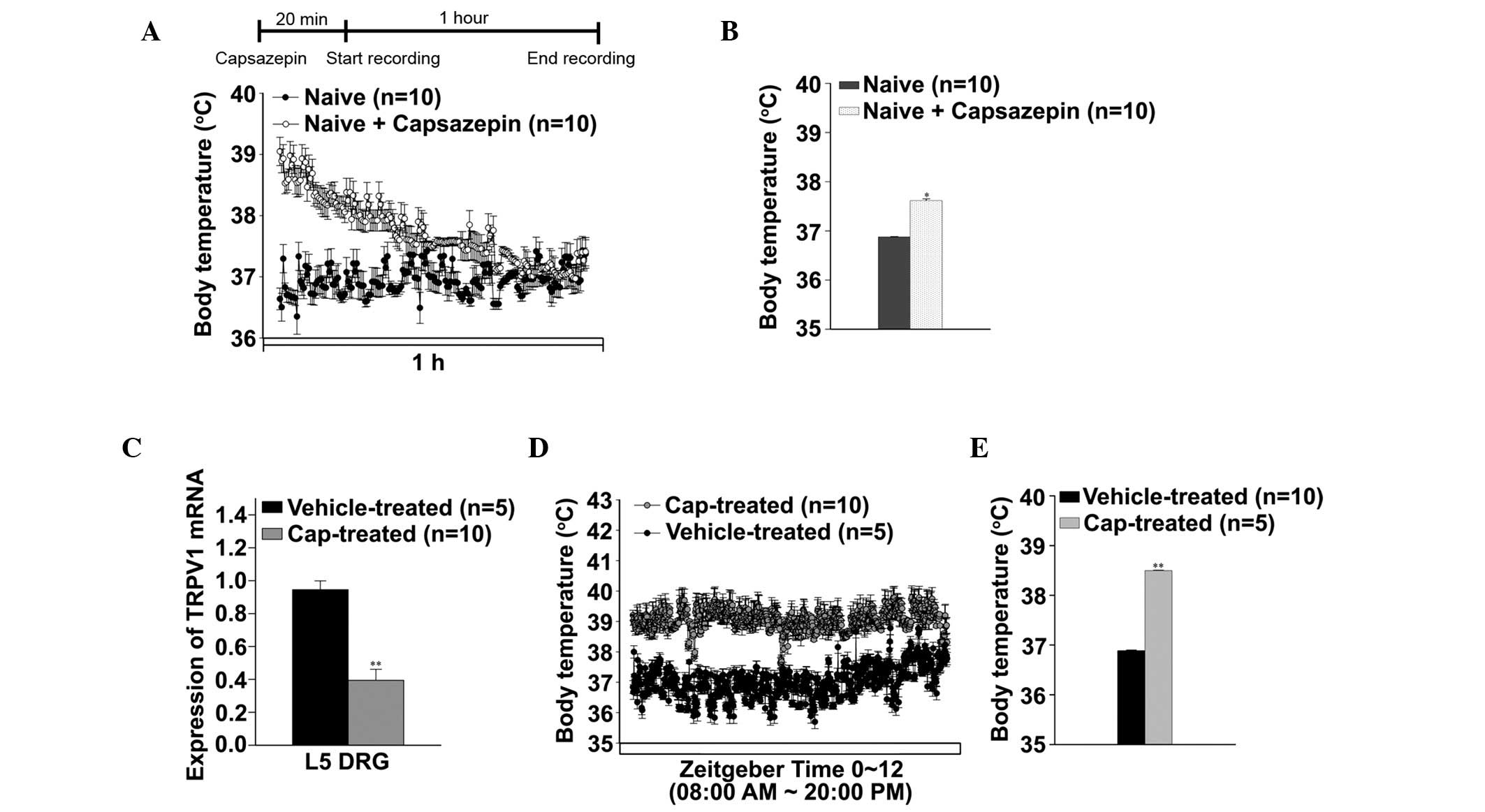
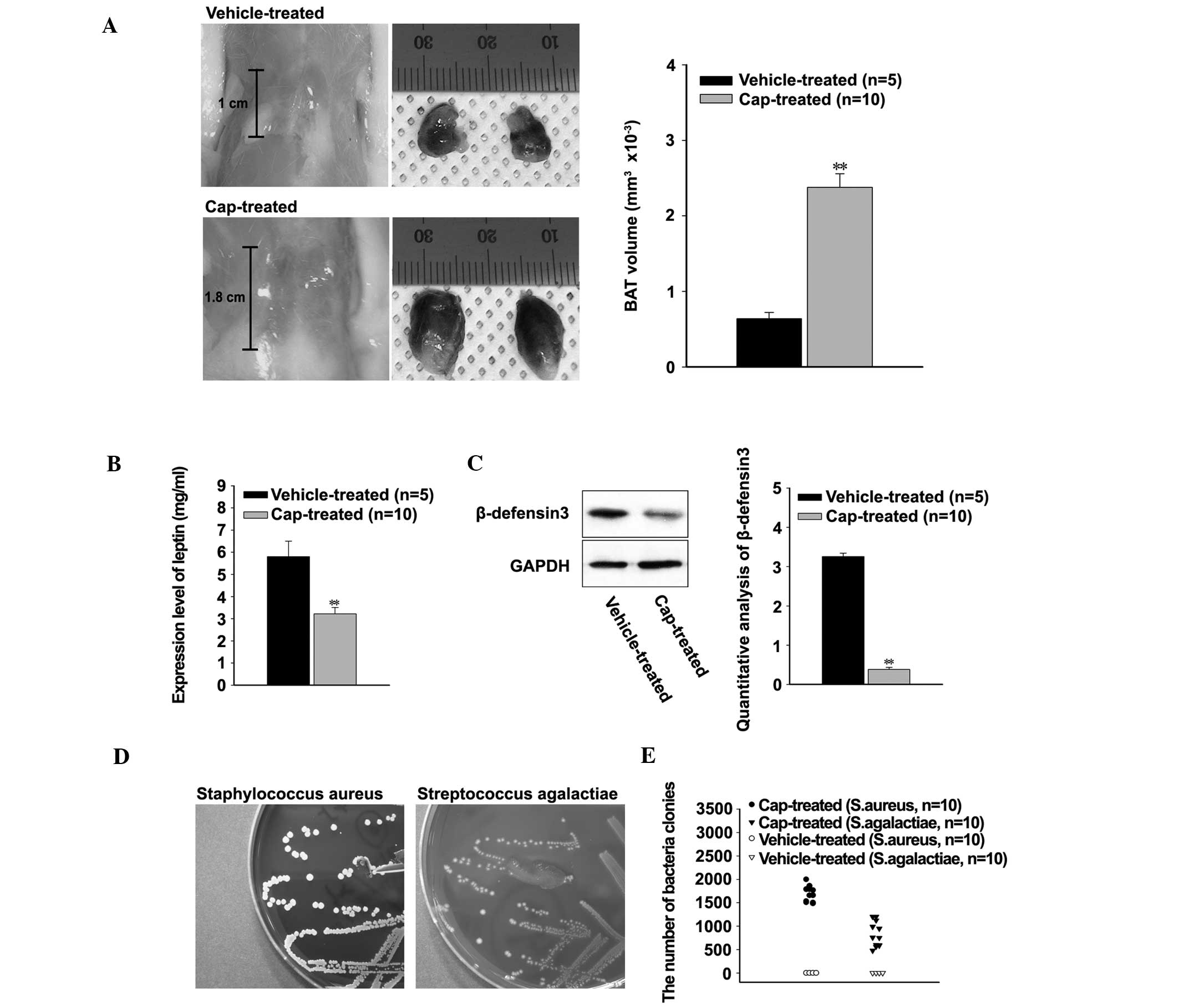
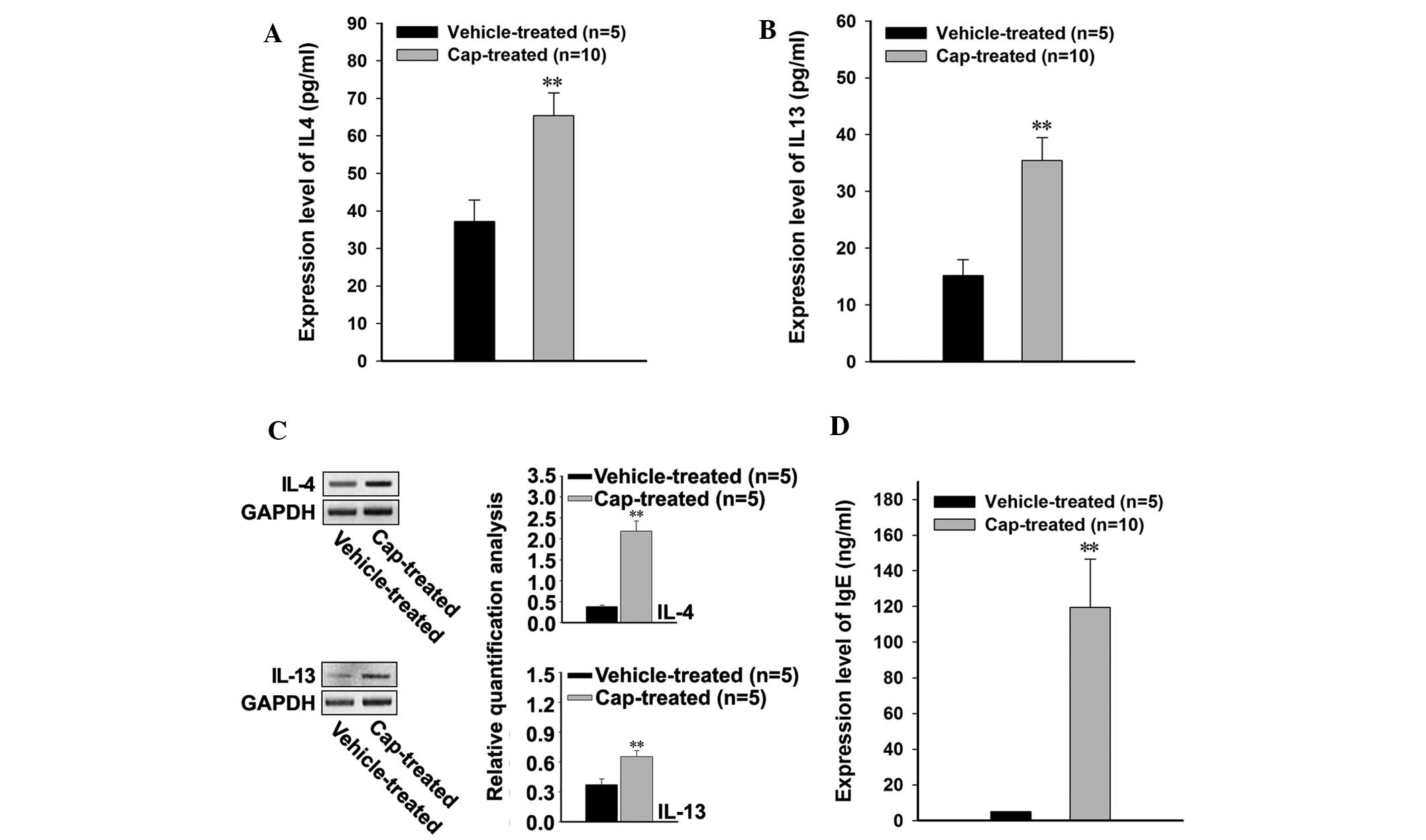
|
1
|
Morrison SF, Madden CJ and Tupone D:
Central neural regulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and
energy expenditure. Cell Metab. 19:741–756. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Desruisseaux MS, Trujillo Nagajyothi ME,
Tanowitz HB and Scherer PE: Adipocyte, adipose tissue, and
infectious disease. Infect Immun. 75:1066–1078. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lateef DM, Abreu-Vieira G, Xiao C and
Reitman ML: Regulation of body temperature and brown adipose tissue
thermogenesis by bombesin receptor subtype-3. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 306:E681–E687. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wen JJ, Nagajyothi F, Machado FS, Weiss
LM, Scherer PE, Tanowitz HB and Garg NJ: Markers of oxidative
