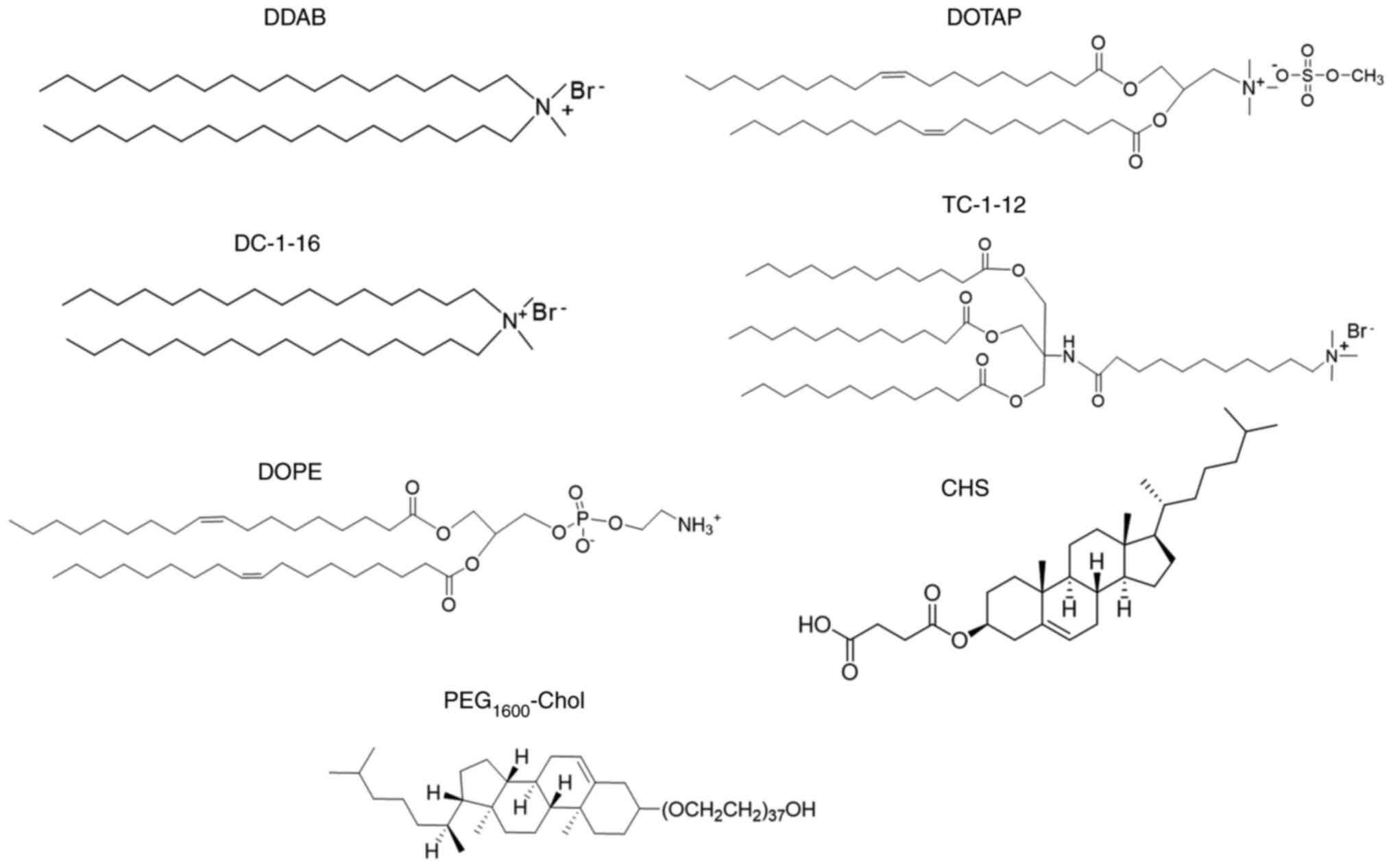
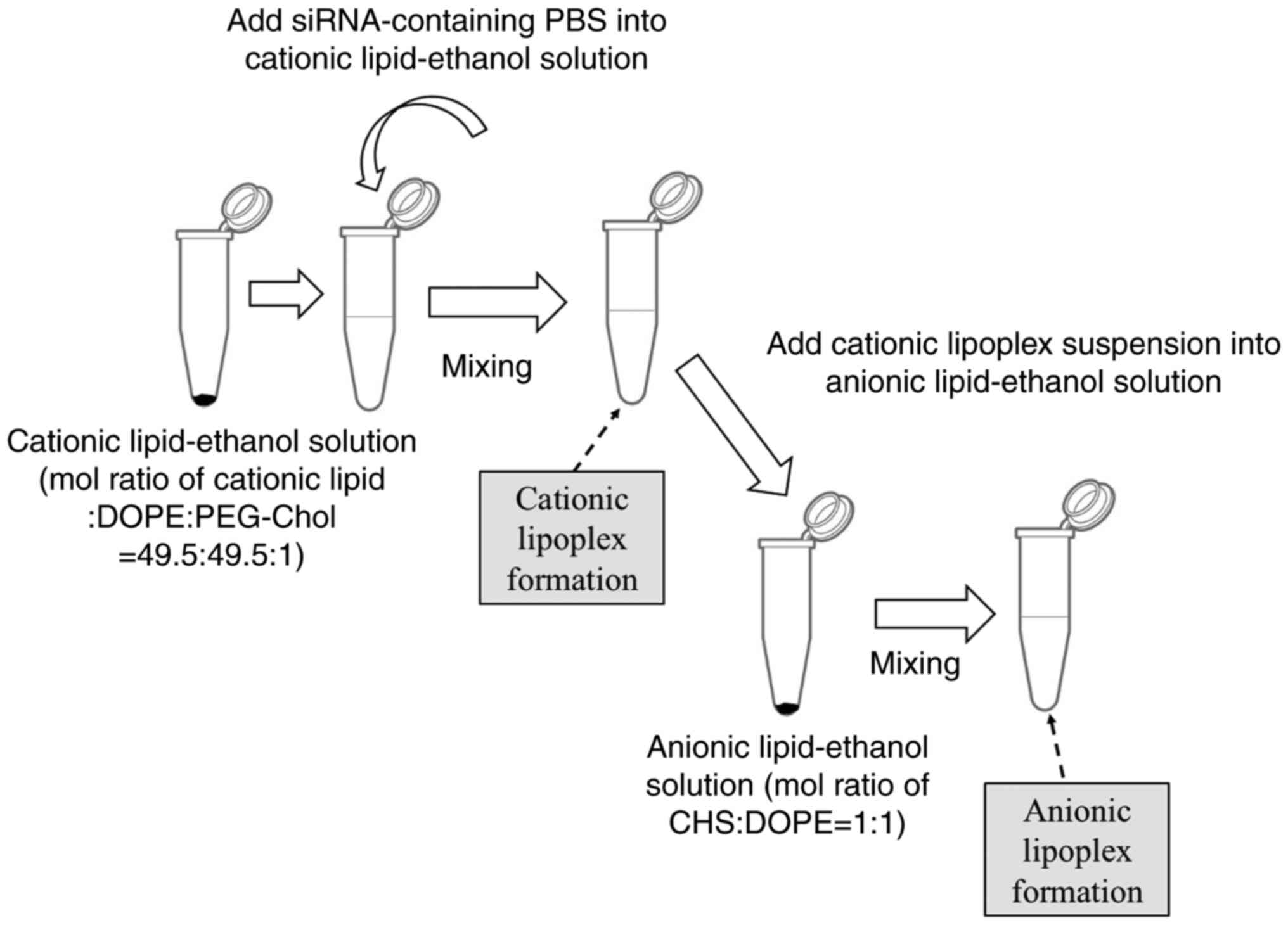
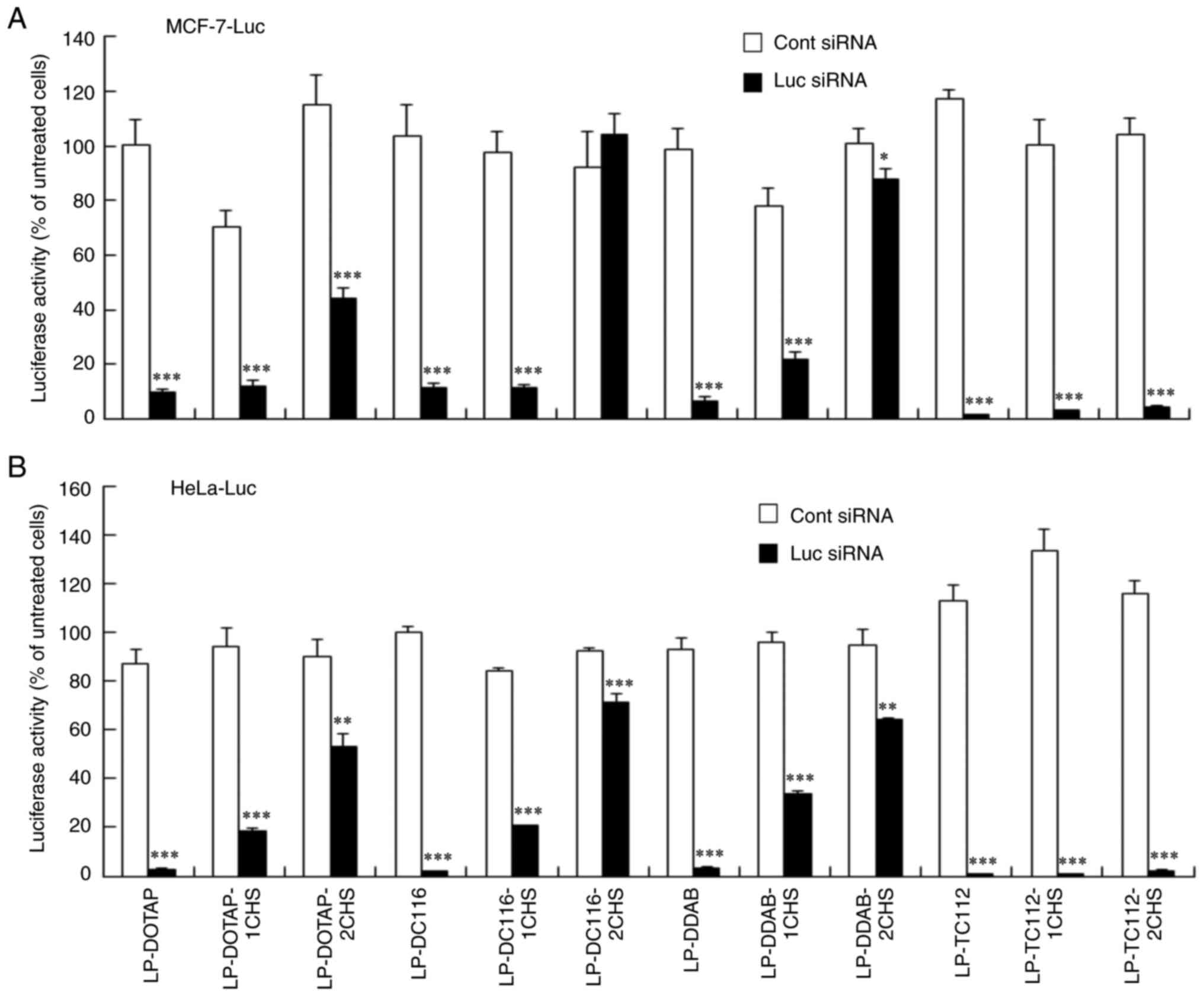
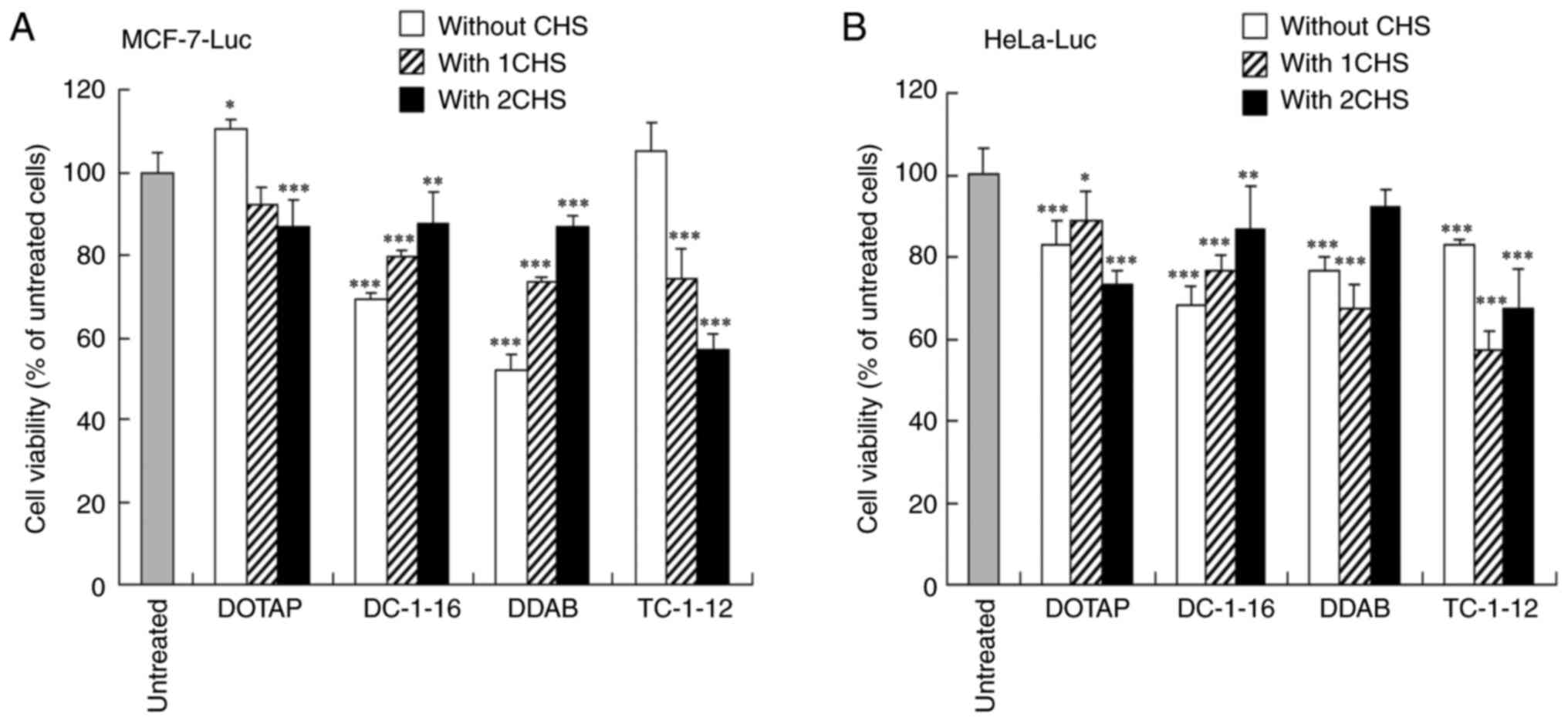
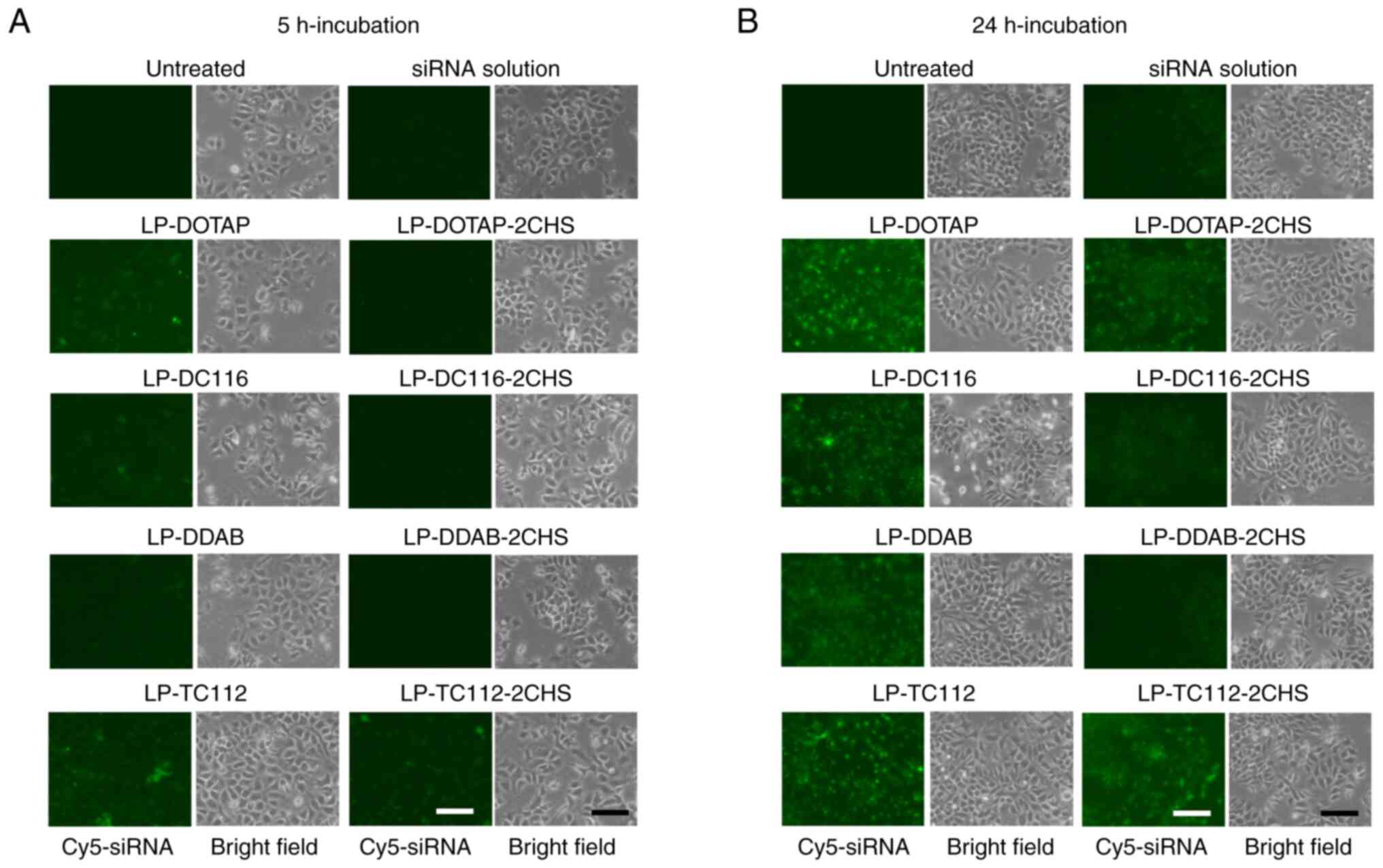
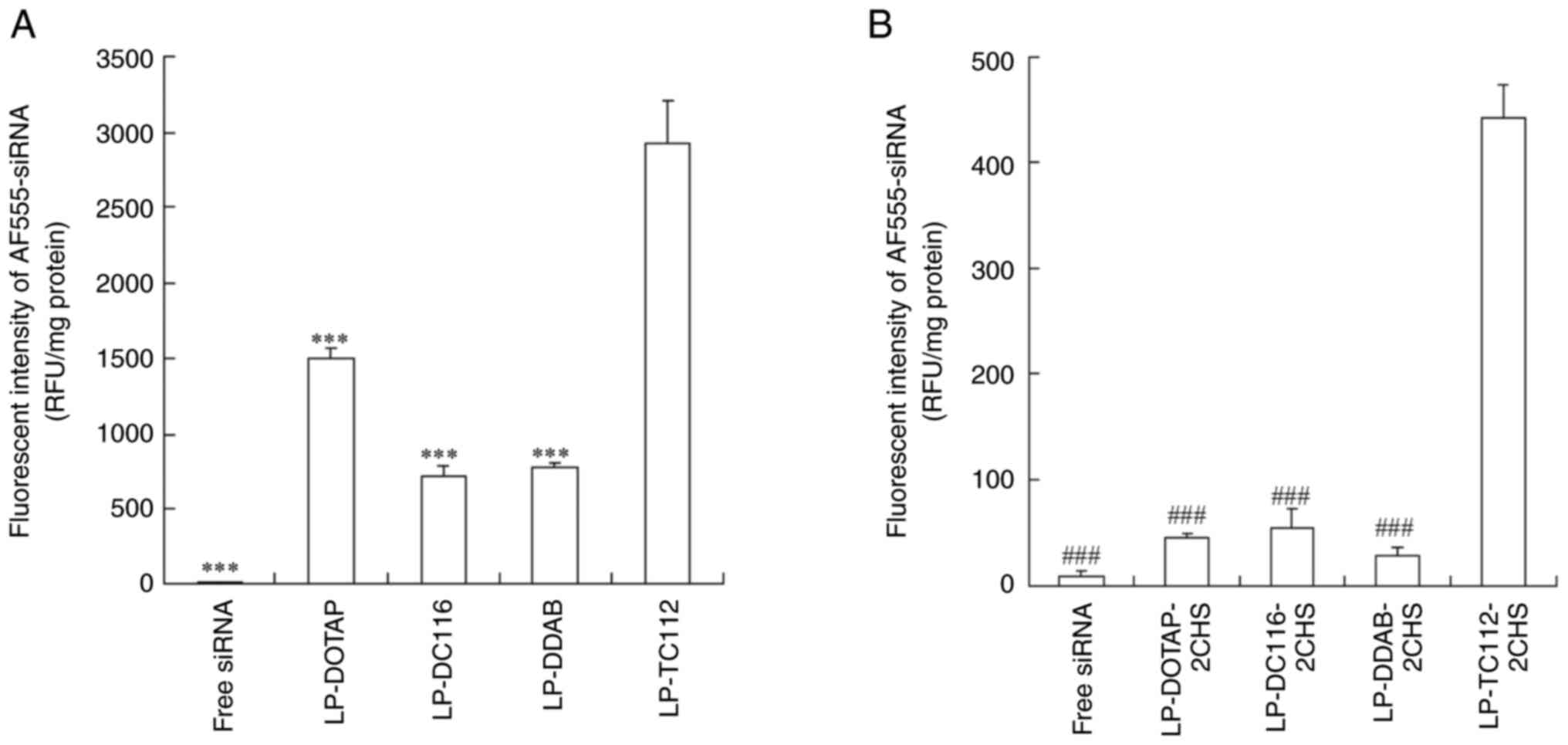
