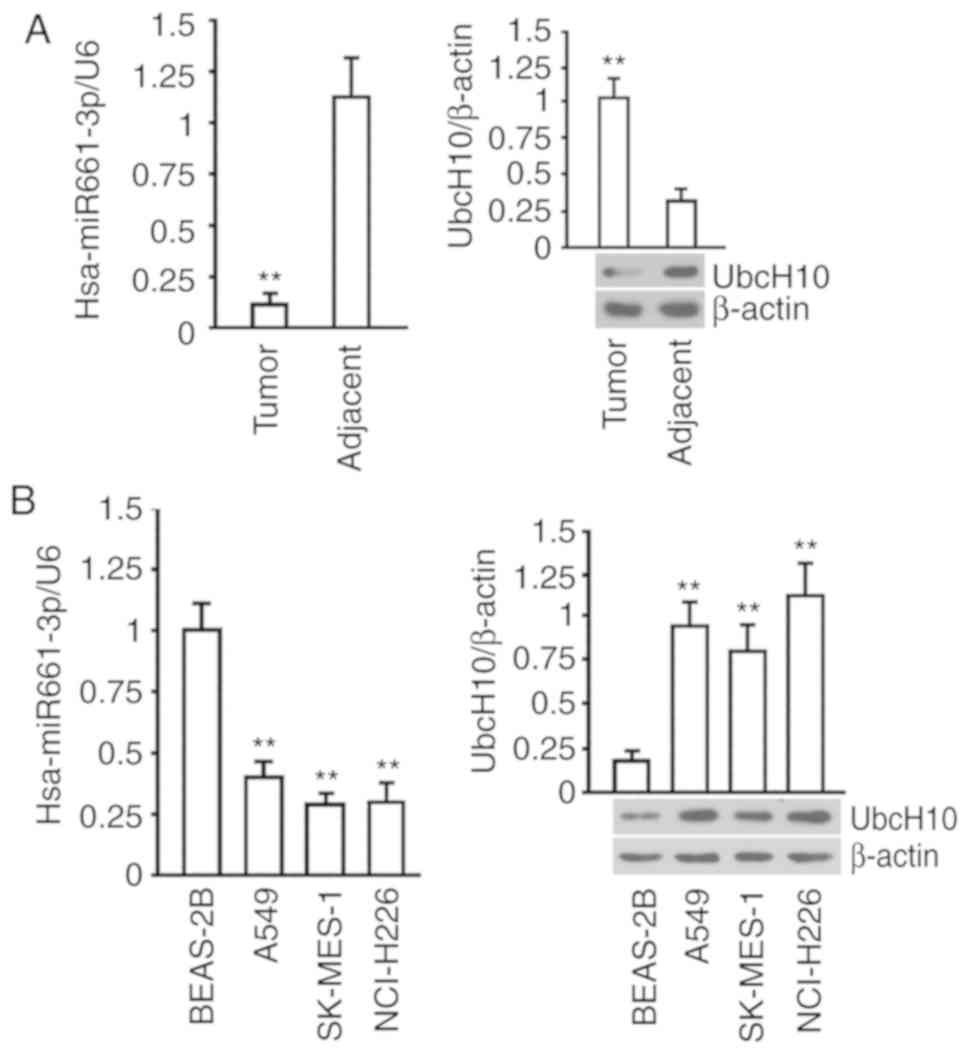
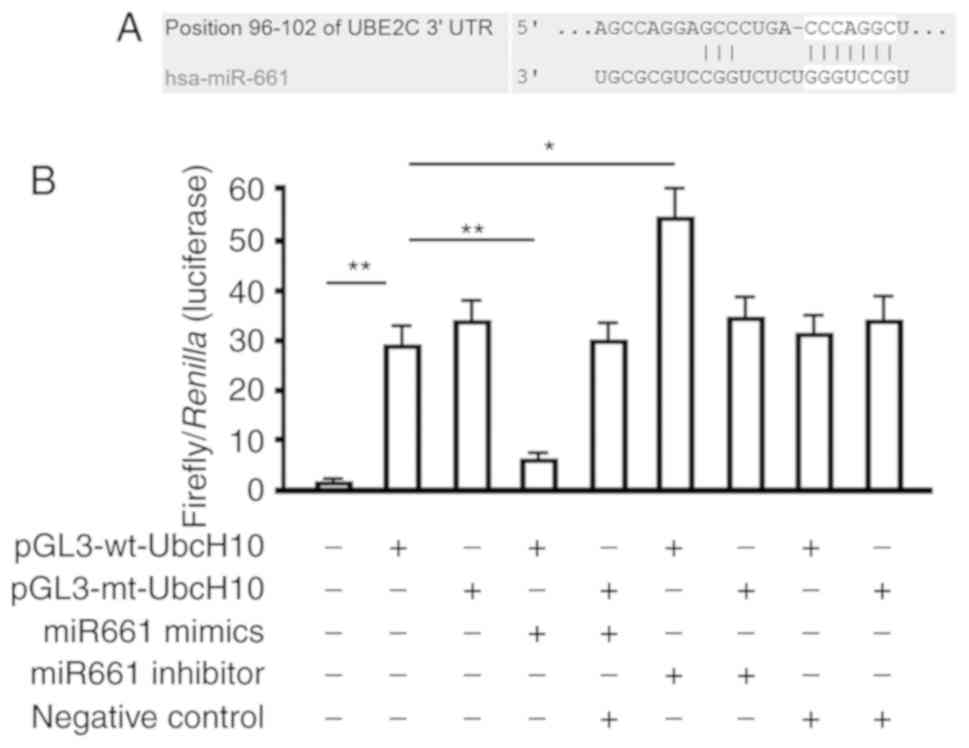
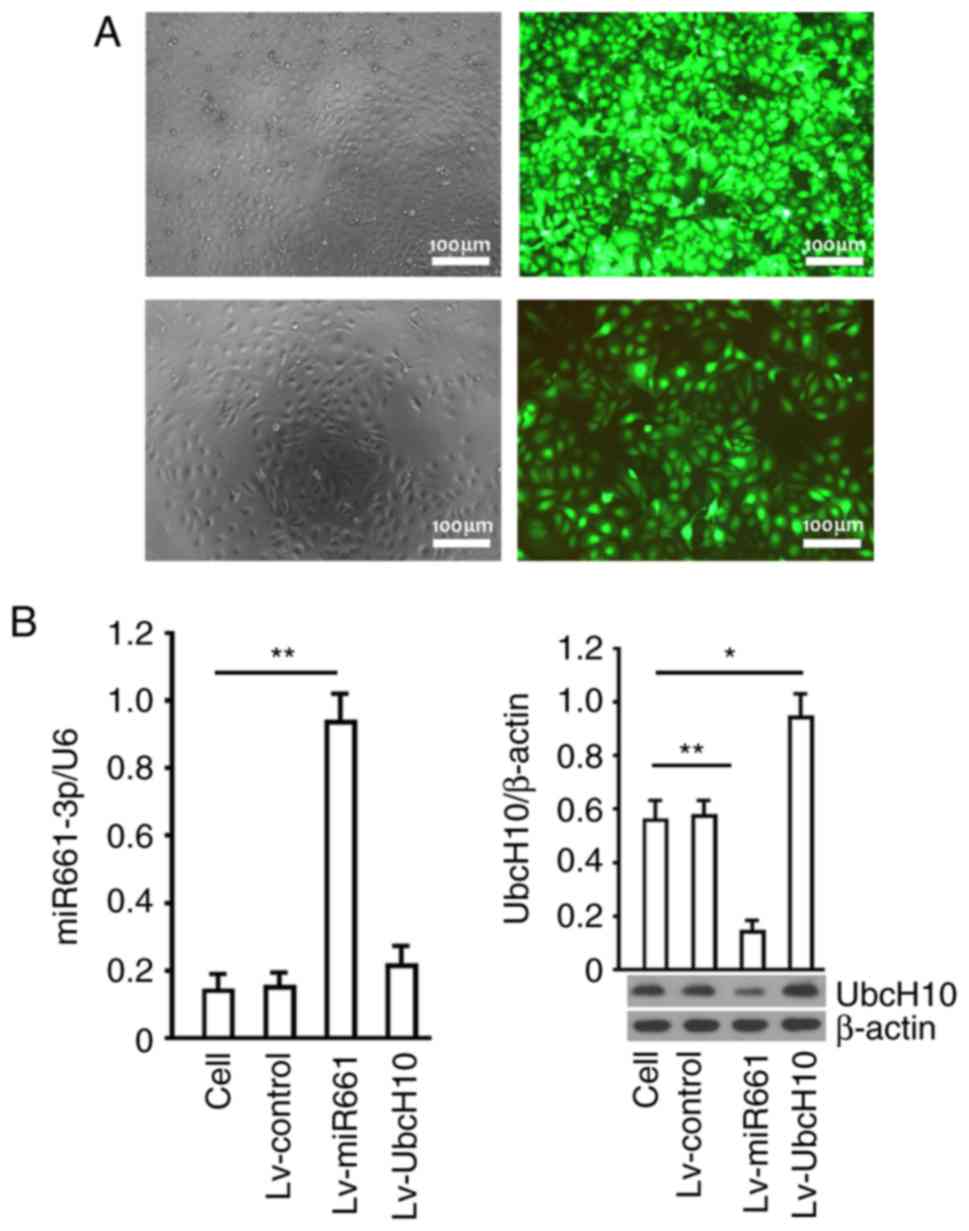
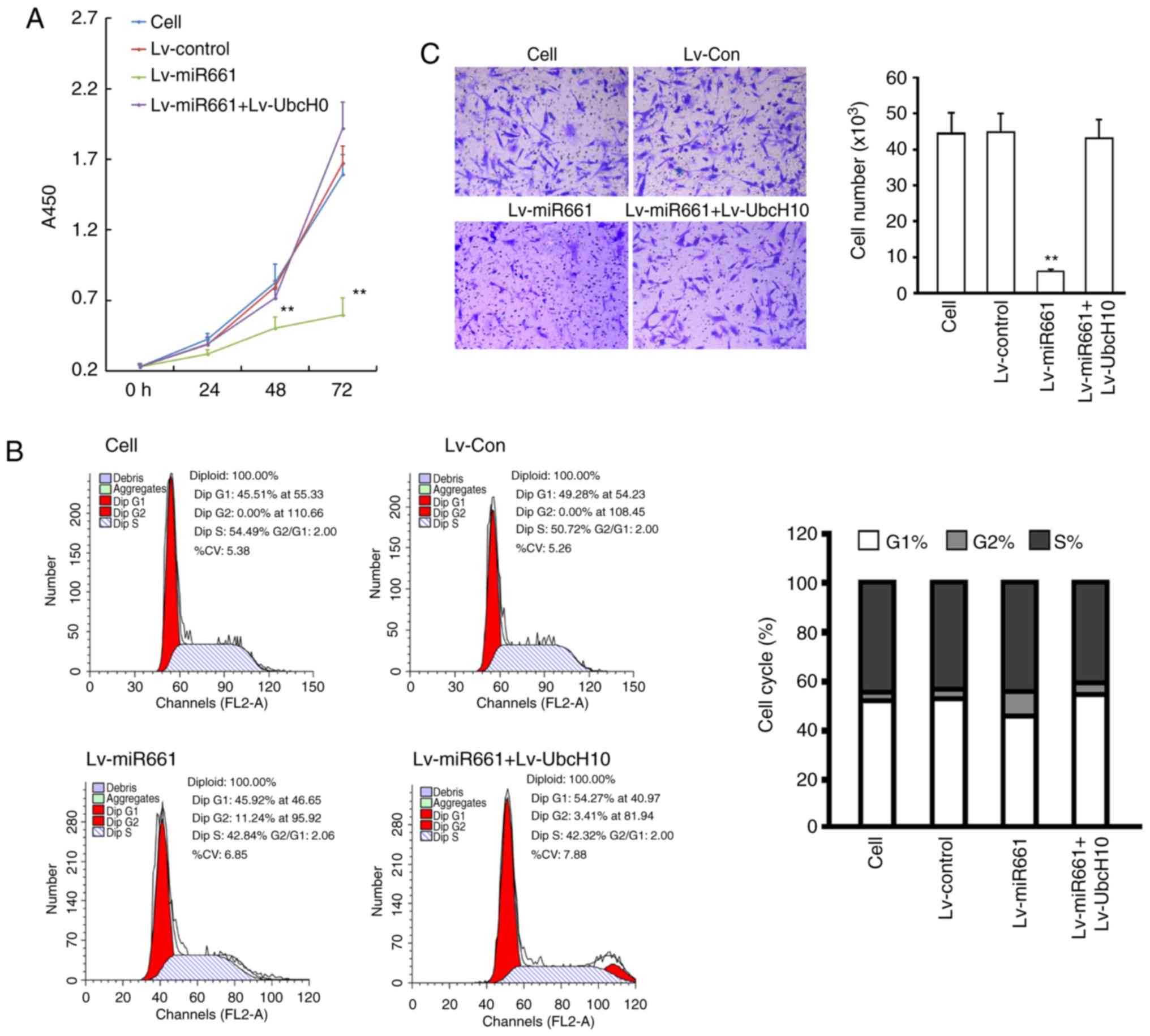
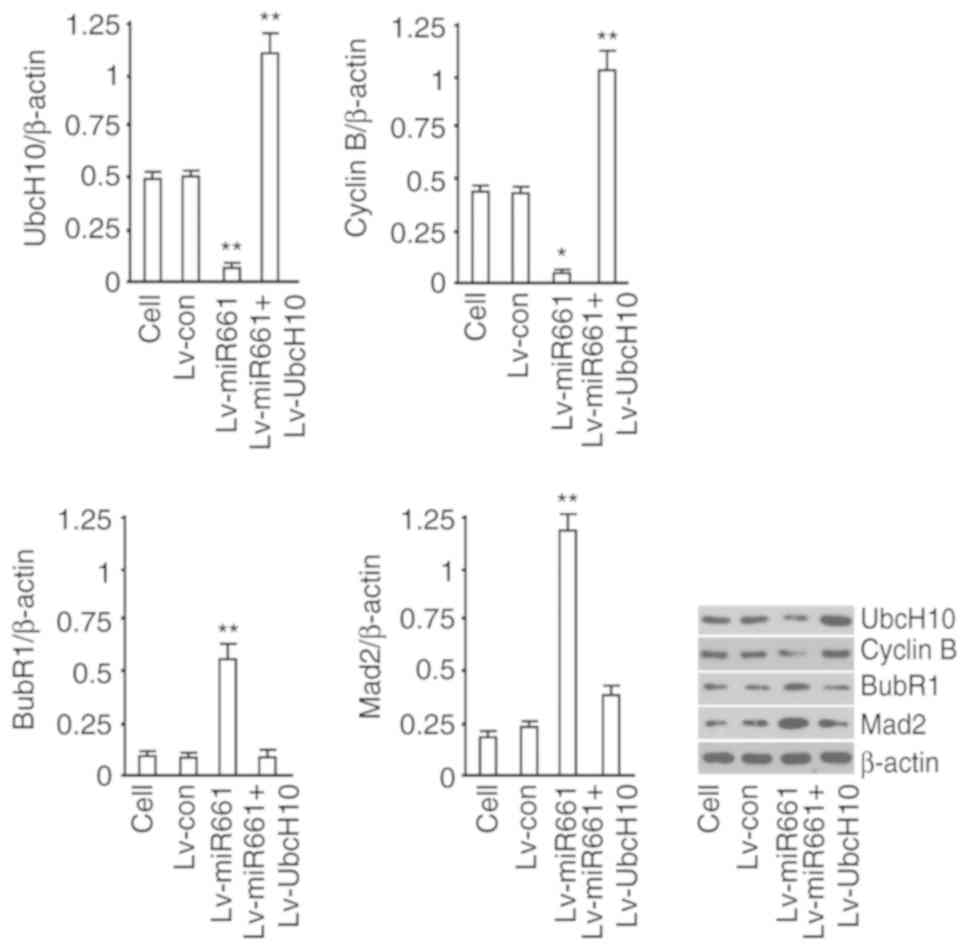
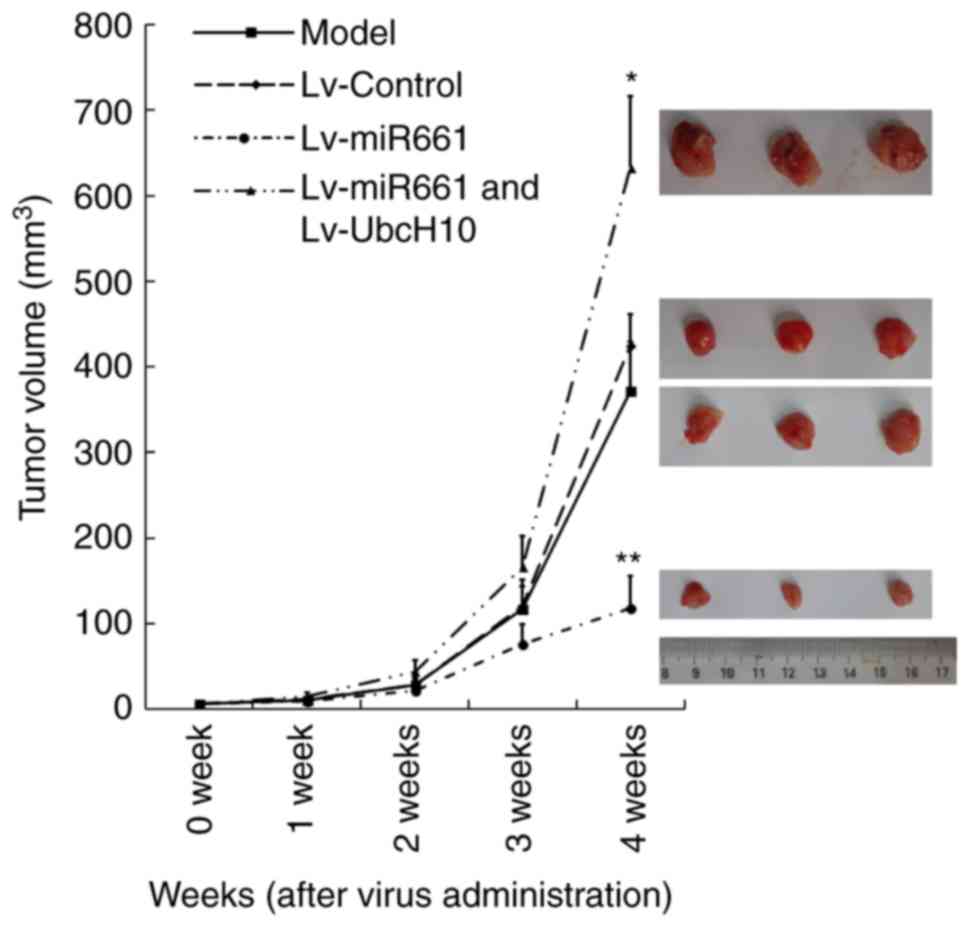
|
1
|
Hoeijmakers JH: Genome maintenance
mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature. 411:366–374. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blagosklonny MV and Pardee AB: Exploiting
cancer cell cycling for selective protection of normal cells.
Cancer Res. 61:4301–4305. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berlingieri MT, Pallante P, Sboner A,
Barbareschi M, Bianco M, Ferraro A, Mansueto G, Borbone E,
