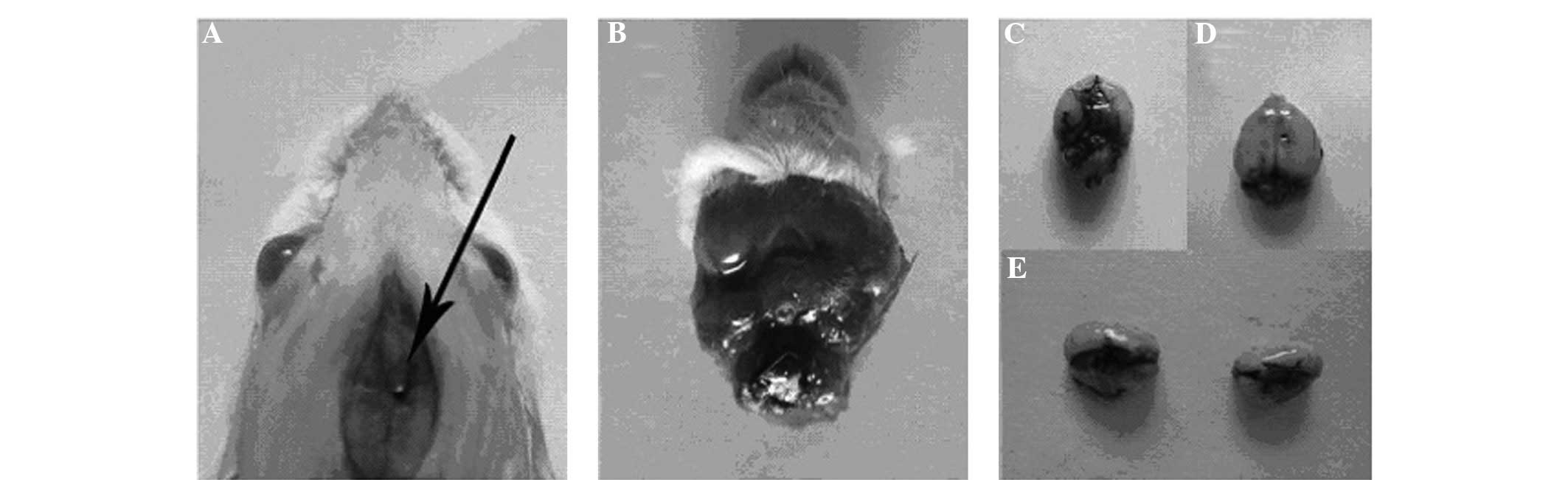
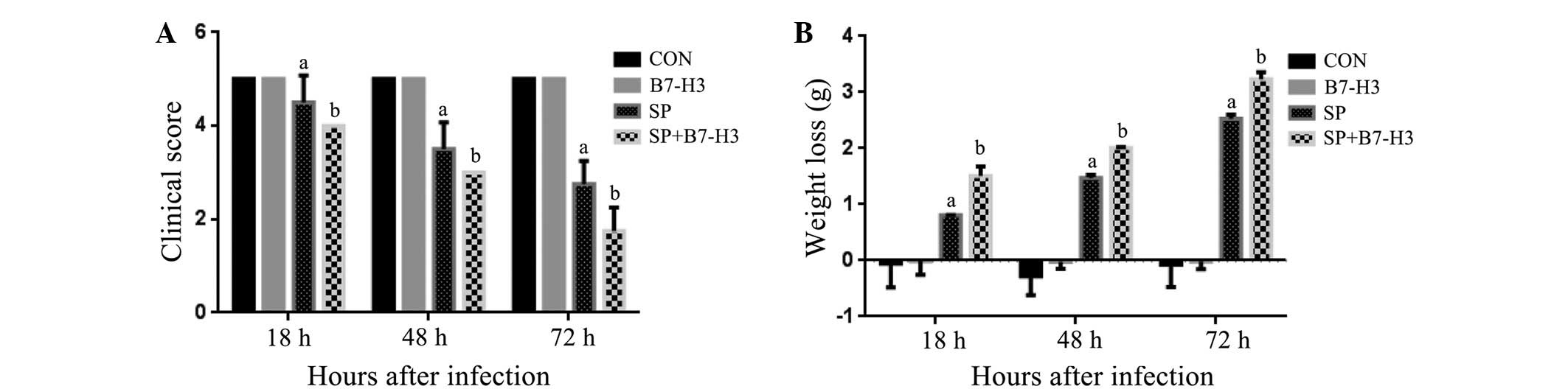
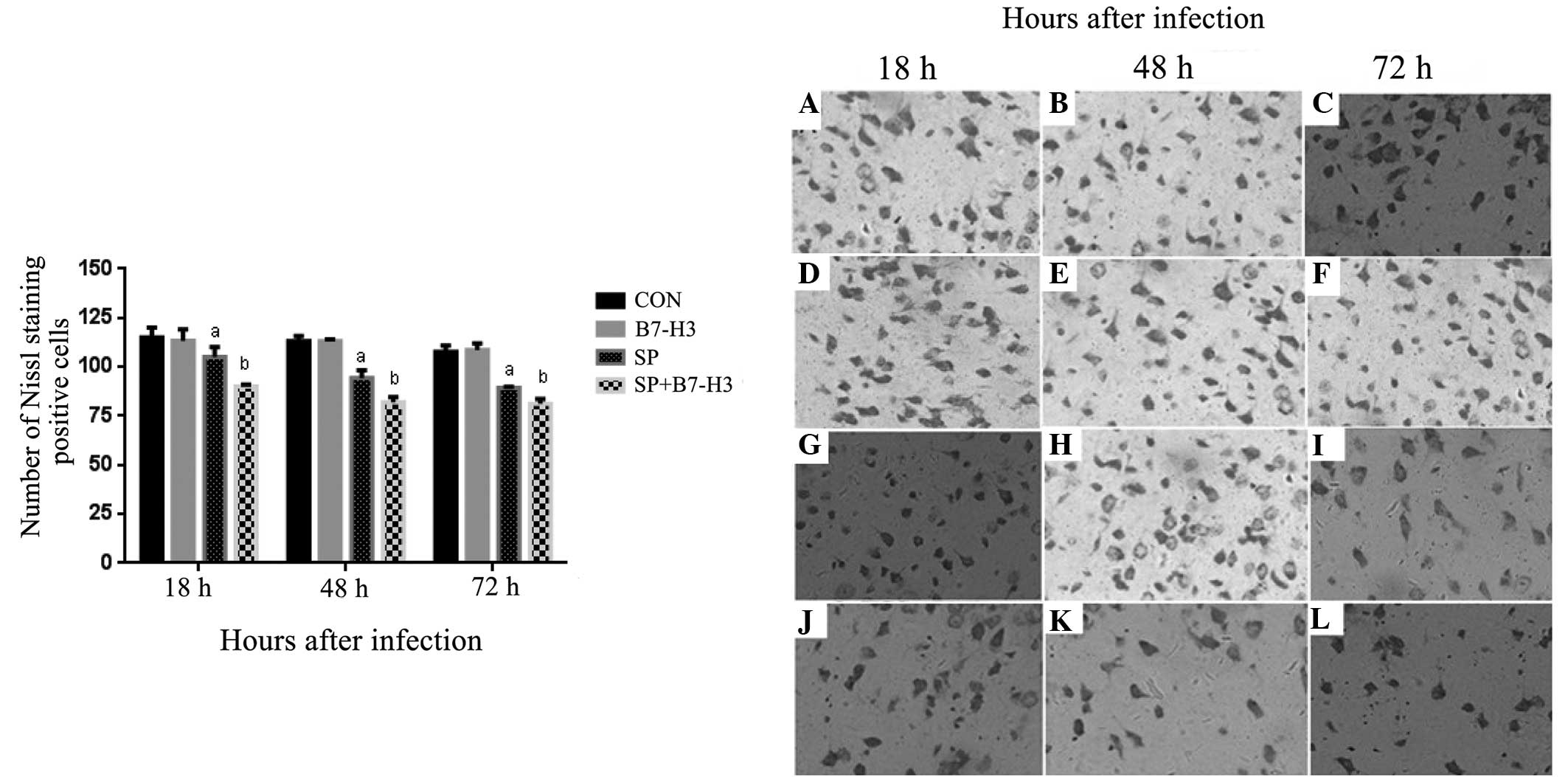
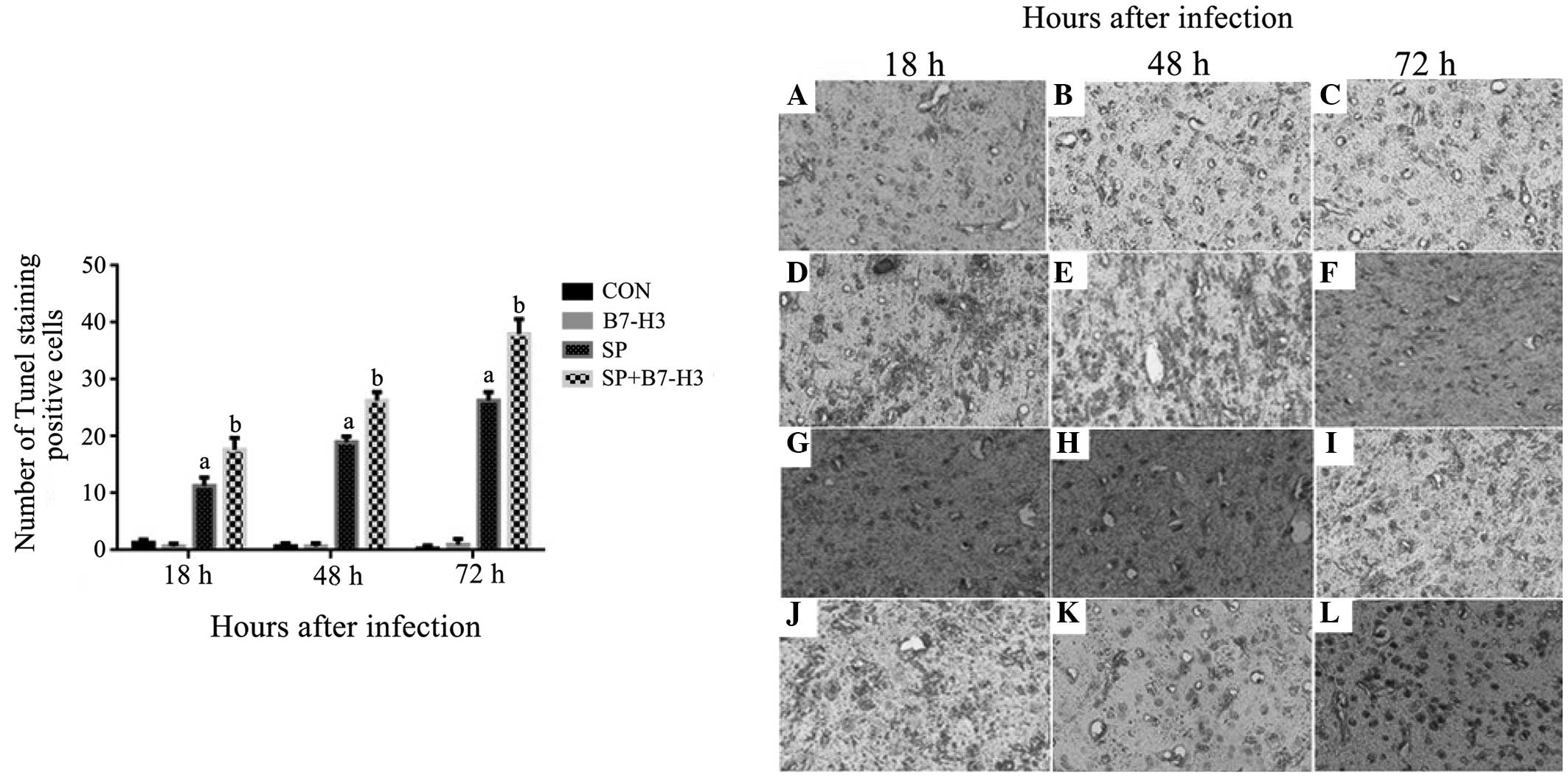
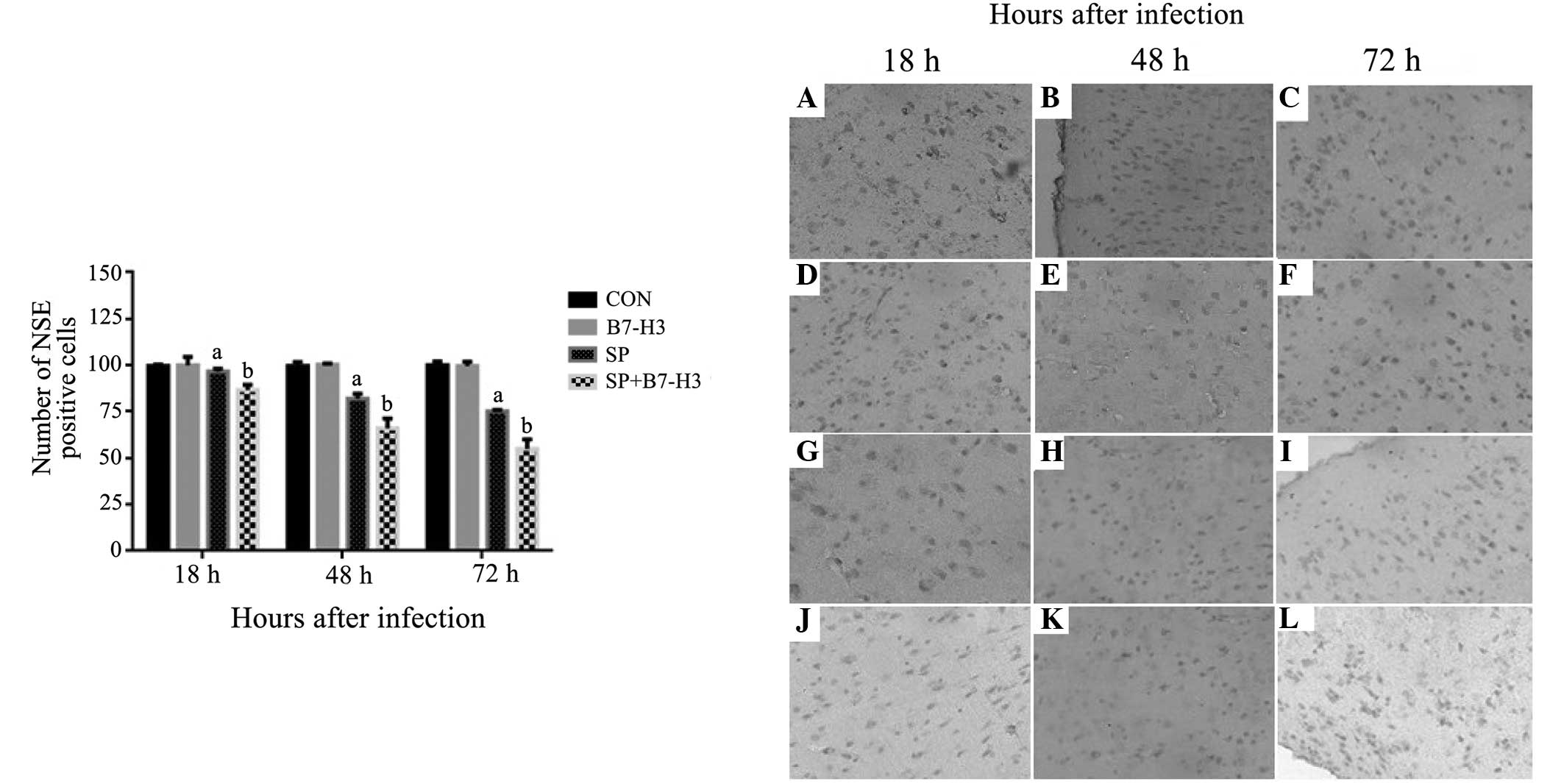
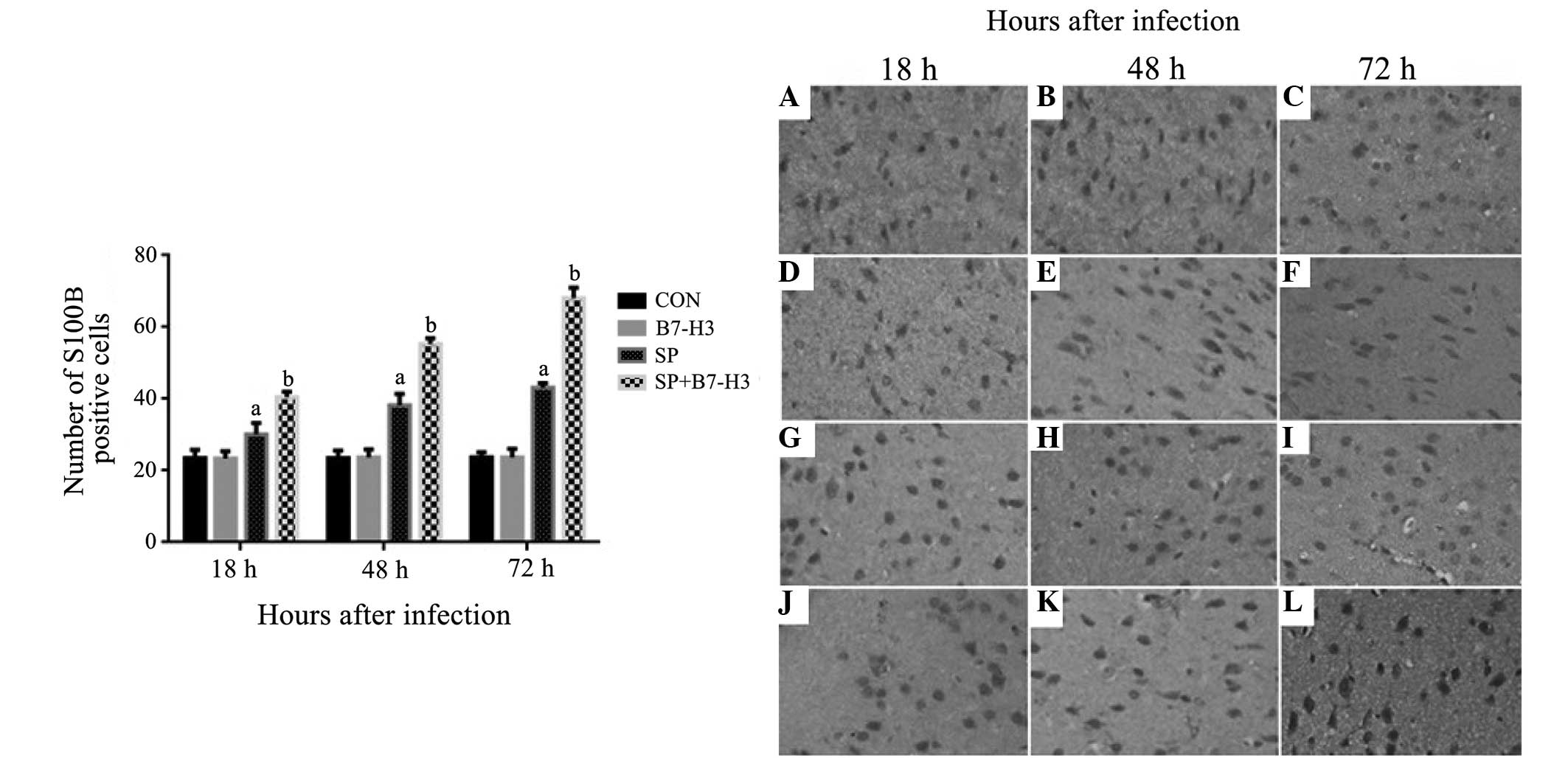
|
1
|
Barichello T, Generoso JS, Collodel A,
Moreira AP and Almeida SM: Pathophysiology of acute meningitis
caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and adjunctive therapy
approaches. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 70:366–372. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shapiro MA, Donovan KD and Gage JW:
Comparative therapeutic efficacy of clinafloxacin in a pneumococcal
meningitis mouse model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 45:489–492. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Streitbürger DP, Arelin K, Kratzsch J,
Thiery J, Steiner J, Villringer A, Mueller K and Schroeter ML:
Validating serum S100B and neuron-specific enolase as biomarkers
for the human brain - A combined serum, gene expression and MRI
study. PLoS One. 7:e432842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao X, Li DC, Zhu XG, et al: B7-H3