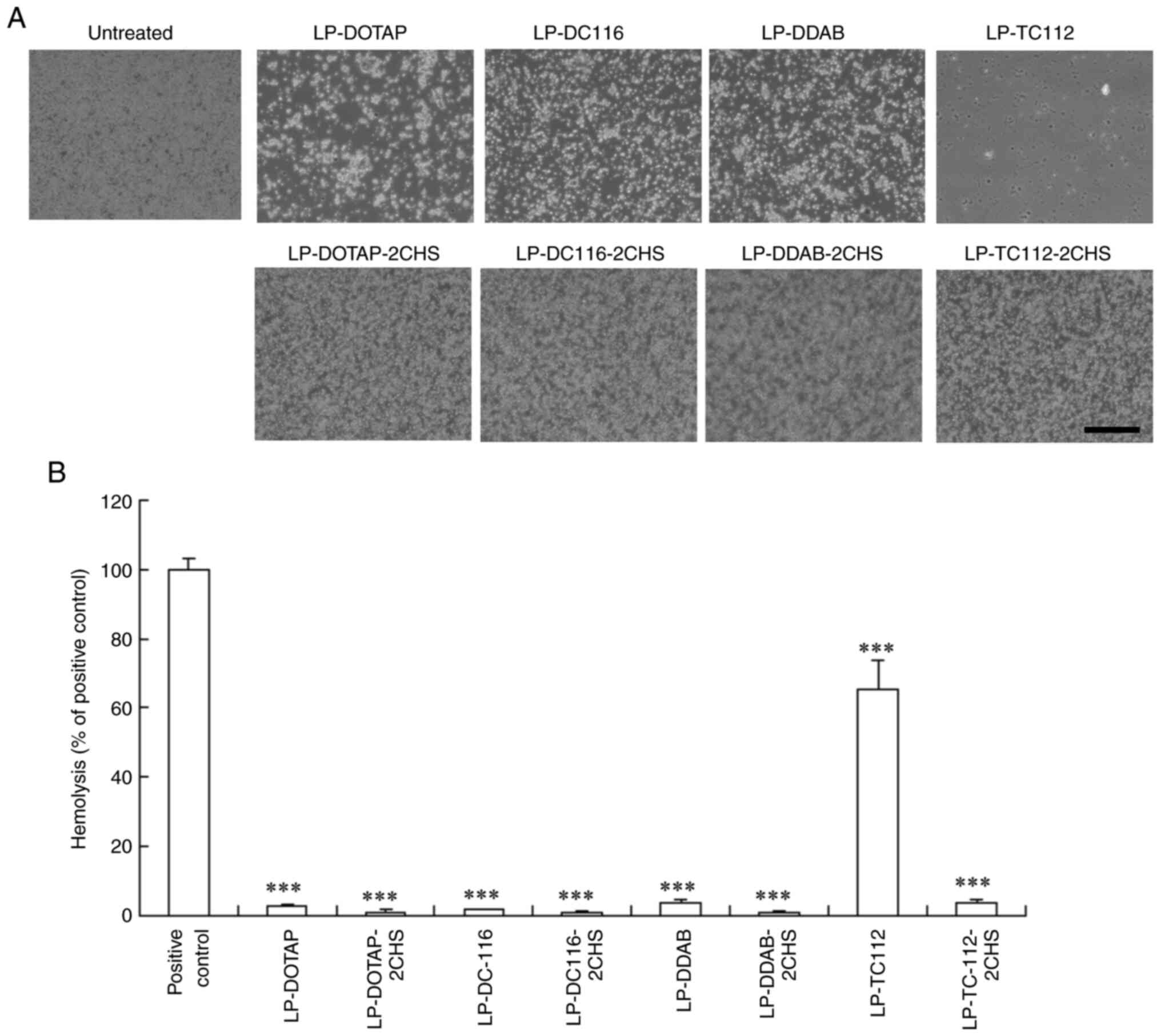
|
1
|
Kim DH, Behlke MA, Rose SD, Chang MS, Choi
S and Rossi JJ: Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi
potency and efficacy. Nat Biotechnol. 23:222–226. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kubowicz P, Żelaszczyk D and Pękala E:
RNAi in clinical studies. Curr Med Chem. 20:1801–1816.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xue HY, Guo P, Wen WC and Wong HL:
Lipid-based nanocarriers for RNA delivery. Curr Pharm Des.
21:3140–3147. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang S, Zhi D and Huang L: Lipid-based
vectors for siRNA delivery. J Drug Target. 20:724–735.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hattori Y, Tamaki K, Sakasai S, Ozaki KI
and Onishi H: Effects of PEG anchors in pegylated siRNA lipoplexes
on in vitro gene-silencing effects and siRNA biodistribution in
mice. Mol Med Rep. 22:4183–4196. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hattori Y, Tamaki K, Ozaki KI, Kawano K
and Onishi H: Optimized combination of cationic lipids and neutral
helper lipids in cationic liposomes for siRNA delivery into the
lung by intravenous injection of siRNA lipoplexes. J Drug Deliv Sci
Technol. 52:1042–1050. 2019.
|
|
7
|
Lechanteur A, Furst T, Evrard B, Delvenne
P, Hubert P and Piel G: PEGylation of lipoplexes: The right balance
between cytotoxicity and siRNA effectiveness. Eur J Pharm Sci.
