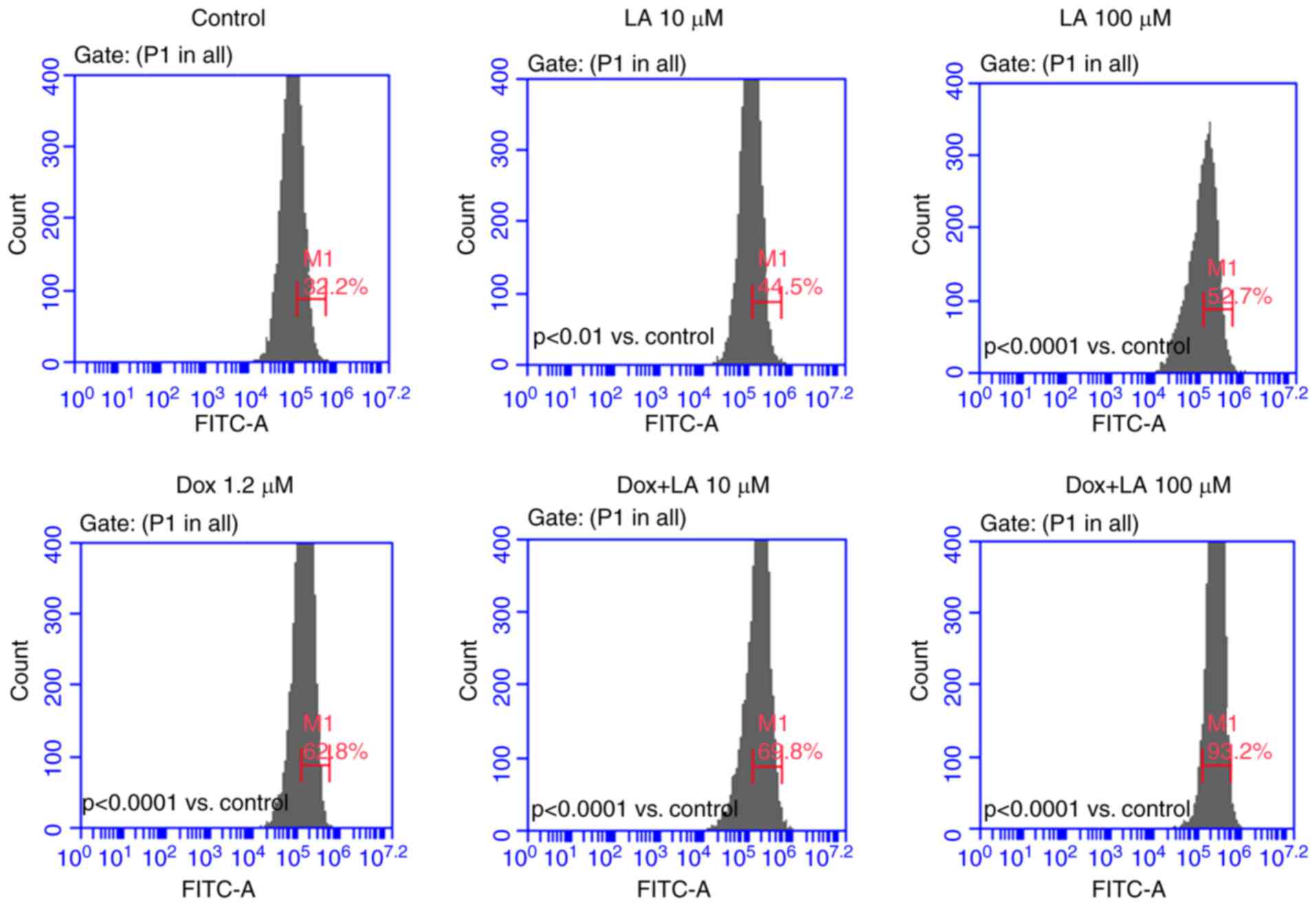
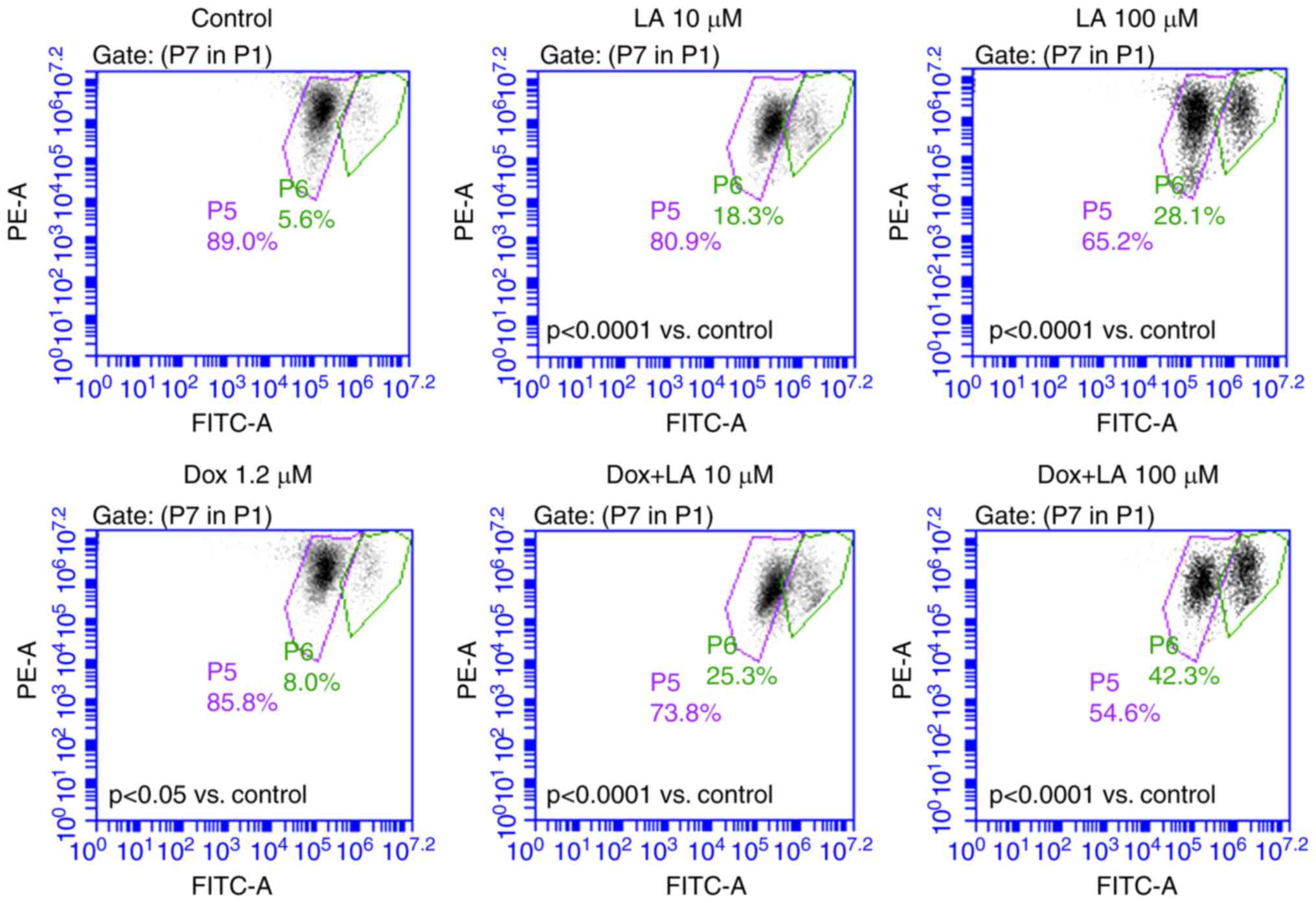
