Introduction
Mitomycin C (MMC) is a quinone-containing antibiotic
isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus, with a wide spectrum
of antitumor activities against several tumor types, including
colon, breast and head and neck (1). Notably, MMC is used as a prototype
drug to study the mechanisms associated with bioreductive drug
activation. This drug is reductively activated to
2,7-diaminomitosene, which cross-links DNA and subsequently leads
to cell death (1,2). Apart from the mechanism of
MMC-induced DNA cross-linkage, its mode of action has been also
associated with the formation of DNA monoadducts and free
radical-induced DNA strand breaks (3,4).
However, MMC has also been associated with significant adverse side
effects in cancer patients, including cardiotoxicity, hematologic
toxicity and renal toxicity (5).
Thus, combined cancer therapy may alternatively allow a lower
dosage of MMC treatment, while ensuring its continued effectiveness
in killing cancer cells.
Among the 25 selenoproteins identified in the human
and 24 in rodents (6), thioredoxin
reductase 1 (Trr1) is the most well-characterized selenoprotein in
mammalian cells and plays an essential role in the thioredoxin
system as an enzyme that governs the redox state and maintains the
function of thioredoxin by keeping this protein in a reduced state
(7). In mammals, Trr1 acts as a
redox regulator with a major role in several biological processes,
e.g., cell proliferation, transcription, angiogenesis,
embryogenesis and DNA repair, as well as antioxidant defense with
an antioxidant activity (8).
However, Trr1 has a deleterious effect with a role
in promoting cancer as its overexpression has been manifested in
many types of cancers with characteristics of malignant phenotypes,
including resistance to anticancer drugs (9,10).
Resistance to MMC is induced and developed in cancer cells, such as
colon cancer, leading to the limitation of such chemotherapeutic
agents in clinical use (11–13).
A number of possible mechanisms associated with MMC resistance
include an elevated level of protective agents (e.g., glutathione)
and increased drug efflux.
Extensive studies have revealed that targeting Trr1
inhibition with a number of anticancer drugs and potent inhibitors
alters cancer-related properties of malignancy (14,15).
Notably, a previous study found that reduction of Trr1 in animal
lung carcinoma cells caused a reversal of the characteristic
malignant phenotype (16).
Furthermore, animals injected with stably transfected Trr1 siRNA
cells were found to exhibit a strong reduction in tumor progression
and metastasis compared to control animals (16). Accordingly, a previous study found
that an animal cancer cell line exhibited morphological changes
upon Trr1 knockdown. These characteristic changes included loss of
self-sufficient growth, defective progression to the S phase and
decreased expression of DNA polymerase α (17). Thus, it is worth noting that Trr1
is essential for tumor growth in animal models. It has also been
discovered that Trr1 is uniquely overexpressed in cancer cells.
These points may lead to the proposal that Trr1, strongly acting as
a pro-cancer protein, is a potential target for anticancer
therapy.
In this regard, researchers have demonstrated that
the overexpression of Trr1 has a strong impact on controlling the
process of malignancy (17,18).
Therefore, investigation of the significant role of an endogenously
high expression of selenoprotein Trr1 on MMC resistance in a human
colon cancer cell line (RKO) using knockdown of Trr1 is warranted.
The present study hypothesized that the knockdown of the expression
level of Trr1 using a specific shRNA viral vector improves MMC
efficacy in killing human colon cancer RKO cells. Importantly, we
revealed that decreasing the elevated level of Trr1 expression in
human colon cancer cells enhances the effectiveness of MMC-induced
apoptosis, possibly via an increase in free radical-mediated
double-strand damage to DNA.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
RKO human colon cancer cells (ATCC no. CRL-257) were
cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine
serum (FBS), while Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells were grown in
RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS and 0.5 μg/ml puromycin. The
cultures were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5%
CO2/95% air.
Stable knockdown of Trr1 using a
short-hairpin RNA vector
The Escherichia coli clone, which harbors
retroviral vector pSM2c containing the Trr1-specific short-hairpin
RNA (shRNA) target, was provided from Open Biosystems (USA) and
subjected to plasmid extraction using the HiSpeed Plasmid Midi kit
(Qiagen, Germany). The purified plasmids were then submitted to
sequencing to verify the Trr1-specific shRNA target (sense,
CATCCCGGTGACAAAGAA and anti-sense, CATCCCTGGTGACAAAGAA). Stably
transfected Trr1 shRNA (knockdown) cells were prepared using
transfection reagent Fugen6 (Roche, Germany) according to the
manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 5×104 RKO cells in
a 2-ml suspension were seeded in each well of a 6-well plate.
Subsequently, the 12-h cultured cells were transfected with the
Trr1-specific shRNA construct using Fugen6, and selection of
puromycin-resistant clones was performed in the presence of 0.5
μg/ml puromycin after 48 h of incubation. The reduced Trr1
expression level in each puromycin-resistant clone was verified by
Western blotting.
