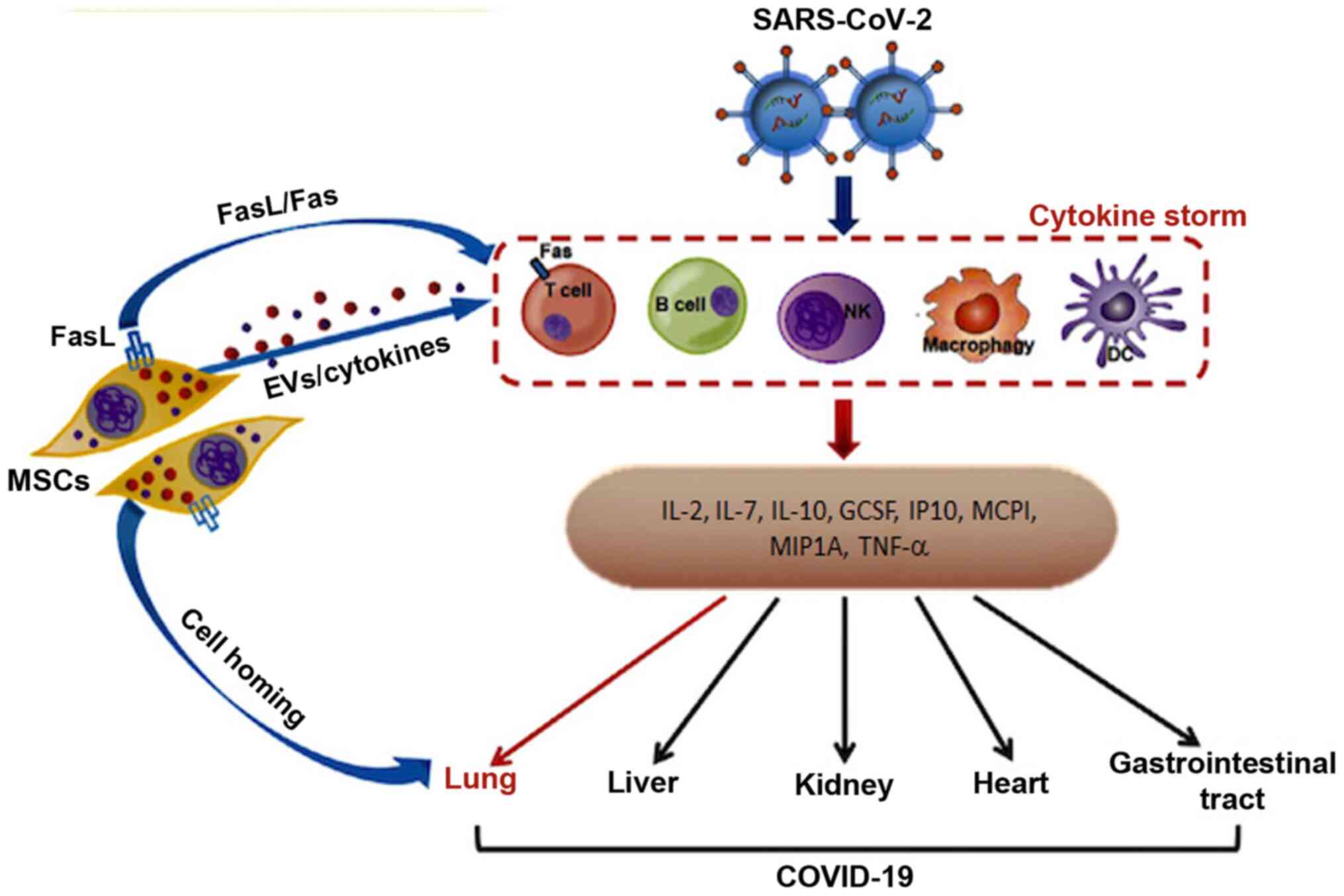
|
1
|
Uğraş Dikmen A, Kına HM, Özkan S and
İlhan MN: Epidemiology of COVID-19: What we learn from pandemic. J
Biotechnol and Strategic Health Res. 1:29–36. 2020.
|
|
2
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song
J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al: A novel coronavirus from
patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 382:727–33.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zumla A, Chan JFW, Azhar EI, Hui DS and
Yuen KY: Coronaviruses-drug discovery and therapeutic options. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 15:327–347. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H,
Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, et al: Genomic characterisation and
epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus
origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 395:565–574. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wan Y, Shang J, Graham R, Baric RS and Li
F: Receptor recognition by novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An
analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS. J Virol.
94:e00127–20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L,
Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, et al: A pneumonia outbreak
associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature.