stress in adipose tissue during Trypanosoma cruzi infection.
Parasitol Res. 113:3159–3165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szallasi A, Cortright DN, Blum CA and Eid
SR: The vanilloid receptor TRPV1: 10 years from channel cloning to
antagonist proof-of-concept. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:357–372. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tékus V, Bölcskei K, Kis-Varga A, Dézsi L,
Szentirmay E, Visegrády A, Horváth C, Szolcsányi J and Petho G:
Effect of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor
antagonist compounds SB705498, BCTC and AMG9810 in rat models of
thermal hyperalgesia measured with an increasing-temperature water
bath. Eur J Pharmacol. 641:135–141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gavva NR, Bannon AW, Hovland DN Jr, Lehto
SG, Klionsky L, Surapaneni S, Immke DC, Henley C, Arik L, Bak A, et
al: Repeated administration of vanilloid receptor TRPV1 antagonists
attenuates hyperthermia elicited by TRPV1 blockade. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 323:128–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Szelényi Z, Hummel Z, Szolcsányi J and
Davis JB: Daily body temperature rhythm and heat tolerance in TRPV1
knockout and capsaicin pretreated mice. Eur J Neurosci.
19:1421–1424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gavva NR, Bannon AW, Surapaneni S, Hovland
DN Jr, Lehto SG, Gore A, Juan T, Deng H, Han B and Klionsky L: The
vanilloid receptor TRPV1 is tonically activated in vivo and
involved in body temperature regulation. J Neurosci. 27:3366–3374.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M,
Rosen TA, Levine JD and Julius D: The capsaicin receptor: A
heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature.