Western blot analysis
The Trr1 shRNA transfectant and wild-type cells were
harvested by centrifugation at 1,500 rpm for 5 min and then lysed
in RIPA lysis buffer [50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.5 mM
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 150 mM NaCl, 1% (v/v)
Triton-100, 0.1% (v/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 1 mM
dithiothreitol (DTT) and a protease inhibitor cocktail]. Cell
lysates (40 μg) were subjected to 10% sodium dodecyl
sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) at 60 V for
180 min and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)
membranes. Blotted membranes were blocked with a blocking buffer
[Tris-buffered saline (TBS), 5% skim milk, 0.02% NaN3
and 0.001% Tween-20] at 25°C for 2 h. After washing, the Trr1
protein was immunologically detected using a goat polyclonal
antibody against Trr1 at a 1:2,000 dilution ratio (Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, USA). A peroxidase-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG
(Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used as a secondary antibody.
Immunoreactive bands were visualized with an enhanced
chemiluminescence (ECL) Plus Western blotting detection system (GE
Healthcare, UK). GADPH was used as a control for protein loading.
The entire procedure was performed three times independently.
Cell viability assay
Cell viability was monitored by a
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)
assay using a cell proliferation kit (Roche). Briefly,
1×104 cells in a 100-μl suspension were seeded in each
well of 96-well plates. After 18 h of incubation, both RKO and Trr1
shRNA knockdown cells were treated with various concentrations of
MMC (0, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 20 μM) for 1 h, following an
additional 24-h incubation in fresh selective media. After
incubation, MTT-labeling reagent was added at a final concentration
of 0.5 mg/ml to each culture well and further incubated for 4 h.
Subsequently, 200 μl of solubilization solution was added to
dissolve formazan crystal-forming products. The percentage of cell
survival was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 595 nm
(A595) with a microplate reader 680 (Bio-Rad, USA).
Acridine orange staining
The apoptotic fraction was evaluated as
morphological change indicator of apoptosis using acridine orange
(AO) staining. The RKO and Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells
(6×105 cells in a 3-ml suspension) were seeded in 60-mm
dishes. The cells were harvested after a 24-h (5 μM) MMC treatment,
following incubation in a selective fresh media for another 24 h.
The cell pellets were resuspended in AO staining solution (Sigma,
USA). The stained cells were dropped onto a glass slide and
observed under a fluorescence microscope (Nikon). The apoptotic
fraction was determined by cell counting.
Measurement of reactive oxygen species
(ROS)
The detection of ROS was determined as a measure of
intracellular accumulation of free radicals in the MMC-treated Trr1
shRNA knockdown cells compared to the RKO cells. The ROS level was
evaluated using 5 (and
6)-chloromethyl-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate, acetyl
ester (CM-H2DCFDA; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) as an ROS
indicator. In brief, 6×105 RKO and Trr1 shRNA knockdown
cells in a 3-ml suspension were seeded in 60-mm dishes and treated
without and with 5 μM MMC (Sigma) for 24 h, and then exposed to 0.5
μM CM-H2DCFDA in PBS for 20 min at 37°C in the dark. Subsequently,
the cells were washed with PBS and examined under a fluorescence
microscope (Nikon). Image analysis was carried out with
NIS-Elements BR 3.0 software (Nikon).
γ-H2AX detection
The formation of phosphorylated histone H2AX
(γ-H2AX) foci was determined using the immunofluorescence staining
approach (19). Briefly, either
RKO or Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells grown on glass coverslips were
treated without and with 5 μM MMC (Sigma) for 24 h, following
incubation in selective fresh media for an additional 12 h. The
cells were fixed with chilled methanol at −20°C for 30 min and
rinsed with chilled acetone for a few seconds. After washing with
PBS, the cells were incubated with an anti-γ-H2AX primary antibody
(Active Motif, USA) at 4°C overnight and an anti-rabbit-cy3
secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, USA) at room
temperature for 1 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were mounted
with mounting solution containing DAPI nuclear stain. The
coverslips were placed face-down onto glass slides, and the foci
were visualized under fluorescence microscope (Nikon).
Neutral single-cell gel electrophoresis
(SCGE or comet assay)
The comet assay under neutral conditions mainly
allows the detection of DNA double-strand breaks which basically
trigger apoptotic processes, but not necrotic events (20,21).
In brief, the RKO and Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells (6×105
cells in a 3-ml suspension) were seeded in 60-mm dishes. After 24 h
of 5 μM MMC treatment following an additional 24-h of fresh media
incubation, the cells were harvested by trypsinization, resuspended
in 1 ml resuspending buffer [Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS),
20 mM EDTA and 10% DMSO freshly added 1 h prior to use] and chilled
on ice. Cells (1×104 in 10 μl) were embedded in 90 μl low-melting
point agarose (0.5% in PBS at 37°C) onto agarose-coated (1.0% in
PBS) and dried glass slides that were submersed for 1 h in
pre-chilled lysis buffer pH 9.5 [2.5 M NaCl, 100 mM EDTA, 10 mM
Tris-base; 1 h prior to use 1% (v/v) Triton X-100 and 10% (v/v)
dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO) were added]. Slides were electrophoresed
at 25 V for 1 h at 4°C in electrophoresis buffer pH 9.0 [100 mM
Tris-HCl (pH 9.0) and 300 mM sodium acetate]. Afterwards, DNA
precipitation was carried out in 90% ethanol containing 1 M
ammonium acetate at 4°C for 30 min. After ethanol dehydration, the
slides were subjected to air drying and then SYBR Gold staining
(1:10,000 dilution ratio in TE buffer, pH 7.6) (Invitrogen, USA).