overexpression in pancreatic cancer promotes tumor progression. Int
J Mol Med. 31:283–91. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen X, Zhang G, Li Y, Feng X, Wan F,
Zhang L, Wang J and Zhang X: Circulating B7-H3(CD276) elevations in
cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of children with bacterial
meningitis. J Mol Neurosci. 37:86–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen X, Quinn EM, Ni H, Wang J, Blankson
S, Redmond HP, Wang JH and Feng X: B7-H3 participates in the
development of experimental pneumococcal meningitis by augmentation
of the inflammatory response via a TLR2-dependent mechanism. J
Immunol. 189:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leib SL, Clements JM, Lindberg RL, et al:
Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases and tumour necrosis factor
alpha converting enzyme as adjuvant therapy in pneumococcal
meningitis. Brain. 124:1734–1742. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Q, Wang C, Shu Z, et al: Valeriana
amurensis improves Amyloid-beta 1–42 induced cognitive deficit by
enhancing cerebral holinergic function and protecting the brain
neurons from apoptosis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 153:318–325.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rohlwink UK and Figaji AA: Biomarkers of
brain injury in cerebral infections. Clin Chem. 60:823–834. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marangos PJ and Schmechel DE: Neuron
specific enolase, a clinically useful marker for neurons and
neuroendocrine cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 10:269–295. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Naga RN, Ahmed HI2 and Abd Al Haleem
EN: Effects of indole-3-carbinol on clonidine-induced neurotoxicity
in rats: Impact on oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and
monoamine levels. Neurotoxicology. 44:48–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Adami C, Sorci G, Blasi E, Agneletti AL,
Bistoni F and Donato R: S100B expression in and effects on
microglia. Glia. 33:131–142. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hamed SA, Hamed EA and Zakary MM:
Oxidative stress and S-100B protein in children with bacterial
