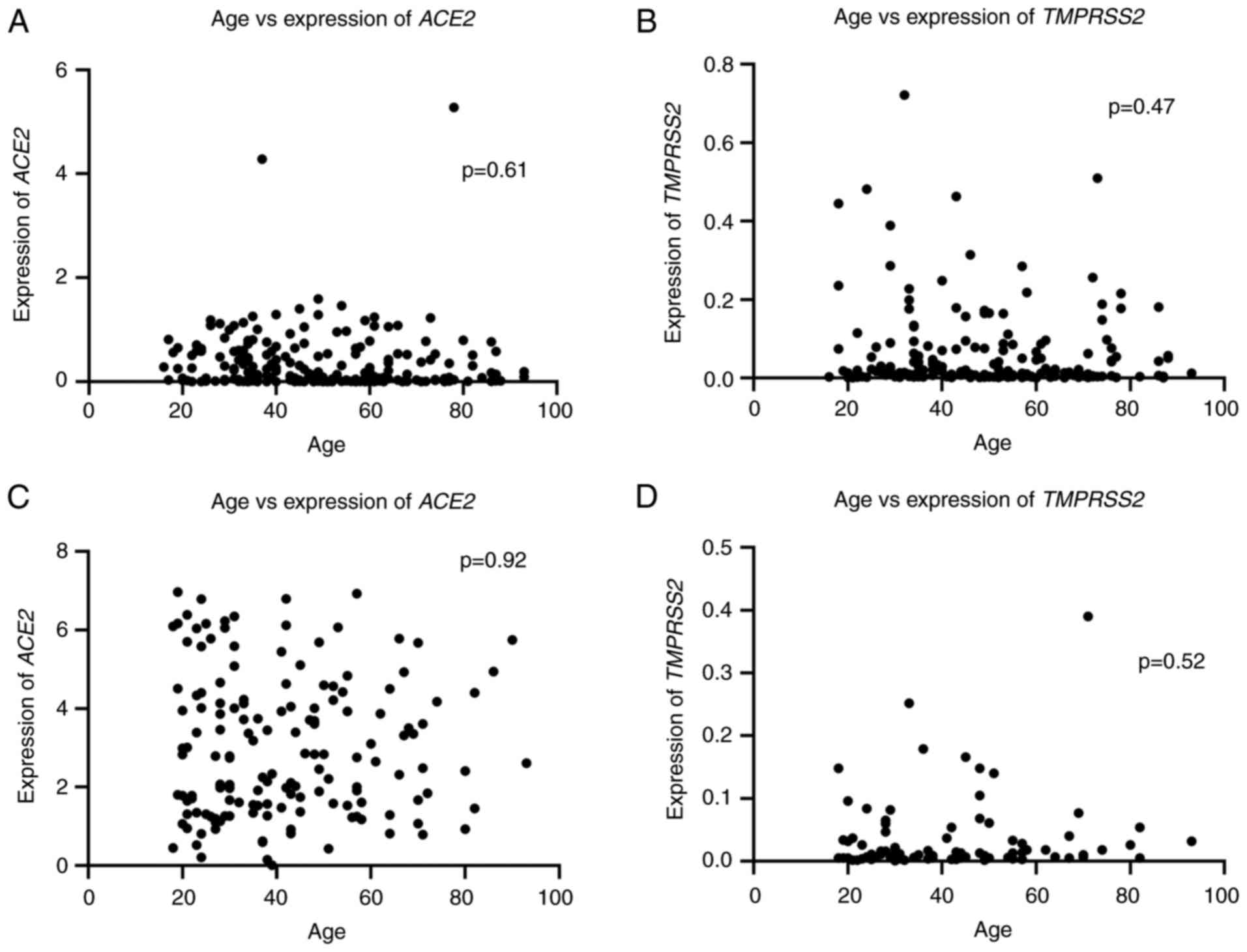
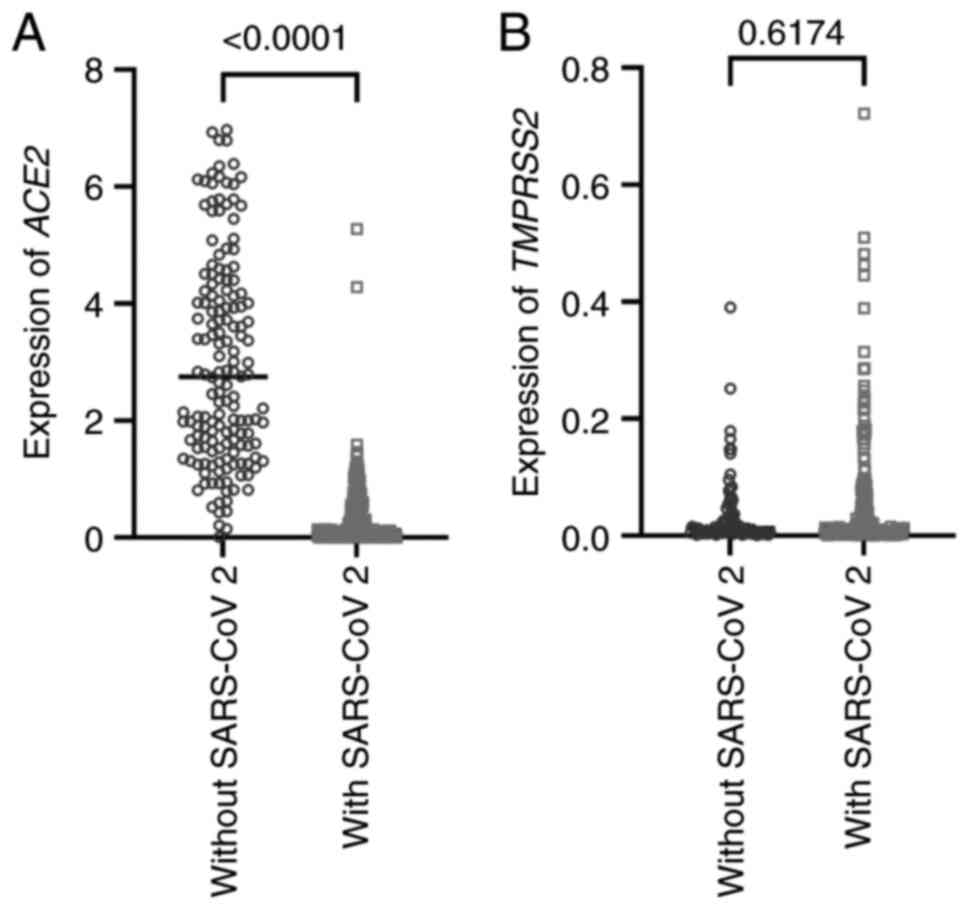
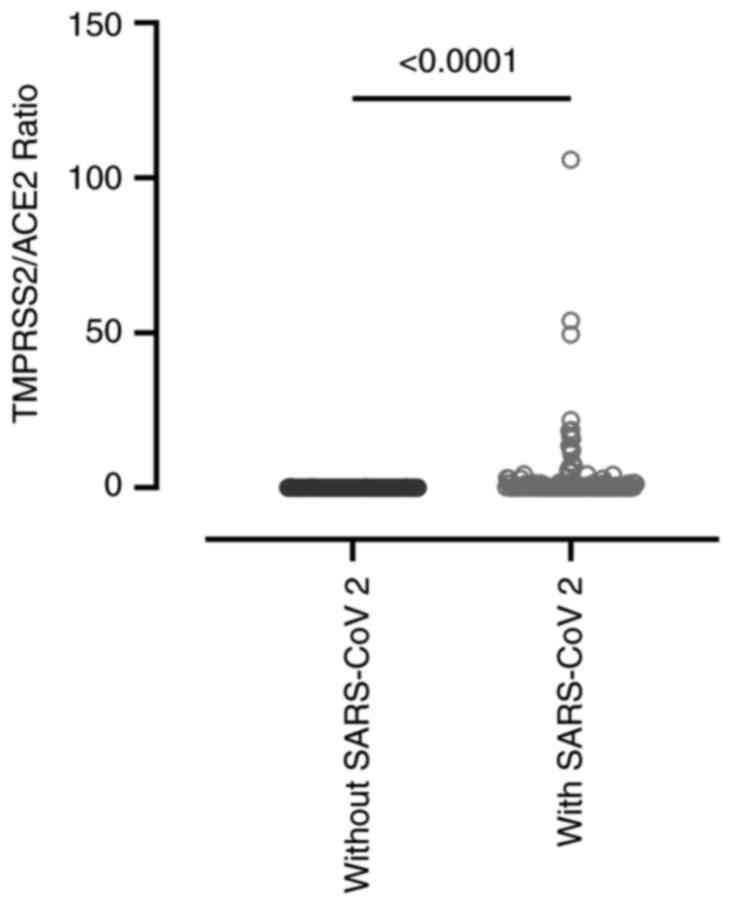