At this step, the slides could be stored in a refrigerator in
light-tight boxes without any loss of assay sensitivity. Finally,
the stained DNA was visualized under a fluorescence microscope
(Nikon). One hundred cells per slide were scored.
Results
Induced cellular sensitivity via Trr1
inhibition under MMC treatment
Trr1 was targeted for knockdown in the RKO cells by
transfection using a Trr1-specific shRNA retroviral vector. The
decreased protein level of Trr1 was confirmed by Western blotting.
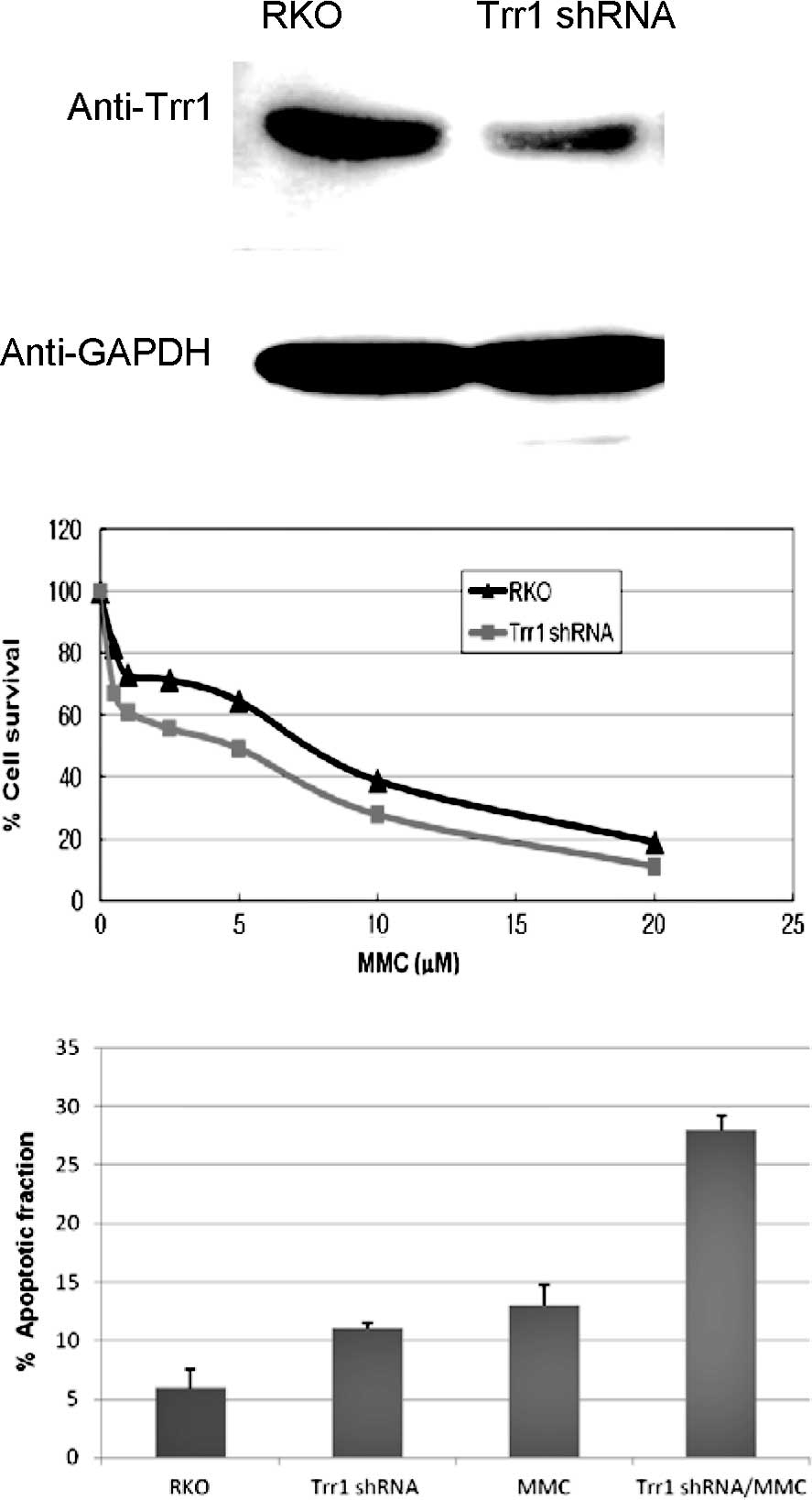
As shown in Fig. 1A, the protein
level of Trr1 was markedly reduced in the Trr1 shRNA transfectant
cells relative to the wild-type RKO cells, while there was
apparently no difference in the expression level of the internal
control GAPDH between the Trr1 shRNA transfectant and the wild-type
RKO cells. This indicated that suppression of Trr1 expression via
shRNA transfection in the colon cancer RKO cells was successfully
conducted.
