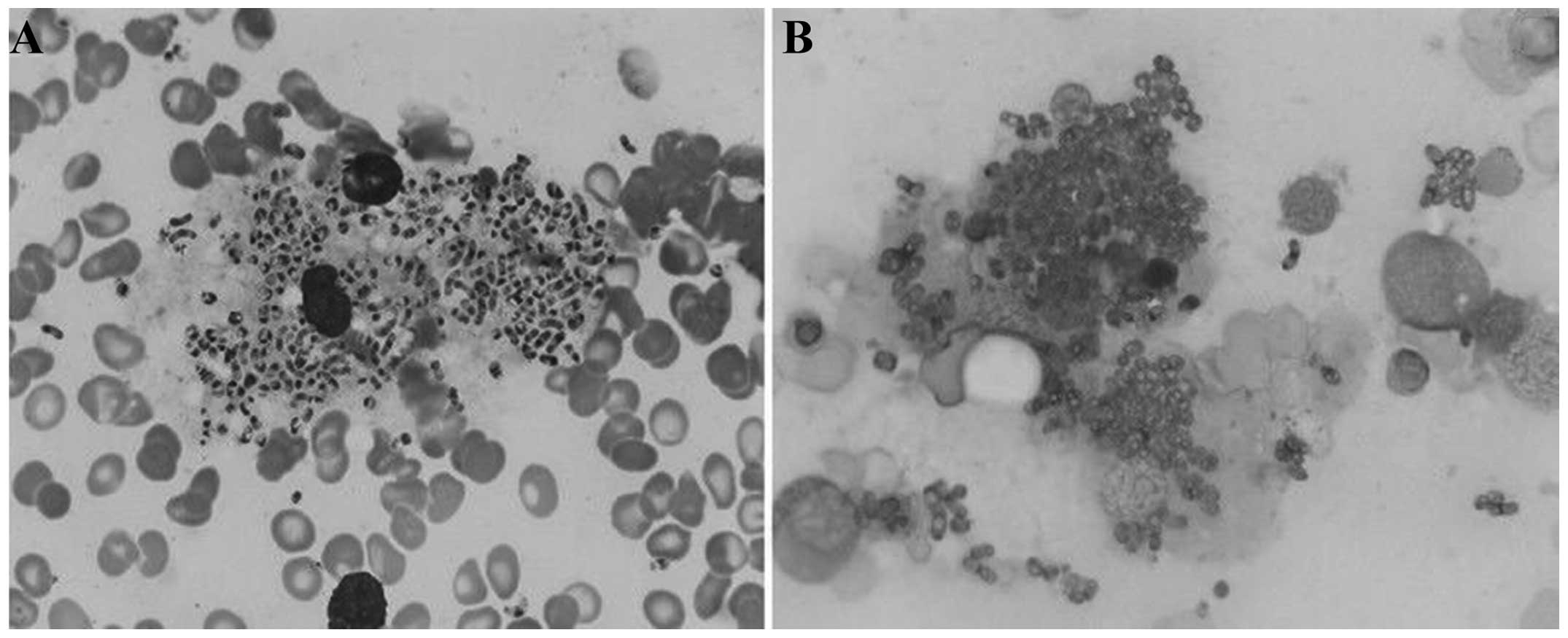
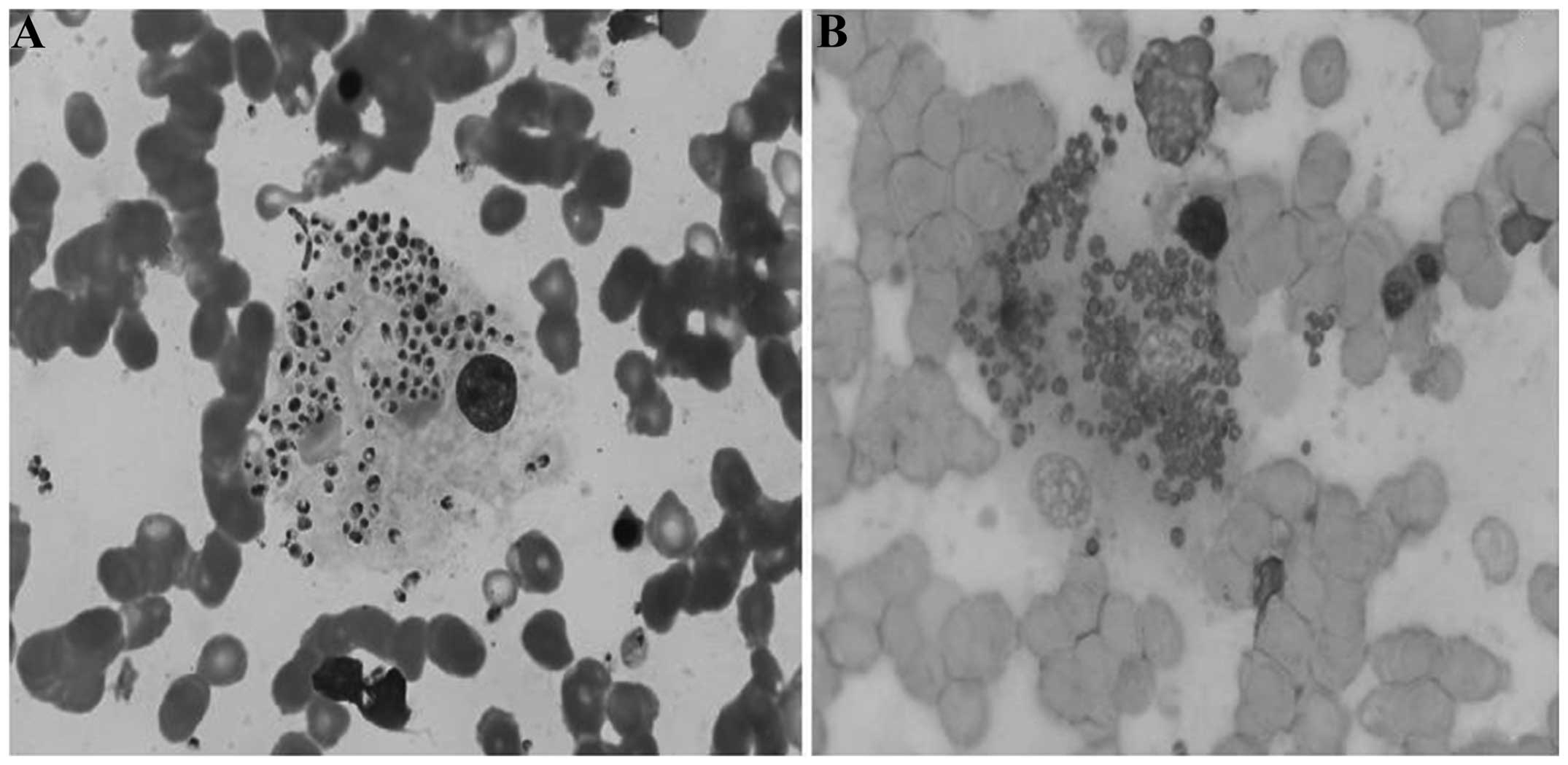
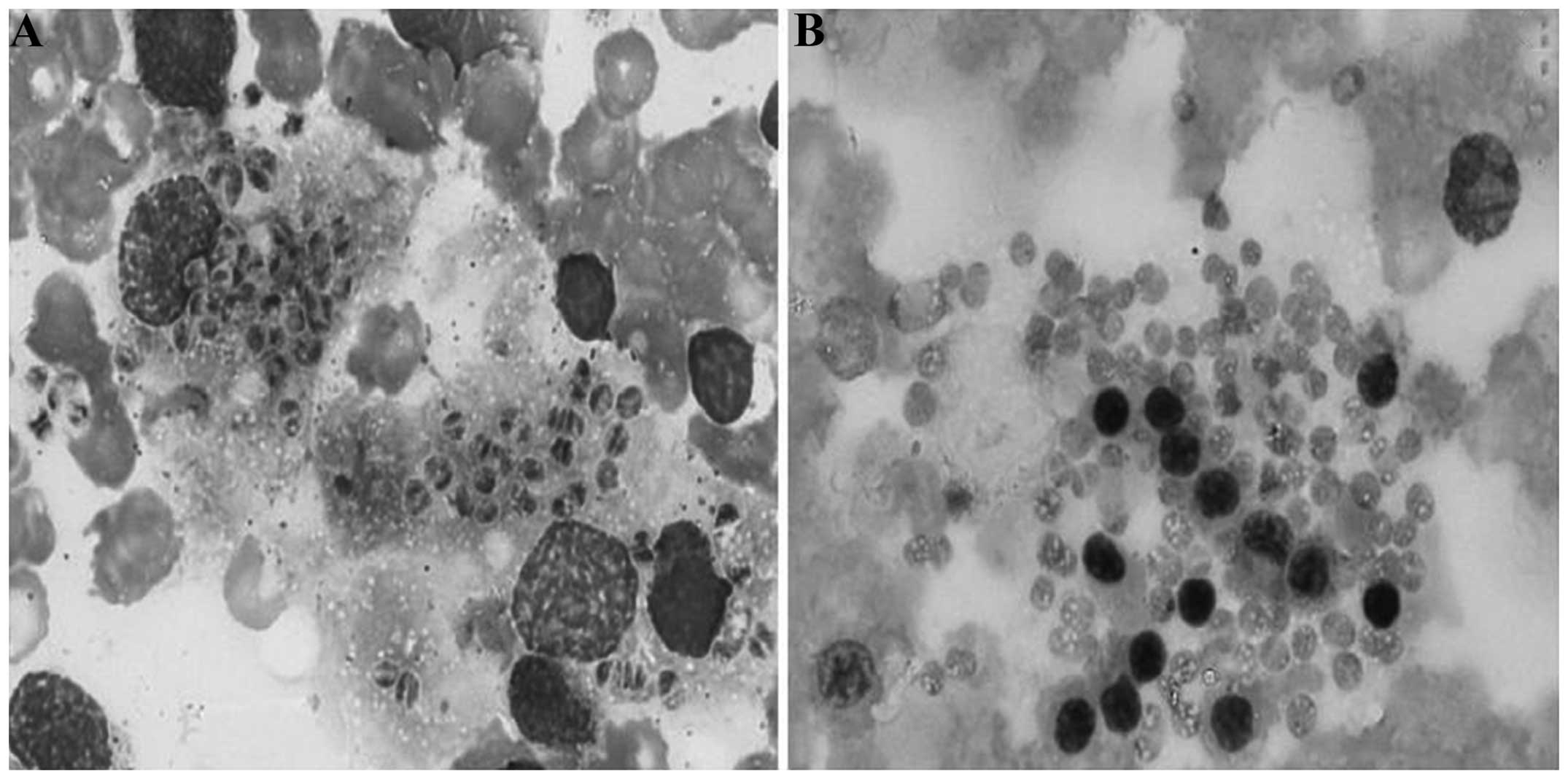
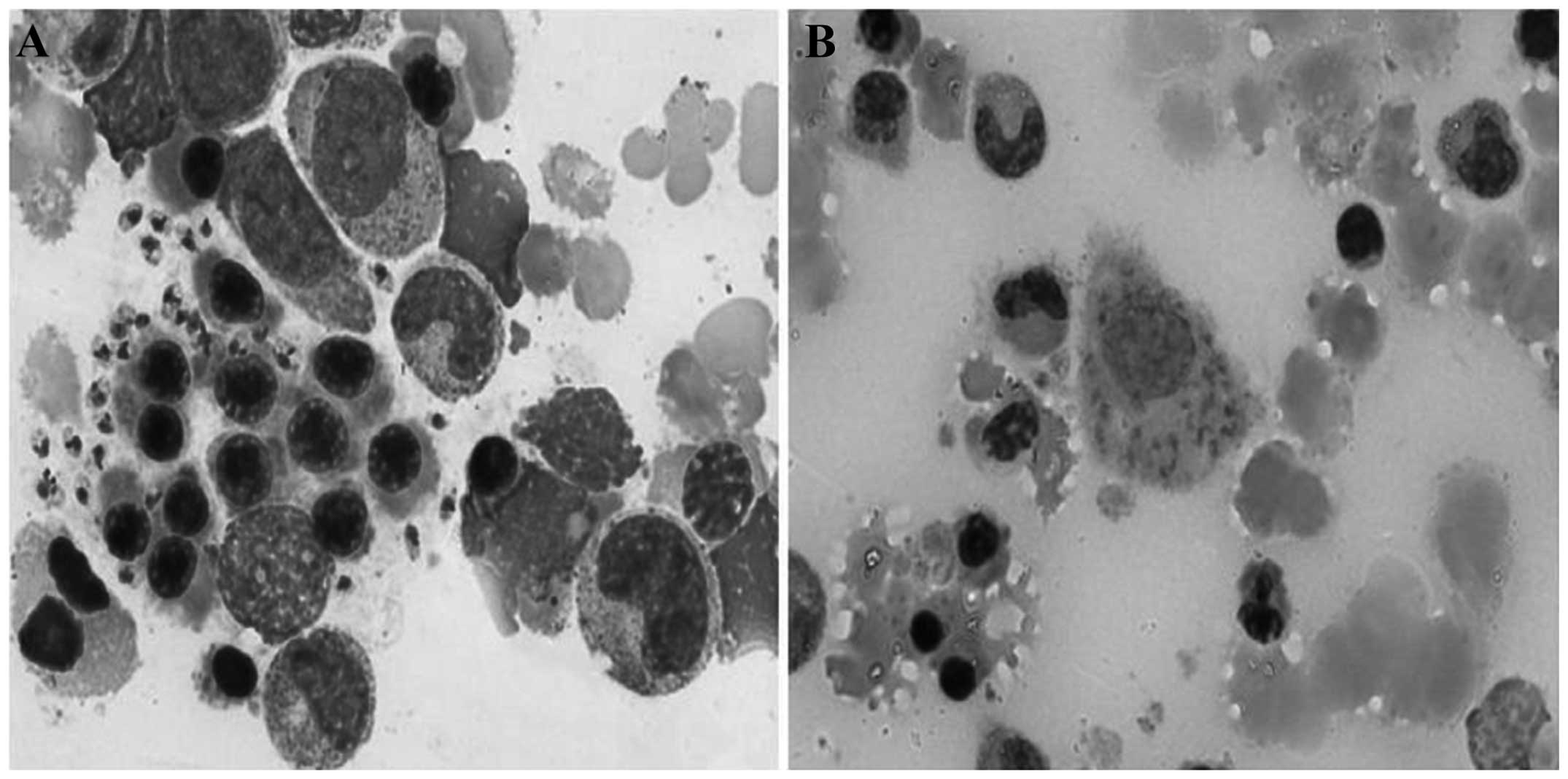
Spandidos Publications style
Qin L, Zhao L, Tan C, Chen X, Yang Z and Mo W: A novel method of combining Periodic Acid Schiff staining with Wright-Giemsa staining to identify the pathogens Penicillium marneffei, Histoplasma capsulatum, Mucor and Leishmania donovani in bone marrow smears. Exp Ther Med 9: 1950-1954, 2015.
APA
Qin, L., Zhao, L., Tan, C., Chen, X., Yang, Z., & Mo, W. (2015). A novel method of combining Periodic Acid Schiff staining with Wright-Giemsa staining to identify the pathogens Penicillium marneffei, Histoplasma capsulatum, Mucor and Leishmania donovani in bone marrow smears. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 9, 1950-1954. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2357
MLA
Qin, L., Zhao, L., Tan, C., Chen, X., Yang, Z., Mo, W."A novel method of combining Periodic Acid Schiff staining with Wright-Giemsa staining to identify the pathogens Penicillium marneffei, Histoplasma capsulatum, Mucor and Leishmania donovani in bone marrow smears". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 9.5 (2015): 1950-1954.
Chicago
Qin, L., Zhao, L., Tan, C., Chen, X., Yang, Z., Mo, W."A novel method of combining Periodic Acid Schiff staining with Wright-Giemsa staining to identify the pathogens Penicillium marneffei, Histoplasma capsulatum, Mucor and Leishmania donovani in bone marrow smears". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 9, no. 5 (2015): 1950-1954. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2357