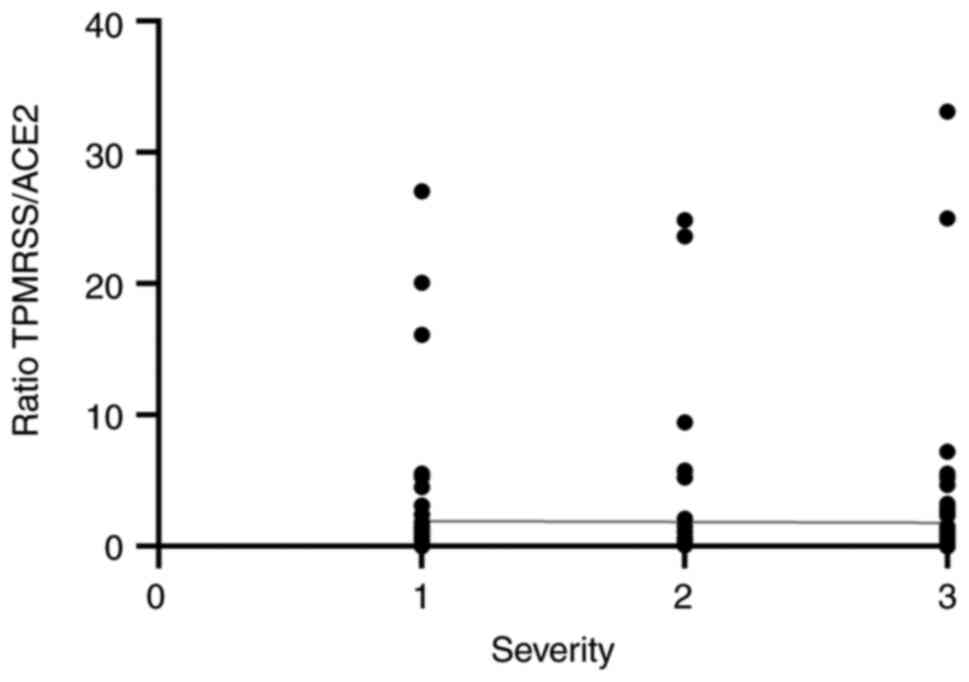
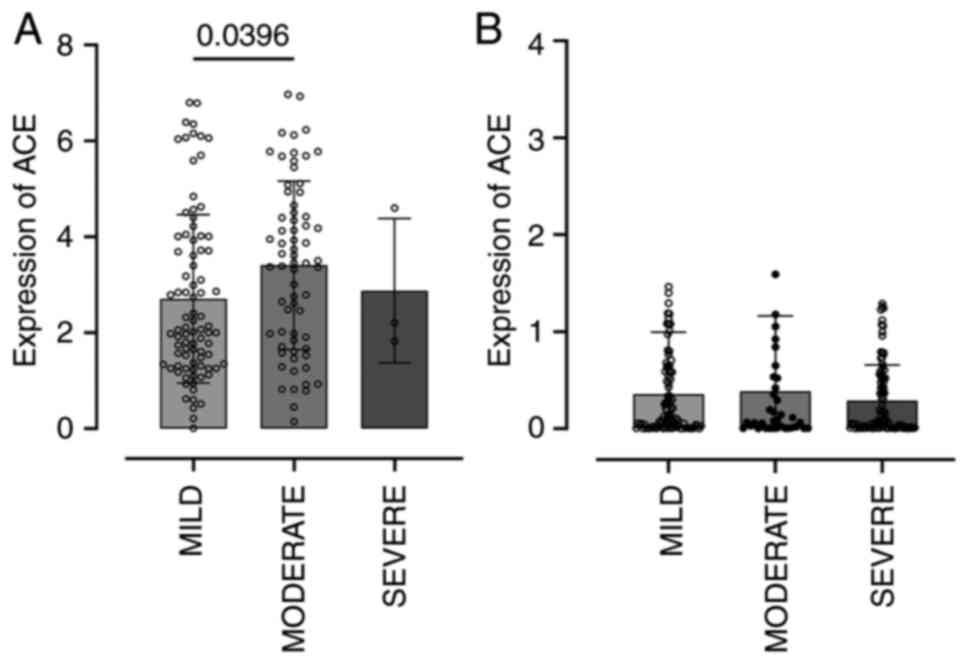