Highly expressed Trr1 is noted in many cancer types
with malignant phenotypes, including resistance to anticancer drugs
(9,10). This raises the question whether
Trr1 suppression via shRNA leads to enhanced MMC-mediated
cytotoxicity in colon cancer RKO cells. An MTT assay was performed
to evaluate cell viability towards MMC. The result showed that the
Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells displayed higher sensitivity to MMC
treatment compared to the wild-type RKO cells (Fig. 1B). This suggests that Trr1 may be a
potent mediator for cell survival caused by MMC toxicity in colon
cancer RKO cells. Additionally, the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells also
showed a higher rate of MMC-induced apoptosis, relative to the
wild-type cells (Fig. 1C). This
implies that the inhibition of Trr1 expression is potentially
effective for inducing apoptosis in colon cancer RKO cells, as a
tentative approach to enhance the antitumor effects of MMC
treatment.
Increased ROS level with Trr1 deficiency
in response to MMC
As MMC is one of the quinone anticancer agents to
generate free radicals (22,23),
enhancement of the ROS level in the Trr1-deficient cells in
comparison to wild-type RKO cells was assessed. The intracellular
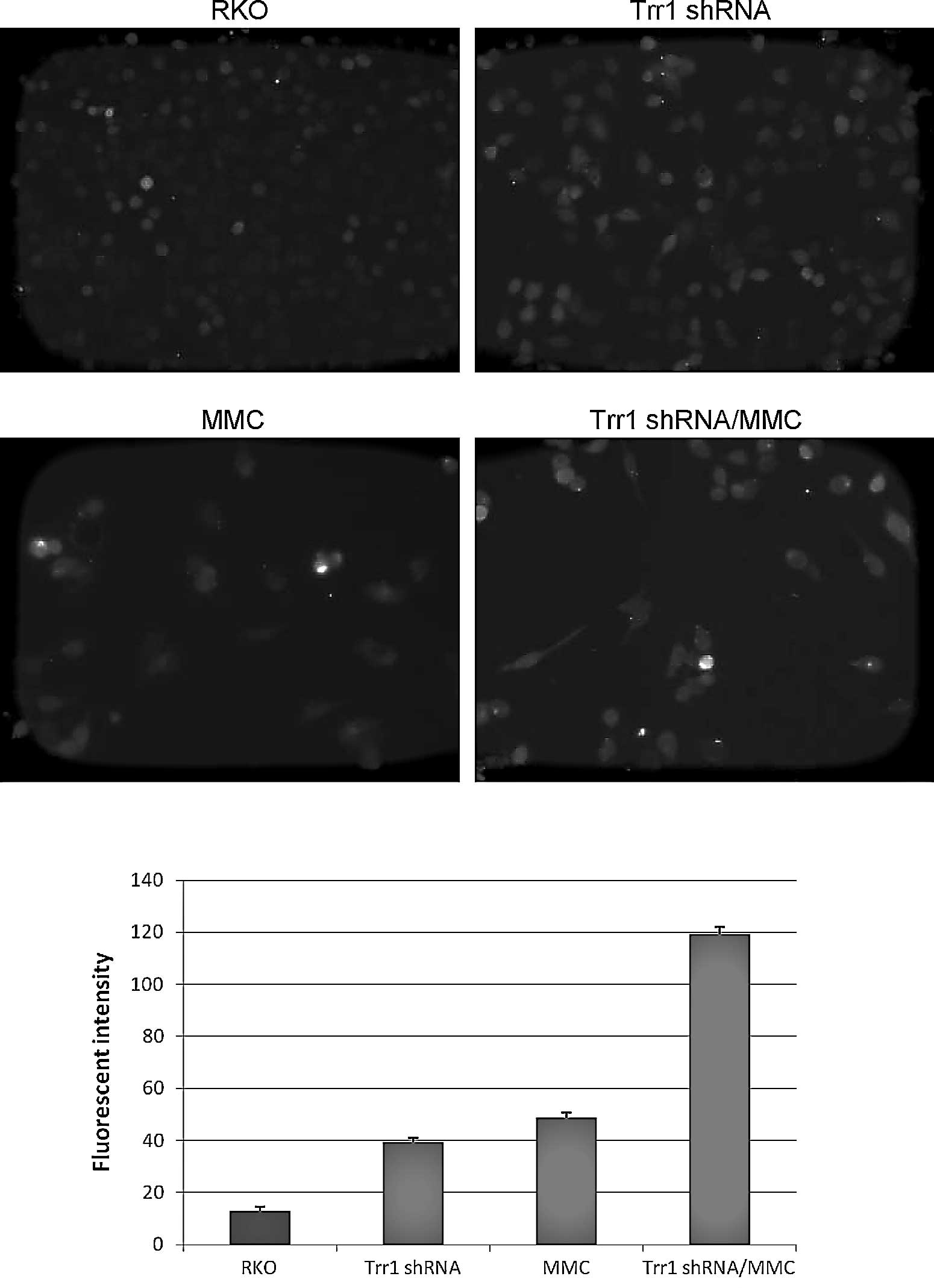
ROS was detected using fluorescent probe CM-H2DCFDA. Exposure to 5
μM MMC for 24 h induced the generation of intracellular ROS to a
greater extent in the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells as compared to
that in the wild-type RKO cells (Fig.
