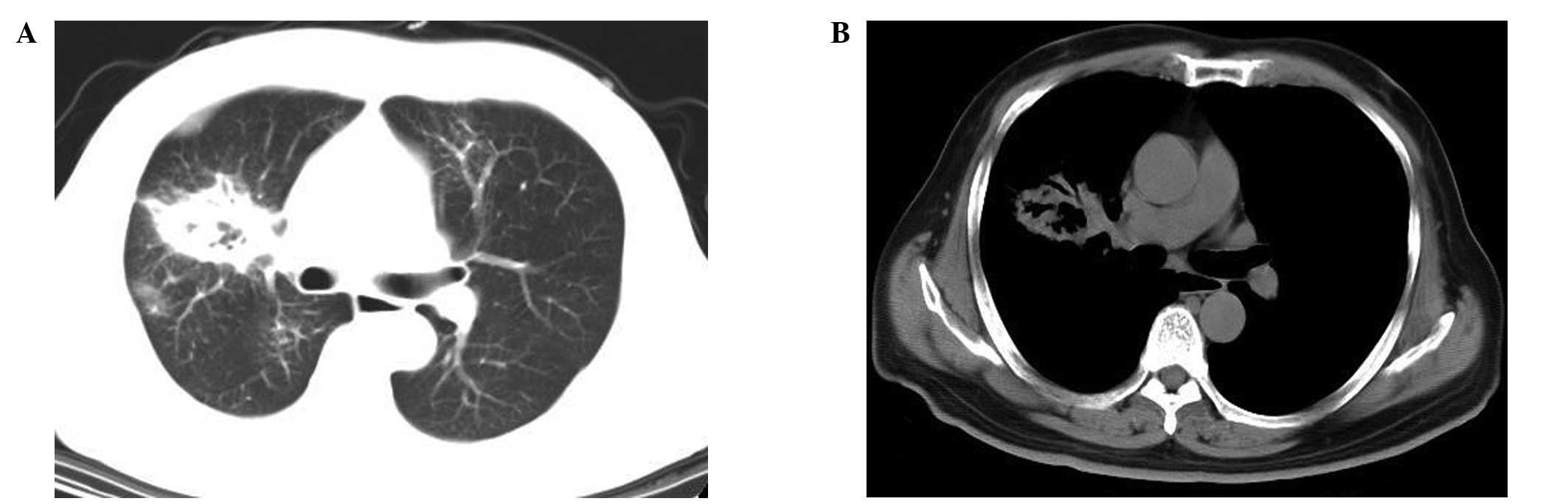
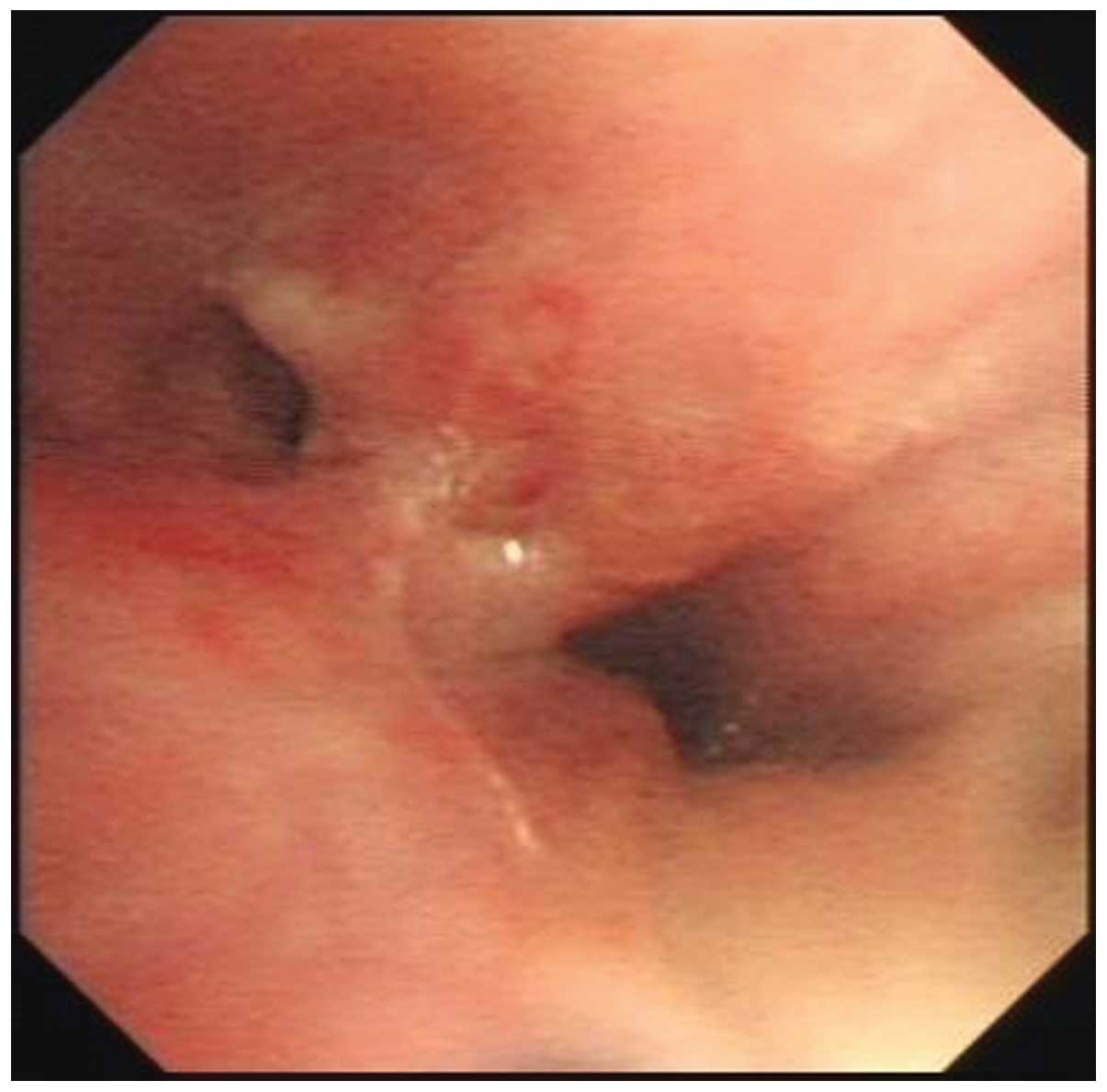
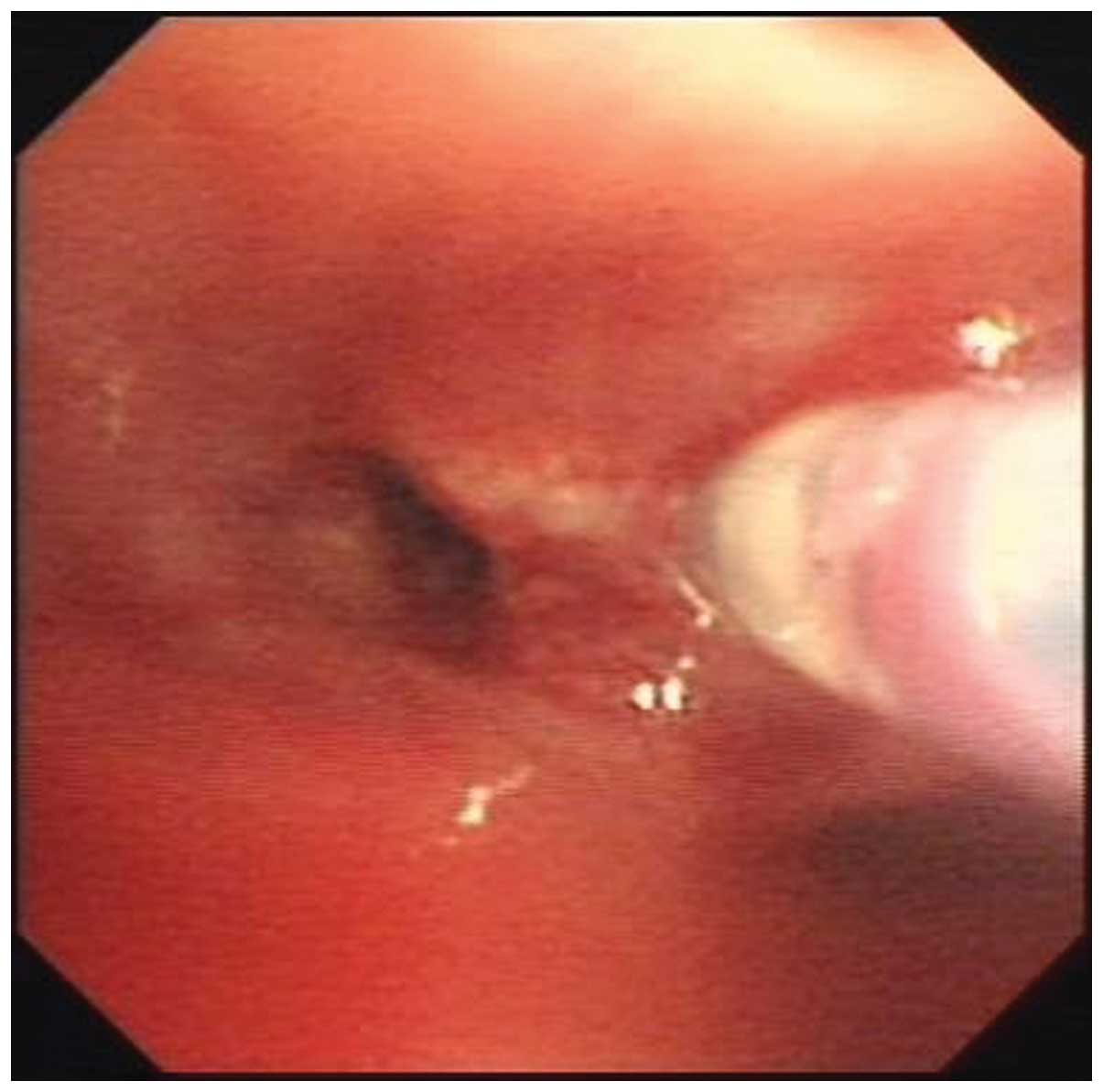
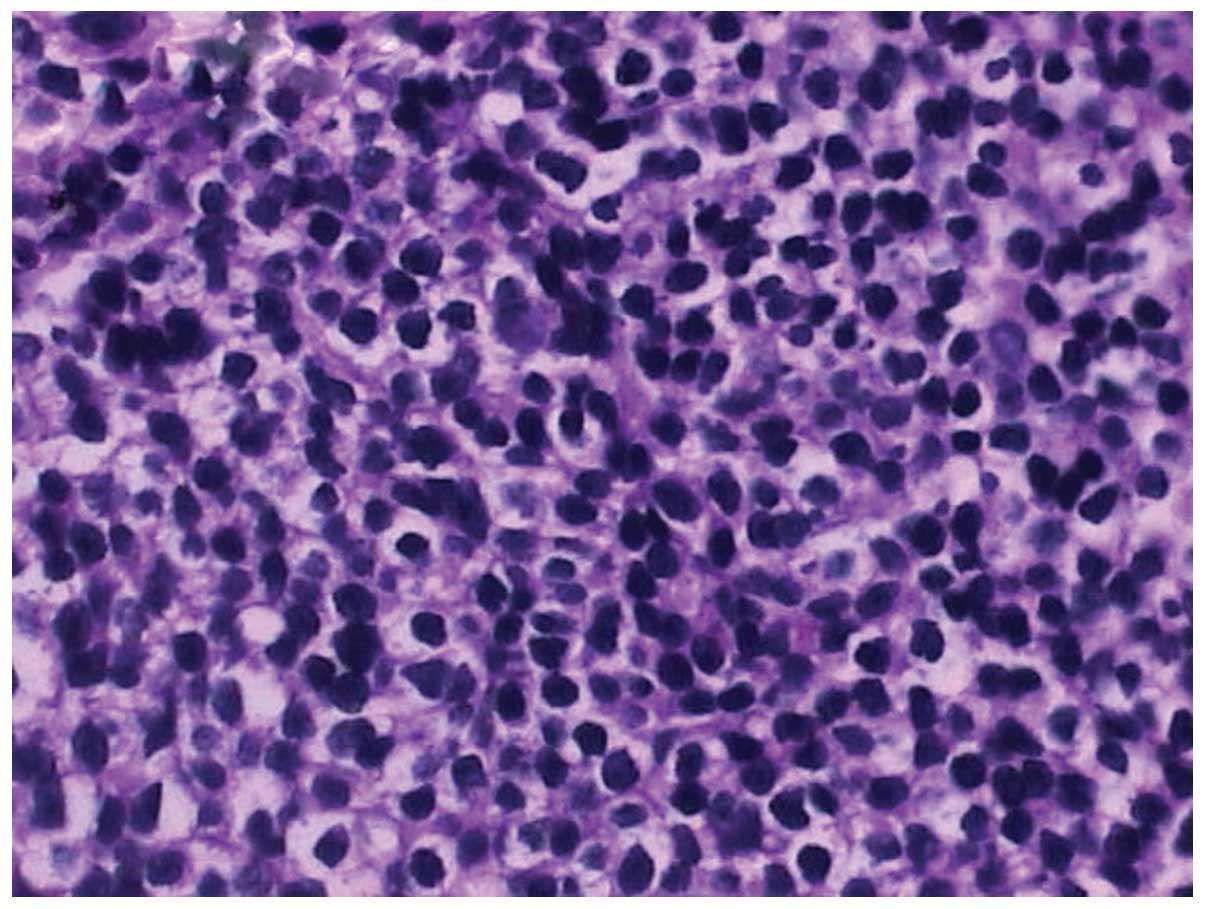
|
1
|
Zinzani PL, Martelli M, Poletti V, et al;
Italian Society of Hematology; Italian Society of Experimental
Hematology; Italian Group for Bone Marrow Transplantation. Practice
guidelines for the management of extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
of adult non-immunodeficient patients. Part I: primary lung and
mediastinal lymphomas A project of the Italian Society of
Hematology, the Italian Society of Experimental Hematology and the
Italian Group for Bone Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica.
93:1364–1371. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Kim JH, Lee SH, Park J, et al: Primary
pulmonary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 34:510–514.
2004.
|
|
3
|
Ferraro P, Trastek VF, Adlakha H,
Deschamps C, Allen MS and Pairolero PC: Primary non-Hodgkin’s
lymphoma of the lung. Ann Thorac Surg. 69:993–997. 2000.
|
|
4
|
Seeram V, Shujaat A, Jones L and Bajwa A:
An 82-year-old woman with left upper lobe atelectasis. Diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. Chest. 142:1669–1674. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Hu YX, Tong GQ, et al: Clinical and
radiological features of primary pulmonary non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 34:1057–1059. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Cadranel J, Wislez M and Antoine M:
Primary pulmonary lymphoma. Eur Respir J. 20:750–762. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chilosi M, Zinzani PL and Poletti V:
Lymphoproliferative lung disorders. Semin Respir Crit Care Med.
26:490–501. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hu YH, Hsiao LT, Yang CF, et al:
Prognostic factors of Chinese patients with primary pulmonary
non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: the single-institute experience in Taiwan.
Ann Hematol. 88:839–846. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wróbel T, Dzietczenia J,
Prochorec-Sobieszek M, Mazur G and Piwkowski P: Primary pulmonary
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 87:107–108.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang H, Wu D, Xiang H, Chen A and Liu J:
Pulmonary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma developed during long-term
methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int.
32:3639–3642. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Ferry JA, Sohani AR, Longtine JA, Schwartz
RA and Harris NL: HHV8-positive, EBV-positive Hodgkin lymphoma-like
large B-cell lymphoma and HHV8-positive intravascular large B-cell
lymphoma. Mod Pathol. 22:618–626. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsu PK, Hsu HS, Li AF, et al:
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting as a large chest wall mass. Ann
Thorac Surg. 81:1214–1218. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Peters P, Butler N, Mundy J and Shah P:
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting as an isolated soft-tissue chest
wall mass. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 37:4872010.
|
|
14
|
Yu H, Chen G, Zhang R and Jin X: Primary
intravascular large B-cell lymphoma of lung: a report of one case
and review. Diagn Pathol. 7:702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Li X, Chen J, et al: Value of
computed tomography-guided core needle biopsy in diagnosis of
primary pulmonary lymphomas. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 24:97–102. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cordier JF, Chailleux E, Lauque D, et al:
Primary pulmonary lymphomas. A clinical study of 70 cases in
nonimmunocompromised patients. Chest. 103:201–208. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xia Y and Wang KP: Transbronchial needle
aspiration: where are we now? J Thorac Dis. 5:678–682.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Neri N, Jesús Nambo M and Avilés A:
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma primary of lung. Hematology.
16:110–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aviles A, Nambo MJ, Huerta-Guzman J, Silva
L and Neri N: Rituximab in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma primary of the lung. Hematology. 18:81–84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|