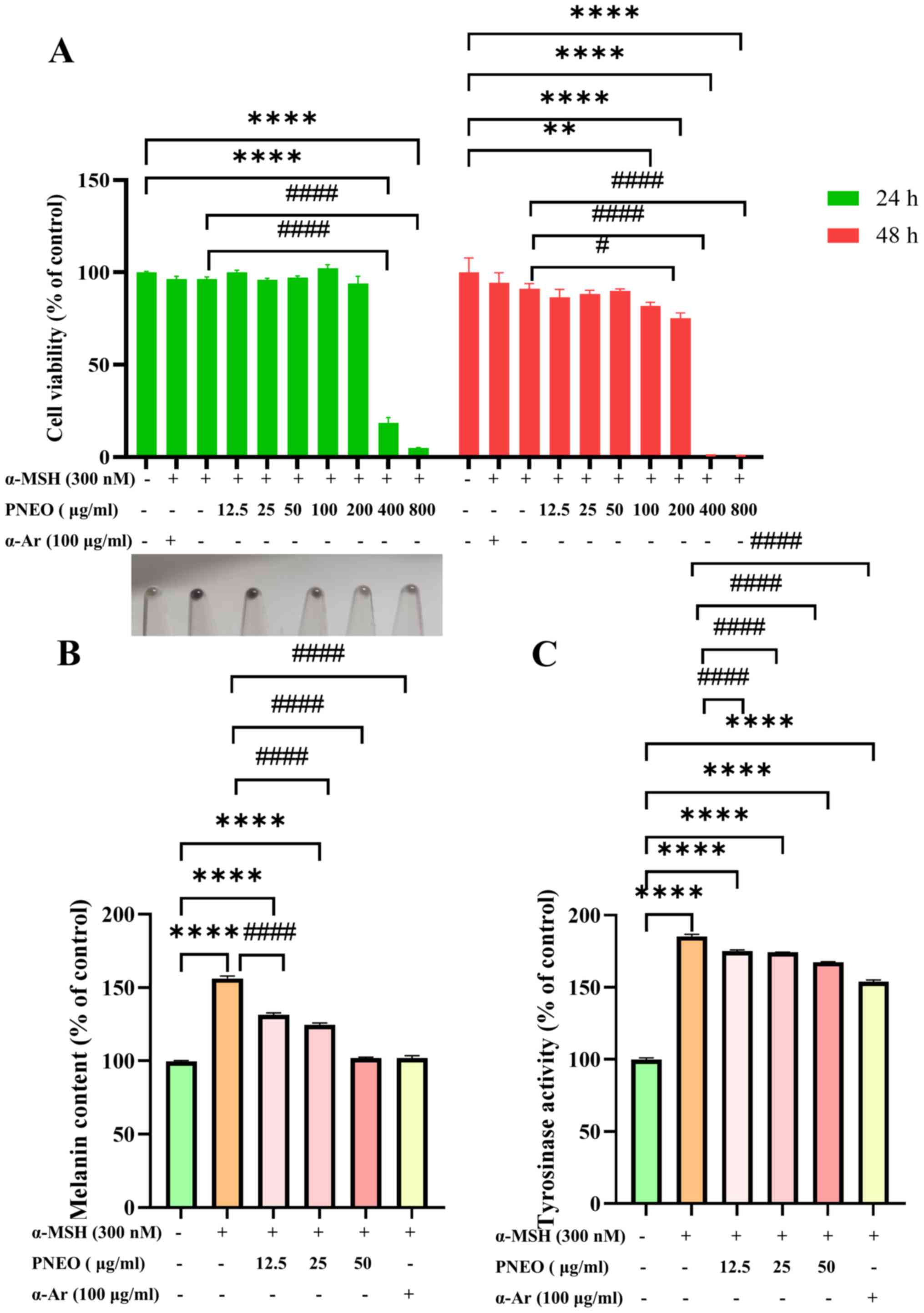
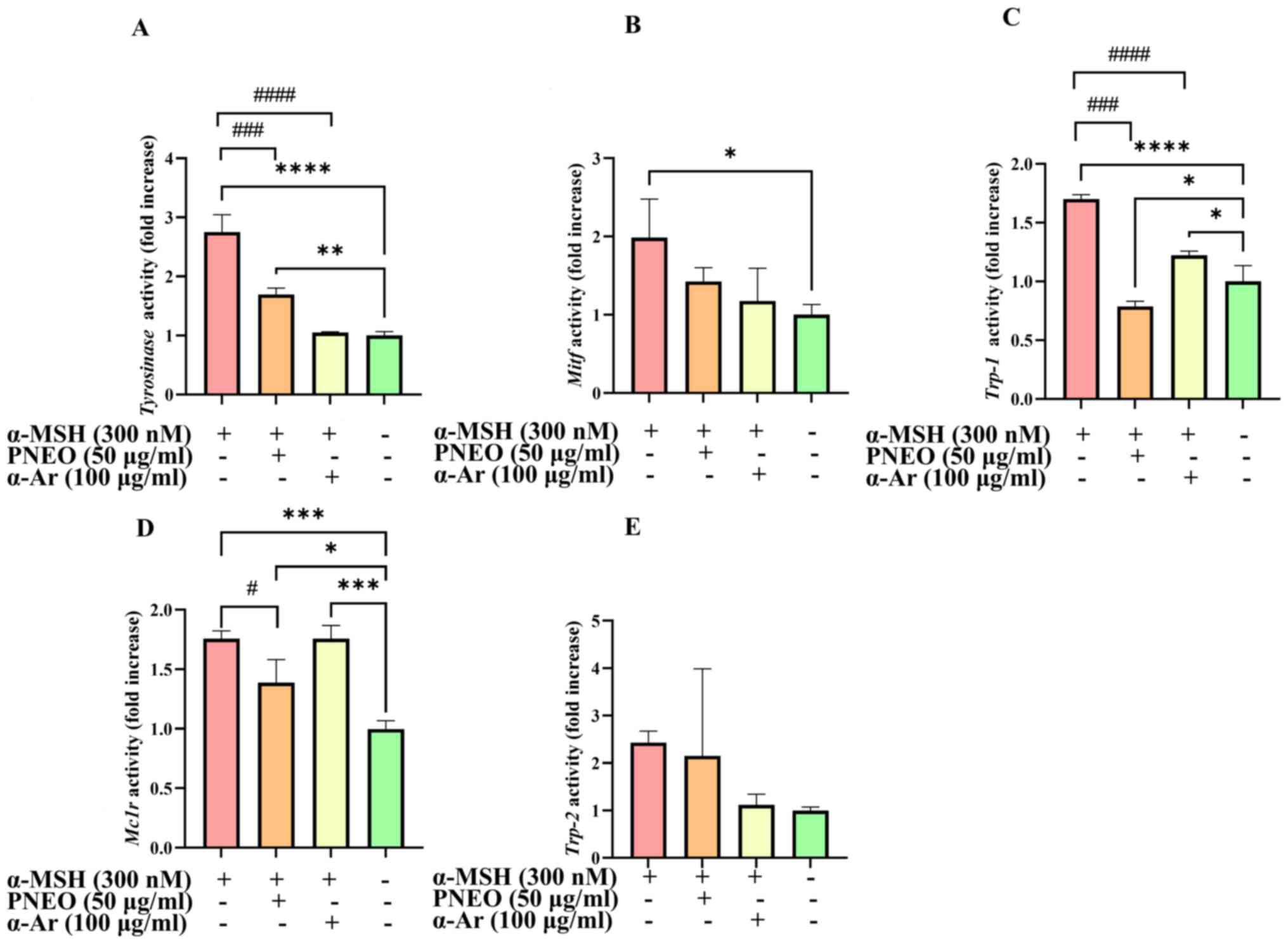
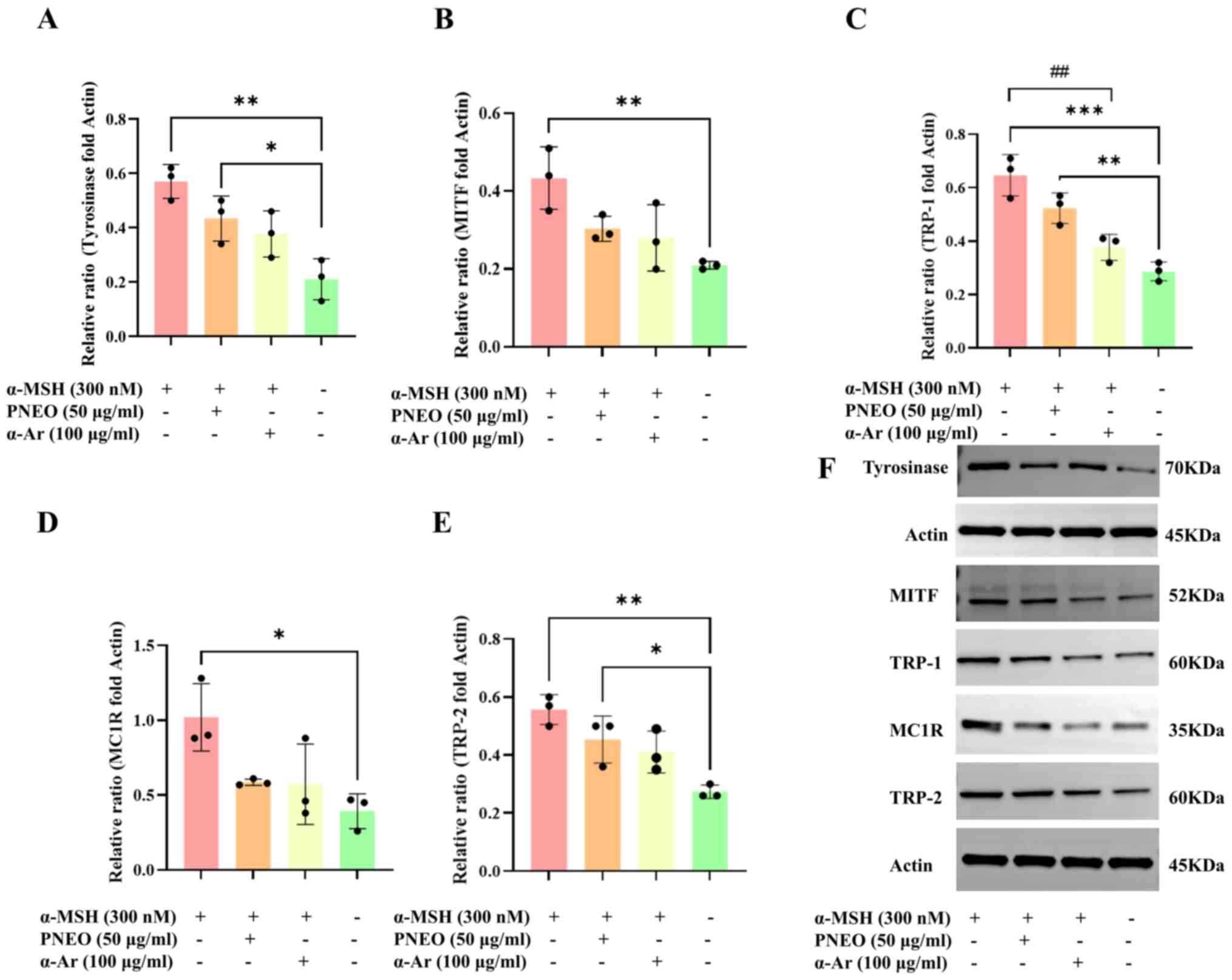
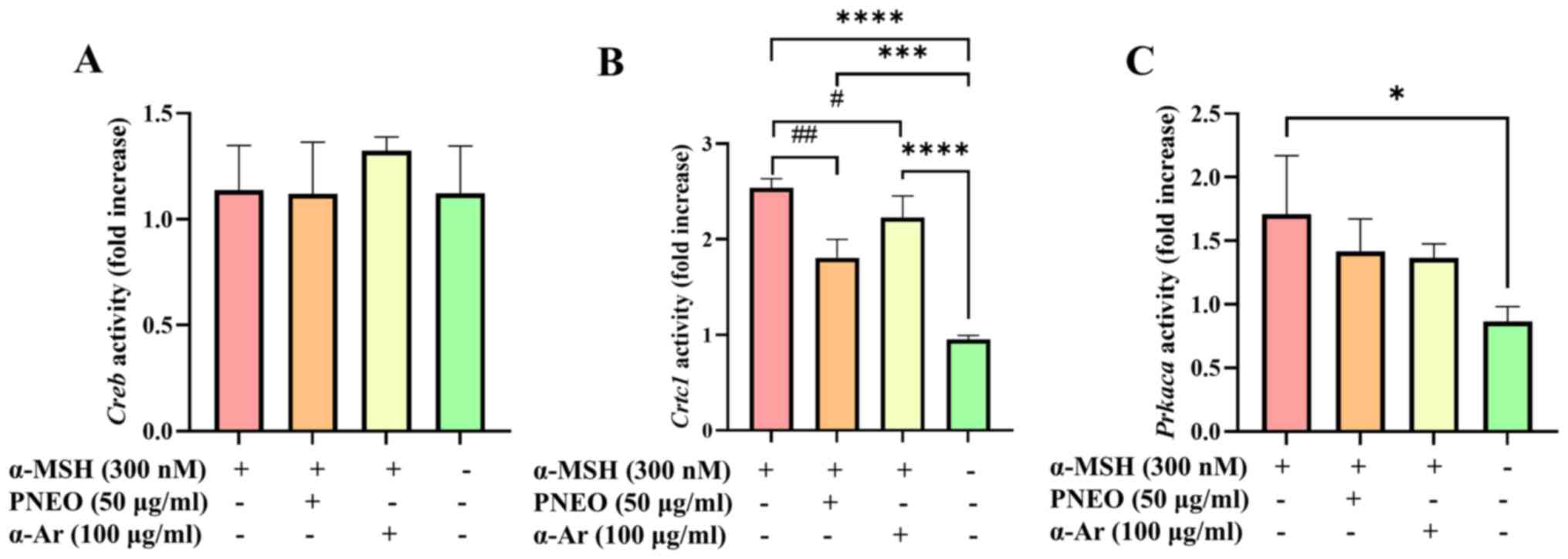
|
1
|
Uong A and Zon LI: Melanocytes in
development and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 222:38–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cui YZ and Man XY: Biology of melanocytes
in mammals. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11(1309557)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hou L and Pavan WJ: Transcriptional and
