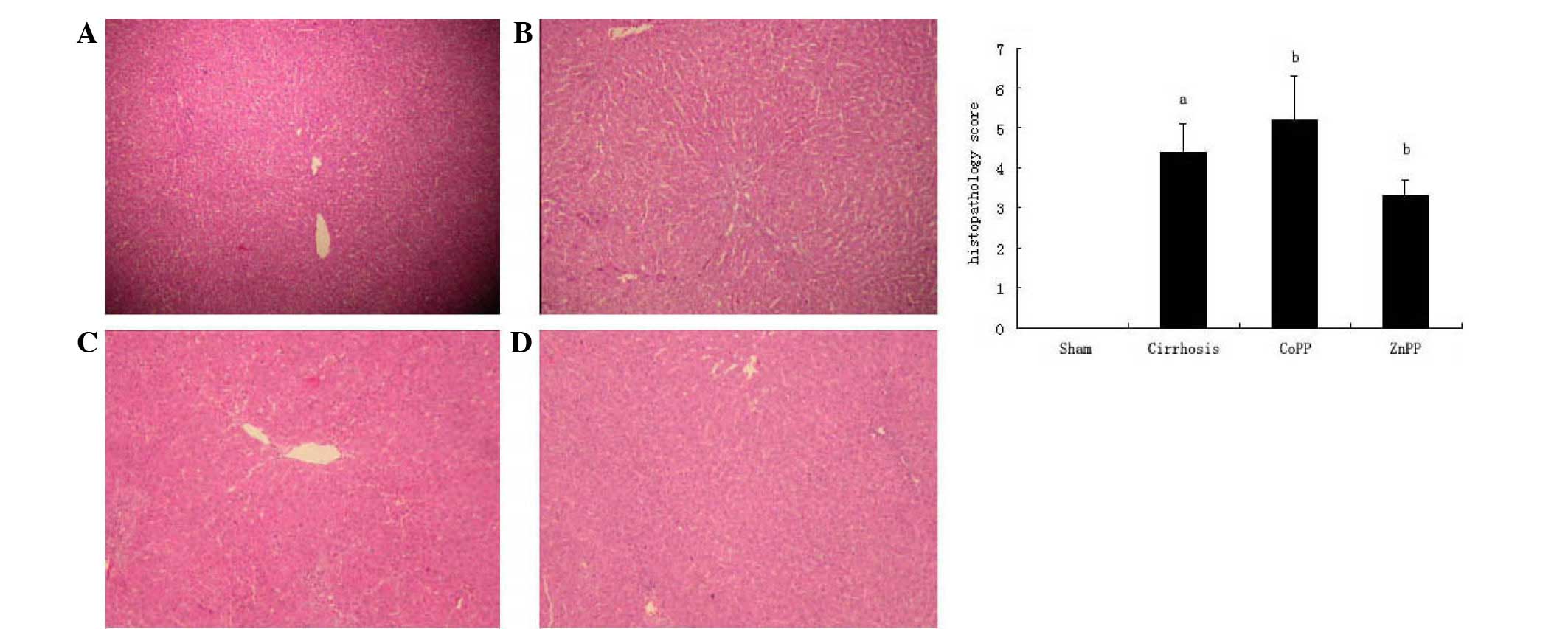
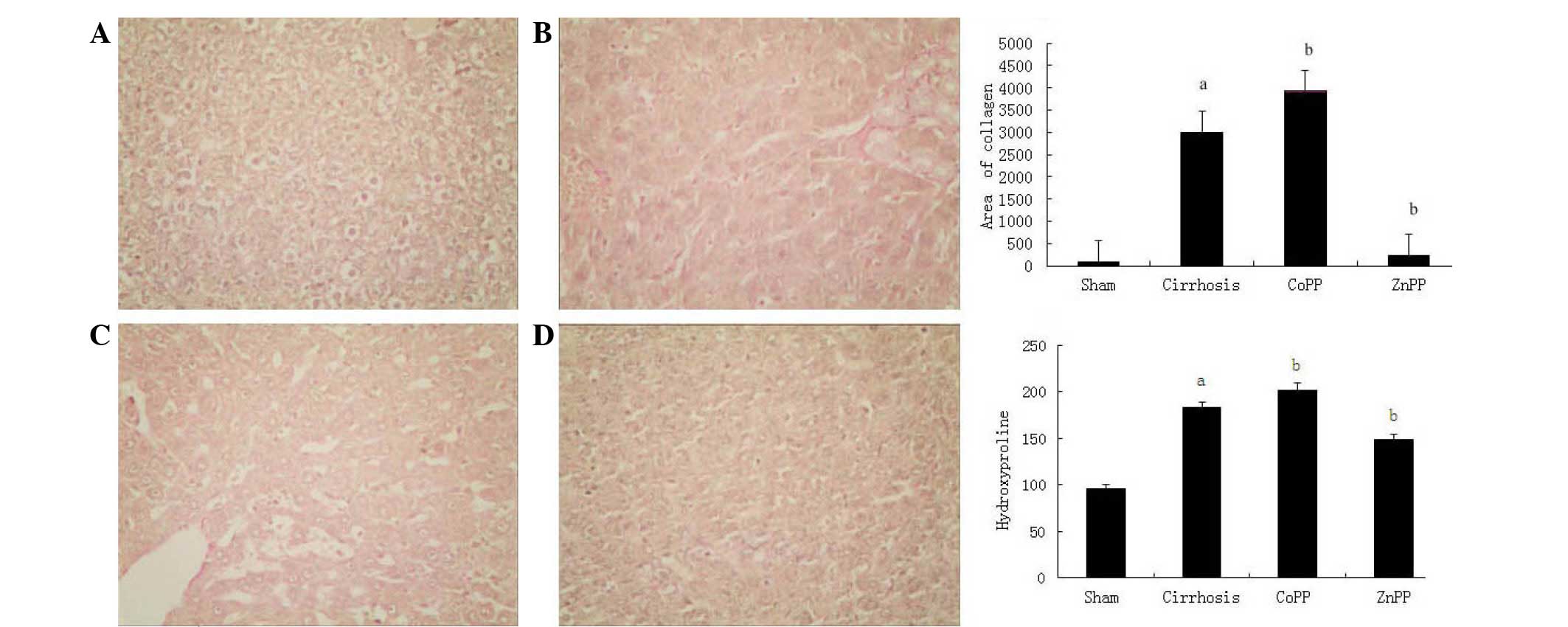
