|
1
|
Ryu TY, Park J and Scherer PE:
Hyperglycemia as a risk factor for cancer progression. Diabetes
Metab J. 38:330–336. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Varghese E, Samuel SM, Líšková A, Samec M,
Kubatka P and Büsselberg D: Targeting glucose metabolism to
overcome resistance to anticancer chemotherapy in breast cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 12(2252)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Qiu J, Zheng Q and Meng X: Hyperglycemia
and chemoresistance in breast cancer: From cellular mechanisms to
treatment response. Front Oncol. 11(628359)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Flores-López LA, Martínez-Hernández MG,
Viedma-Rodríguez R, Díaz-Flores M and Baiza-Gutman LA: High glucose
and insulin enhance uPA expression, ROS formation and invasiveness
in breast cancer-derived cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 39:365–378.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bergandi L, Mungo E, Morone R, Bosco O,
Rolando B and Doublier S: Hyperglycemia promotes chemoresistance
through the reduction of the mitochondrial DNA damage, the
Bax/Bcl-2 and Bax/Bcl-XL ratio, and the cells in sub-G1 phase due
to antitumoral drugs induced-cytotoxicity in human colon
adenocarcinoma cells. Front Pharmacol. 9(866)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Viedma-Rodríguez R, Martínez-Hernández MG,
Flores-López LA and Baiza-Gutman LA: Epsilon-aminocaproic acid
prevents high glucose and insulin induced-invasiveness in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, modulating the plasminogen
activator system. Mol Cell Biochem. 437:65–80. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huang Y, Hong W and Wei X: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression
and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 15(129)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Panigrahi G, Candia J, Dorsey TH, Tang W,
Ohara Y, Byun JS, Minas TZ, Zhang AL, Ajao A, Cellini A, et al:
Diabetes-associated breast cancer is molecularly distinct and shows
a DNA damage repair deficiency. JCI Insight.
8(e170105)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Hushmandi K,
Kalantari M, Mohammadinejad R, Javaheri T and Sethi G: Association
of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) with cisplatin
resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 21(4002)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Frossard M, Blank D, Joukhadar Ch, Bayegan
K, Schmid R, Luger A and Müller M: Interstitial glucose in skeletal
muscle of diabetic patients during an oral glucose tolerance test.
Diabet Med. 22:56–60. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gorji-Bahri G, Moradtabrizi N, Vakhshiteh
F and Hashemi A: Validation of common reference genes stability in
exosomal mRNA-isolated from liver and breast cancer cell lines.
Cell Biol Int. 45:1098–1110. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Xie J, Liu Z, Gong Q, Tian R and Su
G: Identification and validation of reference genes for
quantitative RT-PCR analysis of retinal pigment epithelium cells
under hypoxia and/or hyperglycemia. Gene. 580:41–46.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J and
Jensen LJ: Cytoscape StringApp: Network analysis and visualization
of proteomics data. J Proteome Res. 18:623–632. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4)(S11)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yasunaga M and Matsumura Y: Role of SLC6A6
in promoting the survival and multidrug resistance of colorectal
cancer. Sci Rep. 4(4852)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shi Y, Zhai H, Wang X, Han Z, Liu C, Lan
M, Du J, Guo C, Zhang Y, Wu K and Fan D: Ribosomal proteins S13 and
L23 promote multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by
suppressing drug-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 296:337–346.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Garcia-Mayea Y, Mir C, Carballo L,
Sánchez-García A, Bataller M and ME LL: TSPAN1, a novel tetraspanin
member highly involved in carcinogenesis and chemoresistance.
Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1877(188674)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tong C, Qu K, Wang G, Liu R, Duan B, Wang
X and Liu C: Knockdown of DNA-binding protein A enhances the
chemotherapy sensitivity of colorectal cancer via suppressing the
Wnt/β-catenin/Chk1 pathway. Cell Biol Int. 44:2075–2085.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
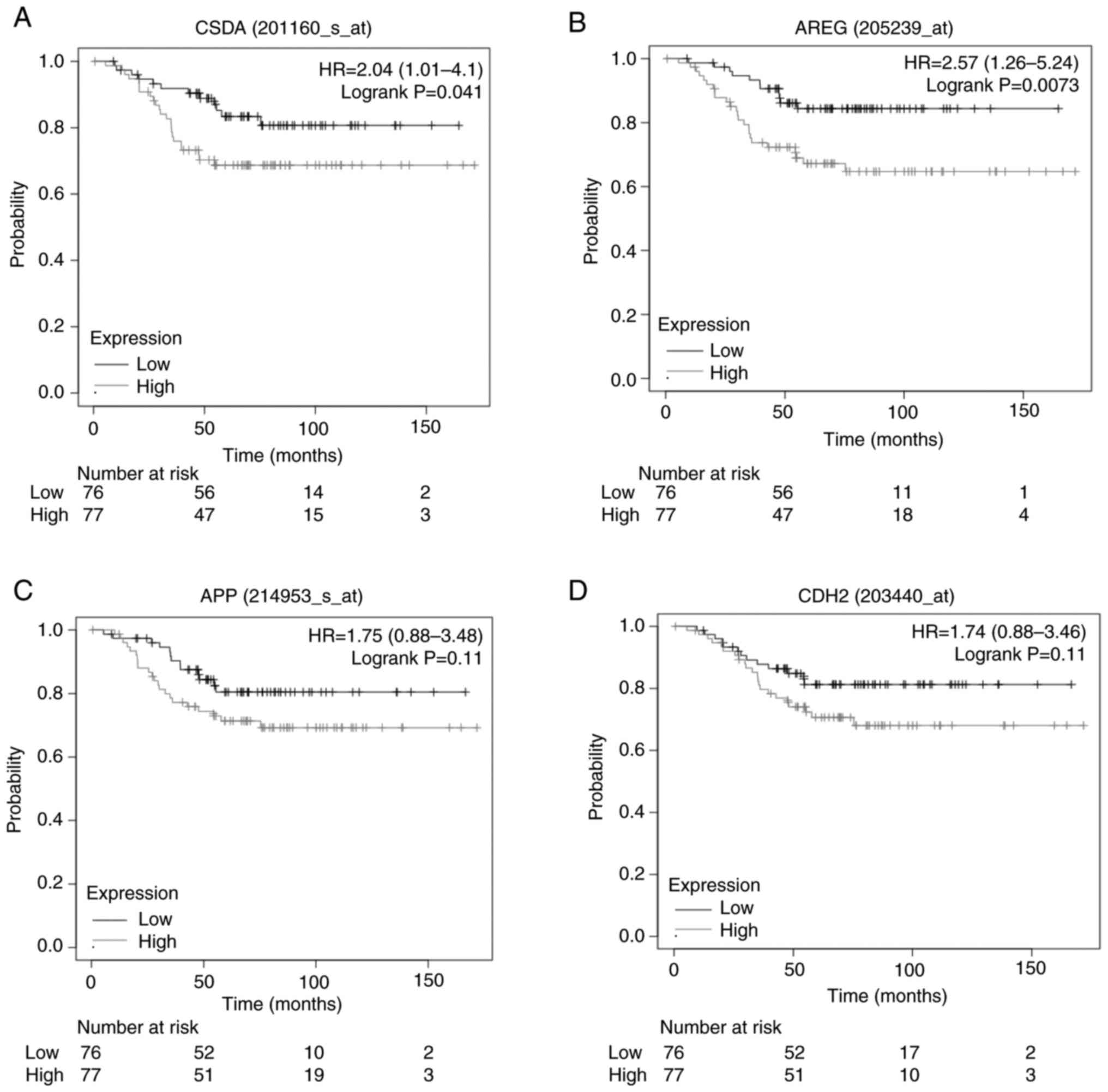
Lánczky A and Győrffy B: Web-based
survival analysis tool tailored for medical research (KMplot):
Development and implementation. J Med Internet Res.
23(e27633)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu N, Sheng X, Liu Y, Zhang X and Yu J:
Increased CD70 expression is associated with clinical resistance to
cisplatin-based chemotherapy and poor survival in advanced ovarian
carcinomas. Onco Targets Ther. 6:615–619. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hartman ML and Czyz M: BCL-w: Apoptotic
and non-apoptotic role in health and disease. Cell Death Dis.
11(260)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bano D and Prehn JHM: Apoptosis-inducing
factor (AIF) in physiology and disease: The tale of a repented
natural born killer. EBioMedicine. 30:29–37. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zheng HC: The molecular mechanisms of
chemoresistance in cancers. Oncotarget. 8:59950–59964.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gozuacik D, Bialik S, Raveh T, Mitou G,
Shohat G, Sabanay H, Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Kimchi A:
DAP-kinase is a mediator of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
caspase activation and autophagic cell death. Cell Death Differ.