2). This implicates the intracellular accumulation of ROS in
the Trr1 shRNA knockdown. Therefore, Trr1 deficiency may be a
potent mediator by which to sensitize colon cancer RKO cells to MMC
treatment via enhancement of ROS-mediated oxidative damage.
Elevated γ-H2AX foci as a biomarker of
DNA damage in Trr1 knockdown cells upon MMC exposure
DNA is a target molecule for underlying molecular
mechanisms of MMC toxicity in antitumor therapy (24,25).
Accordingly, the accumulation of intracellular ROS generating
oxidative damage to cellular components, particularly DNA, was
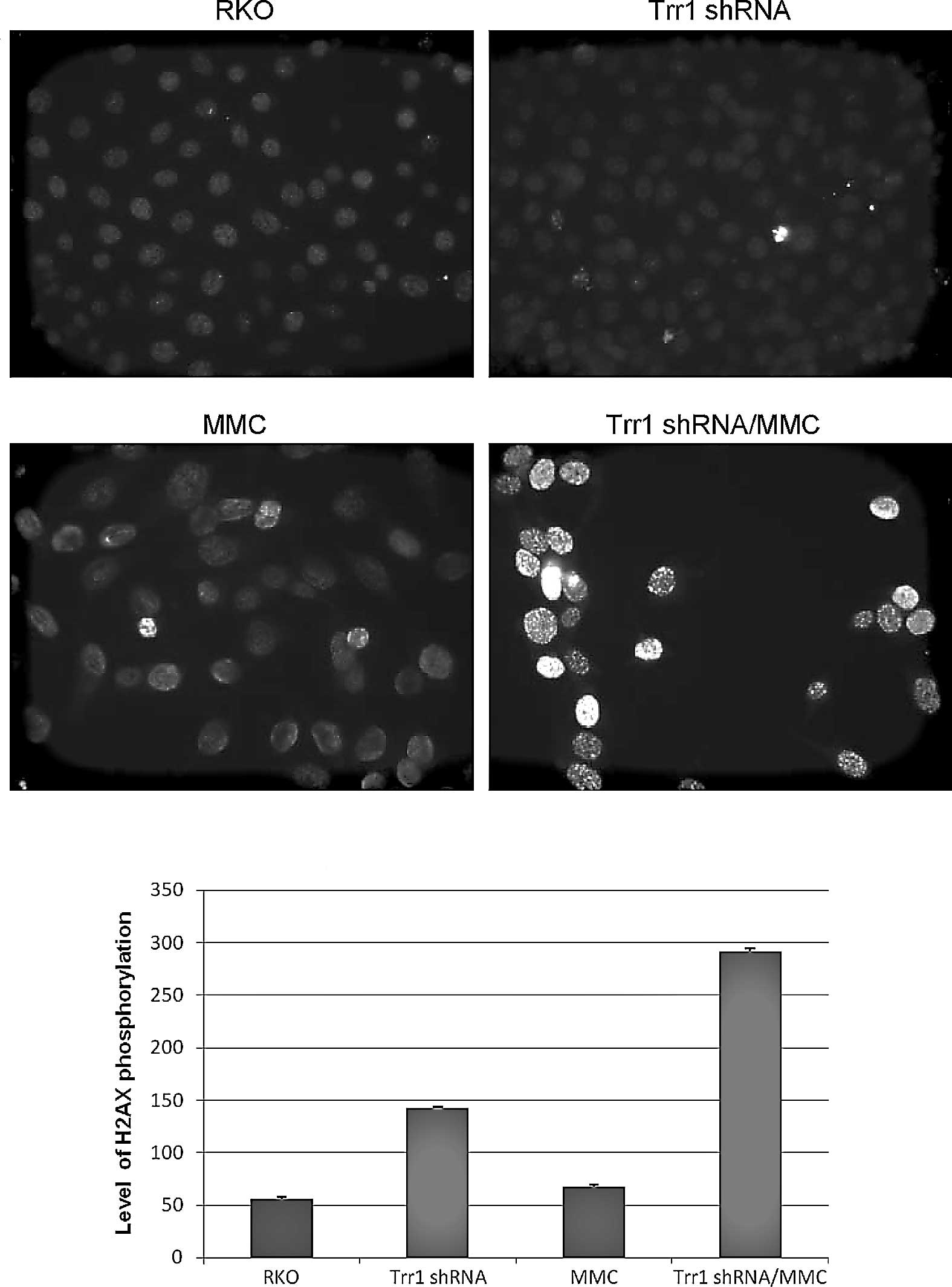
observed in the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells (Fig. 2). Hence, MMC-induced DNA damage in
Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells was examined in comparison to wild-type
RKO cells using γ-H2AX immunostaining. Phosphorylated nuclear
histone protein variant H2AX ‘γ-H2AX’ causes recruitment of DNA
repair protein complexes at sites flanking DNA strand breaks
(19). As shown in Fig. 3, the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells
exhibited a marked increase in DNA strand breaks compared to that
in the wild-type RKO cells after MMC treatment.
