Introduction
Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS), a condition
previously known as veno-occlusive disease (1), is a life-threatening syndrome that
results from sinusoidal congestion and is characterized by
hepatomegaly, ascites, portal hypertension, weight gain and
jaundice (2). This syndrome is
commonly observed as a complication of high-dose chemotherapy
administered prior to hematopoietic progenitor cell (HPC)
transplantation (3). The
development of SOS subsequent to liver transplantation (LT) is
relatively uncommon, being observed in ~2% of LT recipients
(4). SOS is severe and refractory
to medical therapy, with the ultimate solution being
re-transplantation (2).
The mechanism underlying the development of SOS is
not yet completely understood, although sinusoidal endothelial cell
damage leading to alterations in the hemostatic system is regarded
as central to the pathogenesis of SOS (5). SOS has additionally been reported to
be associated with platelet functions. For example, transforming
growth factor (TGF) β-1 secreted by platelets has been shown to
contribute to hypercoagulability in SOS following HPC
transplantation (6). In addition,
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), which is abundant in
platelets, has been suggested to be a specific marker of SOS
(7). Clinically, patients who
experience SOS following HPC transplantation are both
thrombocytopenic and refractory to platelet transfusions (8). These observations suggest that
platelets may be important in the pathogenesis of SOS.
The present case report describes a patient who
experienced liver allograft dysfunction caused by the progression
of SOS following living donor LT (LDLT), with unexplained
thrombocytopenia occurring around the same period of time. We
hypothesized that the platelets had been consumed by the liver
allograft, and therefore the allograft was immunohistochemically
assayed for the presence of platelets using antibody to the
platelet marker cluster of differentiation (CD)42b (platelet
glycoprotein Ib).
Case report
A 59-year-old male patient was diagnosed with
primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome and
end-stage cirrhosis. His Child-Pugh score was C 12 points and his
Model For End-Stage Liver Disease score was 23 (9). The donor was the patient’s
56-year-old wife. Their blood types were compatible (blood type
O→AB), and the lymphocyte cross-match test was negative. The LDLT
involved the right lobe without the middle hepatic vein (500 g).
The graft-to-recipient weight ratio was 0.83, with the graft
constituting 42% of the standard liver volume of the recipient.
Following transplantation, the patient was started on
immunosuppressive treatment with tacrolimus (Tac), mycophenolate
mofetil (MMF) and prednisolone. His immediate postoperative course
was good, and he was moved from the intensive-care unit on
postoperative day (POD) 3.
Approximately 2 months after the LDLT, the patient’s