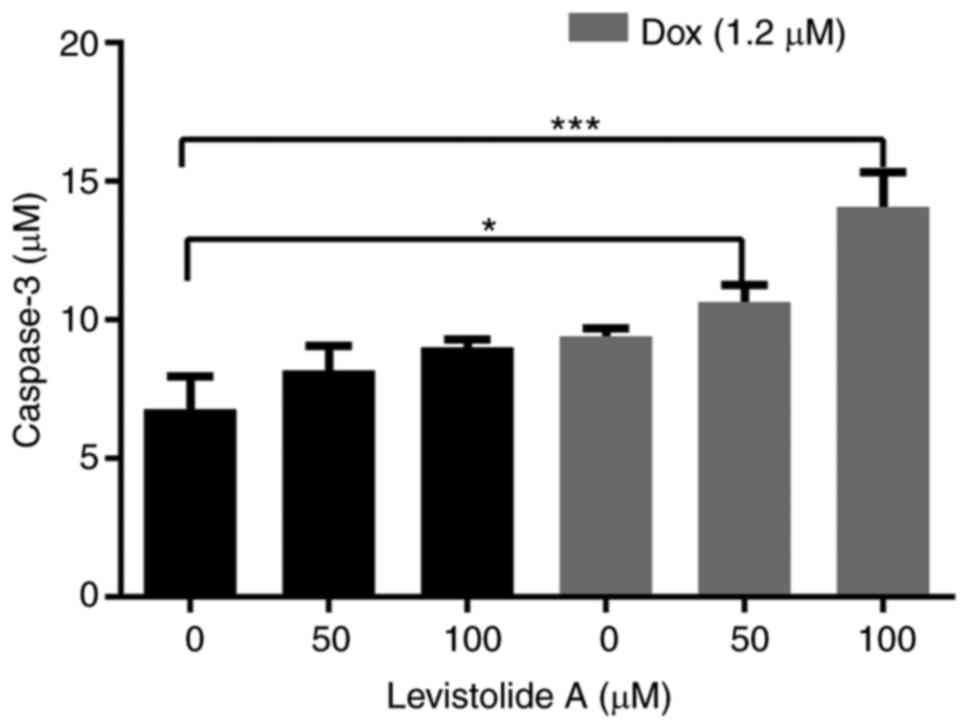
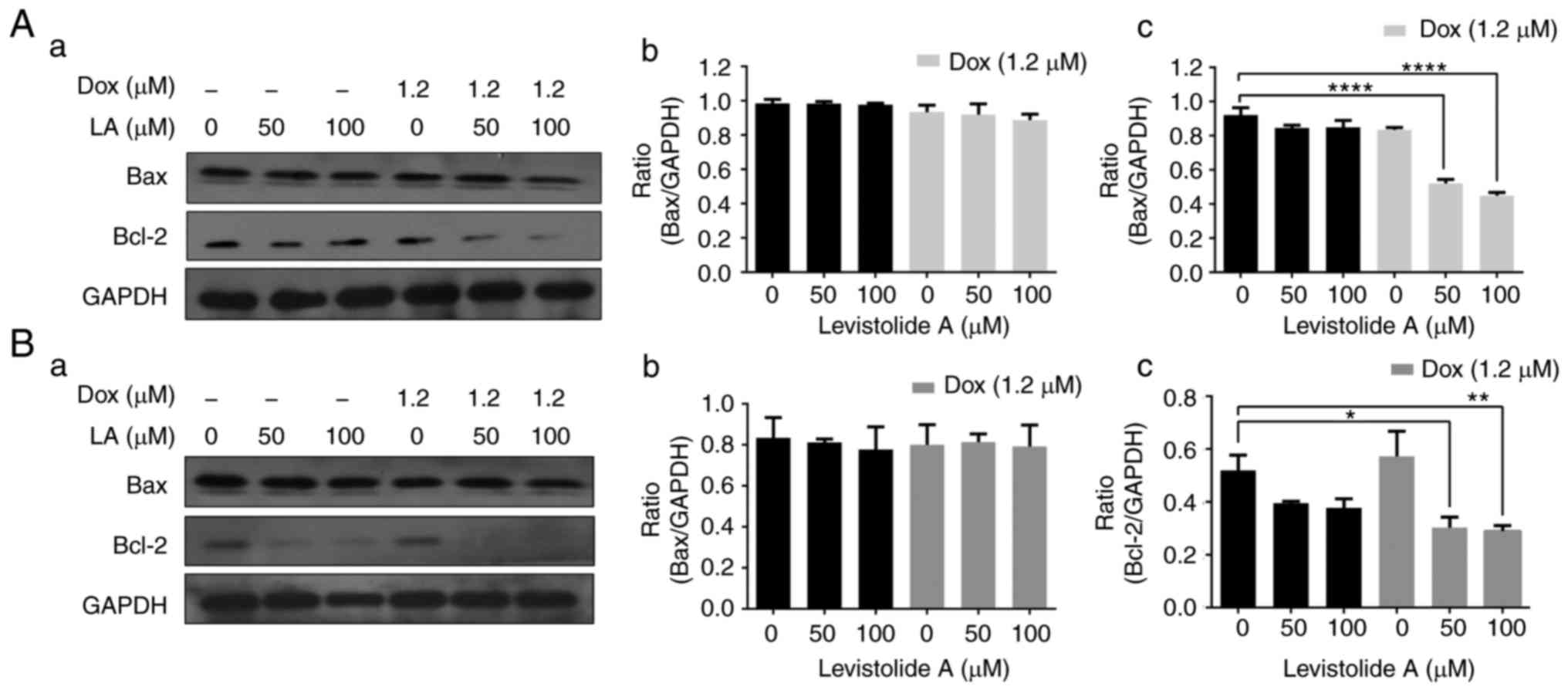
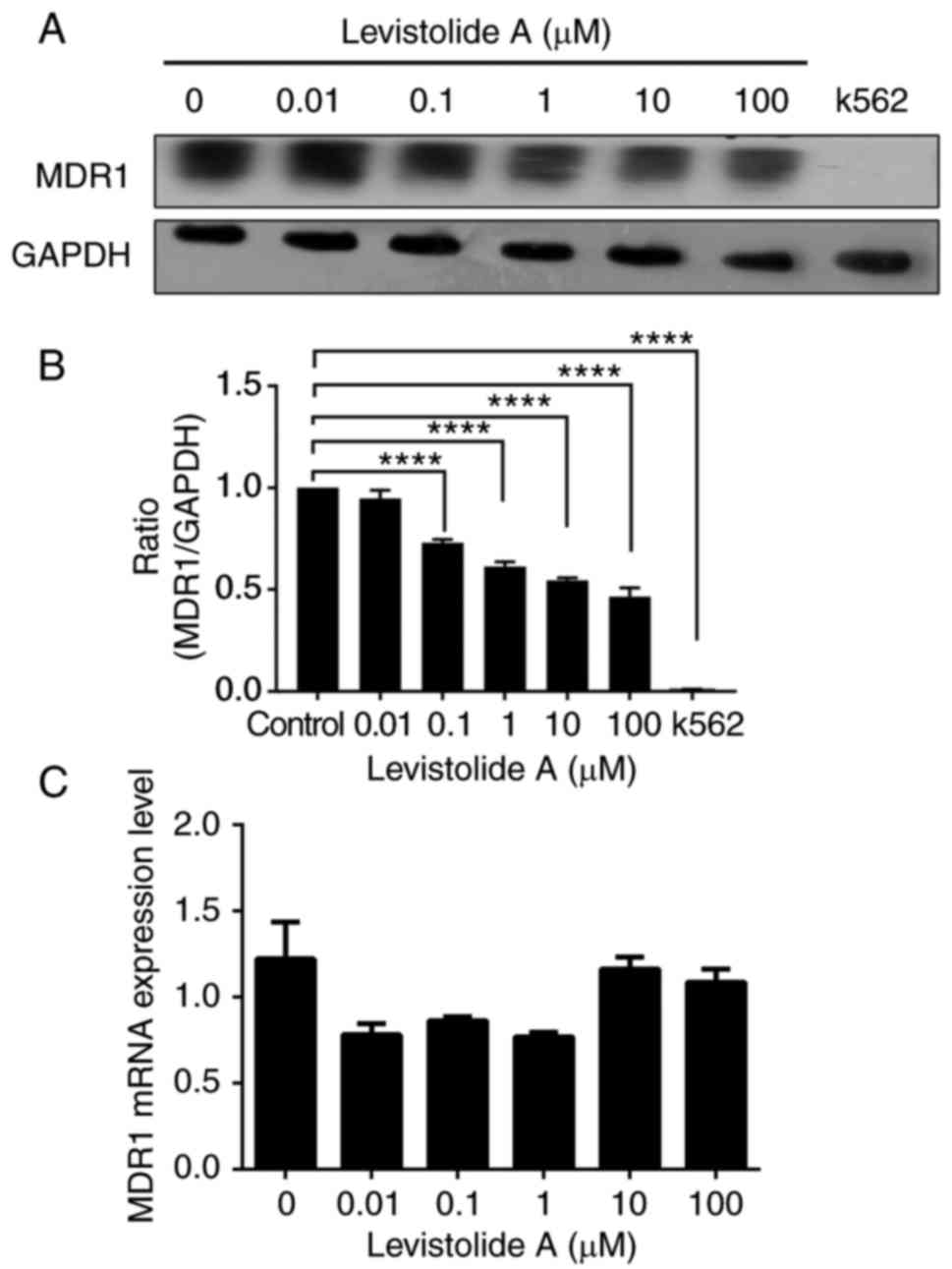