Increased DNA double-strand breaks via
Trr1 inhibition under MMC treatment
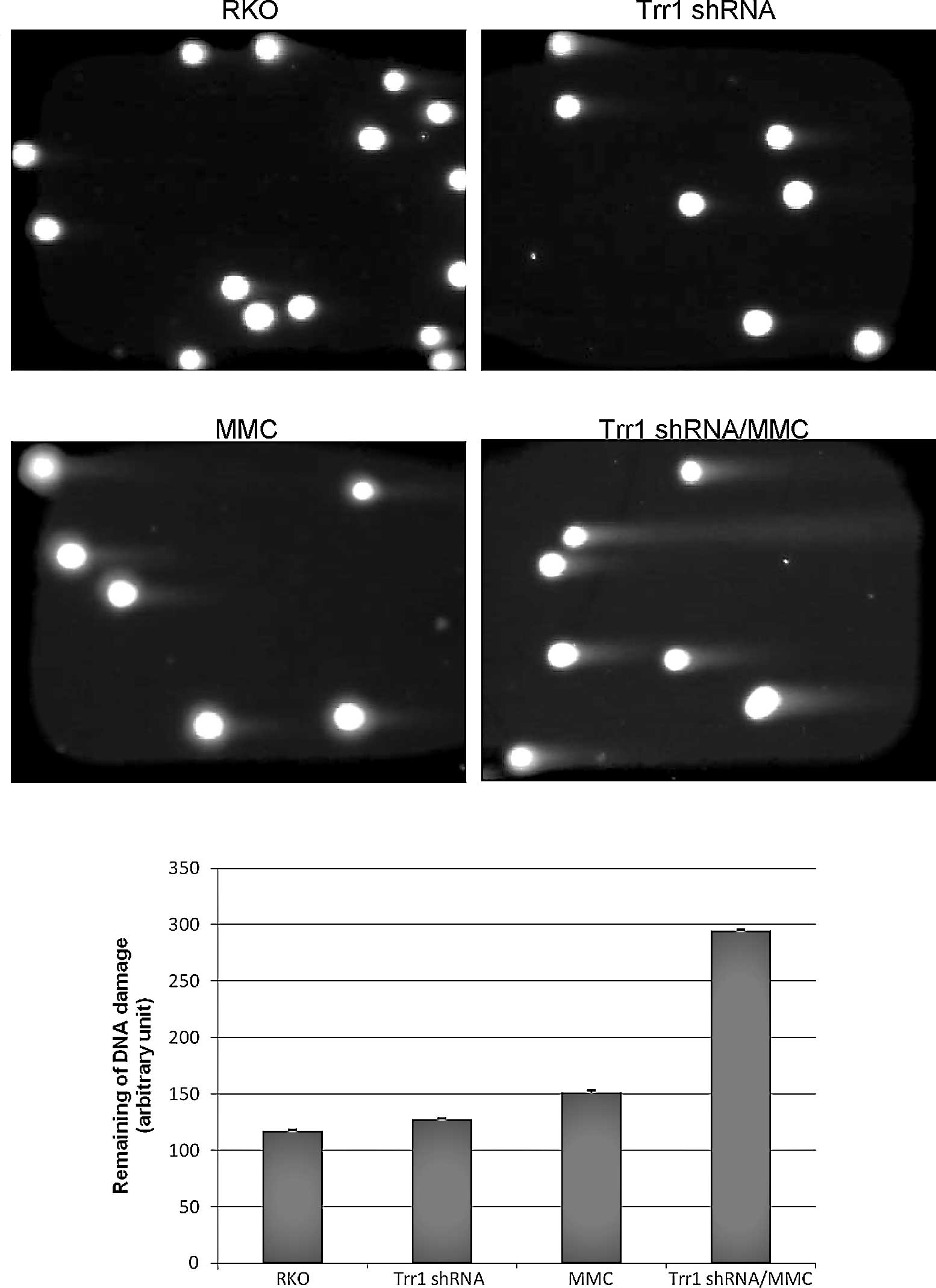
In addition to the γ-H2AX staining, a neutral comet
assay was also utilized to evaluate the relative occurrence of DNA
double-strand breaks at the individual cell level. After MMC
exposure, the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells showed significantly
increased DNA double-strand breaks, represented by a much greater
extent of stretched DNA, compared to the wild-type RKO cells
(Fig. 4).