579:270–273. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rose-John S: Interleukin-6 family
cytokines. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
10(a028415)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen J, Hu C, Che L, Tang L, Zhu Y, Xu X,
Chen L, Gao H, Lu X, Yu L, et al: Clinical study of mesenchymal
stem cell treatment for acute respiratory distress syndrome induced
by epidemic influenza A (H7N9) infection: A hint for COVID-19
treatment. Engineering (Beijing): Feb 28, 2020 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
9
|
Bennardo F, Buffone C and Giudice A: New
therapeutic opportunities for COVID-19 patients with Tocilizumab:
Possible correlation of interleukin-6 receptor inhibitors with
osteonecrosis of the jaws. Oral Oncol. 106(104659)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rothan HA and Byrareddy SN: The
epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
outbreak. J Autoimmun. 109(102433)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT,
Navis G and van Goor H: Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the
functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in
understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 203:631–637.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vergano M, Bertolini G, Giannini A,
Giuseppe G, Livigni S, Mistraletti G and Petrini F: Raccomandazioni
di etica clinica per l'ammissione a trattamenti intensivi e per la
loro sospensione, in condizioni eccezionali di squilibrio tra
necessità e risorse disponibili. versione 01. SIAARTI, 2020.
urihttps://www.siaarti.it/SiteAssets/News/COVID19%20-%20documenti%20SIAARTI/SIAARTI%20-%20Covid19%20-%20Raccomandazioni%20di%20etica%20clinica.pdfsimplehttps://www.siaarti.it/SiteAssets/News/COVID19%20-%20documenti%20SIAARTI/SIAARTI%20-%20Covid19%20-%20Raccomandazioni%20di%20etica%20clinica.pdf.
Accessed March 6, 2020.
|
|
13
|
Leng Z, Zhu R, Hou W, Feng Y, Yang Y, Han
Q, Shan G, Meng F, Du D, Wang S, et al: Transplantation of ACE2
mesenchymal stem cells improves the outcomes of patients with
COVID-19 pneumonia. Aging Dis. 11:216–228. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu
Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al: Clinical features of patients
infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet.
395:497–506. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jaimes JA, Millet JK, Stout AE, Andre NM
and Whittaker GR: A tale of two viruses: The distinct spike
glycoproteins of feline coronaviruses. Viruses.
12(83)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu Z and Mc Googan JM: Characteristics of
and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the
Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA.
323:1239–1242. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Del Rio C and Malani PN: 2019 novel
coronavirus-important information for clinicians. JAMA.
323:1039–1040. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
World Health Organization (WHO): WHO
Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on
COVID-19-24 February 2020. urihttps://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-op-ening-remarks-at-themedia-briefing-on-covid-19-24-february-2020simplehttps://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-op-ening-remarks-at-themedia-briefing-on-covid-19-24-february-2020.
Accessed February 26, 2020.
|
|
19
|
Gattinoni L, Pesenti A, Avalli L, Rossi F
and Bombino M: Pressure-volume curve of total respiratory system in
acute respiratory failure. Computed tomographic scan study. Am Rev
Respir Dis. 136:730–736. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gattinoni L, Caironi P, Cressoni M,
Chiumello D, Ranieri VM, Quintel M, Russo S, Patroniti N, Cornejo R
and Bugedo G: Lung recruitment in patients with the acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 354:1775–1786.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Maiolo G, Collino F, Vasques F, Rapetti F,
Tonetti T, Romitti F, Cressoni M, Chiumello D, Moerer O, Herrmann
P, et al: Reclassifying acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 197:1586–1595. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gattinoni L, Chiumello D, Caironi P,
Busana M, Romitti F, Brazzi L and Camporota L: COVID-19 pneumonia:
Different respiratory treatments for different phenotypes?
Intensive Care Med. 46:1099–1102. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Behrens EM and Koretzky GA: Review:
Cytokine storm syndrome: Looking toward the precision medicine era.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 69:1135–1143. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Us D: Cytokine storm in avian influenza.
Mikrobiyol Bul. 42:365–380. 2008.PubMed/NCBI(In Turkish).
|
|
25
|
Mares CA, Ojeda SS, Morris EG, Li Q and
Teale JM: Initial delay in the immune response to Francisella
tularensis is followed by hypercytokinemia characteristic of severe
sepsis and correlating with upregulation and release of
damage-associated molecular patterns. Infect Immun. 76:3001–3010.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
de Castro IF, Guzmán-Fulgencio M,
García-Alvarezand M and Resino S: First evidence of a
pro-inflammatory response to severe infection with influenza virus
H1N1. Crit Care. 14(115)2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tisoncik JR, Korth MJ, Simmons CP, Farrar
J, Martin TR and Katze MG: Into the eye of the cytokine storm.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 76:16–32. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pugin J, Ricou B, Steinberg KP, Suter PM
and Martin TR: Proinflammatory activity in bronchoalveolar lavage
fluids from patients with ARDS, a prominent role for interleukin-1.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 153:1850–1856. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Metcalfe SM: Mesenchymal stem cells and
management of COVID-19 pneumonia. Med Drug Discov.