signaling regulation in neural crest stem cell-derived melanocyte
development: Do all roads lead to Mitf? Cell Res. 18:1163–1176.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tadokoro R, Shikaya Y and Takahashi Y:
Wide coverage of the body surface by melanocyte-mediated skin
pigmentation. Dev Biol. 449:83–89. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lin JY and Fisher DE: Melanocyte biology
and skin pigmentation. Nature. 445:843–850. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Maranduca MA, Branisteanu D, Serban DN,
Branisteanu DC, Stoleriu G, Manolache N and Serban IL: Synthesis
and physiological implications of melanic pigments. Oncol Lett.
17:4183–4187. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
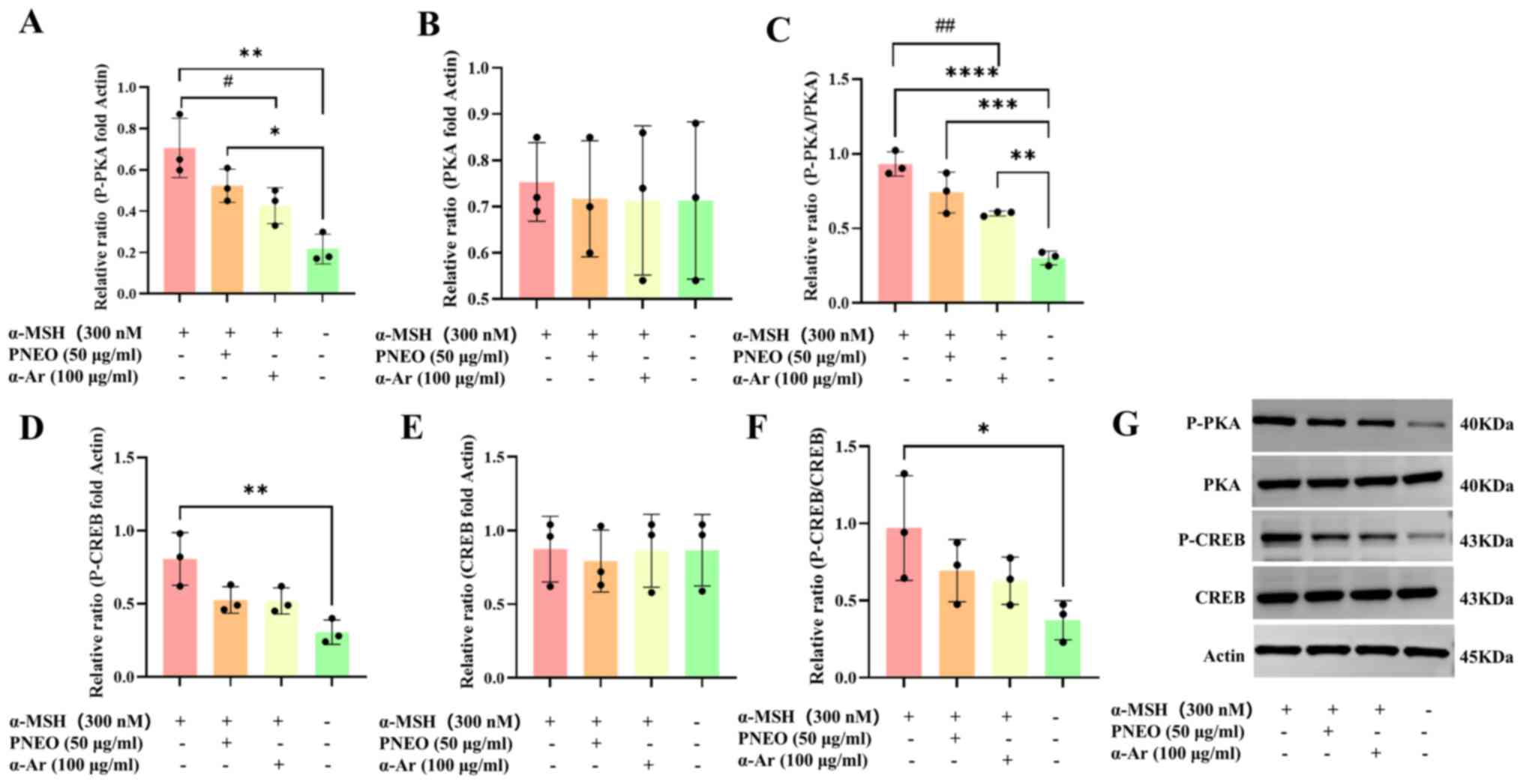
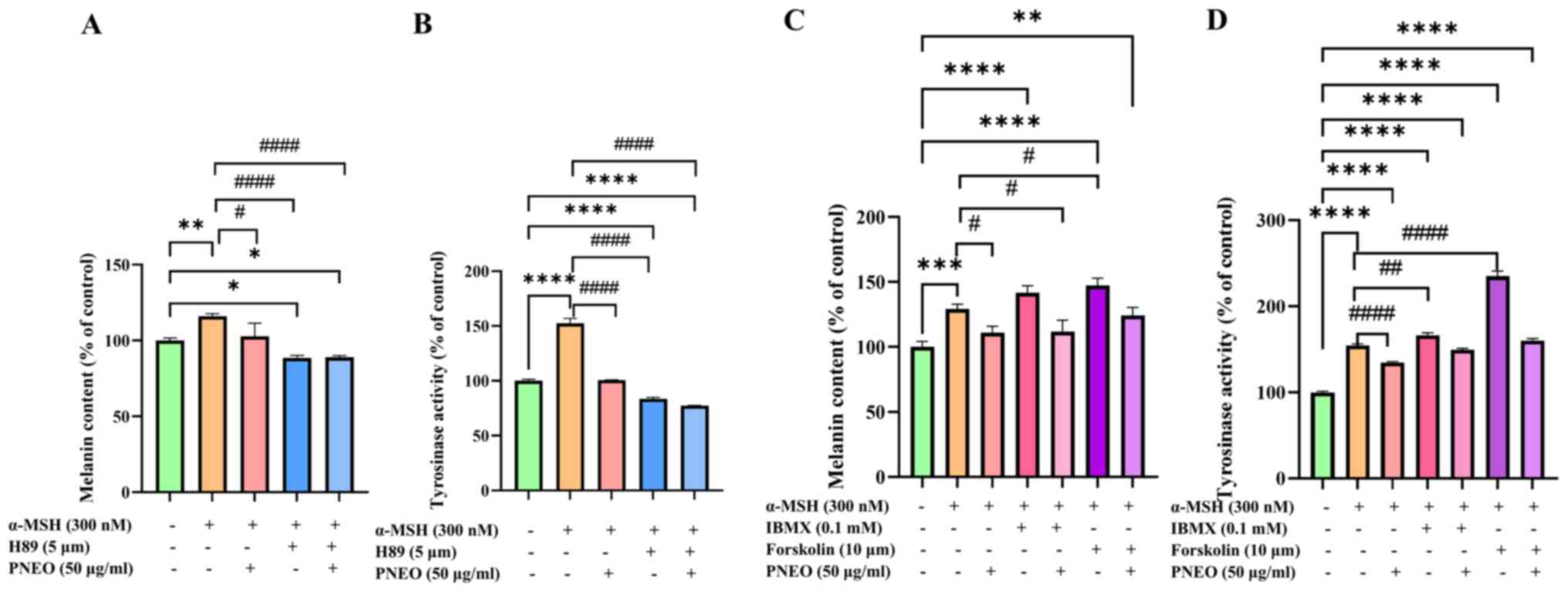
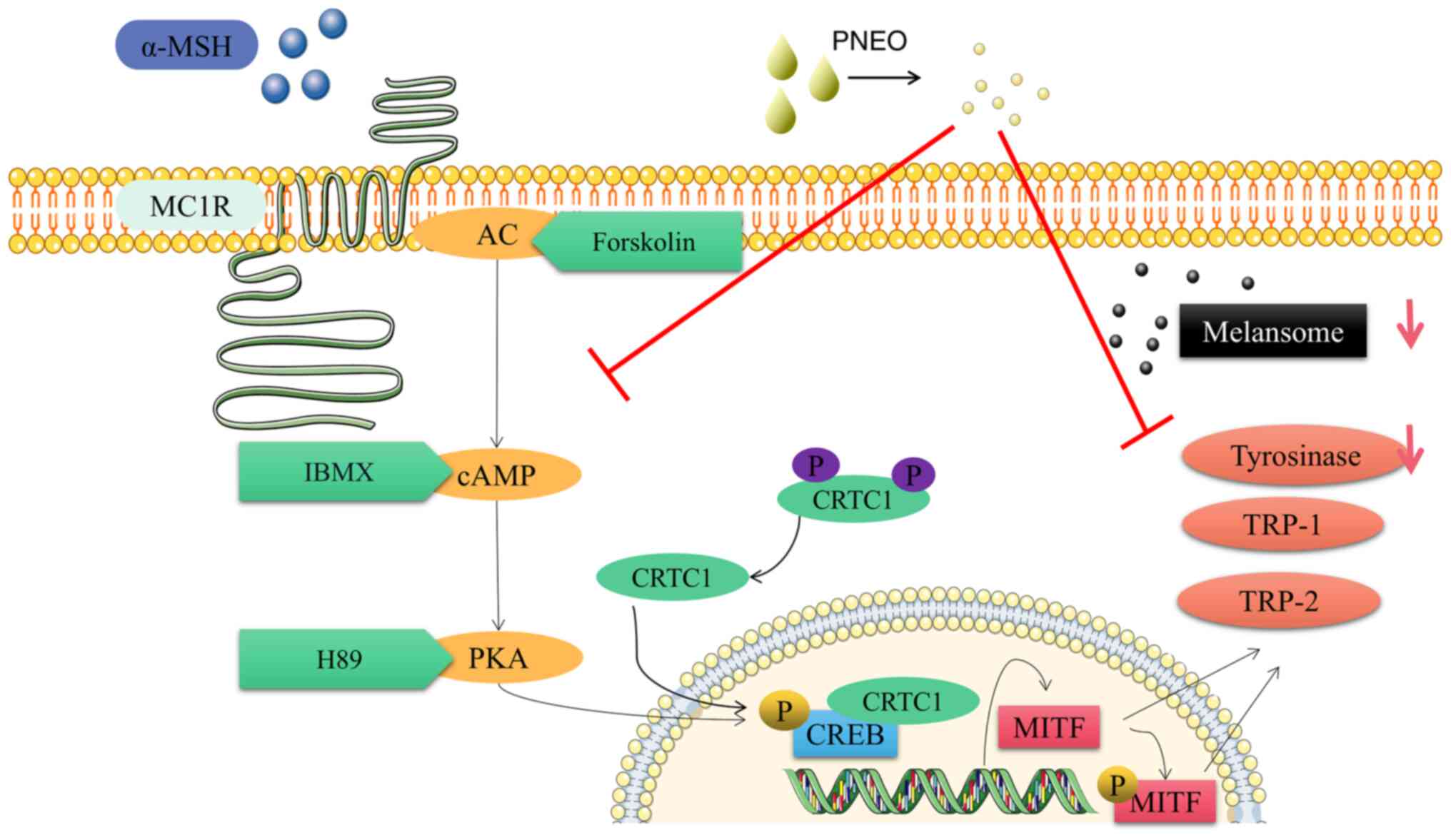
D'Mello SA, Finlay GJ, Baguley BC and
Askarian-Amiri ME: Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int J Mol