Guerriero E, Troncone G and Fusco A: UbcH10 is overexpressed in
malignant breast carcinomas. Eur J Cancer. 43:2729–2735. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berlingieri MT, Pallante P, Guida M, Nappi
C, Masciullo V, Scambia G, Ferraro A, Leone V, Sboner A,
Barbareschi M, et al: UbcH10 expression may be a useful tool in the
prognosis of ovarian carcinomas. Oncogene. 26:2136–2140. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Troncone G, Guerriero E, Pallante P,
Berlingieri MT, Ferraro A, Del Vecchio L, Gorrese M, Mariotti E,
Iaccarino A, et al: UbcH10 expression in human lymphomas.
Histopathology. 54:731–740. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ieta K, Ojima E, Tanaka F, Nakamura Y,
Haraguchi N, Mimori K, Inoue H, Kuwano H and Mori M: Identification
of over expressed genes in hepatocellular carcinoma, with special
reference to ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C gene expression. Int
J Cancer. 121:33–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okamoto Y, Ozaki T, Miyazaki K, Aoyama M,
Miyazaki M and Nakagawara A: UbcH10 is the cancer-related E2
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Cancer Res. 63:4167–4173.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao L, Jiang L, Wang L, He J, Yu H, Sun
G, Chen J, Xiu Q and Li B: UbcH10 expression provides a useful tool
for the prognosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1951–1961. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carmichael JA, Wing-San Mak D and O'Brien
MA: Review of recent advances in the treatment of elderly and poor
performance NSCLC. Cancers (Basel). 10:E2362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma N and Graziano S: Overview of the
LUX-lung clinical trial program of afatinib for non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 69:143–151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bassanelli M, Sioletic S, Martini M,
Giacinti S, Viterbo A, Staddon A, Liberati F and Ceribelli A:
Heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression and relationship with biology of
NSCLC. Anticancer Res. 38:3789–3796. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rubin H: Cancer development: The rise of
epigenetics. Eur J Cancer. 28:1–2. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tomasini R, Tsuchihara K, Tsuda C, Lau SK,
Wilhelm M, Ruffini A, Tsao MS, Iovanna JL, Jurisicova A, Melino G
and Mak TW: TAp73 regulates the spindle assembly checkpoint by
modulating BubR1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:797–802.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Ree JH, Jeganathan KB, Malureanu L and
van Deursen JM: Overexpression of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating
enzyme UbcH10 causes chromosome missegregation and tumor formation.