concentrations of biliary tract enzymes and total bilirubin (T-Bil)
began to increase progressively. Endoscopic retrograde
cholangiopancreatography revealed no stenosis of the biliary
anastomosis, and color doppler ultrasonography and computed
tomography revealed no abnormalities. A liver biopsy on POD 77
showed minimal inflammation of the portal area and slight
endothelial inflammation of the central venules. At that time, the
patient’s platelet counts were <10×105/mm3
and his T-Bil concentration continued to increase, to 17 mg/dl. The
patient was regarded as experiencing late-onset acute rejection and
was treated with augmented immunosuppressive therapy, consisting of
intravenous corticosteroid pulse therapy, increased doses of MMF
and adjustment of the Tac trough level to maintain a whole-blood
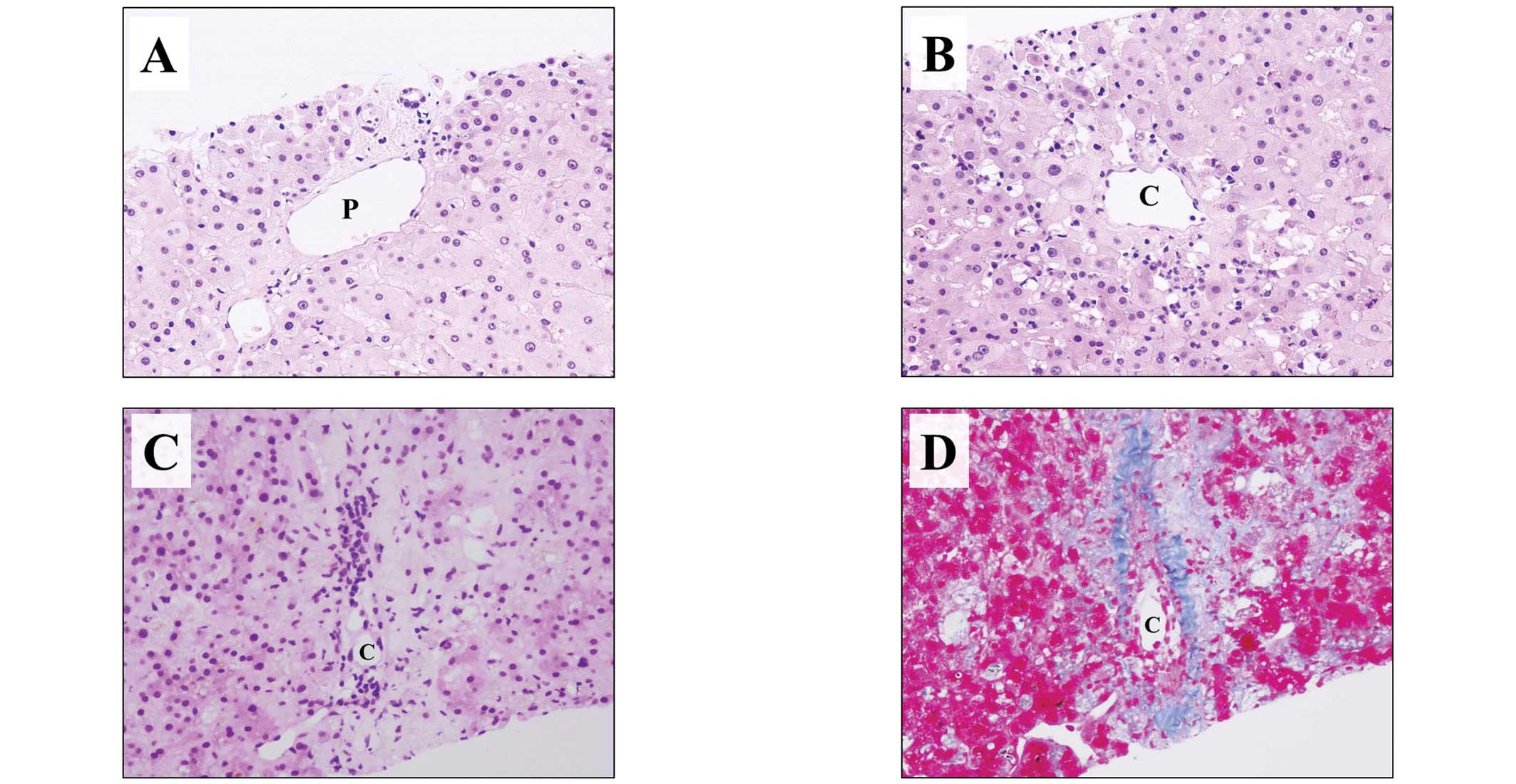
concentration of 5–10 ng/ml. A liver biopsy taken on POD 91 showed
minimal inflammation and no bile duct injury in the portal area
(Fig. 1A), similar to the previous
biopsy. Zone 3, however, showed chronic inflammation and a loss of
hepatocytes (Fig. 1B). The sample
was negative for C4d staining, a marker of antibody-mediated
rejection. Based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with
late-onset acute rejection accompanied by mild central
perivenulitis, resulting in an intensification of
immunosuppression. Since the concentration of Tac could not be
maintained >10 ng/ml, despite increased doses, the patient’s
calcineurin inhibitor treatment was switched from Tac to
cyclosporin A (CsA), with the CsA dose adjusted to maintain a
target level in the blood of 150–200 ng/ml, and everolimus was
added as a third immunosuppressive agent. In addition, the patient
was administered two doses of basiliximab (50 mg/day) to suppress
the antibody-mediated rejection. The patient’s platelet counts
declined to ~5×105/mm3, despite the lack of
any apparent causes of the thrombocytopenia, such as disseminated
intravascular coagulation, thrombotic microangiopathy or any other
thrombotic diseases; however, his T-Bil concentration increased to
21.4 mg/dl. A liver biopsy taken on POD 203 showed inflammatory
cells infiltrating the liver parenchyma in zone 3, as well as
marked reductions in hepatocytes and central vein obliteration, as
revealed by hematoxylin and eosin staining (Fig. 1C). Masson’s trichrome stain showed
basement membrane formation caused by fibrous tissue and sinusoidal
fibrosis (Fig. 1D). By contrast,
the portal area (zone 1) showed minimal inflammation, similar to
the previous biopsy. The patient’s central perivenulitis had
progressively worsened, resulting in the development of SOS. His
platelet count was ~5×105/mm3, the allograft
was less responsive to augmented immunosuppressive therapy and his
condition was considered irreversible. Re-transplantation was
indicated if feasible, but a donor could not be found. He
subsequently experienced liver and renal failure and succumbed on
POD 250.
