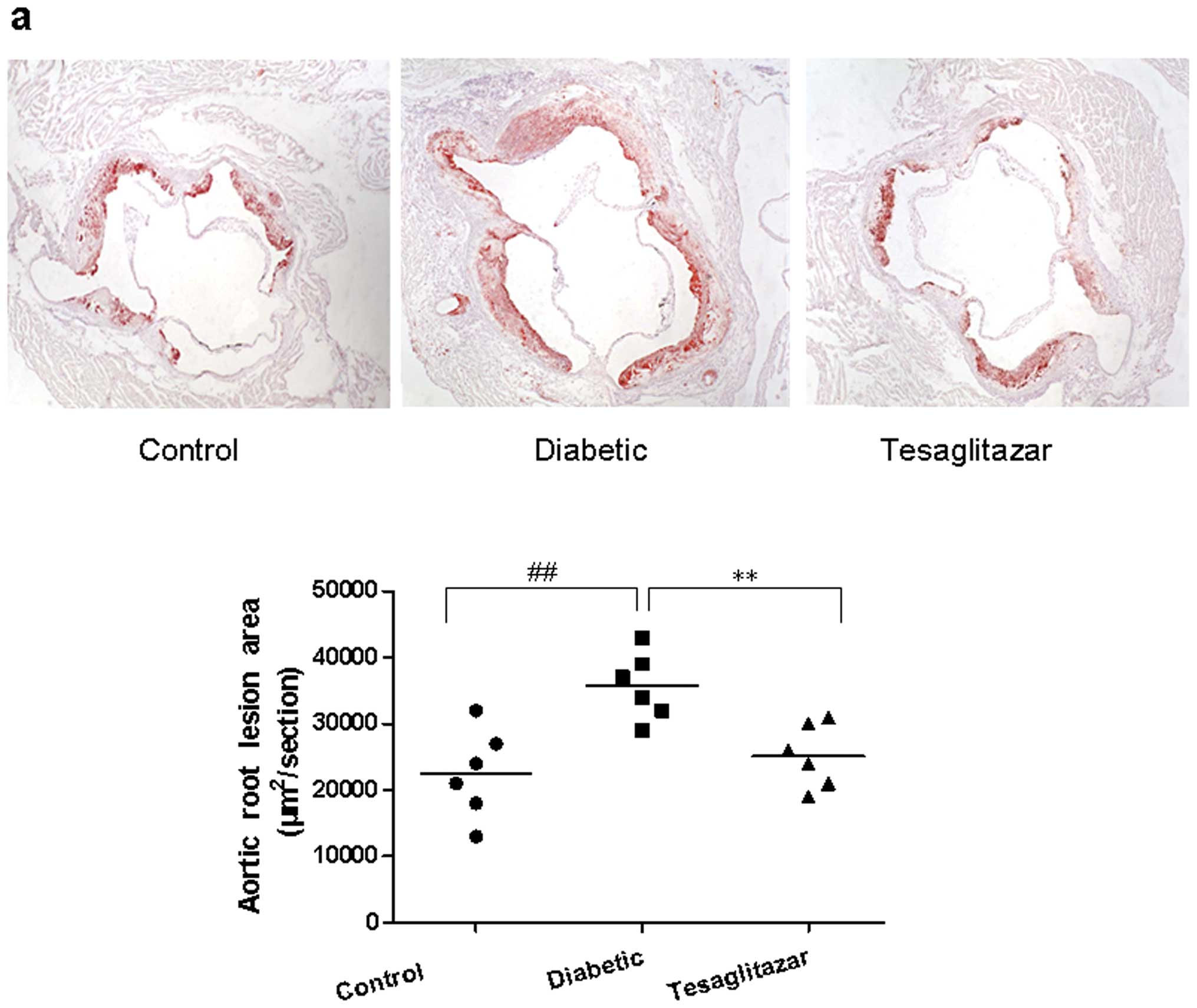
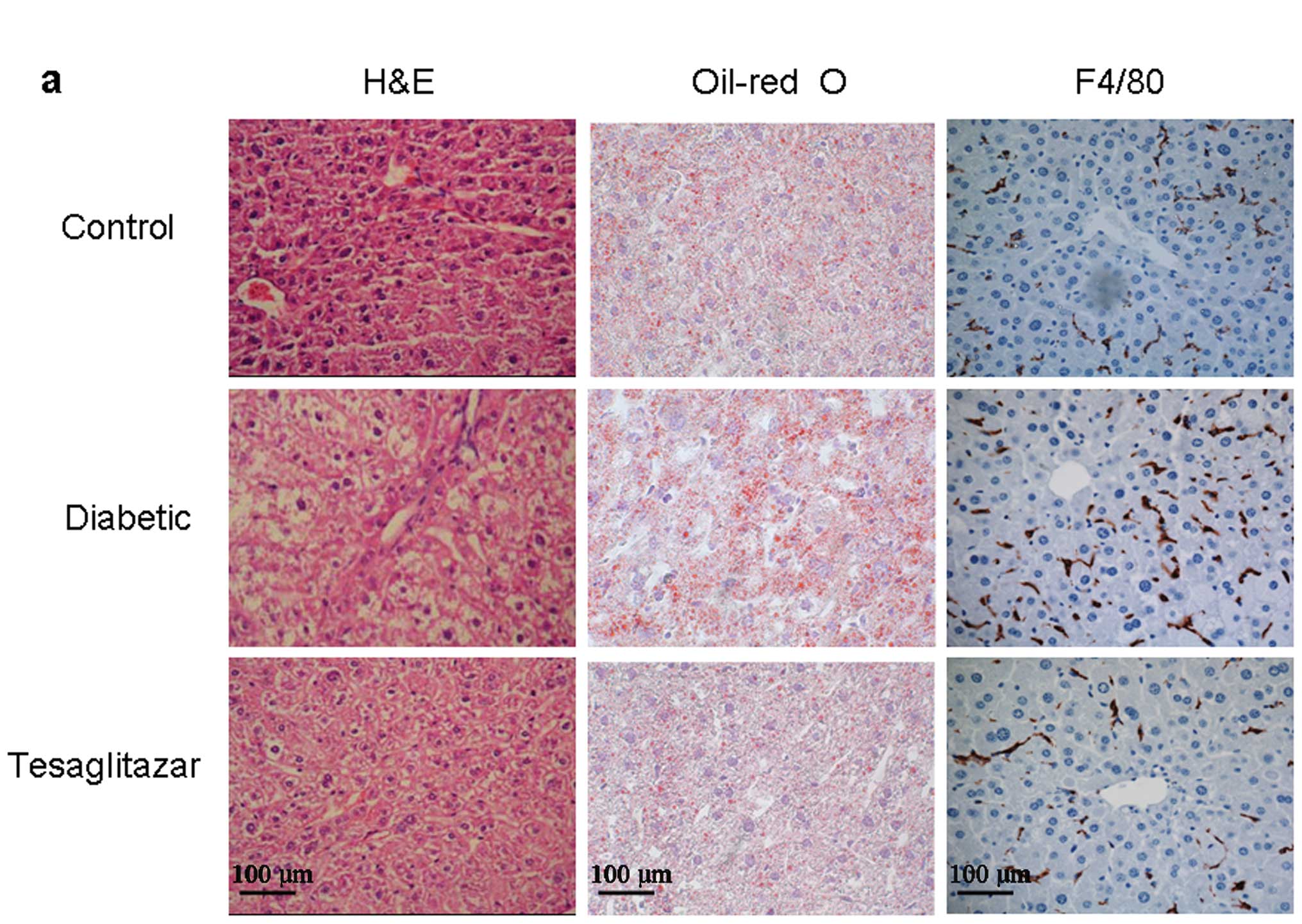
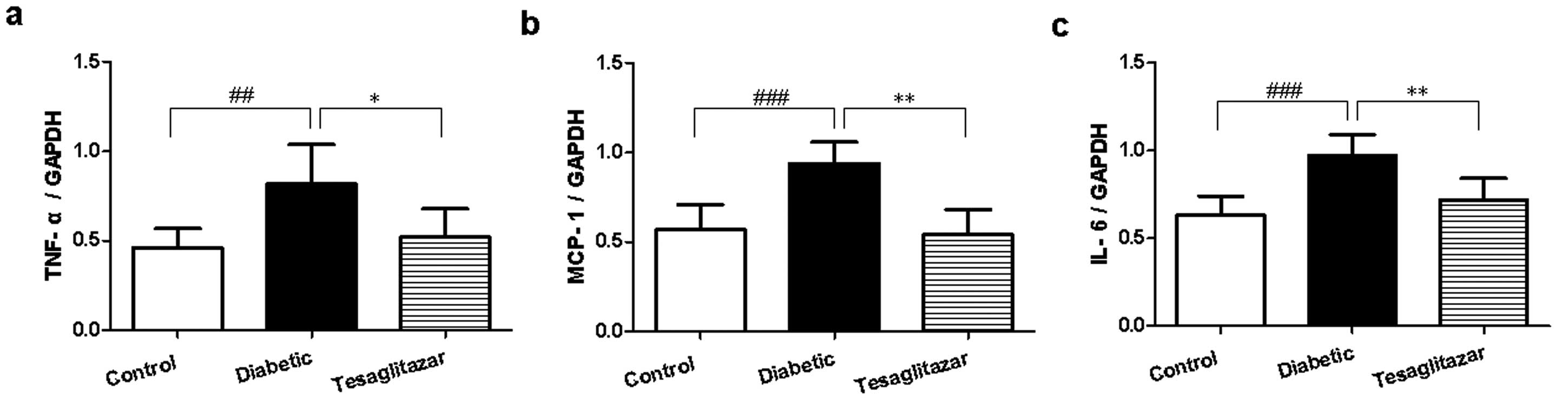
|
1
|
Menghini R, Casagrande V, Menini S, et al:
TIMP3 overexpression in macrophages protects from insulin
resistance, adipose inflammation, and nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease in mice. Diabetes. 61:454–462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scorletti E, Calder PC, Byrne CD, et al:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk:
metabolic aspects and novel treatments. Endocrine. 40:332–343.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baeck C, Wehr A, Karlmark KR, et al:
Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes
liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic
hepatic injury. Gut. 61:416–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Serino M, Menghini R, Fiorentino L, et al:
Mice heterozygous for tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme
are protected from obesity-induced insulin resistance and diabetes.