J Cell Biol. 188:83–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Draviam VM, Xie S and Sorger PK:
Chromosome segregation and genomic stability. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
14:120–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nasmyth K, Peters JM and Uhlmann F:
Splitting the chromosome: Cutting the ties that bind sister
chromatids. Science. 288:1379–1385. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu L, Liu X, Chervona Y, Yang F, Tang MS,
Darzynkiewicz Z and Dai W: Chromium induces chromosomal
instability, which is partly due to deregulation of BubR1 and Emi1,
two APC/C inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 10:2373–2379. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kato T, Daigo Y, Aragaki M, Ishikawa K,
Sato M, Kondo S and Kaji M: Overexpression of MAD2 predicts
clinical outcome in primary lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer.
74:124–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Doherty FJ, Dawson S and Mayer RJ: The
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway of intracellular proteolysis. Essays
Biochem. 38:51–63. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Summers MK, Pan B, Mukhyala K and Jackson
PK: The unique N terminus of the UbcH10 E2 enzyme controls the
threshold for APC activation and enhances checkpoint regulation of
the APC. Mol Cell. 31:544–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barad O, Meiri E, Avniel A, Aharonov R,
Barzilai A, Bentwich I, Einav U, Gilad S, Hurban P, Karov Y, et al:
MicroRNA expression detected by oligonucleotide microarrays: System
establishment and expression profiling in human tissues. Genome
Res. 14:2486–2494. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lai EC, Tomancak P, Williams RW and Rubin
GM: Computational identification of Drosophila microRNA genes.
Genome Biol. 4:R422003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee I, Ajay SS, Yook JI, Kim HS, Hong SH,
Kim NH, Dhanasekaran SM, Chinnaiyan AM and Athey BD: New class of
microRNA targets containing simultaneous 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR
interaction sites. Genome Res. 19:1175–1183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gilad S, Lithwick-Yanai G, Barshack I,
Benjamin S, Krivitsky I, Edmonston TB, Bibbo M, Thurm C, Horowitz
L, Huang Y, et al: Classification of the four main types of lung
cancer using a microRNA-based diagnostic assay. J Mol Diagn.
14:510–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Landi MT, Zhao Y, Rotunno M, Koshiol J,
Liu H, Bergen AW, Rubagotti M, Goldstein AM, Linnoila I, Marincola
FM, et al: MicroRNA expression differentiates histology and
predicts survival of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:430–441.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lebanony D, Benjamin H, Gilad S, Ezagouri
M, Dov A, Ashkenazi K, Gefen N, Izraeli S, Rechavi G, Pass H, et
al: Diagnostic assay based on hsa-miR-205 expression distinguishes
squamous from nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 27:2030–2037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lima Queiroz A, Zhang B, Comstock DE, Hao
Y, Eriksson M, Hydbring P, Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg H and Norberg E:
miR-126-5p targets malate dehydrogenase 1 in non-small cell lung
carcinomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 499:314–320. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karagur ER, Ozay C, Mammadov R and Akca H:
Anti-invasive effect of Cyclamen pseudibericum extract on A549
non-small cell lung carcinoma cells via inhibition of ZEB1 mediated
by miR-200c. J Nat Med. 72:686–693. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ali MA, Matboli M, El-Khazragy N, Saber O,
El-Nakeep S, Abdelzaher HM, Shafei AE and Mostafa R: Investigating
miRNA-661 and ATG4-B mRNA expression as potential biomarkers for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark Med. 12:245–256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gómez de Cedrón M, Acín Pérez R,
Sánchez-Martínez R, Molina S, Herranz J, Feliu J, Reglero G,
Enríquez JA and Ramírez de Molina A: MicroRNA-661 modulates redox
and metabolic homeostasis in colon cancer. Mol Oncol. 11:1768–1787.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lara-Gonzalez P, Scott MI, Diez M, Sen O
and Taylor SS: BubR1 blocks substrate recruitment to the APC/C in a
KEN-box-dependent manner. J Cell Sci. 124:4332–4345. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rape M, Reddy SK and Kirschner MW: The
processivity of multiubiquitination by the APC determines the order
of substrate degradation. Cell. 124:89–103. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Townsley FM, Aristarkhov A, Beck S,
Hershko A and Ruderman JV: Dominant-negative cyclin-selective
ubiquitin carrier protein E2-C/UBCH10 blocks cells in metaphase.
Proc Natl AcadSci USA. 94:2362–2367. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Patel D and McCance DJ: Compromised
spindle assembly checkpoint due to altered expression of UBCH10 and
Cdc20 in human papillomavirus type 16 E6- and E7-expressing
keratinocytes. J Virol. 84:10956–10964. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|