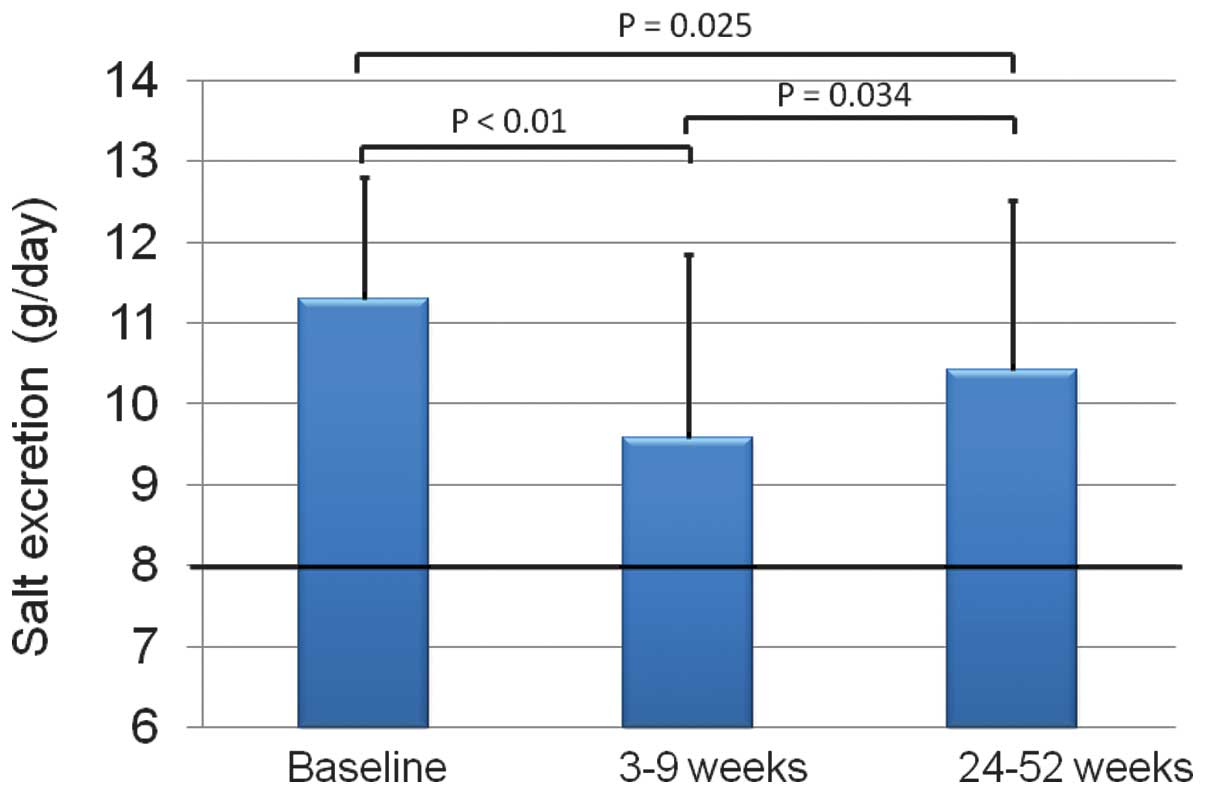
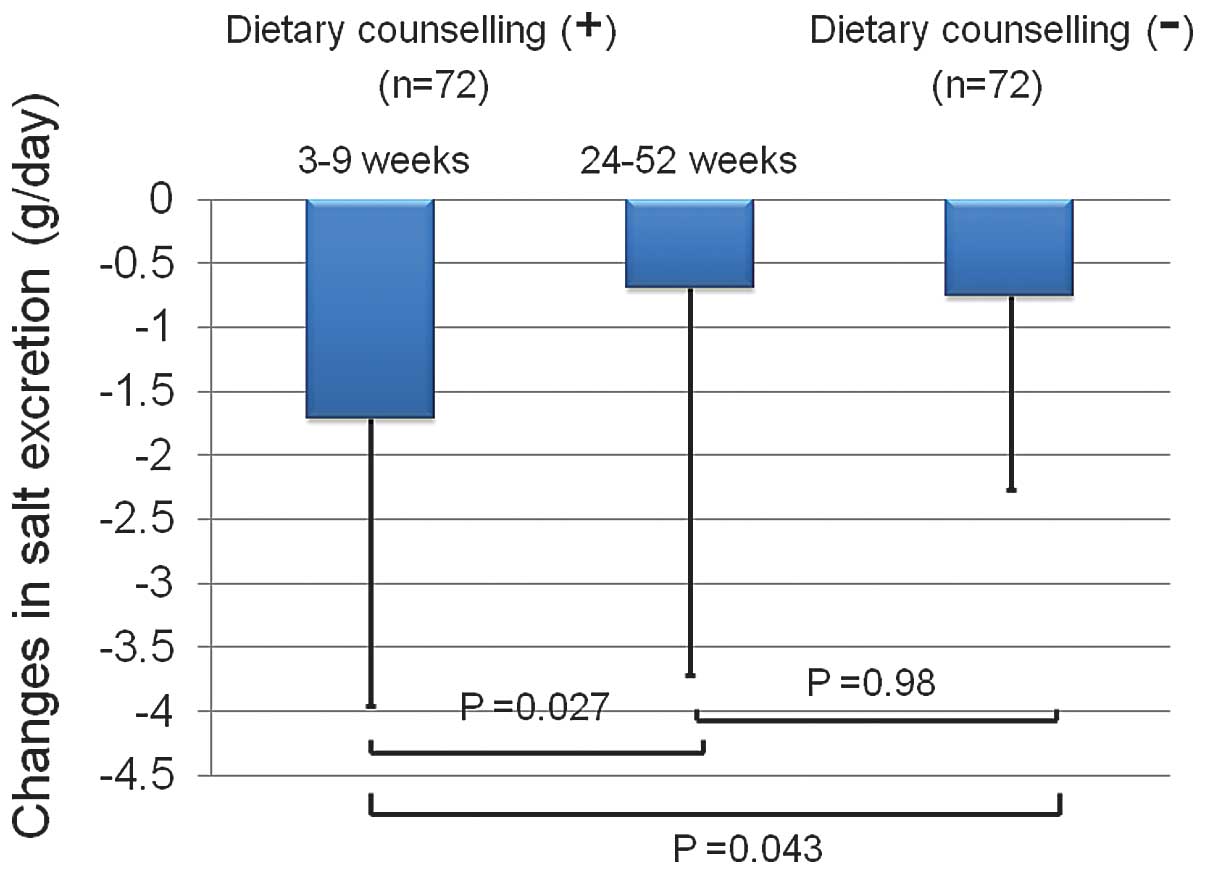
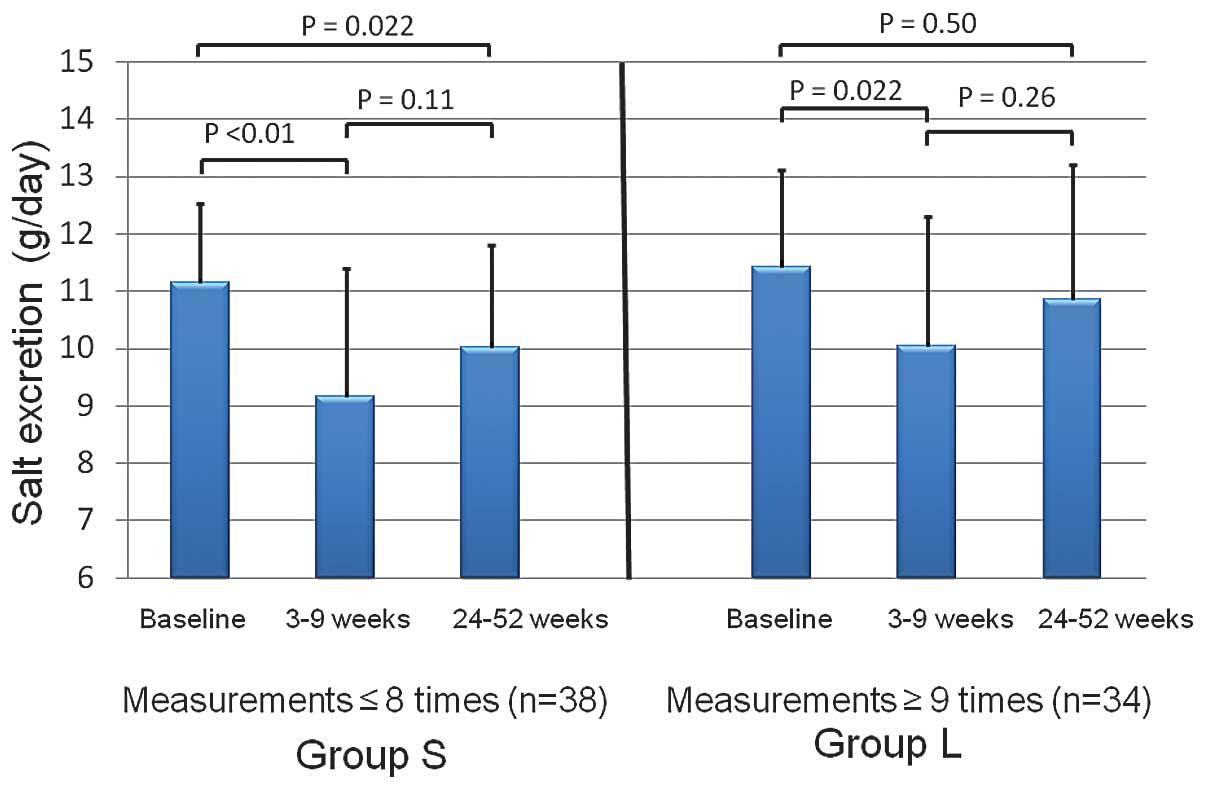
|
1
|
Appel LJ, Frohlich ED, Hall JE, Pearson
TA, Sacco RL, Seals DR, Sacks FM, Smith SC Jr, Vafiadis DK and Van
Horn LV: The importance of population-wide sodium reduction as a
means to prevent cardiovascular disease and stroke. A call to
action from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
123:1138–1143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He FJ and MacGregor GA: A comprehensive
review on salt and health and current experience of worldwide salt
reduction programmes. J Hum Hypertens. 23:363–384. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hirota S, Sadanaga T, Mitamura H and
Fukuda K: Spot urine-guided salt reduction is effective in Japanese
cardiology outpatients. Hypertens Res. 35:1069–1071. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirota S, Sadanaga T, Mitamura H and
Fukuda K: Long-term compliance with salt restriction assessed using
the spot urine method in Japanese cardiology outpatients. Hypertens
Res. 36:1096–1099. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y,
Tomita K, Nitta K, Yamagata K, Tomino Y, Yokoyama H and Hishida A:
Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR:
Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan.