389:816–824. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lambert DG: Capsaicin receptor
antagonists: A promising new addition to the pain clinic. Br J
Anaesth. 102:153–155. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valenzano KJ and Sun Q: Current
perspectives on the therapeutic utility of VR1 antagonists. Curr
Med Chem. 11:3185–3202. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hiura A: Neuroanatomical effects of
capsaicin on the primary afferent neurons. Arch Histol Cytol.
63:199–215. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Benham CD, Davis JB and Randall AD:
Vanilloid and TRP channels: A family of lipid-gated cation
channels. Neuropharmacology. 42:873–888. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tominaga M: Function of TRP channel as a
thermal receptor. Nihon Seirigaku Zasshi. 65:130–137. 2003.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leung DY and Bieber T: Atopic dermatitis.
Lancet. 361:151–160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mancuso P, Gottschalk A, Phare SM,
Peters-Golden M, Lukacs NW and Huffnagle GB: Leptin-deficient mice
exhibit impaired host defense in Gram-negative pneumonia. J
Immunol. 168:4018–4024. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim YI, Na HS, Han JS and Hong SK:
Critical role of the capsaicin-sensitive nerve fibers in the
development of the causalgic symptoms produced by transecting some
but not all of the nerves innervating the rat tail. J Neurosci.
15:4133–4139. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raymond EA and Traub WH: Identification of
staphylococci isolated from clinical material. Appl Microbiol.
19:919–922. 1970.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cuenca-Estrella M, Gomez-Lopez A,
Alastruey-Izquierdo A, Bernal-Martinez L, Cuseta I and Buitrago MJ:
Comparison of the Vitek 2 antifungal susceptibility system with the
clinical and laboratory standards institute (CLSI) and European
Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) Broth
Microdilution Reference Methods and with the Sensititre YeastOne
and Etest techniques for in vitro detection of antifungal
resistance in yeast isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 48:1782–1786. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brandt MR, Beyer CE and Stahl SM: TRPV1
Antagonists and chronic pain: Beyond thermal perception.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 5:114–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nedergaard J, Bengtsson T and Cannon B:
Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult
humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E444–E452. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
King VL, Dwoskin LP and Cassis LA: Cold
exposure regulates the norepinephrine uptake transporter in rat
brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 276:R143–R151. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Williamson JR, Prusiner S, Olson MS and
Fukami M: Control of metabolism in brown adipose tissue. Lipids.
5:1–14. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dessolin S, Schalling M, Champigny O,
Lönnqvist F, Ailhaud G, Dani C and Ricquier D: Leptin gene is
expressed in rat brown adipose tissue at birth. FASEB J.
11:382–387. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bennett BD, Solar GP, Yuan JQ, Mathias J,
Thomas GR and Matthews W: A role for leptin and its cognate
receptor in hematopoiesis. Curr Biol. 6:1170–1180. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sarraf P, Frederich RC, Turner EM, Ma G,
Jaskowiak NT, Rivet DJ III, Flier JS, Lowell BB, Fraker DL and
Alexander HR: Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse
leptin levels: Potential role in inflammatory anorexia. J Exp Med.
185:171–175. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ,
Bloom SR and Lechler RI: Leptin modulates the T-cell immune
response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature.
394:897–901. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wieland CW, Stegenga ME, Florquin S,
Fantuzzi G and van der Poll T: Leptin and host defense against
Gram-positive and Gram-negative pneumonia in mice. Shock.
25:414–419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanda N and Watanabe S: Leptin enhances
human beta-defensin-2 production in human keratinocytes.
Endocrinology. 149:5189–5198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Jongh GJ, Zeeuwen PL, Kucharekova M,
Pfundt R, van der Valk PG, Blokx W, Dogan A, Hiemstra PS, van de
Kerkhof PC and Schalkwijk J: High expression levels of keratinocyte
antimicrobial proteins in psoriasis compared with atopic
dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 125:1163–1173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dhople V, Krukemeyer A and Ramamoorthy A:
The human beta-defensin-3, an antibacterial peptide with multiple
biological functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1758:1499–1512. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Namkung JH, Lee JE, Kim E, Kim HJ, Seo EY,
Jang HY, Shin ES, Cho EY and Yang JM: Association of polymorphisms
in genes encoding IL-4, IL-13 and their receptors with atopic
dermatitis in a Korean population. Exp Dermatol. 20:915–919. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Varin A, Mukhopadhyay S, Herbein G and
Gordon S: Alternative activation of macrophages by IL-4 impairs
phagocytosis of pathogens but potentiates microbial-induced
signalling and cytokine secretion. Blood. 115:353–362. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Janković BD, Popesković L, Janezić A and
Lukić ML: Brown adipose tissue: Effect on immune reactions in the
rat. Naturwissenschaften. 61:361974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Himms-Hagen J: Brown adipose tissue
thermogenesis: Interdisciplinary studies. FASEB J. 4:2890–2898.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|