Diabetes. 56:2541–2546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wunderlich FT, Ströhle P, Könner AC, et
al: Interleukin-6 signaling in liver-parenchymal cells suppresses
hepatic inflammation and improves systemic insulin action. Cell
Metab. 12:237–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hanley AJ, Williams K, Festa A, et al:
Liver markers and development of the metabolic syndrome: the
insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes. 54:3140–3147.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bieghs V, Rensen PC, Hofker MH and
Shiri-Sverdlov R: NASH and atherosclerosis are two aspects of a
shared disease: central role for macrophages. Atherosclerosis.
220:287–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gui T, Shimokado A, Sun Y, et al: Diverse
roles of macrophages in atherosclerosis: from inflammatory biology
to biomarker discovery. Mediators Inflamm.
2012:6930832012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Truman JP, Al Gadban MM, Smith KJ, et al:
Differential regulation of acid sphingomyelinase in macrophages
stimulated with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and oxidized
LDL immune complexes: role in phagocytosis and cytokine release.
Immunology. 136:30–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wouters K, van Gorp PJ, Bieghs V, et al:
Dietary cholesterol, rather than liver steatosis, leads to hepatic
inflammation in hyperlipidemic mouse models of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 48:474–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Evans JL, Lin JJ and Goldfine ID: Novel
approach to treat insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and the
metabolic syndrome: simultaneous activation of PPARalpha,
PPARgamma, and PPARdelta. Curr Diabetes Rev. 1:299–307. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zandbergen F and Plutzky J: PPARalpha in
atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1771:972–982. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ciudin A, Hernandez C and Simó R: Update
on cardiovascular safety of PPARgamma agonists and relevance to
medicinal chemistry and clinical pharmacology. Curr Top Med Chem.
12:585–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mu J, Woods J, Zhou YP, et al: Chronic
inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 with a sitagliptin analog
preserves pancreatic beta-cell mass and function in a rodent model
of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 55:1695–1704. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zadelaar AS, Boesten LS, Jukema JW, et al:
Dual PPARalpha/gamma agonist tesaglitazar reduces atherosclerosis
in insulin-resistant and hypercholesterolemic ApoE*3Leiden mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2560–2566. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chira EC, McMillen TS, Wang S, et al:
Tesaglitazar, a dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
alpha/gamma agonist, reduces atherosclerosis in female low density
lipoprotein receptor deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 195:100–109.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ma KL, Ruan XZ, Powis SH, et al:
Inflammatory stress exacerbates lipid accumulation in hepatic cells
and fatty livers of apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Hepatology.
48:770–781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Woollard KJ and Geissmann F: Monocytes in
atherosclerosis: subsets and functions. Nat Rev Cardiol. 7:77–86.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Targher G, Marra F and Marchesini G:
Increased risk of cardiovascular disease in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease: causal effect or epiphenomenon? Diabetologia.
51:1947–1953. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhatia LS, Curzen NP, Calder PC and Byrne
CD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a new and important
cardiovascular risk factor? Eur Heart J. 33:1190–1200. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kleemann R, Verschuren L, van Erk MJ, et
al: Atherosclerosis and liver inflammation induced by increased
dietary cholesterol intake: a combined transcriptomics and
metabolomics analysis. Genome Biol. 8:R2002007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maina V, Sutti S, Locatelli I, et al: Bias
in macrophage activation pattern influences non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice. Clin Sci (Lond). 122:545–553. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lingrel JB, Pilcher-Roberts R, Basford JE,
et al: Myeloid-specific Krüppel-like factor 2 inactivation
increases macrophage and neutrophil adhesion and promotes
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 110:1294–1302. 2012.
|
|
24
|
Amar J, Fauvel J, Drouet L, et al:
Interleukin 6 is associated with subclinical atherosclerosis: a
link with soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1. J Hypertens.
24:1083–1088. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|