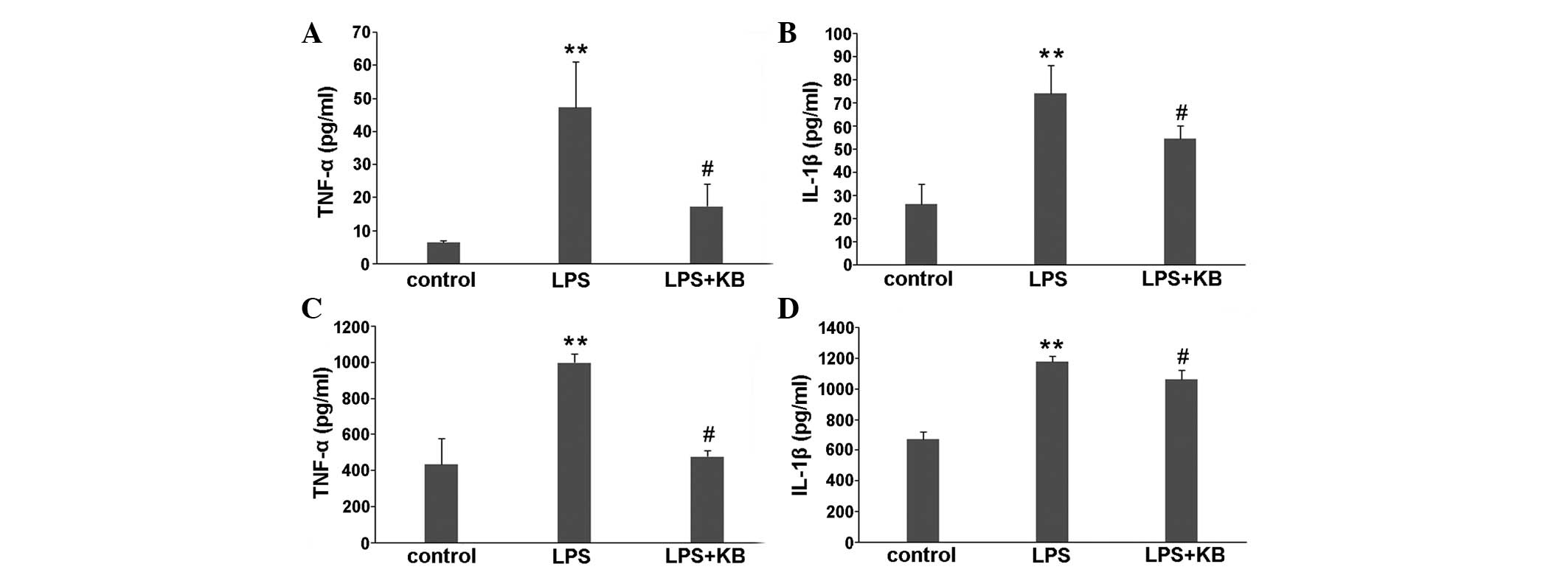
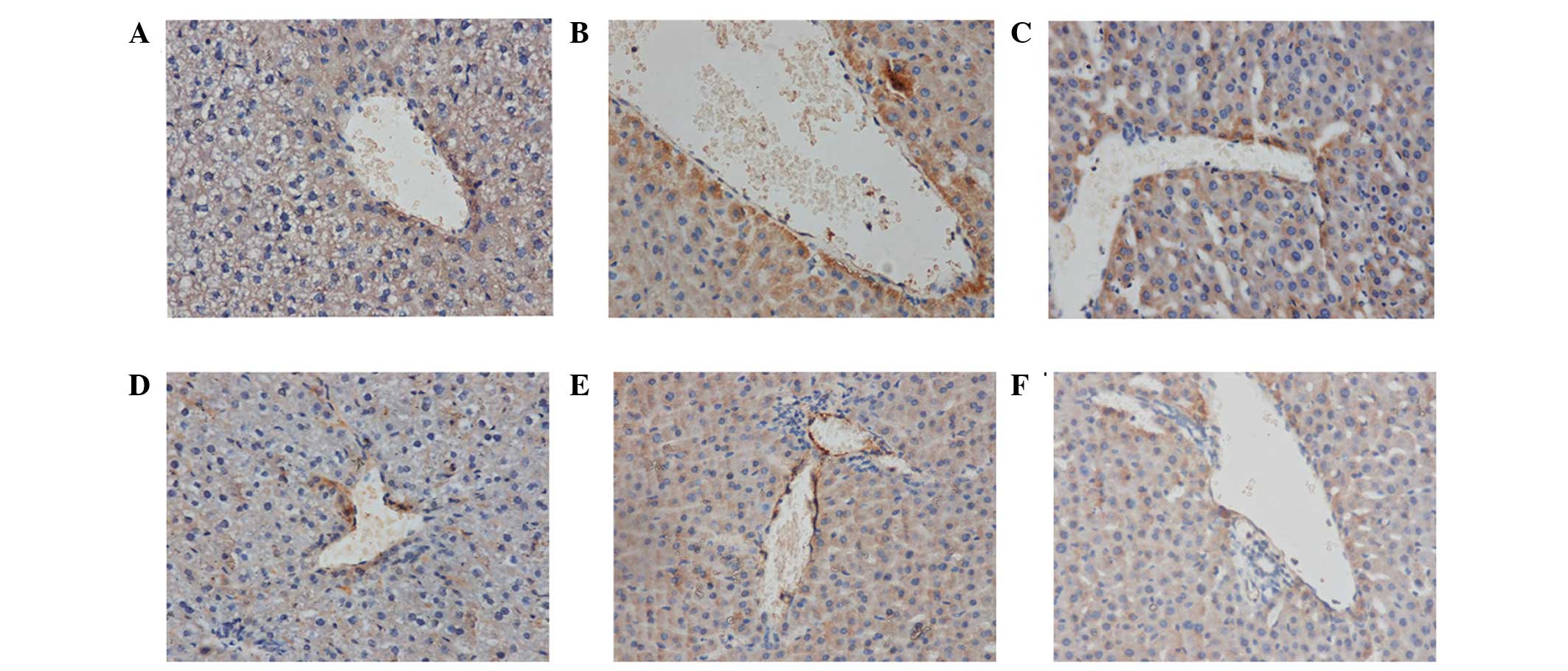
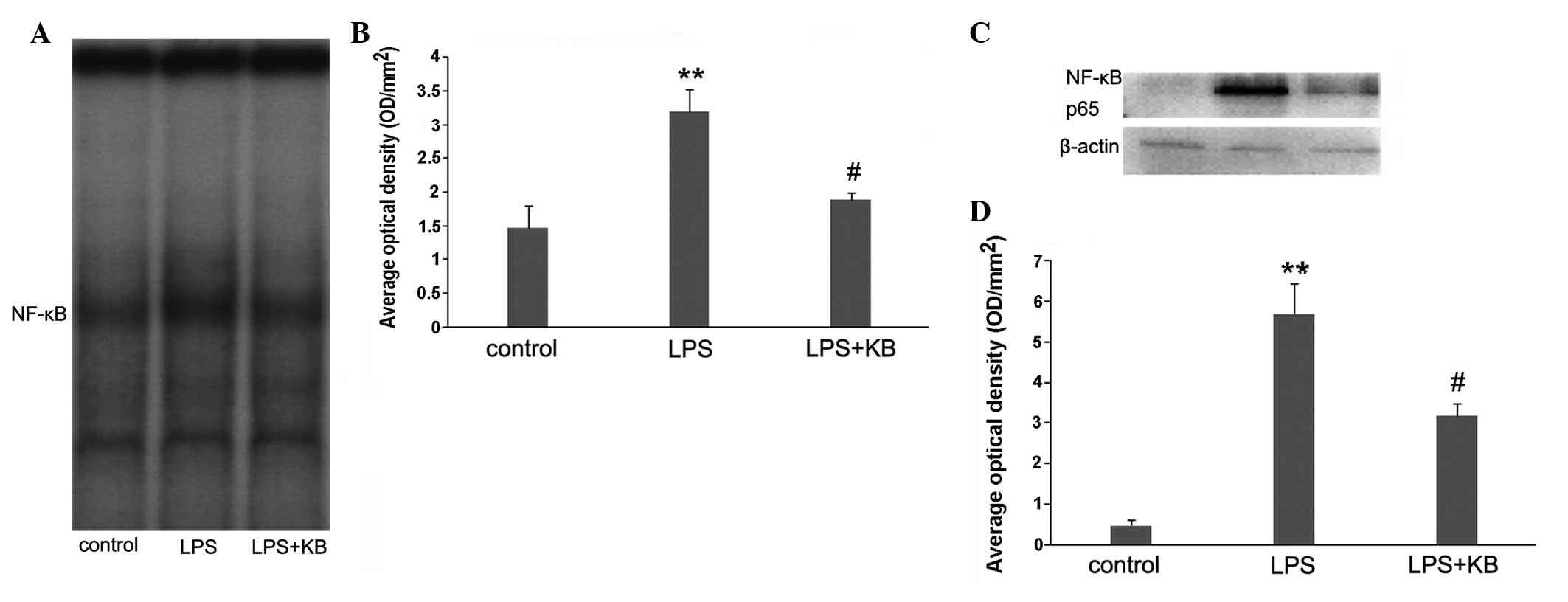
|
1
|
Annane D, Bellissant E and Cavaillon JM:
Septic shock. Lancet. 365:63–78. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM and Moss M: The
effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit
Care Med. 34:15–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Roberts LA, Glenn HL, Whitfield RA and
Jacobson BS: Regulation of cell-substrate adhesion by the
lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase branches of arachidonic acid
metabolism. Adv Exp Med Biol. 507:525–529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hume DA, Underhill DM, Sweet MJ, Ozinsky
AO, Liew FY and Aderem A: Macrophages exposed continuously to
lipopolysaccharide and other agonists that act via toll-like
receptors exhibit a sustained and additive activation state. BMC
Immunol. 2:112001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Nardo D, De Nardo CM, Nguyen T,
Hamilton JA and Scholz GM: Signaling crosstalk during sequential
TLR4 and TLR9 activation amplifies the inflammatory response of
mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 183:8110–8118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alexander C and Rietschel ET: Bacterial
lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity. J Endotoxin Res.
7:167–202. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sparwasser T, Miethke T, Lipford G, et al:
Bacterial DNA causes septic shock. Nature. 386:336–337. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Angus DC, Birmingham MC, Balk RA, et al:
E5 murine monoclonal antiendotoxin antibody in gram-negative
sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. E5 Study Investigators.