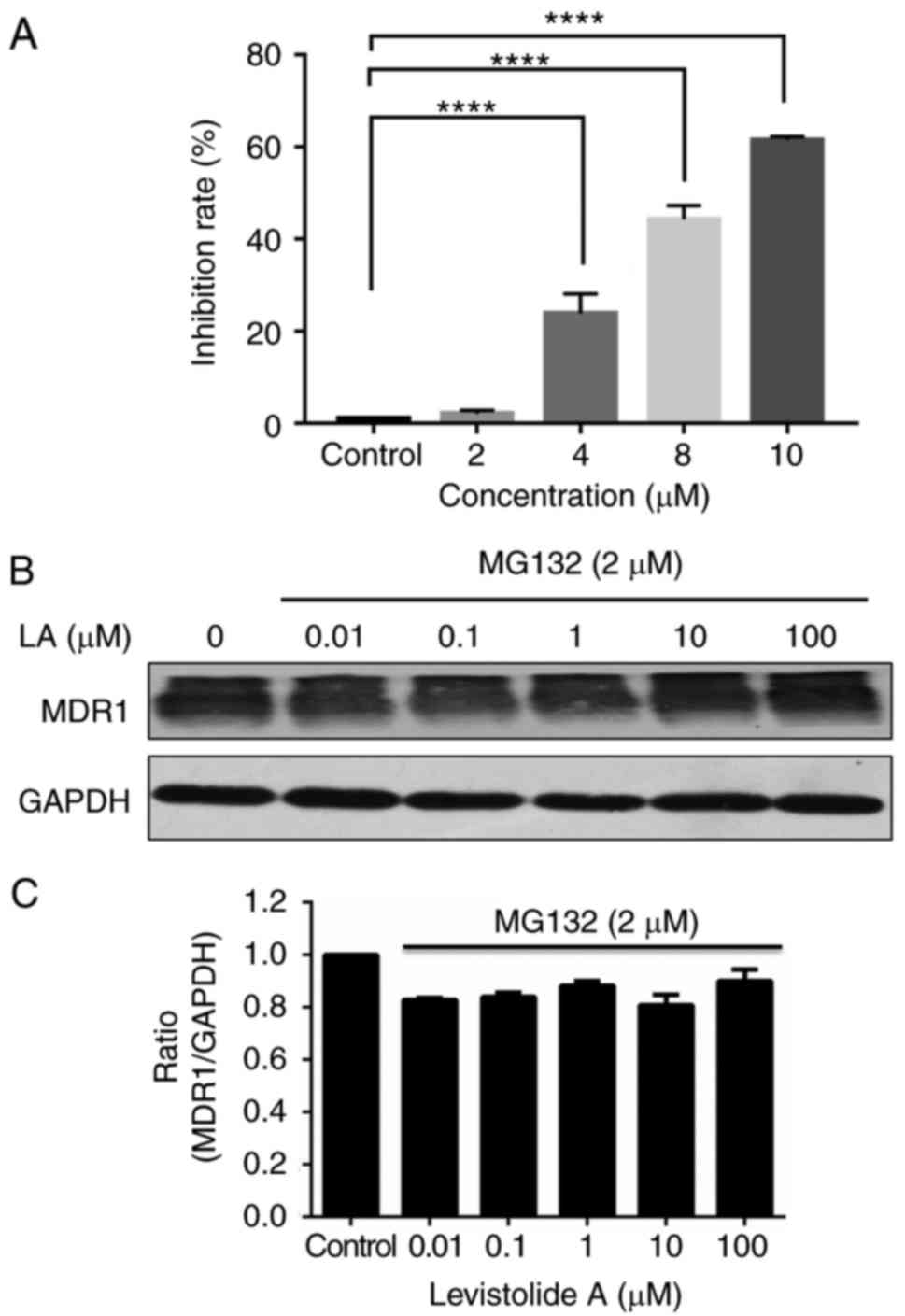
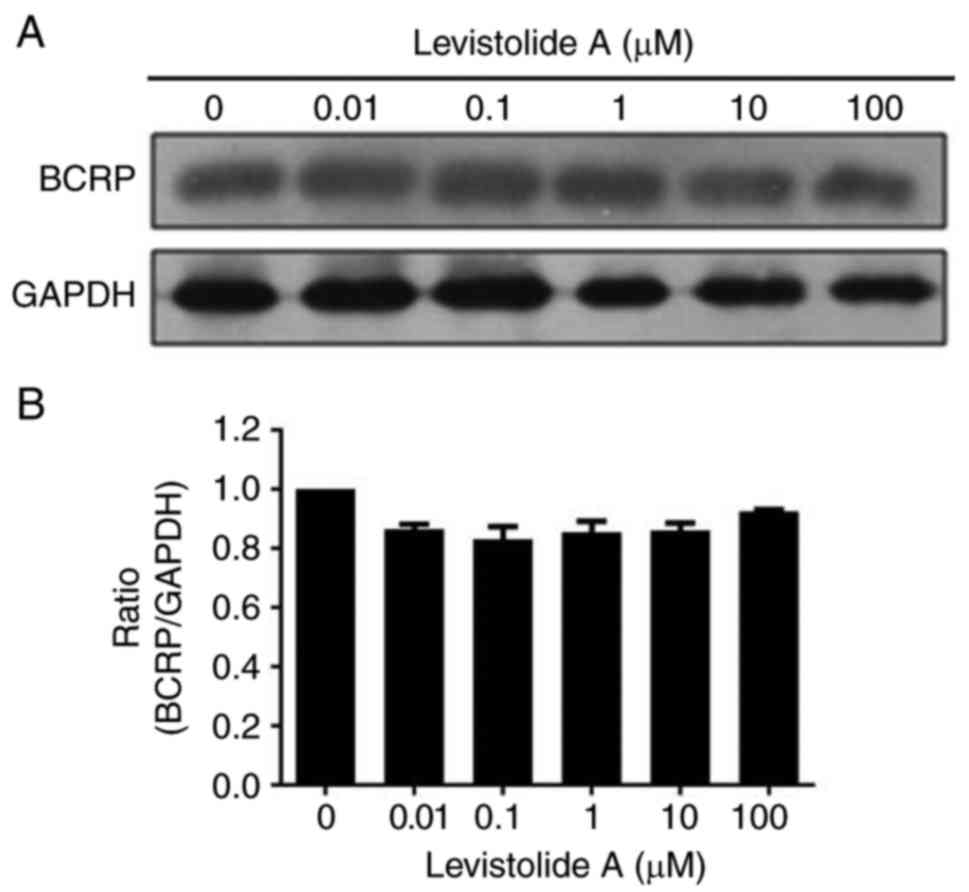
|
1
|
Wang YL: Tiny mutation triggers drug
resistance for patients with one type of leukemia. The University
of Chicago Medicine Communications. http://www.uchospitals.edu/news/2014/20140528-leukemia.html
|
|
2
|
Chai S, To KK and Lin G: Circumvention of
mult-drug resistance of cancer cells by Chinese herbal medicines.