Immunohistochemistry of CD42b
The presence of platelets in the liver tissue
samples was assayed using a mouse monoclonal antibody to CD42b
(1:100; cat. no. EPR6995; Abcam, Tokyo, Japan), a marker expressed
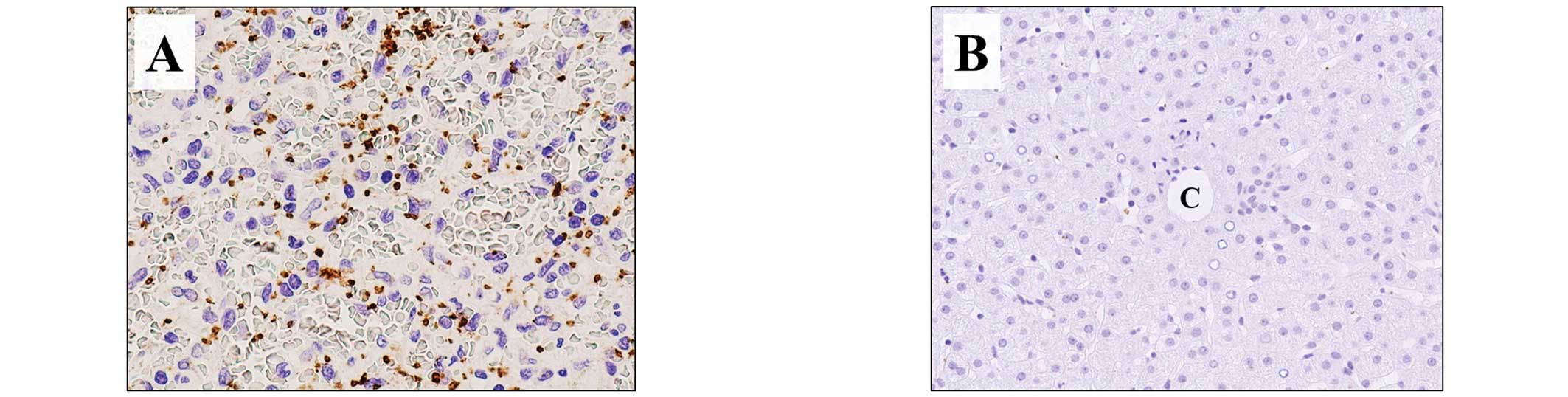
on both inactive and activated platelets. In normal spleen tissue,
used as a positive control, CD42b expression was evident as dots,
morphologically characterized as platelets (Fig. 2A), whereas there was no staining of
normal liver tissue, used as the negative control (Fig. 2B). Assay of the liver allograft
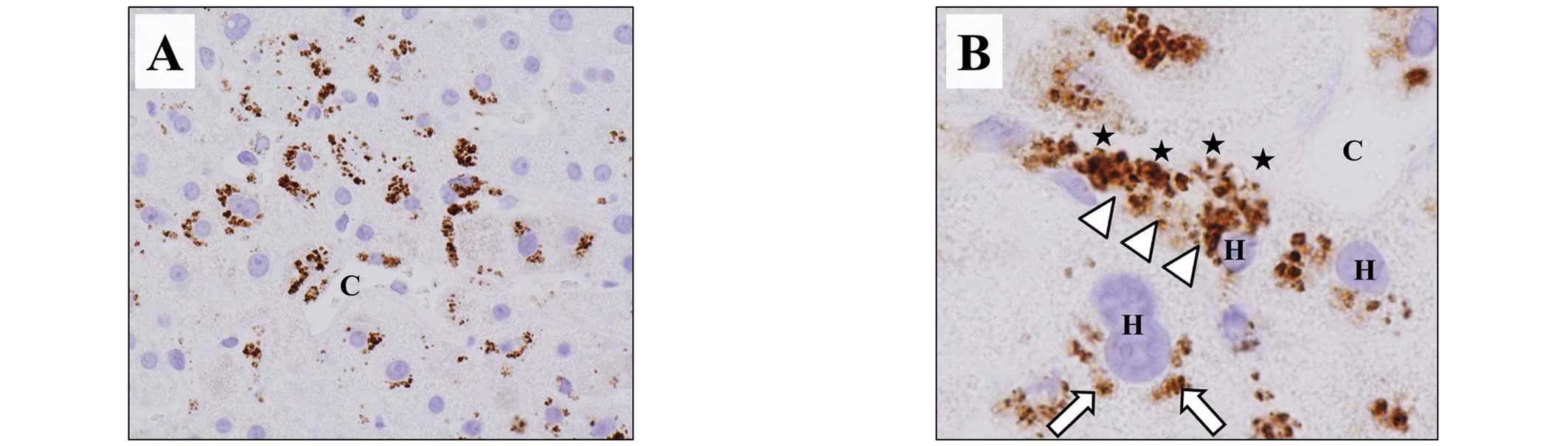
tissue obtained from the patient on POD 91 showed CD42b expression
in zone 3 (Fig. 3A). At greater
magnification, the CD42b appeared as aggregates attached to
hepatocytes along the sinusoids. CD42b was also expressed in the
cytoplasm of the hepatocytes (Fig.
3B) but was not observed in zone 1.
Discussion
SOS is believed to result from sinusoidal
endothelial cell damage in zone 3 of the liver (5). Red blood cells subsequently leak into
the space of Disse, depositing fibrin (1). The basement membrane that forms from
the fibrous tissue leads to hepatocyte ischemia, followed by
hepatocyte necrosis (1). Tac
administration following transplantation may be due to sinusoidal
endothelial cell damage of the small hepatic vein in zone 3
(10,11). To date, however, the
pathophysiology of SOS remains incompletely understood, with no
definitive mechanisms or effective treatments identified.
There are few reports concerning a pathologic
association between platelets and SOS. One study, in which liver
samples taken at autopsy from HPC transplant recipients with SOS
were stained with an anti-platelet antibody, found no evidence of
platelet deposition (12);
however, to prevent SOS, its pathogenetic mechanism must be
clarified prior to it becoming irreversible. The present study
therefore assessed liver tissue samples taken from an LDLT
recipient in the development process of SOS. Zone 3 of the liver
was positive for CD42b, with the staining pattern observed as
aggregates attached to hepatocytes along the sinusoid and in the
cytoplasm of the hepatocytes. These findings suggest that
extravasated platelet aggregation (EPA) was present in the space of
Disse, and that the platelets were phagocytized by hepatocytes. It
is likely that these aggregated and activated platelets in the
space of Disse had a greater influence on hepatocytes than did the
platelets in the sinusoidal vessels.