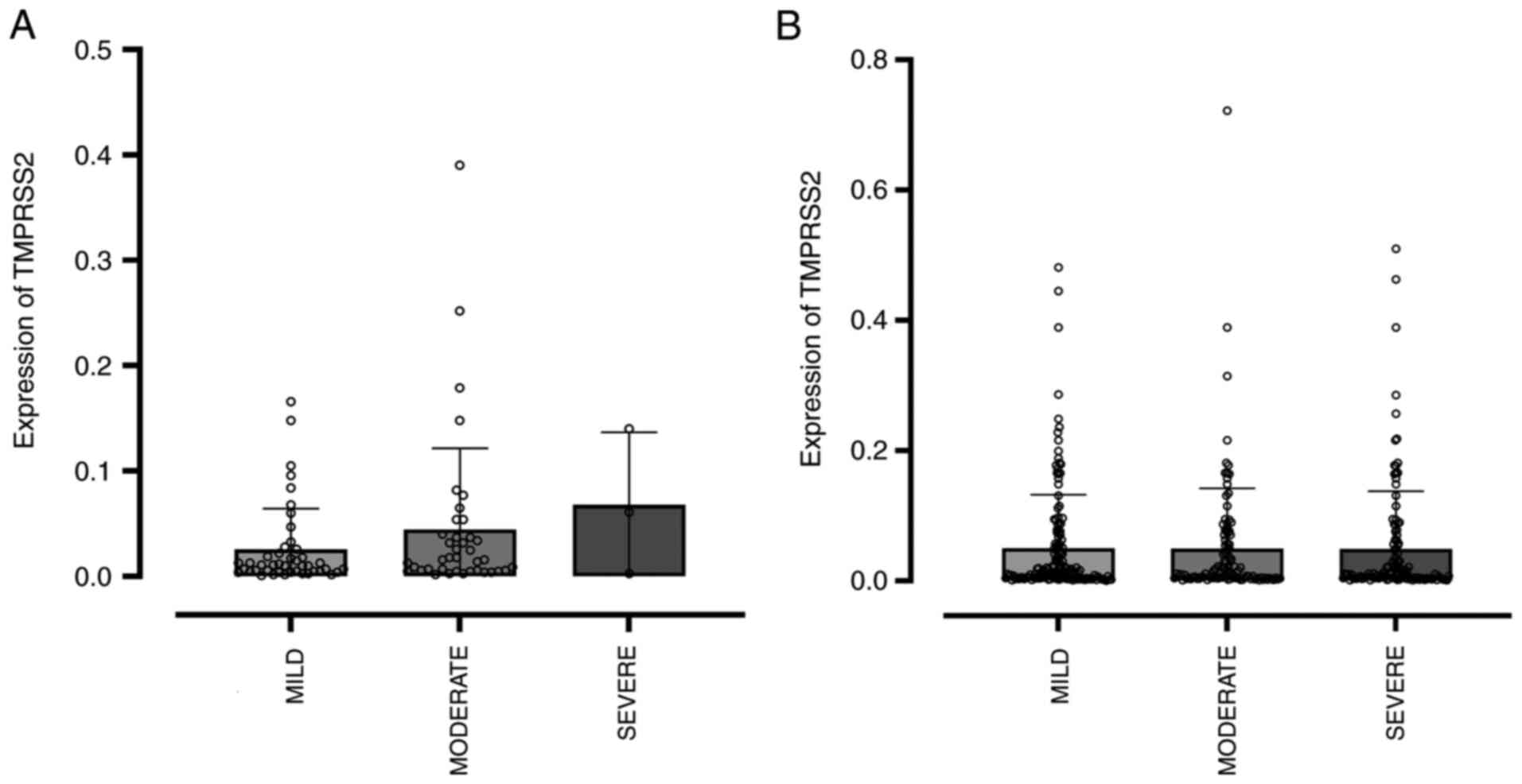
|
1
|
Riou J and Althaus CL: Pattern of early
human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus
(2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020. Euro Surveill.