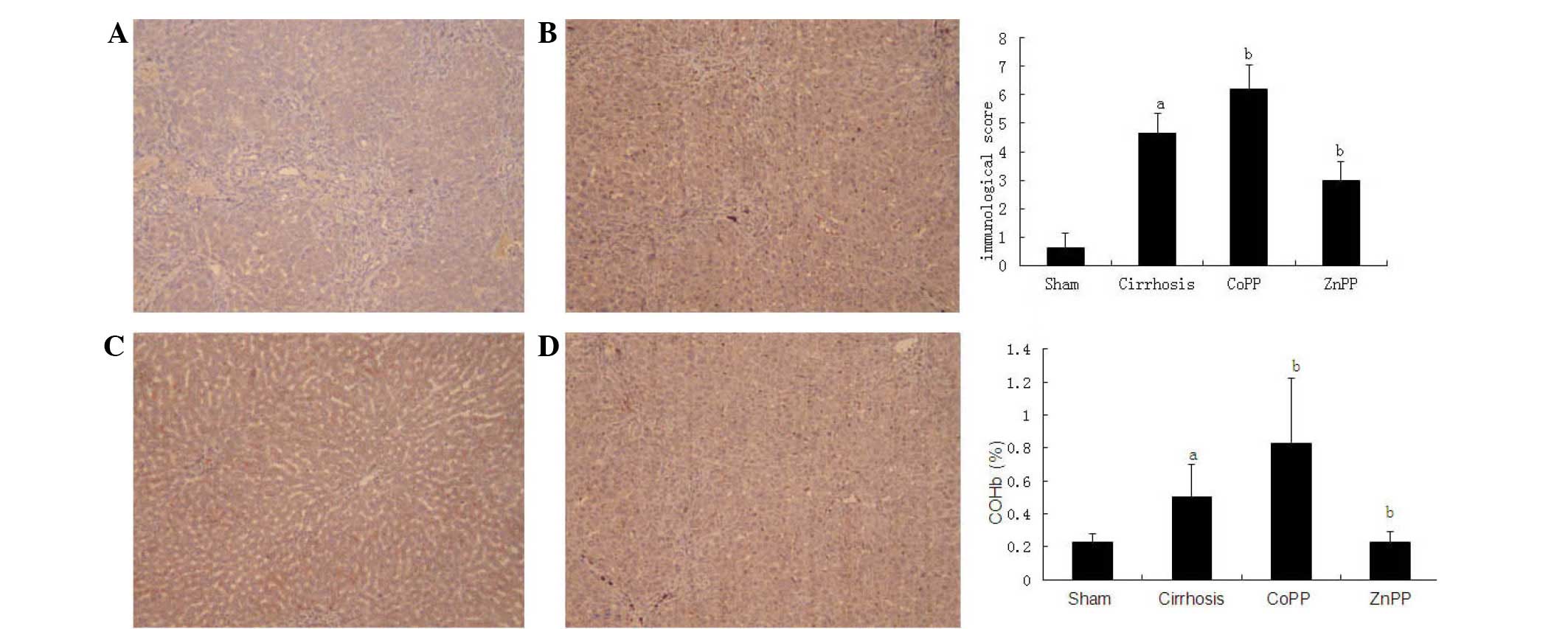
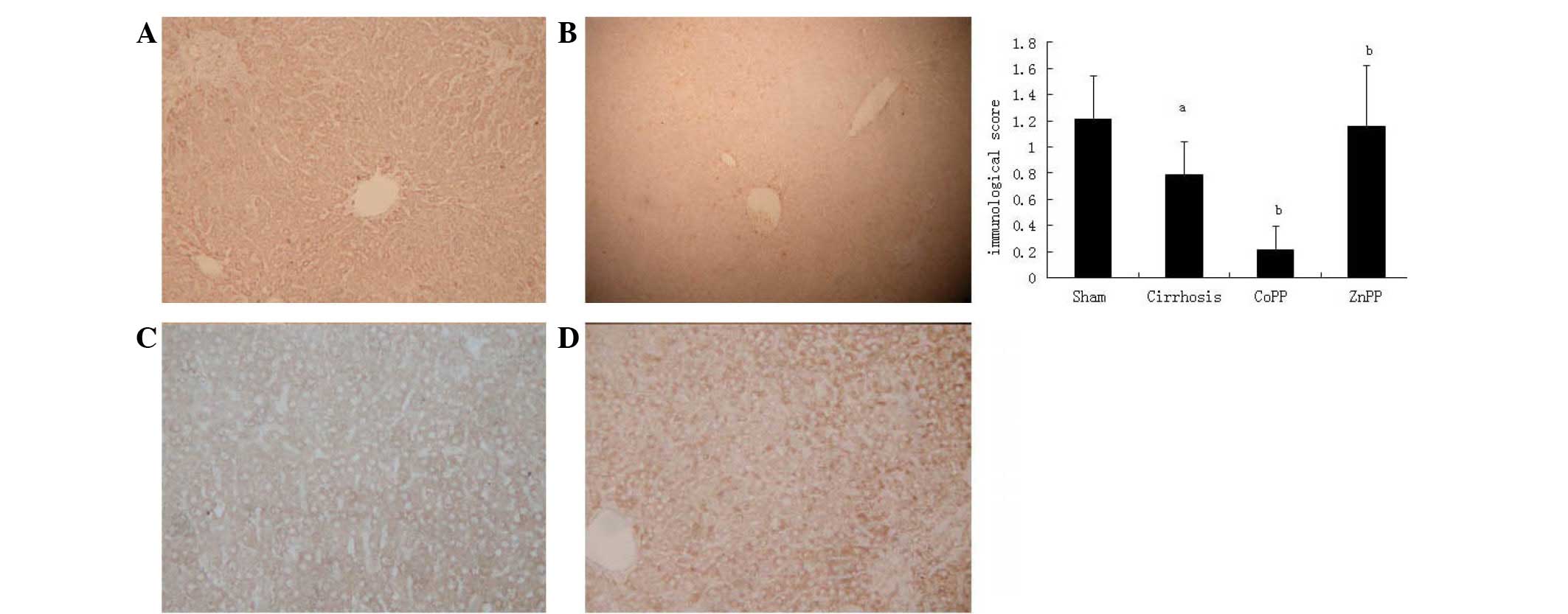
|
1
|
Montaño-Loza A and Meza-Junco J:
Pathogenesis of portal hypertension. Rev Invest Clin. 57:596–607.