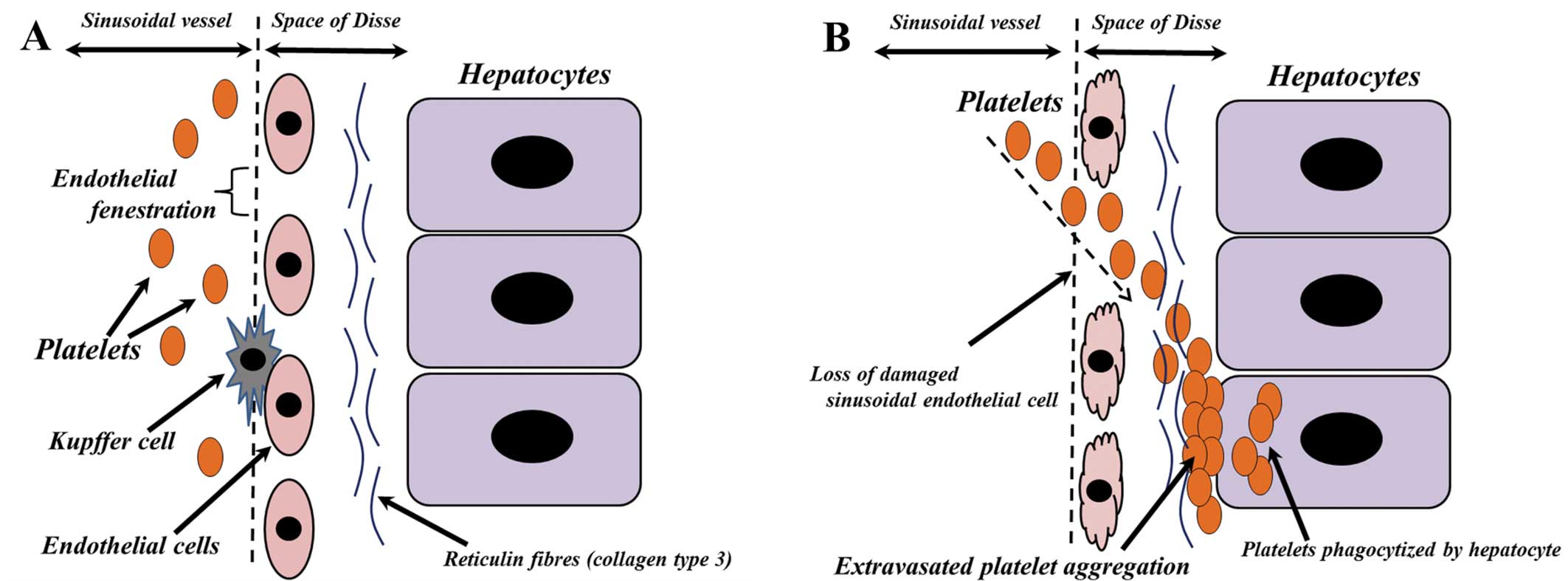
Liver sinusoids are a type of sinusoidal blood
vessel with endothelial fenestrations (13) (Fig.
4A), the diameters of which are increased by sinusoidal
endothelial cell damage (14). The
sinusoidal endothelial cells in the patient described in the
present report had been exposed to Tac or a corticosteroid pulse,
resulting in sinusoidal endothelial cell damage. This damage likely
contributed to the denuding of the endothelium or loss of the
fenestrations, allowing platelets to enter the space of Disse
(Fig. 4B). This space contains
reticulin fibers, most of which contain collagen type 3 (15). Platelets have been found to bind to
and form aggregates with collagen type 3 (16), resulting in platelet aggregation in
the space of Disse (Fig. 4B).
Hepatocytes contribute to blood homeostasis by
endocytosing a number of proteins present in plasma (17). The asialoglycoprotein receptor
(ASGR), a membrane-bound lectin, removes the target glycoproteins
from the circulation (18). These
glycoproteins are also found on the surface of platelets, and human
platelets have been reported to be sequestered by hepatocytes
through the ASGR (19). In the
patient in the present report, the extravasated platelets in the
space of Disse may have been phagocytized by hepatocytes through
the ASGR (Fig. 4B).
Platelets contain α and dense granules (20). Upon activation, platelets excrete
the contents of these granules into their canalicular systems or
the surrounding blood (20). These
granules also contain negative regulators of liver regeneration,
including thromboxane A2 (TXA2), vascular endothelial growth
factor-A (VEGF-A), TGF-β and PAI-1 (6,21,22).
TXA2 is a vasoconstrictor that increases portal venous resistance
(23) and causes portal
hypertension. Although VEGF-A acts as a vasodilator under ordinary
circumstances, it acts, paradoxically, as a vasoconstrictor in
patients with endothelial failure (24). Bevacizumab, an antibody against
VEGF-A, protects against liver injury associated with SOS (25). PAI-1 suppresses fibrinolysis and
the progression to fibrosis in the tissue microenvironment. In
addition, PAI-1 acts as a negative regulator of hepatocyte
proliferation by inhibiting urokinase-type plasminogen activator,
which activates hepatocyte growth factor (26,27).