15:1875–1886. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Viedma-Rodríguez R, Martínez-Hernández MG,
Martínez-Torres DI and Baiza-Gutman LA: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition and progression of breast cancer promoted by diabetes
mellitus in mice are associated with increased expression of
glycolytic and proteolytic enzymes. Horm Cancer. 11:170–181.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Vaughn AE and Deshmukh M: Glucose
metabolism inhibits apoptosis in neurons and cancer cells by redox
inactivation of cytochrome c. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1477–1483.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu DM, Liu T, Deng SH, Han R and Xu Y:
SLC39A4 expression is associated with enhanced cell migration,
cisplatin resistance, and poor survival in non-small cell lung
cancer. Sci Rep. 7(7211)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ren X, Cui H, Wu J, Zhou R, Wang N, Liu D,
Xie X, Zhang H, Liu D, Ma X, et al: Identification of a combined
apoptosis and hypoxia gene signature for predicting prognosis and
immune infiltration in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 11:3886–3901.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wen P, Wang R, Xing Y, Ouyang W, Yuan Y,
Zhang S, Liu Y and Peng Z: The prognostic value of the GPAT/AGPAT
gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma and its role in the tumor
immune microenvironment. Front Immunol. 14(1026669)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu Y, Chen W, Gong Y, Liu H and Zhang B:
Tetraspanin 1 (TSPAN1) promotes growth and transferation of breast
cancer cells via mediating PI3K/Akt pathway. Bioengineered.
12:10761–10770. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Merikhian P, Eisavand MR and Farahmand L:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Understanding Wnt signaling in drug
resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 21(419)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wong GT, Gavin BJ and McMahon AP:
Differential transformation of mammary epithelial cells by Wnt
genes. Mol Cell Biol. 14:6278–6286. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ayyanan A, Civenni G, Ciarloni L, Morel C,
Mueller N, Lefort K, Mandinova A, Raffoul W, Fiche M, Dotto GP and
Brisken C: Increased Wnt signaling triggers oncogenic conversion of
human breast epithelial cells by a Notch-dependent mechanism. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3799–3804. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jin X, Jeon HY, Joo KM, Kim JK, Jin J, Kim
SH, Kang BG, Beck S, Lee SJ, Kim JK, et al: Frizzled 4 regulates
stemness and invasiveness of migrating glioma cells established by
serial intracranial transplantation. Cancer Res. 71:3066–3075.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lin CC, Lo MC, Moody R, Jiang H, Harouaka
R, Stevers N, Tinsley S, Gasparyan M, Wicha M and Sun D: Targeting