5(1000192)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Williams AE and Chambers RC: The mercurial
nature of neutrophils: Still an enigma in ARDS? Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 306:L217–L230. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Channappanavar R and Perlman S: Pathogenic
human coronavirus infections: Causes and consequences of cytokine
storm and immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol. 39:529–539.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cameron MJ, Bermejo-Martin JF, Danesh A,
Muller MP and Kelvin DJ: Human immunopathogenesis of severe acute
respiratory syndrome (SARS). Virus Res. 133:13–19. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L,
Zhang C, Liu S, Zhao P, Liu H, Zhu L, et al: Pathological findings
of COVID-19 associated with acute espiratory distress syndrome.
Lancet Resp Med. 8:420–422. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Imai Y, Parodo J, Kajikawa O, de Perrot M,
Fischer S, Edwards V, Cutz E, Liu M, Keshavjee S, Martin TR, et al:
Injurious mechanical ventilation and end-organ epithelial cell
apoptosis and organ dysfunction in an experimental model of acute
respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA. 289:2104–2112. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kögler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, Trapp T,
Müschen M, Feldhahn N, Liedtke S, Sorg RV, Fischer J, Rosenbaum C,
et al: A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with
intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med.
200:123–135. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Tang N, Song WX, Luo
J, Luo X, Chen J, Bennett E, Reid R, Manning D, et al: Regulation
of osteogenic differentiation during skeletal development. Front
Biosci. 13:2001–2021. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova
AI and Frolova GP: Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of
precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues.
Transplantation. 6:230–247. 1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, Manning D, Luo J,
Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Montag AG, Haydon RC and He TC: Distinct roles
of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 25:665–677. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Entschladen F and Zänker KS (eds): Cell
migration: Signalling and mechanisms. Karger, Basel, pp1-6,
2010.
|
|
40
|
Müller I, Kordowich S, Holzwarth C,
Isensee G, Lang P, Neunhoeffer F, Dominici M, Greil J and
Handgretinger R: Application of multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells in pediatric patients following allogeneic stem cell
transplantation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 40:25–32. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Prasad VK, Lucas KG, Kleiner GI, Talano
JA, Jacobsohn D, Broadwater G, Monroy R and Kurtzberg J: Efficacy
and safety of ex vivo cultured adult human mesenchymal stem cells
(Prochymal™) in pediatric patients with severe refractory acute
graft-versus-host disease in a compassionate use study. Biol Blood
Marrow Transplant. 17:534–541. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kebriaei P, Isola L, Bahceci E, Holland K,
Rowley S, McGuirk J, Devetten M, Jansen J, Herzig R, Schuster M, et
al: Adult human mesenchymal stem cells added to corticosteroid
therapy for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol
Blood Marrow Transplant. 15:804–811. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wu KH, Chan CK, Tsai C, Chang YH, Sieber
M, Chiu TH, Ho M, Peng CT, Wu HP and Huang JL: Effective treatment
of severe steroid-resistant acute graft-versus- host disease with
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation.
91:1412–1416. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, Locatelli
F, Roelofs H, Lewis I, Lanino E, Sundberg B, Bernardo ME, Remberger
M, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of
steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase
II study. Lancet. 371:1579–1586. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sun L, Wang D, Liang J, Zhang H, Feng X,
Wang H, Hua B, Liu B, Ye S, Hu X, et al: Umbilical cord mesenchymal
stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus
erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 62:2467–2475. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Carrion F, Nova E, Ruiz C, Diaz F,
Inostroza C, Rojo D, Mönckeberg G and Figueroa FE: Autologous
mesenchymal stem cell treatment increased T regulatory cells with
no effect on disease activity in two systemic lupus erythematosus
patients. Lupus. 19:317–322. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ciccocioppo R, Bernardo ME, Sgarella A,
Maccario R, Avanzini MA, Ubezio C, Minelli A, Alvisi C, Vanoli A,
Calliada F, et al: Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stromal cells in the treatment of fistulising Crohn's disease. Gut.
60:788–798. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Duijvestein M, Vos AC, Roelofs H,
Wildenberg ME, Wendrich BB, Verspaget HW, Kooy-Winkelaar EM, Koning
F, Zwaginga JJ, Fidder HH, et al: Autologous bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stromal cell treatment for refractory luminal Crohn's
disease: Results of a phase I study. Gut. 59:1662–1669.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mehta P, Mcauley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E,
Tattersall RS and Manson JJ: HLH Across Speciality Collaboration,
UK. Correspondence COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and
immunosuppression. Lancet. 395:1033–1034. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bari E, Ferrarotti I, Saracino L,
Perteghella S, Torre ML and Corsico AG: Mesenchymal stromal cell
secretome for severe COVID-19 infections: Premises for the
therapeutic use. Cells. 9(924)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Singer NG and Caplan AI: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Mechanisms of inflammation. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:457–478.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Bernardo ME and Fibbe WE: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: Sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem
Cell. 13:392–402. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M,
Milanesi M, Longoni PD, Matteucci P, Grisanti S and Gianni AM:
Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress t-lymphocyte proliferation
induced by cellular or non- specific mitogenic stimuli. Blood.
