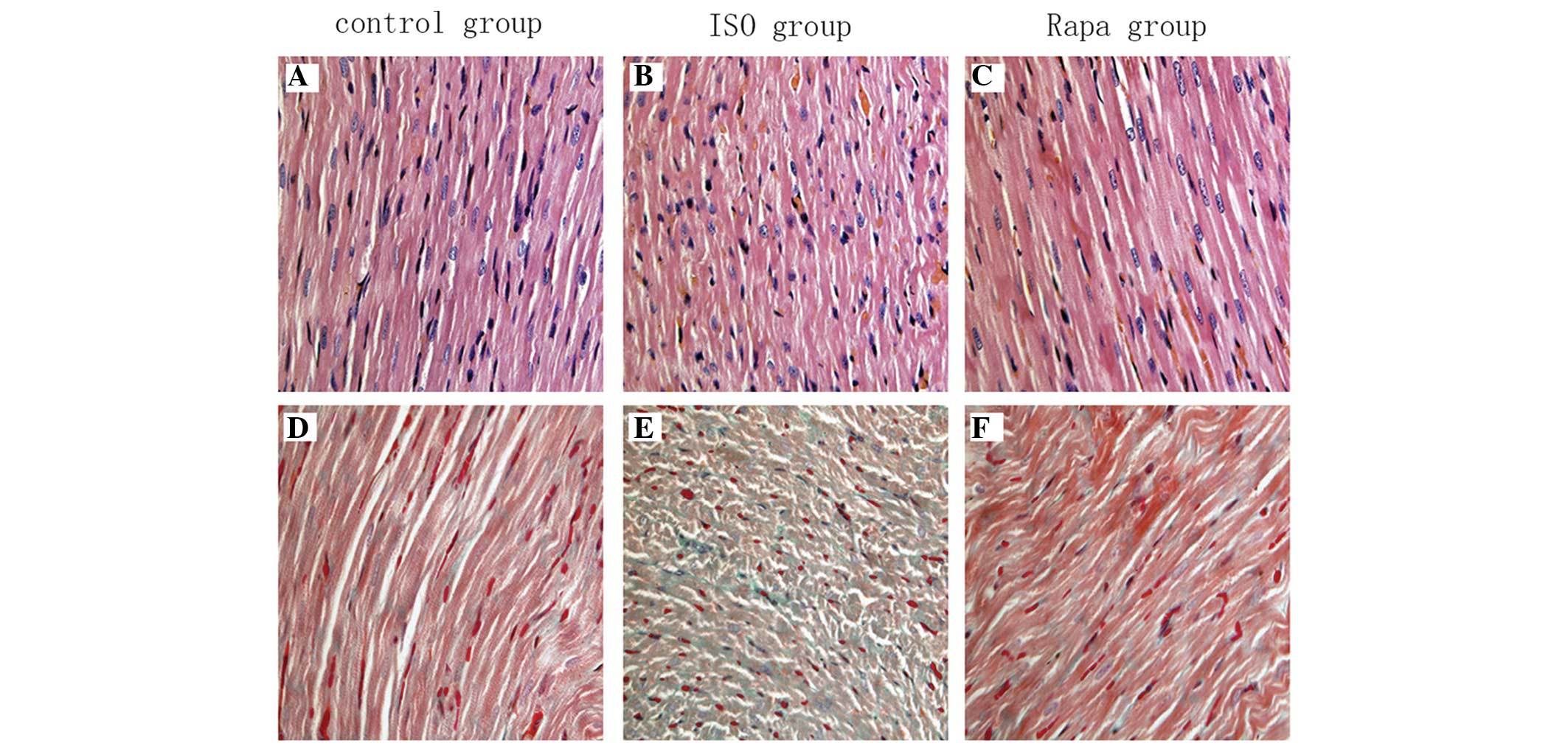
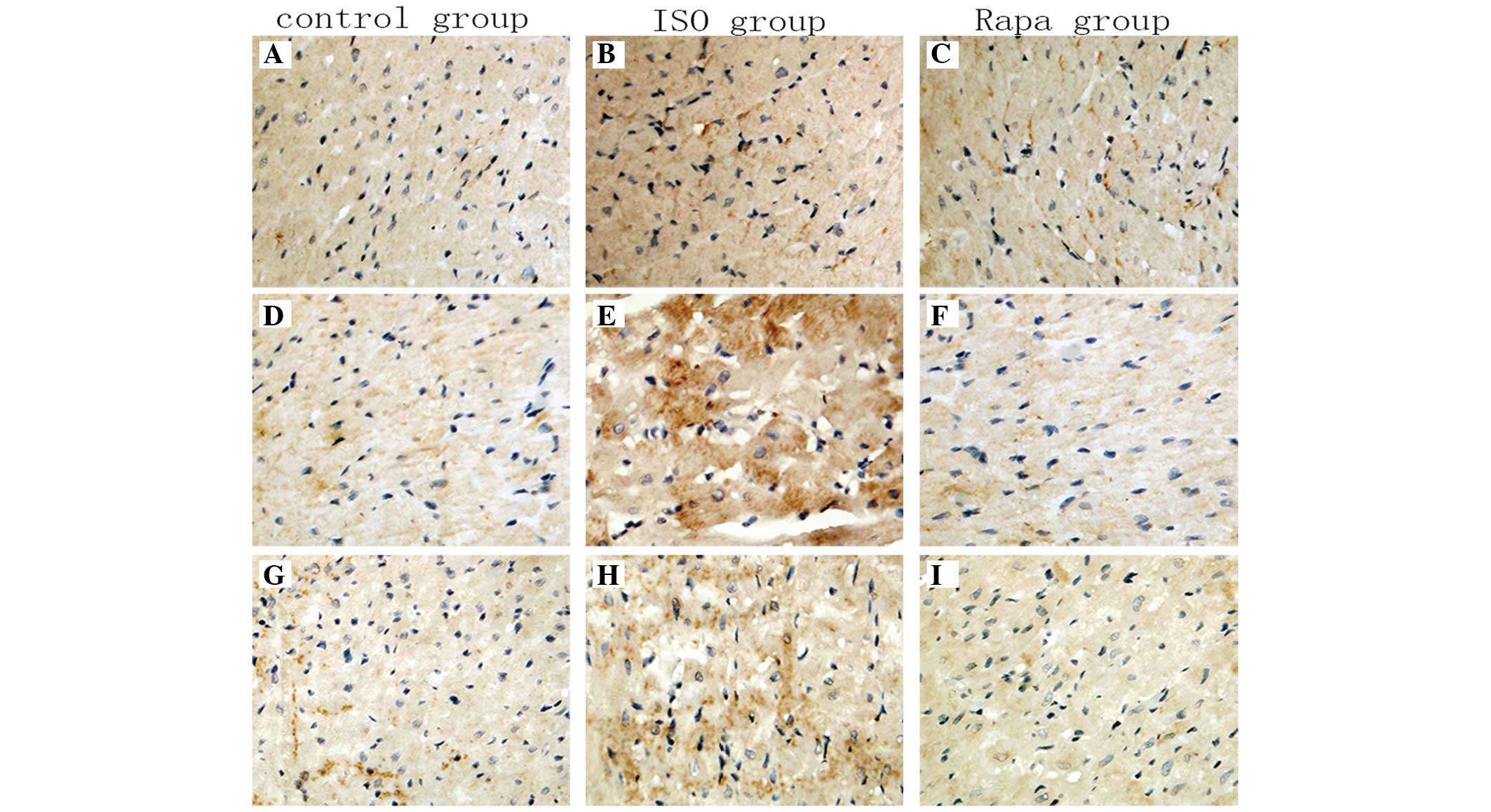
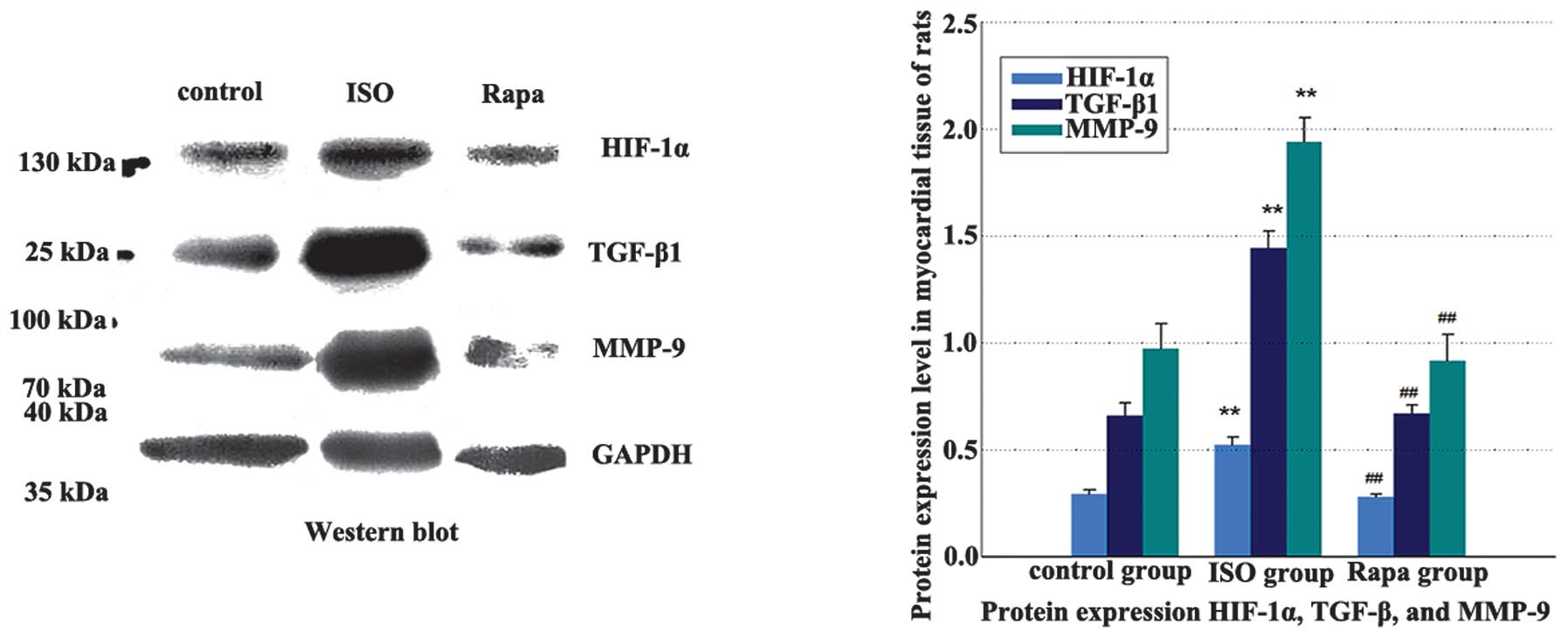
|
1
|
Meiltz A, Zimmermann M, Urban P and Bloch
A: Association of Cardiologists of the Canton of Geneva: Atrial
fibrillation management by practice cardiologists: a prospective
survey on the adherence to guidelines in the real world. Europace.
10:674–680. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Vaziri SM, D’Agostino
RB, Belanger AJ and Wolf PA: Independent risk factors for atrial
fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The Framingham Heart
Study. JAMA. 271:840–844. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pan CH, Lin JL, Lai LP, Chen CL, Stephen
Huang SK and Lin CS: Downregulation of angiotensin converting
enzyme II is associated with pacing-induced sustained atrial
fibrillation. FEBS Lett. 581:526–534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frustaci A, Chimenti C, Bellocci F,
Morgante E, Russo MA and Maseri A: Histological substrate of atrial
biopsies in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Circulation.
96:1180–1184. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Everett TH IV, Li H, Mangrum JM, et al:
Electrical, morphological, and ultrastructural remodeling and
reverse remodeling in a canine model of chronic atrial
fibrillation. Circulation. 102:1454–1460. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li D, Shinagawa K, Pang L, et al: Effects
of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on the development of
the atrial fibrillation substrate in dogs with ventricular
tachypacing-induced congestive heart failure. Circulation.