TGF-β is a major antiproliferative factor for hepatocytes (28) that stimulates collagen synthesis
through activated hepatic stellate cells (29). In the patient in the present
report, the release by platelets of these negative regulators may
have induced portal hypertension and the progression of hepatic
fibrosis, as well as the suppression liver regeneration, a
mechanism responsible, at least in part, for the initiation of
liver damage with SOS (Fig.
5).
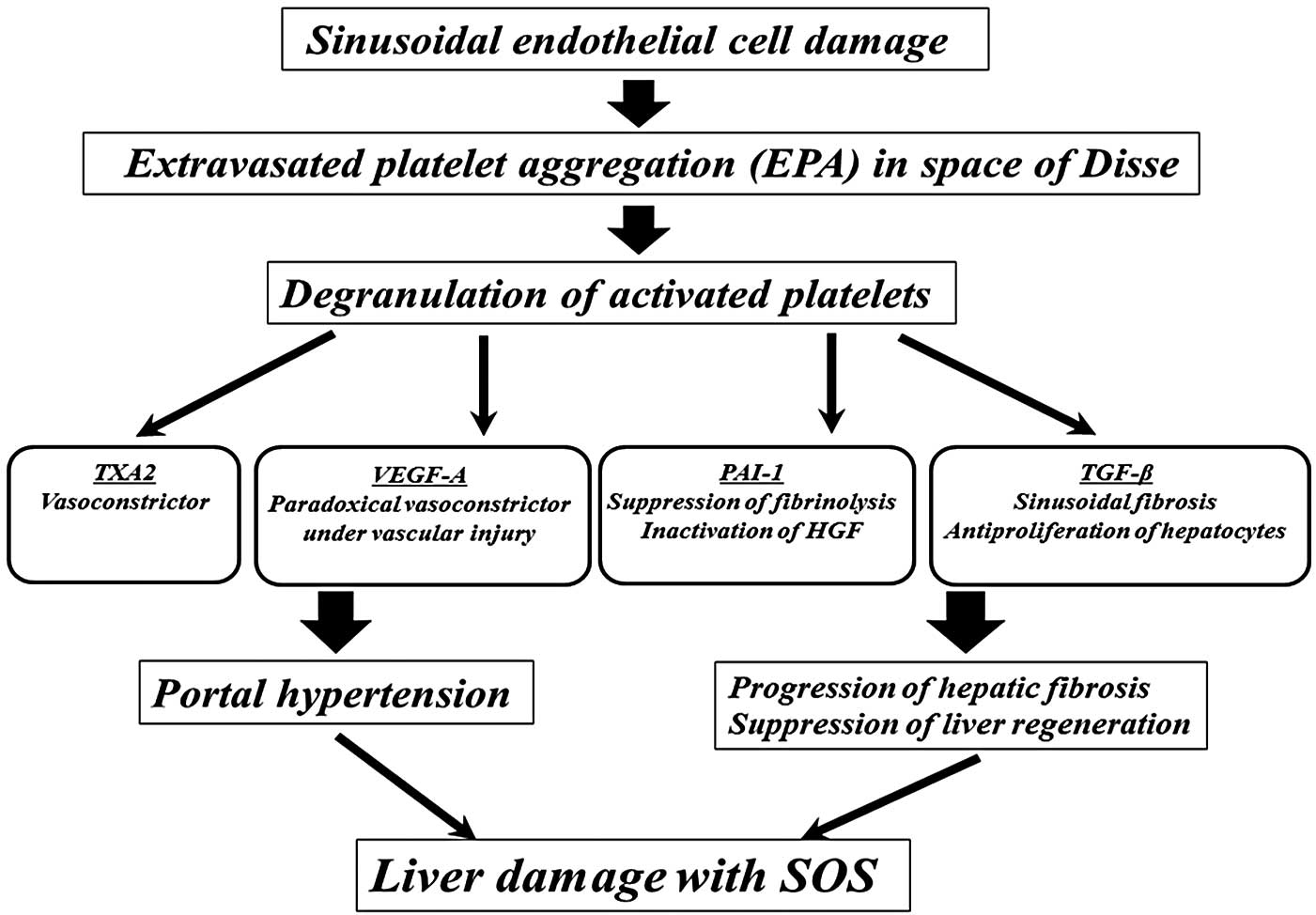 | Figure 5The predicted pathogenic mechanism of
SOS in the patient in the present study. Extravasated platelet
aggregation in the space of Disse was initiated by damage to the
sinusoidal endothelium induced by tacrolimus or a corticosteroid
pulse. The negative regulators released by activated platelets,
including TXA2, VEGF-A, PAI-1 and TGF-β, may have induced portal
hypertension and the progression of hepatic fibrosis, as well as
suppressed liver regeneration, initiating liver damage with SOS.