2005.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo SB, Li Q, Duan ZJ, Wang QM, Zhou Q and
Sun XY: Octreotide attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic
heme oxygenase-1 expression. Mol Med Rep. 11:83–90. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Volti G, Sacerdoti D, Di Giacomo C,
Barcellona ML, Scacco A, Murabito P, Biondi A, Basile F, Gazzolo D,
Abella R, et al: Natural heme oxygenase-1 inducers in hepatobiliary
function. World J Gastroenterol. 14:6122–6132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tarquini R, Masini E, La Villa G, Barletta
G, Novelli M, Mastroianni R, Romanelli RG, Vizzutti F, Santosuosso
U and Laffi G: Increased plasma carbon monoxide in patients with
viral cirrhosis and hyperdynamic circulation. Am J Gastroenterol.
104:891–897. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Mencarelli A,
Orlandi S, Renga B, Rizzo G, Distrutti E, Shah V and Morelli A: The
third gas: H2S regulates perfusion pressure in both the
isolated and perfused normal rat liver and in cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 42:539–548. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stipanuk MH and Beck PW: Characterization
of the enzymic capacity for cysteine desulphhydration in liver and
kidney of the rat. Biochem J. 206:267–277. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Geng B, Yang J, Qi Y, Zhao J, Pang Y, Du J
and Tang C: H2S generated by heart in rat and its
effects on cardiac function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:362–368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP)
channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hartsfield CL: Cross talk between carbon
monoxide and nitric oxide. Antioxid Redox Signal. 4:301–307. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Altaany Z, Yang G and Wang R: Crosstalk
between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in endothelial cells. J
Cell Mol Med. 17:879–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li RN, Zeng XJ, Chen YH, Lu LQ and Hao G:
Interaction between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide on cardiac
protection in rats with metabolic syndrome. Zhong Guo Yi Xue Ke Xue
Yuan Xue Bao. 33:25–32. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Jin HF, Du JB, Li XH, Wang YF, Liang YF
and Tang CS: Interaction between hydrogen sulfide/cystathionine
gamma-lyase and carbon monoxide/heme oxygenase pathways in aortic
smooth muscle cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:1561–1566. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kabil O, Vitvitsky V, Xie P and Banerjee
R: The quantitative significance of the transsulfuration enzymes
for H2S production in murine tissues. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 15:363–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pereira RM, dos Santos RA, Oliveira EA,
Leite VH, Dias FL, Rezende AS, Costa LP, Barcelos LS, Teixeira MM
and Simoese Silva AC: Development of hepatorenal syndrome in bile
duct ligated rats. World J Gastroenterol. 14:4505–4511. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amersi F, Buelow R, Kato H, Ke B, Coito
AJ, Shen XD, Zhao D, Zaky J, Melinek J, Lassman CR, et al:
Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 protects genetically fat Zucker
rat livers from ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest.
104:1631–1639. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown KE, Poulos JE, Li L, Soweid AM, Ramm
GA, O'Neill R, Britton RS and Bacon BR: Effect of vitamin E
supplementation on hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic dietary iron
overload. Am J Physiol. 272:G116–G123. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Makino N, Suematsu M, Sugiura Y, Morikawa
H, Shiomi S, Goda N, Sano T, Nimura Y, Sugimachi K and Ishimura Y:
Altered expression of heme oxygenase-1 in the livers of patients
with portal hypertensive diseases. Hepatology. 33:32–42. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei CL, Lee KH, Khoo HE and Hon WM:
Expression of haem oxygenase in cirrhotic rat liver. J Pathol.
199:324–334. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fujii K, Sakuragawa T, Kashiba M, Sugiura
Y, Kondo M, Maruyama K, Goda N, Nimura Y and Suematsu M: Hydrogen
sulfide as an endogenous modulator of biliary bicarbonate excretion
in the rat liver. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:788–794. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leung TM, Fung ML, Liong EC, Lau TY, Nanji
AA and Tipoe GL: Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of
fibrogenic factors in experimental liver fibrosis in mice. Histol
Histopathol. 26:201–211. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matei V, Rodríguez-Vilarrupla A, Deulofeu
R, García-Calderó H, Fernández M, Bosch J and Garcia-Pagán JC:
Three-day tetrahydrobiopterin therapy increases in vivo hepatic NOS
activity and reduces portal pressure in CCl4 cirrhotic rats. J
Hepatol. 49:192–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Yang W and Cao G:
H2S inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells
and downregulates the expression of urotensin II. Hepatol Res.