25(2000058)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
World Health Organization (WHO):
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report-52. WHO,
Geneva, 2020.
|
|
3
|
Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z
and Tong S: Epidemiology of COVID19 among children in China.
Pediatrics. 145(e20200702)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hou Y, Zhao J, Martin W, Kallianpur A,
Chung MK, Jehi L, Sharifi N, Erzurum S, Eng C and Cheng F: New
insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: An ACE2 and
TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis. BMC Med. 18(216)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ejaz H, Alsrhani A, Zafar A, Javed H,
Junaid K, Abdalla AE, Abosalif KOA, Ahmed Z and Younas S: COVID-19
and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients. J
Infect Public Health. 13:1833–1839. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hassanpour M, Rezaie J, Nouri M and Panahi
Y: The role of extracellular vesicles in COVID-19 virus infection.
Infect Genet Evol. 85(104422)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chaudhry F, Lavandero S, Xie X, Sabharwal
B, Zheng YY, Correa A, Narula J and Levy P: Manipulation of ACE2
expression in COVID-19. Open Heart. 7(e001424)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zmora P, Moldenhauer AS, Hofmann-Winkler H
and Pöhlmann S: TMPRSS2 isoform 1 activates respiratory viruses and
is expressed in viral target cells. PLoS One.
10(e0138380)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hoffmann M, Hofmann-Winkler H, Smith JC,
Krüger N, Arora P, Sørensen LK, Søgaard OS, Hasselstrøm JB, Winkler
M, Hempel T, et al: Camostat mesylate inhibits SARS-CoV-2
activation by TMPRSS2-related proteases and its metabolite GBPA
exerts antiviral activity. EbioMedicine. 65(103255)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Matsuyama S, Nagata N, Shirato K, Kawase
M, Takeda M and Taguchi F: Efficient activation of the severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein by the transmembrane
protease TMPRSS2. J Virol. 84:12658–12664. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bilinska K, Jakubowska P, Von Bartheld CS
and Butowt R: Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 entry proteins, ACE2 and
TMPRSS2, in cells of the olfactory epithelium: Identification of
cell types and trends with age. ACS Chem Neurosci. 11:1555–1562.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ren HL, Wen GM, Zhao ZY, Liu DH and Xia P:
Can CD147 work as a therapeutic target for tumors through COVID-19
infection? Int J Med Sci. 19:2087–2092. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cheng Z, Zhou J, To KKW, Chu H, Li C, Wang
D, Yang D, Zheng S, Hao K, Bossé Y, et al: Identification of
TMPRSS2 as a susceptibility gene for severe 2009 pandemic A(H1N1)
influenza and A(H7N9) influenza. J Infect Dis. 212:1214–1221.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cetinkaya EA: Coincidence of COVID-19
infection and smell-taste perception disorders. J Craniofac Surg.
31:e625–e626. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tolouian R, Tolouian AC and Ardalan M:
Blocking serine protease (TMPRSS2) by bromhexine; looking at
potential treatment to prevent COVID-19 infection. Marshall J Med.
6:11–14. 2020.
|
|
16
|
World Health Organization (WHO): Clinical
management of COVID-19: Living guideline, 18 August 2023. WHO,
Geneva, 2023.
|
|
17
|
Hannemann J, Schmidt-Hutten L, Hannemann
J, Kleinsang F and Böger R: Selection of reference genes for
normalization of gene expression after exposure of human
endothelial and epithelial cells to hypoxia. Int J Mol Sci.