93:493–503. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hatakeyama H, Akita H and Harashima H: The
polyethyleneglycol dilemma: Advantage and disadvantage of
PEGylation of liposomes for systemic genes and nucleic acids
delivery to tumors. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:892–899. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fang Y, Xue J, Gao S, Lu A, Yang D, Jiang
H, He Y and Shi K: Cleavable PEGylation: A strategy for overcoming
the ‘PEG dilemma’ in efficient drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 24
(Supp1):S22–S32. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kapoor M and Burgess DJ: Physicochemical
characterization of anionic lipid-based ternary siRNA complexes.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818:1603–1612. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Han X, Lu Y, Xu Z, Chu Y, Ma X, Wu H, Zou
B and Zhou G: Anionic liposomes prepared without organic solvents
for effective siRNA delivery. IET Nanobiotechnol. 17:269–280.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hattori Y, Nakamura A, Arai S, Nishigaki
M, Ohkura H, Kawano K, Maitani Y and Yonemochi E: In vivo siRNA
delivery system for targeting to the liver by poly-l-glutamic
acid-coated lipoplex. Results Pharm Sci. 4:1–7. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ribeiro MCS, de Miranda MC, Cunha PDS,
Andrade GF, Fulgêncio GO, Gomes DA, Fialho SL, Pittella F,
Charrueau C, Escriou V and Silva-Cunha A: Neuroprotective effect of
siRNA entrapped in hyaluronic acid-coated lipoplexes by
intravitreal administration. Pharmaceutics. 13(845)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Maeki M, Okada Y, Uno S, Niwa A, Ishida A,
Tani H and Tokeshi M: Production of siRNA-loaded lipid
nanoparticles using a microfluidic device. J Vis Exp.
22(181)2022.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Maeki M, Uno S, Niwa A, Okada Y and
Tokeshi M: Microfluidic technologies and devices for lipid
nanoparticle-based RNA delivery. J Control Release. 344:80–96.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hattori Y, Saito H, Nakamura K, Yamanaka
A, Tang M and Ozaki KI: In vitro and in vivo transfections using
siRNA lipoplexes prepared by mixing siRNAs with a lipid-ethanol
solution. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 75(103635)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hattori Y, Tang M, Suzuki H, Hattori A,
Endo S, Ishii A, Aoki A, Ezaki M and Sakai H: Optimization of
transfection into cultured cells with siRNA lipoplexes prepared
using a modified ethanol injection method. J Drug Deliv Sci
Technol. 99(106000)2024.
|
|
18
|
Hattori Y, Tang M, Aoki A, Ezaki M, Sakai
H and Ozaki KI: Effect of the combination of cationic lipid and
phospholipid on gene-knockdown using siRNA lipoplexes in breast
tumor cells and mouse lungs. Mol Med Rep. 28(180)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hattori Y, Kikuchi T, Ozaki KI and Onishi
H: Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo therapeutic antitumor
efficacy of transduction of polo-like kinase 1 and heat shock
transcription factor 1 small interfering RNA. Exp Ther Med.
14:4300–4306. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hattori Y and Shimizu R: Effective mRNA
transfection of tumor cells using cationic triacyl lipid-based mRNA
lipoplexes. Biomed Rep. 22(25)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Alshalani A, AlSudais H, Binhassan S and
Juffermans NP: Sex discrepancies in blood donation: Implications
for red blood cell characteristics and transfusion efficacy.
Transfus Apher Sci. 63(104016)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hattori Y, Shinkawa M, Kurihara A and
Shimizu R: Optimization of PEGylation for cationic triacyl
lipid-based siRNA lipoplexes prepared using the modified ethanol
injection method for tumor therapy. J Liposome Res. 35:300–311.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Djuric Z, Heilbrun LK, Lababidi S,
Everett-Bauer CK and Fariss MW: Growth inhibition of MCF-7 and
MCF-10A human breast cells by alpha-tocopheryl hemisuccinate,
cholesteryl hemisuccinate and their ether analogs. Cancer Lett.
111:133–139. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rajesh M, Sen J, Srujan M, Mukherjee K,
Sreedhar B and Chaudhuri A: Dramatic influence of the orientation
of linker between hydrophilic and hydrophobic lipid moiety in
liposomal gene delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 129:11408–11420.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hattori Y, Hagiwara A, Ding W and Maitani
Y: NaCl improves siRNA delivery mediated by nanoparticles of
hydroxyethylated cationic cholesterol with amido-linker. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 18:5228–5232. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Koulov AV, Vares L, Jain M and Smith BD:
Cationic triple-chain amphiphiles facilitate vesicle fusion
compared to double-chain or single-chain analogues. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1564:459–465. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Sun J, Lu Y, Tao C, Huang J, Zhang
H, Yu Y, Zou H, Gao J and Zhong Y: Complexes containing cationic
and anionic pH-sensitive liposomes: Comparative study of factors
influencing plasmid DNA gene delivery to tumors. Int J
Nanomedicine. 8:1573–1593. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|