LRP8 inhibits breast cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Lett. 438:165–173. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Prieto-Vila M, Shimomura I, Kogure A,
Usuba W, Takahashi RU, Ochiya T and Yamamoto Y: Quercetin inhibits
Lef1 and resensitizes docetaxel-resistant breast cancer cells.
Molecules. 25(2576)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Tümen D, Heumann P, Huber J, Hahn N, Macek
C, Ernst M, Kandulski A, Kunst C and Gülow K: Unraveling cancer's
Wnt signaling: Dynamic control through protein kinase regulation.
Cancers (Basel). 16(2686)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Galland L, Ballot E, Mananet H, Boidot R,
Lecuelle J, Albuisson J, Arnould L, Desmoulins I, Mayeur D,
Kaderbhai C, et al: Efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in
metastatic breast cancer and HRD biomarkers: Utility of exome
sequencing. NPJ Breast Cancer. 8(28)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
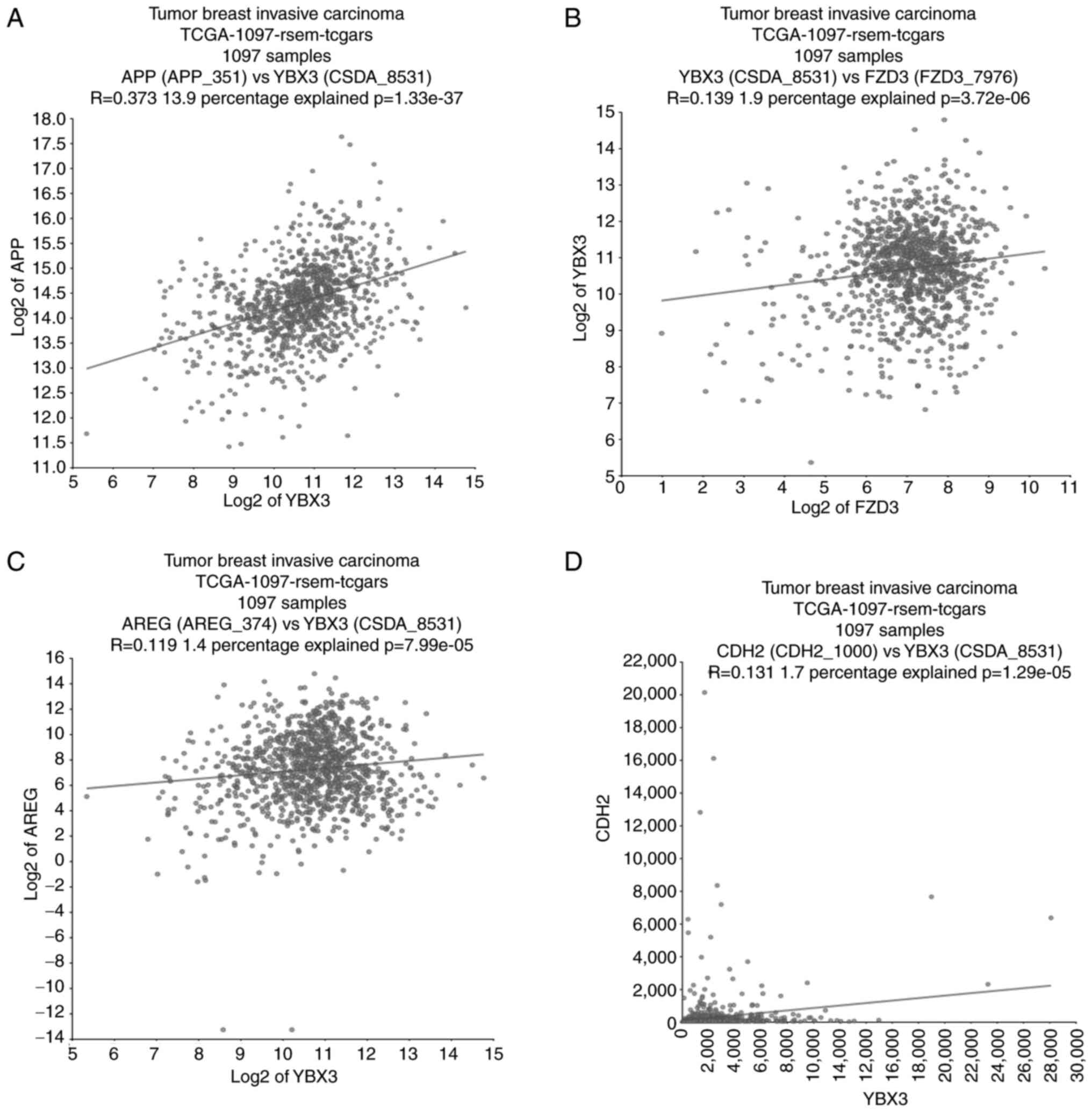
Wang C, You Z, He Y and Chen X:
Identification of RNA-binding protein YBX3 as an oncogene in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics.
23(225)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sun Y, Li Z, Wang W, Zhang X, Li W, Du G,
Yin J, Xiao W and Yang H: Identification and verification of YBX3
and its regulatory gene HEIH as an oncogenic system: A
multidimensional analysis in colon cancer. Front Immunol.
13(957865)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Panupinthu N, Yu S, Zhang D, Zhang F,
Gagea M, Lu Y, Grandis JR, Dunn SE, Lee HY and Mills GB:
Self-reinforcing loop of amphiregulin and Y-box binding protein-1
contributes to poor outcomes in ovarian cancer. Oncogene.
33:2846–2856. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bolitho C, Moscova M, Baxter RC and Marsh
DJ: Amphiregulin increases migration and proliferation of
epithelial ovarian cancer cells by inducing its own expression via
PI3-kinase signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
533(111338)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wu X, Chen S and Lu C: Amyloid precursor
protein promotes the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
45:162–174. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cao ZQ, Wang Z and Leng P: Aberrant
N-cadherin expression in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
118(109320)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ge R, Wang Z, Wu S, Zhuo Y, Otsetov AG,
Cai C, Zhong W, Wu CL and Olumi AF: Metformin represses cancer
cells via alternate pathways in N-cadherin expressing vs N-cadherin
deficient cells. Oncotarget. 6:28973–28987. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Townsend MH, Felsted AM, Ence ZE, Piccolo
SR, Robison RA and O'Neill KL: Falling from grace: HPRT is not
suitable as an endogenous control for cancer-related studies. Mol
Cell Oncol. 6(1575691)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|