104:2608–2614. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang Z, Tang L, Zhu Q, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α contributes to the profibrotic action
of angiotensin II in renal medullary interstitial cells. Kidney
Int. 79:300–310. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Zhang YG, Li YG, Liu BG, et al: Urotensin
II accelerates cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy of rats induced by
isoproterenol. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:36–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, et al:
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and
function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol.
22:7004–7014. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dong Y, Huang YF, Wang LQ and Chen B:
Experimental study on the effects of rapamycin in prevention of rat
corneal allograft rejection. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 41:930–935.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Matsushita K, Wu Y, Okamoto Y, Pratt RE
and Dzau VJ: Local renin angiotensin expression regulates human
mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to adipocytes. Hypertension.
48:1095–1102. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang WZ, Wang ZG, Chen YQ, et al: Effects
of valsartan and U0126 on atrial fibrosis and connexin40 remodeling
in rats. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 39:1129–1134. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Fine LG and Norman JT: Chronic hypoxia as
a mechanism of progression of chronic kidney diseases: from
hypothesis to novel therapeutics. Kidney Int. 74:867–872. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Copple BL, Kaska S and Wentling C:
Hypoxia-inducible factor activation in myeloid cells contributes to
the development of liver fibrosis in cholestatic mice. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 341:307–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rosmorduc O and Housset C: Hypoxia: a link
between fibrogenesis, angiogenesis, and carcinogenesis in liver
disease. Semin Liver Dis. 30:258–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ueno M, Maeno T, Nomura M, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α mediates TGF-β-induced PAI-1 production
in alveolar macrophages in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 300:L740–L752. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Haase VH: Hypoxia-inducible factor
signaling in the development of kidney fibrosis. Fibrogenesis
Tissue Repair. 5(Suppl 1): S162012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thijssen VL, van der Velden HM, van
Ankeren EP, et al: Analysis of altered gene expression during
sustained atrial fibrillation in the goat. Cardiovasc Res.
54:427–437. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gramley F, Lorenzen J, Jedamzik B, et al:
Atrial fibrillation is associated with cardiac hypoxia. Cardiovasc
Pathol. 19:102–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rosenkranz S, Flesch M, Amann K, et al:
Alterations of beta-adrenergic signaling and cardiac hypertrophy in
transgenic mice overexpressing TGF-beta(1). Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 283:H1253–H1262. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lim JY, Park SJ, Hwang HY, et al:
TGF-beta1 induces cardiac hypertrophic responses via PKC-dependent
ATF-2 activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 39:627–636. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mihout F, Shweke N, Bigé N, et al:
Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) induces chronic kidney disease
through a mechanism involving collagen and TGF-β1 synthesis. J
Pathol. 223:37–45. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM, et al:
Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1 stimulation of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 117:3810–3820.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogi H, Nakano Y, Niida S, et al: Is
structural remodeling of fibrillated atria the consequence of
tissue hypoxia? Circ J. 74:1815–1821. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Isobe K, Kuba K, Maejima Y, et al:
Inhibition of endostatin/collagen XVIII deteriorates left
ventricular remodeling and heart failure in rat myocardial
infarction model. Circ J. 74:109–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu J, Cui G, Esmailian F, et al: Atrial
extracellular matrix remodeling and the maintenance of atrial
fibrillation. Circulation. 109:363–368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakano Y, Niida S, Dote K, et al: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 contributes to human atrial remodeling during
atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 43:818–825. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Santibañez JF, Guerrero J, Quintanilla M,
Fabra A and Martínez J: Transforming growth factor-beta1 modulates
matrix metalloproteinase-9 production through the Ras/MAPK
signaling pathway in transformed keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 296:267–273. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang BB, Cai WM, Weng HL, et al:
Diagnostic value of platelet derived growth factor-BB, transforming
growth factor-beta1, matrix metalloproteinase-1, and tissue
inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in serum and peripheral
blood mononuclear cells for hepatic fibrosis. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:2490–2496. 2003.
|