meningitis. BMC Neurol. 9:512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park JW, Suh GI and Shin HE: Association
between cerebrospinal fluid S100B protein and neuronal damage in
patients with central nervous system infections. Yonsei Med J.
54:567–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang XY, Lin J, Lu XY and Zhao XY:
Expression of S100B protein levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid
with different forms of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus
erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 27:353–357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lins H, Wallesch CW and Wunderlich MT:
Sequential analyses of neurobiochemical markers of cerebral damage
in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in CNS infections. Acta Neurol
Scand. 112:303–308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raabe A and Seifert V: Protein S-100B as a
serum marker of brain damage in severe head injury: Preliminary
results. Neurosurg Rev. 23:136–138. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Raabe A and Seifert V: Fatal secondary
increase in serum S-100B protein after severe head injury. Report
of three cases. J Neurosurg. 91:875–877. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Steiner J, Bernstein HG, Bielau H, Berndt
A, Brisch R, Mawrin C, et al: Evidence for a wide extraastrocytic
distribution of S100B in human brain. BMC Neurosci. 8:22007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leib SL, Kim YS, Chow LL, Sheldon RA and
Tӓuber MG: Reactive oxygen intermediates contribute to necrotic and
apoptotic neuronal injury in an infant rat model of bacterial
meningitis due to group B streptococci. J Clin Invest.
98:2632–2639. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tauber SC, Harms K, Falkenburger B, Weis
J, Sellhaus B, Nau R, Schulz JB and Reich A: Modulation of
hippocampal neuroplasticity by Fas/CD95 regulatory protein 2
(Faim2) in the course of bacterial meningitis. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 73:2–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zysset-Burri DC, Bellac CL, Leib SL and
Wittwer M: Vitamin B6 reduces hippocampal apoptosis in experimental
pneumococcal meningitis. BMC Infect Dis. 13:3932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Braun JS, Sublett JE, Freyer D, Mitchell
TJ, Cleveland JL, Tuomanen EI and Weber JR: Pneumococcal
pneumolysin and H2O2 mediate brain cell apoptosis during
meningitis. J Clin Invest. 109:19–27. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Opitz B, Eitel J, Meixenberger K and
Suttorp N: Role of Toll-like receptors, NOD-like receptors and
RIG-I-like receptors in endothelial cells and systemic infections.
Thromb Haemost. 102:1103–1109. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koedel U, Bayerlei I, Paul R, Sporer B and
Pfister HW: Pharmacologic interference with NF-kappaB activation
attenuates central nervous system complications in experimental
pneumococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 182:1437–1445. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kastenbauer S, Koedel U, Weih F,
Ziegler-Heitbrock L and Pfister HW: Protective role of NF-kappaB1
(p50) in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. Eur J Pharmacol.
498:315–318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|