Sci. 17(1144)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim HD, Choi H, Abekura F, Park JY, Yang
WS, Yang SH and Kim CH: Naturally-occurring tyrosinase inhibitors
classified by enzyme kinetics and copper chelation. Int J Mol Sci.
24(8226)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Arndt KA and Fitzpatrick TB: Topical use
of hydroquinone as a depigmenting agent. JAMA. 194:965–967.
1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Draelos ZD: Skin lightening preparations
and the hydroquinone controversy. Dermatol Ther. 20:308–313.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
McKesey J, Tovar-Garza A and Pandya AG:
Melasma treatment: An evidence-based review. Am J Clin Dermatol.
21:173–225. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim HM, Byun KA, Oh S, Yang JY, Park HJ,
Chung MS, Son KH and Byun K: A mixture of topical forms of
polydeoxyribonucleotide, vitamin C, and niacinamide attenuated skin
pigmentation and increased skin elasticity by modulating nuclear
factor erythroid 2-like 2. Molecules. 27(1276)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Park HJ, Byun KA, Oh S, Kim HM, Chung MS,
Son KH and Byun K: The combination of niacinamide, vitamin C, and
PDRN mitigates melanogenesis by modulating nicotinamide nucleotide
transhydrogenase. Molecules. 27(4923)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Saeedi M, Eslamifar M and Khezri K: Kojic
acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations.