26(1763)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hampton TH, Koeppen K, Bashor L and
Stanton BA: Selection of reference genes for quantitative PCR:
Identifying reference genes for airway epithelial cells exposed to
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
319:L256–L265. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Biji A, Khatun O, Swaraj S, Narayan R,
Rajmani RS, Sardar R, Satish D, Mehta S, Bindhu H, Jeevan M, et al:
Identification of COVID-19 prognostic markers and therapeutic
targets through meta-analysis and validation of Omics data from
nasopharyngeal samples. EBioMedicine. 70(103525)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bourgonje AR, Abdulle AE, Timens W,
Hillebrands JL, Navis GJ, Gordijn SJ, Bolling MC, Dijkstra G, Voors
AA, Osterhaus AD, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2),
SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19). J Pathol. 251:228–248. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Saheb Sharif-Askari N, Saheb Sharif-Askari
F, Alabed M, Temsah MH, Al Heialy S, Hamid Q and Halwani R: Airways
expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 Is lower in
children than adults and increases with smoking and COPD. Mol Ther
Methods Clin Dev. 18:1–6. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kimura H, Francisco D, Conway M, Martinez
FD, Vercelli D, Polverino F, Billheimer D and Kraft M: Type 2
inflammation modulates ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in airway epithelial cells.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 146:80–88.e8. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Baratchian M, McManus JM, Berk MP,
Nakamura F, Mukhopadhyay S, Xu W, Erzurum S, Drazba J, Peterson J,
Klein EA, et al: Androgen regulation of pulmonary AR, TMPRSS2 and
ACE2 with implications for sex-discordant COVID-19 outcomes. Sci
Rep. 11(11130)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sarver D and Wong G: Obesity alters Ace2
and Tmprss2 expression in lung, trachea, and esophagus in a
sex-dependent manner: Implications for COVID-19. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 538:92–96. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rossi ÁD, de Araújo JLF, de Almeida TB,
Ribeiro-Alves M, de Almeida Velozo C, Almeida JM, de Carvalho
Leitão I, Ferreira SN, da Silva Oliveira J, Alves HJ, et al:
Association between ACE2 and TMPRSS2 nasopharyngeal expression and
COVID-19 respiratory distress. Sci Rep. 11(9658)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Guo J, Huang Z, Lin L and Lv J:
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and cardiovascular disease: A
viewpoint on the potential influence of angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitors/ angiotensin receptor blockers on onset and
severity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
infection. J Am Heart Assoc. 9(e016219)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Datta PK, Liu F, Fischer T, Rappaport J
and Qin X: SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding
SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for
therapy. Theranostics. 10:7448–7464. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu Y, Zhu Q, Fox DM, Gao C, Stanley SA and
Luo K: SARS-CoV-2 down-regulates ACE2 through lysosomal
degradation. Mol Biol Cell. 33(ar147)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Grace JA, Casey S, Burrell LM and Angus
PW: Proposed mechanism for increased COVID-19 mortality in patients
with decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatol Int. 14:884–885.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Triana S, Metz-Zumaran C, Ramirez C, Kee
C, Doldan P, Shahraz M, Schraivogel D, Gschwind AR, Sharma AK,
Steinmetz LM, et al: Single-cell analyses reveal SARS-CoV-2
interference with intrinsic immune response in the human gut. Mol
Syst Biol. 17(e10232)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kuba K, Yamaguchi T and Penninger JM:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the pathogenesis of ARDS
in COVID-19. Front Immunol. 12(732690)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ni W, Yang X, Yang D, Bao J, Li R, Xiao Y,
Hou C, Wang H, Liu J, Yang D, et al: Role of angiotensin-converting
enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19. Crit Care. 24(422)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ji JY, Jo A, Won J, Gil CH, Shin H, Kim S,
Jeon YJ and Kim HJ: The nasal symbiont Staphylococcus species
restricts the transcription of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors in human
nasal epithelium. iScience. 24(103172)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Takabayashi T, Yoshida K, Imoto Y,
Schleimer RP and Fujieda S: Regulation of the expression of
SARS-CoV-2 receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in Nasal
Mucosa. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 36:115–122. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fowler PC, Naluai ÅT, Oscarsson M,
Torkzadeh S, Bohman A, Bende M and Harandi AM: Differential
expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in nasal tissue of
patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps medRxiv,
2021.
|
|
37
|
Pavel AB, Glickman JW, Michels JR,
Kim-Schulze S, Miller RL and Guttman-Yassky E: Th2/Th1 cytokine
imbalance is associated with higher COVID-19 risk mortality. Front
Genet. 12(706902)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bestle D, Heindl MR, Limburg H, Van Lam
van T, Pilgram O, Moulton H, Stein DA, Hardes K, Eickmann M, Dolnik
O, et al: TMPRSS2 and furin are both essential for proteolytic
activation of SARS-CoV-2 in human airway cells. Life Sci Alliance.
3(e202000786)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bunyavanich S, Do A and Vicencio A: Nasal
gene expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in children and
adults. JAMA. 323:2427–2429. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li MY, Li L, Zhang Y and Wang XS:
Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide
variety of human tissues. Infect Dis Poverty. 9(45)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|