Chin Med. 5:262010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goler-Baron V and Assaraf YG: Structure
and function of ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles mediating
multidrug resistance. PLoS One. 6:e160072011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goler-Baron V, Sladkevich I and Assaraf
YG: Inhibition of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway disrupts
ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles and overcomes multidrug
resistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1340–1348.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gonen N and Assaraf YG: Antifolates in
cancer therapy: Structure, activity and mechanisms of drug
resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 15:183–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ifergan I, Scheffer GL and Assaraf YG:
Novel extracellular vesicles mediate an ABCG2-dependent anticancer
drug sequestration and resistance. Cancer Res. 65:10952–10958.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lebedeva IV, Goler-Baron V and Assaraf YG:
Overcoming multidrug resistance via photo destruction of ABCG2-rich
extracellular vesicles sequestering photosensitive
chemotherapeutics. PLoS One. 7:e354872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livney YD and Assaraf YG: Rationally
designed nanovehicles to overcome cancer chemoresistance. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 65:1716–1730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Raz S, Sheban D, Gonen N, Stark M, Berman
B and Assaraf YG: Severe hypoxia induces complete antifolate
resistance in carcinoma cells due to cell cycle arrest. Cell Death
Dis. 5:e10672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhitomirsky B and Assaraf YG: Lysosomal
sequestration of hydrophobic weak base chemotherapeutics triggers
lysosomal biogenesis and lysosome-dependent cancer multidrug
resistance. Oncotarget. 6:1143–1156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhitomirsky B and Assaraf YG: Lysosomes as
mediators of drug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
24:23–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou X, Li D, Wang X, Zhang B, Zhu H and
Zhao J: Galectin-1 is overexpressed CD133+ human lung
adenocarcinoma cells and promotes their growth and invasiveness.
Oncotarget. 6:3111–3122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Genovese I, Ilari A, Assaraf YG, Fazi F
and Colotti G: Not only P-glycoprotein: Amplification of the
ABCB1-containing chromosome region 7q21 confers multidrug
resistance upon cancer cells by coordinated overexpression of an
assortment of resistance related proteins. Drug Resist Updat.
32:23–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Glavinas H, Krajcsi P, Cserepes J and
Sarkadi B: The role of ABC transporters in drug resistance,
metabolism and toxicity. Curr Drug Deliv. 1:27–42. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Varma MV, Ashokraj Y, Dey CS and
Panchagnula R: P-glycoprotein inhibitors and their screening: A
perspective from bioavailability enhancement. Pharmacol Res.
48:347–359. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gottesman MM, Fojo T and Bates SE:
Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:48–58. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hipfner DR, Deeley RG and Cole SP:
Structural, mechanistic and clinical aspects of MRP1. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 146:1359–1376. 1999.
|
|
18
|
Ozvegy C, Litman T, Szakács G, Nagy Z,
Bates S, Váradi A and Sarkadi B: Functional characterization of the
human multidrug transporter, ABCG2, expressed in insect cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 285:111–117. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Roy S, Kenny E, Kennedy S, Larkin A,
Ballot J, Perez De Villarreal M, Grown J and O'Driscoll L:
MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP-1mRNA and protein expression in
non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 27:1325–1330.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sparrebppm A, Danesi R, Ando Y, Chan J and
Figg WD: Phamacogenomics of ABC transporters and its role in cancer
chemotherapy. Drug Resist Updat. 6:71–84. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sanchez C, Mendoza P, Contreras HR,
Vergara J, McCubrey JA, Huidobro C and Castellón EA: Expression of
multidrug resistance proteins in prostate cancer is related with
cell sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs. Prostate. 69:1448–1459.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Igney FH and Krammer PH: Death and
anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:277–288. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shore GC and Nguyen M: Bcl-2 proteins and
apoptosis: Choose your partner. Cell. 135:1004–1006. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Glickman MH and Ciechanover A: The
ubiquitin-proteasome protcolytic pathway: Destruction for the sake
of construction. Physiol Rev. 82:373–428. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee CS, Han ES, Ha YS and Bang H:
Differential effect of calmodulin antagonists on MG132-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in PC12 cells. Brain Res
Bull. 67:225–234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bang JH, Han ES, Lim L and Lee CS:
Differential response of MG132 cytotoxicity against small cell lung
cancer cells to change in cellular GSH contents. Biochem Pharmacol.