Biomed Pharmacother. 110:582–593. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zilles JC, Dos Santos FL,
Kulkamp-Guerreiro IC and Contri RV: Biological activities and
safety data of kojic acid and its derivatives: A review. Exp
Dermatol. 31:1500–1521. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Gao Y, Wang W, Zhang J, Yin J, Le
T, Xue J, Engelhardt UH and Jiang H: Kojic acid showed consistent
inhibitory activity on tyrosinase from mushroom and in cultured
B16F10 cells compared with arbutins. Antioxidants (Basel).
11(502)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bairagi J, Saikia PJ, Boro F and Hazarika
A: A review on the ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and
pharmacology of Polygonum hydropiper Linn. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 74:619–645. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Merecz-Sadowska A, Sitarek P, Stelmach J,
Zajdel K, Kucharska E and Zajdel R: Plants as modulators of
melanogenesis: Role of extracts, pure compounds and patented
compositions in therapy of pigmentation disorders. Int J Mol Sci.
23(14787)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Merecz-Sadowska A, Sitarek P, Kowalczyk T,
Zajdel K, Kucharska E and Zajdel R: The modulation of melanogenesis
in B16 cells upon treatment with plant extracts and isolated plant
compounds. Molecules. 27(4360)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D and
Idaomar M: Biological effects of essential oils-a review. Food Chem
Toxicol. 46:446–475. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Saab AM, Gambari R, Sacchetti G, Guerrini
A, Lampronti I, Tacchini M, El Samrani A, Medawar S, Makhlouf H,
Tannoury M, et al: Phytochemical and pharmacological properties of
essential oils from Cedrus species. Nat Prod Res. 32:1415–1427.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Al-Khayri JM, Banadka A, Nandhini M,
Nagella P, Al-Mssallem MQ and Alessa FM: Essential oil from
Coriandrum sativum: A review on its phytochemistry and
biological activity. Molecules. 28(696)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chao WW, Su CC, Peng HY and Chou ST:
Melaleuca quinquenervia essential oil inhibits
α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanin production and
oxidative stress in B16 melanoma cells. Phytomedicine. 34:191–201.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chou ST, Chang WL, Chang CT, Hsu SL, Lin
YC and Shih Y: Cinnamomum cassia essential oil inhibits
α-MSH-induced melanin production and oxidative stress in murine B16
melanoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 14:19186–191201. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hsiao WW, Kumar KJS, Lee HJ, Tsao NW and
Wang SY: Anti-Melanogenic activity of Calocedrus formosana
wood essential oil and its chemical composition analysis. Plants
(Basel). 11(62)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ailli A, Handaq N, Touijer H, Gourich AA,
Drioiche A, Zibouh K, Eddamsyry B, El Makhoukhi F, Mouradi A, Bin
Jardan YA, et al: Phytochemistry and biological activities of
essential oils from six aromatic medicinal plants with cosmetic
properties. Antibiotics (Basel). 12(721)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sharmeen JB, Mahomoodally FM, Zengin G and
Maggi F: Essential oils as natural sources of fragrance compounds
for cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 26(666)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang S, Xie H, Huang J, Chen Q, Li X,
Chen X, Liang J and Wang L: Ultrasound-assisted extraction of
polyphenols from pine needles (Pinus elliottii):
Comprehensive insights from RSM optimization, antioxidant activity,
UHPLC-Q-exactive orbitrap MS/MS analysis and kinetic model.
Ultrason Sonochem. 102(106742)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Qiu B, Jiang W, Qiu W, Mu W, Qin Y, Zhu Y,
Zhang J, Wang Q, Liu D and Qu Z: Pine needle oil induces G2/M
arrest of HepG2 cells by activating the ATM pathway. Exp Ther Med.
15:1975–1981. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Khoury M, El Beyrouthy M, Ouaini N, Iriti
M, Eparvier V and Stien D: Chemical composition and antimicrobial
activity of the essential oil of Juniperus excelsa M.Bieb.
growing wild in Lebanon. Chem Biodivers. 11:825–830.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lizarraga-Valderrama LR: Effects of
essential oils on central nervous system: Focus on mental health.
Phytother Res. 35:657–679. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ha TKQ, Lee BW, Nguyen NH, Cho HM,
Venkatesan T, Doan TP, Kim E and Oh WK: Antiviral activities of
compounds isolated from Pinus densiflora (pine tree) against
the influenza A virus. Biomolecules. 10(711)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lü SY, Shang BQ, Sun LY, Liu GL, Wu Q and
Geng Y: Process optimization and antioxidant activity of pine
needle essential oil extracted by microwave-assisted extraction.