SOS, sinusoidal obstruction syndrome; TXA2, thromboxane A2; VEGF-A,
vascular endothelial growth factor-A; PAI-1, plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; TGF-β, transforming
growth factor-β. |
No standard method of treating SOS has yet been
established. Systemic anticoagulation and thrombolytic therapies
have been tested extensively (30). Defibrotide, a polydeoxyribonucleic
acid, has been recently shown to have a promising response rate in
patients with severe SOS (31).
When medical treatment fails, transjugular intrahepatic
portosystemic shunt placement or re-transplantation can be
considered (2). Depending on the
extent of the sinusoidal endothelium damage and EPA in the space of
Disse, the prophylactic administration of endothelial protective
and antiplatelet agents may be effective prior to the development
of irreversible damage. Cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3)
inhibitor, may be appropriate, owing to its antiplatelet
properties, its ability to increase tolerance to
ischemia/reperfusion injury (32)
and its induction of immune tolerance via an enhanced regulatory
T-cell response (33). In clinical
practice, we have administered a PDE3 inhibitor to LDLT recipients,
with favorable outcomes (Nakanuma et al, unpublished
data).
In conclusion, the present findings suggest that EPA
in the space of Disse, which was initiated by sinusoidal
endothelial cell damage due to the toxicity of Tac or a
corticosteroid pulse and the negative regulators released by
activated platelets, may have partially contributed to liver damage
with SOS in the patient. Endothelial protective therapy or
antiplatelet treatment may have been useful in the treatment of SOS
in this patient. Studies in additional patients are necessary to
elucidate the role of EPA in the space of Disse on the development
of SOS.
References
|
1
|
Kitajima K, Vaillant JC, Charlotte F, et
al: Intractable ascites without mechanical vascular obstruction
after orthotopic liver transplantation: etiology and clinical
outcome of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Clin Transplant.
24:139–148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Campos-Varela I, Castells L, Dopazo C, et
al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for the treatment
of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in a liver transplant recipient
and review of the literature. Liver Transpl. 18:201–205. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Membreno FE, Ortiz J, Foster PF, Wright F,
et al: Liver transplantation for sinusoidal obstructive syndrome
(veno-occlusive disease): case report with review of the literature
and the UNOS database. Clin Transplant. 22:397–404. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sebagh M, Debette M, Samuel D, et al:
‘Silent’ presentation of veno-occlusive disease after liver
transplantation as part of the process of cellular rejection with
endothelial predilection. Hepatology. 30:1144–1150. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coppell JA, Brown SA and Perry DJ:
Veno-occlusive disease: cytokines, genetics, and haemostasis. Blood
Rev. 17:63–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pihusch V, Pihusch M, Penovici M, et al:
Transforming growth factor beta-1 released from platelets
contributes to hypercoagulability in veno-occlusive disease
following hematopoetic stem cell transplantation. Thromb Res.
116:233–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Salat C, Holler E, Kolb HJ, et al:
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 confirms the diagnosis of hepatic
veno-occlusive disease in patients with hyperbilirubinemia after
bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 89:2184–2188. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oh H, Tahara T, Bouvier M, et al: Plasma
thrombopoietin levels in marrow transplant patients with
veno-occlusive disease of the liver. Bone Marrow Transplant.
22:675–679. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wiesner RH, McDiarmid SV, Kamath PS, et
al: MELD and PELD: application of survival models to liver
allocation. Liver Transpl. 7:567–580. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen H, Wang X, Fan T, et al: A case of
veno-occlusive disease following liver transplantation. Exp Ther
Med. 7:141–144. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Wang SE, Shyr YM and Lee RC: Hepatic
veno-occlusive disease related to tacrolimus after pancreas
transplantation. J Chin Med Assoc. 76:358–360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shulman HM, Gown AM and Nugent DJ: Hepatic
veno-occlusive disease after bone marrow transplantation.