68:659–666. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan XB, Yang DS, Gao X, Feng J, Shi ZL and
Ye Z: Caspase-8 dependent osteosarcoma cell apoptosis induced by
proteasome inhibitor MG132. Cell Biol Int. 31:1136–1143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chung SY, Sung MK, Kim NH, Jang JO, Go EJ
and Lee HJ: Inhibition of Pglycoprotein by natural products in
human breast cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res. 28:823–828. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mothana RA, Lindequist U, Gruenert R and
Bednarski PJ: Studies of the in vitro anticancer, antimicrobial and
antioxidant potentials of selected Yemeni medicinal plants from the
island Soqotra. BMC Complement Altern Med. 9:72009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Patanasethanont D, Nagai J, Matsuura C,
Fukui K, Sutthanut K, Sripanidkulchai BO, Yumoto R and Takano M:
Modulation of function of multidrug resistance associated-proteins
by Kaempferia parviflora extracts and their components. Eur
J Pharmacol. 566:67–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen F, Wang T, Wang J, Wang ZQ and Qian
M: Levistolide A overcomes P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance
in human breast carcinoma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:458–464.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang JC, Zhang JN, Wu YT and Li ZX: Effect
of the water extract and ethanol extract from traditional Chinese
medicines Angelicae sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, Ligusticum
chuanxiong Hort. and Rheum palmatum L on rat liver
cytochrome P450 activity. Phytother Res. 20:1046–1051. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lian N, Liu JB and Yan QM: Effect of
jiawei donggui buxue decoction on the survival time of mice with
cancer. Chin J Clin Rehabil. 8:5736–5737. 2004.
|
|
35
|
Lian N, Liu YM and Liu Y: Effect on
modified Danggui Buxue decoction to curative effect of tumor
treated by chemotherapy. J Chengdu Univ TCM. 26:pp. 18–19. 2003,
http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD2003&filename=CDZY200303006&v=MzI0MTNJOUZZb1I4ZVgx
THV4WVM3RGgxVDNxVHJXTTFGckNVUkxLZVp1ZG1Ge
URrVjc3SkppblJkN0c0SHRMTXI=.
|
|
36
|
Li BH and Lian N: Clinical observation on
synergia and attenuation of Jiawei Danggui buxue decoction to
radiotherapy and chemotherapy of tumor: Attachment report of 392
cases. J Cheng Univ TCM. 28:pp. 7–9. 2005, http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CJFD2005&filename=CDZY200502
002&v=MjE2MzZyV00×RnJDVVJMS2VadWRtRnlEbFZMM0pKaW5SZDdHNEh0VE1yWTlGWm9SOGVYMUx1eFlTN0RoMVQzcVQ=.
|
|
37
|
Zhang T, Ding Y, An H, Feng L and Wang S:
Screening anti-tumor compounds from Ligusticum wallichii
using cell membrane chromatography combined with high performance
liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci.
38:3247–3253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jin ZJ: Addition in drug combination
(author's transl). Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1:70–76. 1980.(In
Chinese). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6461187PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu F, Wang Y, Zeng S, Fu X, Wang L and
Cao J: Involvement of annexin A1 in multidrug resistance of
K562/ADR cells identified by the proteomic study. OMICS.
13:467–476. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen D, Shi Y and Tian G: Chuanxiong and
aspirin treatment of transient ischemic attack of clinical
research. J Int Tra Chi West Med. 12:672–674. 1992.
|
|
42
|
Ling V, Kartner N, Sudo T, Siminovitch L
and Riordan JR: Multidrug resistance phenotype in Chinese hamster
ovary cells. Cancer Treat Rep. 67:869–874. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|