Sci Technol Food Ind. 46:184–191. 2025.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Bagade SB and Patil M: Recent advances in
microwave assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from complex
herbal samples: A review. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 51:138–149.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Masota NE, Vogg G, Heller E and Holzgrabe
U: Comparison of extraction efficiency and selectivity between
low-temperature pressurized microwave-assisted extraction and
prolonged maceration. Arch Pharm (Weinheim).
353(e2000147)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dahmoune F, Nayak B, Moussi K, Remini H
and Madani K: Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of
polyphenols from Myrtus communis L. leaves. Food Chem.
166:585–595. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rahim MA, Ayub H, Sehrish A, Ambreen S,
Khan FA, Itrat N, Nazir A, Shoukat A, Shoukat A, Ejaz A, et al:
Essential components from plant source oils: A review on
extraction, detection, identification, and quantification.
Molecules. 28(6881)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cardoso-Ugarte GA, Juárez-Becerra GP,
Sosa-Morales ME and López-Malo A: Microwave-assisted extraction of
essential oils from herbs. J Microw Power Electromagn Energy.
47:63–72. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pillaiyar T, Manickam M and Namasivayam V:
Skin whitening agents: Medicinal chemistry perspective of
tyrosinase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 32:403–425.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Mansour RB, Wasli H, Bourgou S, Khamessi
S, Ksouri R, Megdiche-Ksouri W and Cardoso SM: Insights on
Juniperus phoenicea essential oil as potential anti-proliferative,
anti-tyrosinase, and antioxidant candidate. Molecules.
28(7547)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yang J, Lee SY, Jang SK, Kim KJ and Park
MJ: Inhibition of melanogenesis by essential oils from the citrus
cultivars peels. Int J Mol Sci. 24(4207)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jimenez-Lopez C, Carpena M, Lourenço-Lopes
C, Gallardo-Gomez M, Lorenzo JM, Barba FJ, Prieto MA and
Simal-Gandara J: Bioactive compounds and quality of extra virgin
olive oil. Foods. 9(1014)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Valverde P, Healy E, Jackson I, Rees JL
and Thody AJ: Variants of the melanocyte-stimulating hormone
receptor gene are associated with red hair and fair skin in humans.
Nat Genet. 11:328–330. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang C, Chery S, Lazerson A, Altman NH,
Jackson R, Holt G, Campos M, Schally AV and Mirsaeidi M:
Anti-inflammatory effects of α-MSH through p-CREB expression in
sarcoidosis like granuloma model. Sci Rep. 10(7277)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ozdeslik RN, Olinski LE, Trieu MM, Oprian
DD and Oancea E: Human nonvisual opsin 3 regulates pigmentation of
epidermal melanocytes through functional interaction with
melanocortin 1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:11508–11517.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cheng MC, Lee TH, Chu YT, Syu LL, Hsu SJ,
Cheng CH, Wu J and Lee CK: Melanogenesis inhibitors from the
rhizoma of ligusticum sinense in B16-F10 melanoma cells in vitro
and zebrafish in vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 19(3994)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lim HY, Kim E, Park SH, Hwang KH, Kim D,
Jung YJ, Kopalli SR, Hong YD, Sung GH and Cho JY: Antimelanogenesis
effects of theasinensin A. Int J Mol Sci. 22(7453)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Xu Y, Vijayasaradhi S and Houghton AN: The
cytoplasmic tail of the mouse brown locus product determines
intracellular stability and export from the endoplasmic reticulum.
J Invest Dermatol. 110:324–331. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li CY, Gao TW, Wang G, Han ZY, Shen Z, Li
TH and Liu YF: The effect of antisense tyrosinase-related protein 1
on melanocytes and malignant melanoma cells. Br J Dermatol.
150:1081–1090. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yun CY, Hong SD, Lee YH, Lee J, Jung DE,
Kim GH, Kim SH, Jung JK, Kim KH, Lee H, et al: Nuclear entry of
CRTC1 as druggable target of acquired pigmentary disorder.
Theranostics. 9:646–660. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Seo GY, Ha Y, Park AH, Kwon OW and Kim YJ:
Leathesia difformis extract inhibits α-MSH-induced
melanogenesis in B16F10 cells via down-regulation of CREB signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 20(536)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wu KC, Hseu YC, Shih YC, Sivakumar G, Syu
JT, Chen GL, Lu MT and Chu PC: Calycosin, a common dietary
isoflavonoid, suppresses melanogenesis through the downregulation
of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
23(1358)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|