The results overall demonstrated that Trr1
suppression sensitizes colon cancer RKO cells to MMC exposure
through augmentation of DNA double-strand damage, probably leading
to enhanced cell death.
Discussion
The potent antitumor agent, MMC, is extensively used
against several tumor types, such as colon and breast (2,26).
MMC is capable of inducing ROS production, leading to enhanced
cancer apoptosis via DNA strand damage (27). However, the development of MMC
resistance in colon cancer cell lines is an obstacle for cancer
therapy (12,13). In addition to cancer prevention,
Trr1 has an opposing role in promoting cancer, as Trr1 expression
has been shown to be elevated in primary human malignancies arising
in the breast, thyroid, prostate and liver, as well as a number of
human cancer cell lines (9,28).
Therefore, the potential association of increased Trr1 and MMC
resistance in cancer can be postulated.
One significant finding of this study is the initial
demonstration that a reduction in the expression of selenoprotein
Trr1 potentiates MMC action on cancer apoptosis through ROS-induced
DNA double-strand damage in human colon cancer RKO cells. In the
present study, stable down-regulated expression of Trr1 was
performed in RKO cells using shRNA vector-based interference
technology (Fig. 1A). Our
observation revealed that stable Trr1-deficient cells exhibited a
higher intracellular ROS level compared to wild-type RKO cells
after 24 h (5 μM) of MMC exposure, implying that Trr1 deficiency
enhances MMC-induced ROS (Fig.
2).
To subsequently investigate whether there is an
association between MMC-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in
the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells following MMC treatment, the DNA
strand breaks were determined using γ-H2AX staining and a neutral
comet assay. Upon MMC exposure, the DNA strand breaks became
significantly increased in the Trr1 knockdown cells relative to
that in the wild-type cells (Figs.
3 and 4). Accordingly, the
extent of DNA damage was also correlated with the level of
generated ROS as an oxidative stress indicator (Figs. 2, 3 and 4).
This demonstrated that the elevated expression of Trr1 in the human
colon cancer RKO cells facilitated cellular protection against
oxidative damage to DNA. Taken together, the antitumor property via
Trr1 suppression is apparently attributed to the stimulation of the
ROS-mediated DNA damage process, particularly DNA double-strand
breakage (Fig. 4).
Since Trr1 is recognized as an anticancer drug
target, recent study has focused on the importance of Trr1 in
drug-specific cytotoxic efficacy in response to various anticancer
agents in the human lung carcinoma A549 cell line expressing a very
high basal level of Trr1 (29). In
accordance with these observations, our results showed for the
first time that cellular sensitivity to MMC was dramatically
increased in the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells relative to the
wild-type RKO cells (Fig. 1B) and
consequently led to induction of cancer apoptosis (Fig. 1C). One strong possible explanation
why shRNA inhibition of Trr1 gave rise to the induction of
MMC-mediated cytotoxicity and concomitant apoptosis is the
enhancement of DNA damage caused by an increase in ROS generation
(Figs. 2, 3 and 4).
Our data first demonstrated that suppression of Trr1 accelerated
intracellular accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks in the
presence of MMC, strongly evidenced by the neutral comet assay
(Fig. 4). This suggested that
specific knockdown of Trr1 enhanced apoptosis of cancer cells
treated with MMC by stimulation of DNA double-strand damage. In
accordance with a supportive study, DNA double-strand breaks are
the most severe lesions and lead to cell lethality (30).
In conclusion, our observations provide compelling
evidence that a specific reduction in Trr1 effectively sensitizes
human colon cancer RKO cells to MMC treatment. MMC treatment
combined with Trr1 deficiency may limit the side effects noted in
normal cells, while enhancing the effectiveness against cancer
cells when compared with the efficacy of classical MMC treatment.
We found, for the first time, that the enhancement of MMC-mediated
apoptosis in the Trr1 shRNA knockdown cells may result from an
increase in ROS-generated DNA double-strand breaks. Therefore,
inhibition of Trr1 via shRNA interference may be a promising
strategy for improving the MMC killing efficacy in cancer
therapy.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Korea
Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD,
Basic Research Promotion Fund) (KRF-2007-313-E00062). The present
study was also supported by a grant from the Ministry of
Environment, Korea (2010-090001-0083-0).
References
|
1.
|
Sartorelli AC: The role of mitomycin
antibiotics in the chemotherapy of solid tumors. Biochem Pharmacol.
35:67–69. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Crooke ST and Bradner WT: Mitomycin C: a
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 3:121–139. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Sartorelli AC, Hodnick WF, Belcourt MF,
Tomasz M, Haffty B, Fischer JJ and Rockwell S: Mitomycin C: a
prototype bioreductive agent. Oncol Res. 6:501–508. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Tomasz M and Palom Y: The mitomycin
bioreductive antitumor agents: cross-linking and alkylation of DNA
as the molecular basis of their activity. Pharmacol Ther. 76:73–87.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Verweij J and Stoter G: Severe side
effects of the cytotoxic drug mitomycin-C. Neth J Med. 30:43–50.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kryukov GV, Castellano S, Novoselov SV,
Lobanov AV, Zehtab O, Guigo R and Gladyshev VN: Characterization of
mammalian selenoproteins. Science. 300:1439–1443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Arnér ES and Holmgren A: Physiological
functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem.