Immunohistochemical identification of the material within occluded
central venules. Am J Pathol. 127:549–558. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cogger VC, McNerney GP and Nyunt T:
Three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy of liver
sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrations. J Struct Biol.
171:382–388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mak KM and Lieber CS: Alterations in
endothelial fenestrations in liver sinusoids of baboons fed
alcohol: a scanning electron microscopic study. Hepatology.
4:386–391. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamamoto M, Sumiyoshi H, Nakagami K and
Tahara E: Distribution of collagen types I, III, and V in fibrotic
and neoplastic human liver. Acta Pathol Jpn. 34:77–86.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jung SM, Takemura Y, Imamura Y, et al:
Collagen-type specificity of glycoprotein VI as a determinant of
platelet adhesion. Platelets. 19:32–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brech A, Kjeken R, Synnes M, et al:
Endocytosed ricin and asialoorosomucoid follow different
intracellular pathways in hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1373:195–208. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Steirer LM, Park EI, Townsend RR, et al:
The asialoglycoprotein receptor regulates levels of plasma
glycoproteins terminating with sialic acid alpha2,6-galactose. J
Biol Chem. 284:3777–3783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Sørensen AL, Rumjantseva V, Nayeb-Hashemi
S, et al: Role of sialic acid for platelet life span: exposure of
beta-galactose results in the rapid clearance of platelets from the
circulation by asialoglycoprotein receptor-expressing liver
macrophages and hepatocytes. Blood. 114:1645–1654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Golebiewska EM and Poole AW: Platelet
secretion: From haemostasis to wound healing and beyond. Blood Rev.
Oct 31–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mohammad SF, Anderson WH, Smith JB, et al:
Effects of heparin on platelet aggregation and release and
thromboxane A2 production. Am J Pathol. 104:132–141.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anitua E, Andia I, Ardanza B, et al:
Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue
regeneration. Thromb Haemost. 91:4–15. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Ruan Z, Shibamoto T, Shimo T, et al:
Effects of platelet-activating factor and thromboxane A2 on
isolated perfused guinea pig liver. Prostaglandins Other Lipid
Mediat. 73:73–85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parenti A, Brogelli L, Filippi S, et al:
Effect of hypoxia and endothelial loss on vascular smooth muscle
cell responsiveness to VEGF-A: role of flt-1/VEGF-receptor-1.
Cardiovasc Res. 55:201–212. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ribero D, Wang H, Donadon M, et al:
Bevacizumab improves pathologic response and protects against
hepatic injury in patients treated with oxaliplatin-based
chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases. Cancer.
110:2761–2767. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mars WM, Zarnegar R and Michalopoulos GK:
Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen
activators uPA and tPA. Am J Pathol. 143:949–958. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Watanabe K, Togo S, Takahashi T, et al:
PAI-1 plays an important role in liver failure after excessive
hepatectomy in the rat. J Surg Res. 143:13–19. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ueda S, Yamanoi A, Hishikawa Y, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 released from the spleen exerts a
growth inhibitory effect on liver regeneration in rats. Lab Invest.
83:1595–1603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Watanabe T, Tajima H, Hironori H, et al:
Sodium valproate blocks the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1
autocrine loop and attenuates the TGF-β1-induced collagen synthesis
in a human hepatic stellate cell line. Int J Mol Med. 28:919–925.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamada N, Urahashi T, Ihara Y, et al:
Veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated
with potential antibody-mediated rejection after pediatric living
donor liver transplantation: a case report. Transplant Proc.
44:810–813. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Wang Y and Huang H: Defibrotide
for the prevention of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review. Clin
Transplant. 26:511–519. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iba T, Kidokoro A, Fukunaga M, et al:
Comparison of the protective effects of type III phosphodiesterase
(PDE3) inhibitor (cilostazol) and acetylsalicylic acid on
intestinal microcirculation after ischemia reperfusion injury in
mice. Shock. 26:522–526. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang S, Yan C, Xu H, Zhao X and Han Y:
Suppression of encephalitogenic T-cell responses by cilostazol is
associated with upregulation of regulatory T cells. Neuroreport.
21:629–635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|