43:670–678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kamoun P: Endogenous production of
hydrogen sulfide in mammals. Amino Acids. 26:243–254. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng Y, Ndisang JF, Tang G, Cao K and
Wang R: Hydrogen sulfide-induced relaxation of resistance
mesenteric artery beds of rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
287:H2316–H2323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang C, Han J, Xiao L, Jin CE, Li DJ and
Yang Z: Role of hydrogen sulfide in portal hypertension and
esophagogastric junction vascular disease. World J Gastroenterol.
20:1079–1087. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ebrahimkhani MR, Mani AR and Moore K:
Hydrogen sulphide and the hyperdynamic circulation in cirrhosis: A
hypothesis. Gut. 54:1668–1671. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang CY, Li XH, Zhang T, Fu J and Cui XD:
Hydrogen sulfide upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression in rats
with volume overload-induced heart failure. Biomed Rep. 1:454–458.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang QY, Du JB, Zhou WJ, Yan H, Tang CS
and Zhang CY: Impact of hydrogen sulfide on carbon monoxide/heme
oxygenase pathway in the pathogenesis of hypoxic pulmonary
hypertension. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 317:30–37. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo SB, Duan ZJ, Li Q and Sun XY: Effect
of heme oxygenase-1 on renal function in rats with liver cirrhosis.
World J Gastroenterol. 17:322–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Naik JS, O'Donaughy TL and Walker BR:
Endogenous carbon monoxide is an endothelial-derived vasodilator
factor in the mesenteric circulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 284:H838–H845. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Poliakova VS, Shakhlamov VA, Stadnikov AA
and Solnyshkova TG: Structural-biochemical reorganization of rat
liver caused by hydrogen sulfide-containing gas mixture.
Morfologiia. 124:84–87. 2003.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fan HN, Wang HJ, Yang-Dan CR, Wang C, Li
YF and Deng Y: Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide on oxidative
stress and fibrosis in hepatic stellate cells. Mol Med Rep.
7:247–253. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu F, Xing J, Zhang X, Dong S, Zhao Y,
Wang L, Li H, Yang F, Xu C and Zhang W: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis from cardiac hypertrophy induced
by isoproterenol. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:41–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang H, Zhao LF, Zhao ZF, Wang Y, Zhao JJ
and Zhang L: Heme oxygenase-1 prevents liver fibrosis in rats by
regulating the expression of PPARγ and NF-κB. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:1680–1688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Barikbin R, Neureiter D, Wirth J, Erhardt
A, Schwinge D, Kluwe J, Schramm C, Tiegs G and Sass G: Induction of
heme oxygenase 1 prevents progression of liver fibrosis in Mdr2
knockout mice. Hepatology. 55:553–562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang QM, Du JL, Duan ZJ, Guo SB, Sun XY
and Liu Z: Inhibiting heme oxygenase-1 attenuates rat liver
fibrosis by removing iron accumulation. World J Gastroenterol.
19:2921–2934. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang QM, Duan ZJ, Du JL, Guo SB, Sun XY
and Liu Z: Heme oxygenase/carbon monoxide pathway inhibition plays
a role in ameliorating fibrosis following splenectomy. Int J Mol
Med. 31:1186–1194. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Geuken E, Buis CI, Visser DS, Blokzijl H,
Moshage H, Nemes B, Leuvenink HG, de Jong KP, Peeters PM, Slooff MJ
and Porte RJ: Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human livers before
transplantation correlates with graft injury and function after
transplantation. Am J Transplant. 5:1875–1885. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duan ZJ, Yang D, Wang F, Sun YJ, Sun XY
and Zheng ML: Heme oxygenase-1 regulates the major route involved
in formation of immune hepatic fibrosis in rats. Chin Med J (Engl).
123:3304–3308. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weston AD and Hood L: Systems biology,
proteomics and the future of health care: Toward predictive,
preventative, and personalized medicine. J Proteome Res. 3:179–196.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|