99:3838–3843. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, Scott D,
Laylor R, Simpson E and Dazzi F: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells
to their cognate peptide. Blood. 101:3722–3729. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ghannam S, Pène J, Moquet-Torcy G,
Jorgensen C and Yssel H: Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit human Th17
cell differentiation and function and induce a T regulatory cell
phenotype. J Immunol. 185:302–312. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Prigione I, Benvenuto F, Bocca P,
Battistini L, Uccelli A and Pistoia V: Reciprocal interactions
between human mesenchymal stem cells and gammadelta T cells or
invariant natural killer T cells. Stem Cells. 27:693–702.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E,
Giunti D, Cappiello V, Cazzanti F, Risso M, Gualandi F, Mancardi
GL, Pistoia V and Uccelli A: Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate
B-cell functions. Blood. 107:367–372. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Raffaghello L, Bianchi G, Bertolotto M,
Montecucco F, Busca A, Dallegri F, Ottonello L and Pistoia V: Human
mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neutrophil apoptosis: A model for
neutrophil preservation in the bone marrow niche. Stem Cells.
26:151–162. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
DelaRosa O, Sánchez-Correa B, Morgado S,
Ramírez C, del Río B, Menta R, Lombardo E, Tarazona R and Casado
JG: Human adipose-derived stem cells impair natural killer cell
function and exhibit low susceptibility to natural killer-mediated
lysis. Stem Cells Dev. 21:1333–1343. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Krampera M, Cosmi L, Angeli R, Pasini A,
Liotta F, Andreini A, Santarlasci V, Mazzinghi B, Pizzolo G,
Vinante F, et al: Role for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory
activity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells.
24:386–398. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Prasanna SJ, Gopalakrishnan D, Shankar SR
and Vasandan AB: Proinflammatory cytokines, IFNgamma and TNFalpha,
influence immune properties of human bone marrow and Wharton jelly
mesenchymal stem cells differentially. PLoS One.
5(e9016)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Frank MH and Sayegh MH: Immunomodulatory
functions of mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 363:1411–1412.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Horwitz EM, Gordon PL, Koo WK, Marx JC,
Neel MD, McNall RY, Muul L and Hofmann T: Isolated allogeneic bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal cells engraft and stimulate growth in
children with osteogenesis imperfecta: Implications for cell
therapy of bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:8932–8937.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Koç ON, Day J, Nieder M, Gerson SL,
Lazarus HM and Krivit W: Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell infusion
for treatment of meta-chromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) and hurler
syndrome (MPS-IH). Bone Marrow Transplant. 30:215–222.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Le Blanc K: Immunomodulatory effects of
fetal and adult mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 5:485–489.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Chen C, Zhang XR, Ju ZY and He WF:
Advances in the research of mechanism and related immunotherapy on
the cytokine storm induced by coronavirus disease 2019. Zhonghua
Shao Shang Za Zhi. 36:471–475. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
67
|
Rawat S, Gupta S and Mohanty S:
Mesenchymal stem cells modulate the immune system in developing
therapeutic interventions 2019.
|
|
68
|
Abraham A and Krasnodembskaya A:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for the
treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Stem Cells Transl
Med. 9:28–38. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Xu AL, Rodriguez LA II, Walker KP III,
Mohammadipoor A, Kamucheka RM, Cancio LC, Batchinsky AI and Antebi
B: Mesenchymal stem cells reconditioned in their own serum exhibit
augmented therapeutic properties in the setting of acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Stem Cells Transl Med. 8:1092–1106.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK,
Kissenpfennig A, McAuley DF, O'Kane CM and Krasnodembskaya AD:
Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate macrophages in clinically
relevant lung injury models by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial
transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 196:1275–1286. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Ji F, Li L, Li Z, Jin Y and Liu W:
Mesenchymal stem cells as a potential treatment for critically ill
patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Stem Cells Transl Med.
9:813–814. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Noël D, Djouad F, Bouffi C, Mrugala D and
Jorgensen C: Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and immune
tolerance. Leuk Lymphoma. 48:1283–1289. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Chen X, Armstrong MA and Li G: Mesenchymal
stem cells in immunoregulation. Immunol Cell Biol. 84:413–421.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Golchin A, Seyedjafari E and
Ardeshirylajimi A: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for COVID-19:
Present or future. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 16:427–433. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|