JAMA. 283:1723–1730. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nahra R and Dellinger RP: Targeting the
lipopolysaccharides: still a matter of debate? Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 21:98–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Cheng J, Zheng X, et al: Targeting
CpG DNA to screen and isolate anti-sepsis fraction and monomers
from traditional Chinese herbs using affinity biosensor technology.
Int Immunopharmacol. 9:1021–1031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang Z, Hong Z, Guo W, et al: A synthetic
peptide derived from bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein
neutralizes endotoxin in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol.
4:527–537. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
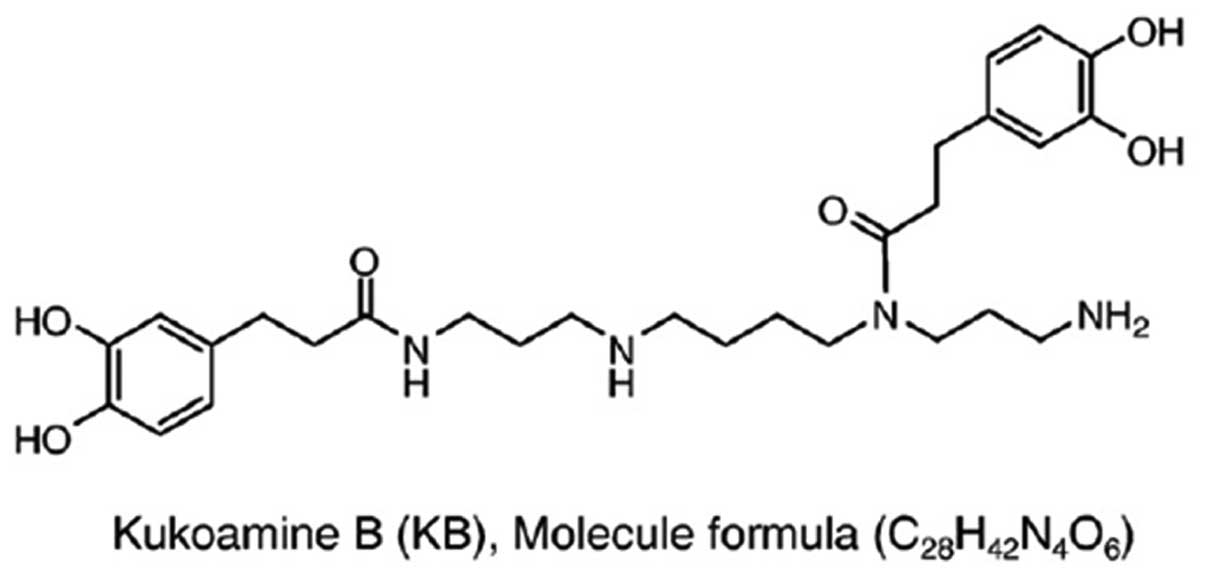
Liu X, Zheng X, Wang N, et al: Kukoamine
B, a novel dual inhibitor of LPS and CpG DNA, is a potential
candidate for sepsis treatment. Br J Pharmacol. 162:1274–1290.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Zheng X, Long Y, et al: Dual
targets guided screening and isolation of Kukoamine B as a novel
natural anti-sepsis agent from traditional Chinese herb Cortex
lycii. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:110–120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nishioku T, Dohgu S, Takata F, et al:
Detachment of brain pericytes from the basal lamina is involved in
disruption of the blood-brain barrier caused by
lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
29:309–316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hillegass LM, Griswold DE, Brickson B and
Albrightson-Winslow C: Assessment of myeloperoxidase activity in
whole rat kidney. J Pharmacol Methods. 24:285–295. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun BW, Chen ZY, Chen X and Liu C:
Attenuation of leukocytes sequestration by carbon
monoxide-releasing molecules: liberated carbon monoxide in the
liver of thermally injured mice. J Burn Care Res. 28:173–181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun B, Sun H, Liu C, Shen J, Chen Z and
Chen X: Role of CO-releasing molecules liberated CO in attenuating
leukocytes sequestration and inflammatory responses in the lung of
thermally injured mice. J Surg Res. 139:128–135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
El-Agamy DS, Makled MN and Gamil NM:
Protective effects of BML-111 against acetaminophen-induced acute
liver injury in mice. J Physiol Biochem. 70:141–149. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim SH, Kim YS, Kang SS, Bae K, Hung TM
and Lee SM: Anti-apoptotic and hepatoprotective effects of gomisin
A on fulminant hepatic failure induced by D-galactosamine and
lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 106:225–233. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukuda T, Mogami A, Tanaka H, Yoshikawa T,
Hisadome M and Komatsu H: Y-40138, a multiple cytokine production
modulator, protects against D-galactosamine and
lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatitis. Life Sci. 79:822–827. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu J, Wang J, Sheng Y, et al: Baicalin
improves survival in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis via
suppressing inflammatory response and lymphocyte apoptosis. PLoS
One. 7:e355232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jaeschke H and Hasegawa T: Role of
neutrophils in acute inflammatory liver injury. Liver Int.
26:912–919. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Odobasic D, Kitching AR, Yang Y, et al:
Neutrophil myeloperoxidase regulates T-cell-driven tissue
inflammation in mice by inhibiting dendritic cell function. Blood.
121:4195–4204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang N, Francis KP, Prakash A and Ansaldi
D: Enhanced detection of myeloperoxidase activity in deep tissues
through luminescent excitation of near-infrared nanoparticles. Nat
Med. 19:500–505. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Barreiro O, Zamai M, Yáñez-Mó M, et al:
Endothelial adhesion receptors are recruited to adherent leukocytes
by inclusion in preformed tetraspanin nanoplatforms. J Cell Biol.
183:527–542. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vestweber D: Adhesion and signaling
molecules controlling the transmigration of leukocytes through
endothelium. Immunol Rev. 218:178–196. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI and
Nourshargh S: Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte
adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:678–689. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schmidt A, Oberle N, Weiss EM, et al:
Human regulatory T cells rapidly suppress T cell receptor-induced
Ca(2+), NF-κB, and NFAT signaling in conventional T cells. Sci
Signal. 4:ra902011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Madonna R and De Caterina R: Relevance of
new drug discovery to reduce NF-κB activation in cardiovascular
disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 57:41–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han EH, Yang JH, Kim HK, et al:
1-Bromopropane up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression via NF-κB
and C/EBP activation in murine macrophages. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:1616–1622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|