267:6102–6109. 2000.
|
|
8.
|
Arnér ES and Holmgren A: The thioredoxin
system in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:420–426. 2006.
|
|
9.
|
Choi JH, Kim TN, Kim S, Baek SH, Kim JH,
Lee SR and Kim JR: Over-expression of mitochondrial thioredoxin
reductase and peroxiredoxin III in hepatocellular carcinomas.
Anticancer Res. 22:3331–3335. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Rundlöf AK and Arnér ES: Regulation of the
mammalian selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1 in relation to
cellular phenotype, growth, and signaling event. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 6:41–52. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Pan SS, Forrest GL, Akman SA and Hu LT:
NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase expression and mitomycin C
resistance developed by human colon cancer HCT 116 cells. Cancer
Res. 55:330–335. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Perry RR, Greaves BR and Kang Y:
Development and initial characterization of a mitomycin C-resistant
colon cancer cell line variant. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
32:326–328. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Willson JKV, Long BH, Marks ME, Brattain
DE, Wiley JE and Brattain MG: Mitomycin C resistance in a human
colon carcinoma cell line associated with cell surface protein
alterations. Cancer Res. 44:5880–5885. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Biaglow JE and Miller RA: The thioredoxin
reductase/thioredoxin system: novel redox targets for cancer
therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:6–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Fujino G, Noguchi T, Takeda K and Ichijo
H: Thioredoxin and protein kinases in redox signaling. Semin Cancer
Biol. 16:427–435. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Yoo MH, Xu XM, Carlson BA, Patterson AD,
Gladyshev VN and Hatfield DL: Thioredoxin reductase 1 deficiency
reverses tumor phenotype and tumorigenicity of lung carcinoma
cells. J Biol Chem. 281:13005–13008. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yoo MH, Xu XM, Carlson BA, Patterson AD,
Gladyshev VN and Hatfield DL: Targeting thioredoxin reductase 1
reduction in cancer cells inhibits self-sufficient growth and DNA
replication. PLoS One. 2:e11122007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Hatfield DL, Yoo MH, Carlson BA and
Gladyshev VN: Selenoproteins that function in cancer prevention and
promotion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1790:1541–1545. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Taneja N, Davis M, Choy JS, Beckett MA,
Singh R, Kron SJ and Weichselbaum RR: Histone H2AX phosphorylation
as a predictor of radiosensitivity and target for radiotherapy. J
Biol Chem. 279:2273–2280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Fairbairn DW and O'Neill KL: The neutral
comet assay is sufficient to identify an apoptotic ‘window’ by
visual inspection. Apoptosis. 1:91–94. 1996.
|
|
21.
|
Wojewodzka M, Buraczewska I and Kruszewski
M: A modified neutral comet assay: elimination of lysis at high
temperature and validation of the assay with anti-single-stranded
DNA antibody. Mutat Res. 518:9–20. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Bachur NR, Gordon SL and Gee MV: A general
mechanism for microsomal activation of quinone anticancer agents to
free radicals. Cancer Res. 38:1745–1750. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Handa K and Sato S: Generation of free
radicals of quinone group-containing anti-cancer chemicals in
NADPH-microsome system as evidenced by initiation of sulfite
oxidation. Gann. 66:43–47. 1975.
|
|
24.
|
Brendel M and Ruhland A: Relationships
between functionality and genetic toxicology of selected
DNA-damaging agents. Mutat Res. 133:51–85. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lawley PD and Phillips DH: DNA adducts
from chemotherapeutic agents. Mutat Res. 355:13–40. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Adikesavan AK and Jaiswal AK:
Thioredoxin-like domains requied for glucose regulatory protein
58-mediated reductive activation of mitomycin C leading to DNA
cross-linking. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2719–2727. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Kennedy KA, McGurl JD, Leondaridis L and
Alabaster O: pH dependence of mitomycin C-induced cross-linking
activity in EMT6 tumor cells. Cancer Res. 45:3541–3547.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Berggren M, Gallegos A, Gasdaska JR,
Gasdaska PY, Warneke J and Powis G: Thioredoxin and thioredoxin
reductase gene expression in human tumors and cell lines, and the
effects of serum stimulation and hypoxia. Anticancer Res.
16:3459–3466. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Eriksson SE, Prast-Nielsen S, Flaberg E,
Szekely L and Arnér ES: High levels of thioredoxin reductase 1
modulate drug-specific cytotoxic efficacy. Free Radic Biol Med.
47:1661–1671. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Jeggo PA and Löbrich M: DNA double-strand
breaks: their cellular and clinical impact? Oncogene. 26:7717–7719.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|