Am J Kidney Dis. 53:982–992. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka T, Okamura T, Miura K, Kadowaki T,
Ueshima H, Nakagawa H and Hashimoto T: A simple method to estimate
populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion using a
casual urine specimen. J Hum Hypertens. 16:97–103. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kawano Y, Tsuchihashi T, Matsuura H, Ando
K, Fujita T and Ueshima H: Working Group for Dietary Salt Reduction
of the Japanese Society of Hypertension: Report of the Working
Group for Dietary Salt Reduction of the Japanese Society of
Hypertension: (2) Assessment of salt intake in the management of
hypertension. Hypertens Res. 30:887–893. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ogihara T, Kikuchi K, Matsuoka H, Fujita
T, Higaki J, Horiuchi M, Imai Y, Imaizumi T, Ito S, Iwao H, Kario
K, Kawano Y, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Kimura G, Matsubara H, Matsuura H,
Naruse M, Saito I, Shimada K, Shimamoto K, Suzuki H, Takishita S,
Tanahashi N, Tsuchihashi T, Uchiyama M, Ueda S, Ueshima H, Umemura
S, Ishimitsu T and Rakugi H: Japanese Society of Hypertension
Committee: The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the
Management of Hypertension (JSH 2009). Hypertens Res. 32:3–107.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buccicone J and McAllister RG Jr: Failure
of single-session dietary counseling to reduce salt intake in
hypertensive patients. South Med J. 70:1436–1438. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Korhonen M, Kastarinen M, Uusitupa M,
Puska P and Nissinen A: The effect of intensified diet counseling
on the diet of hypertensive subjects in primary health care: A
2-year open randomized controlled trial of lifestyle intervention
against hypertension in eastern Finland. Prev Med. 36:8–16. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Korhonen MH, Litmanen H, Rauramaa R,
Väisänen SB, Niskanen L and Uusitupa M: Adherence to the salt
restriction diet among people with mildly elevated blood pressure.
Eur J Clin Nutr. 53:880–885. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elmer PJ, Grimm RH Jr, Flack J and Laing
B: Dietary sodium reduction for hypertension prevention and
treatment. Hypertension. 17:(Suppl 1). I182–I189. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruzicka M, Hiremath S, Steiner S, Helis E,
Szczotka A, Baker P and Fodor G: What is the feasibility of
implementing effective sodium reduction strategies to treat
hypertension in primary care settings? A systematic review. J
Hypertens. 32:1388–1394. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|