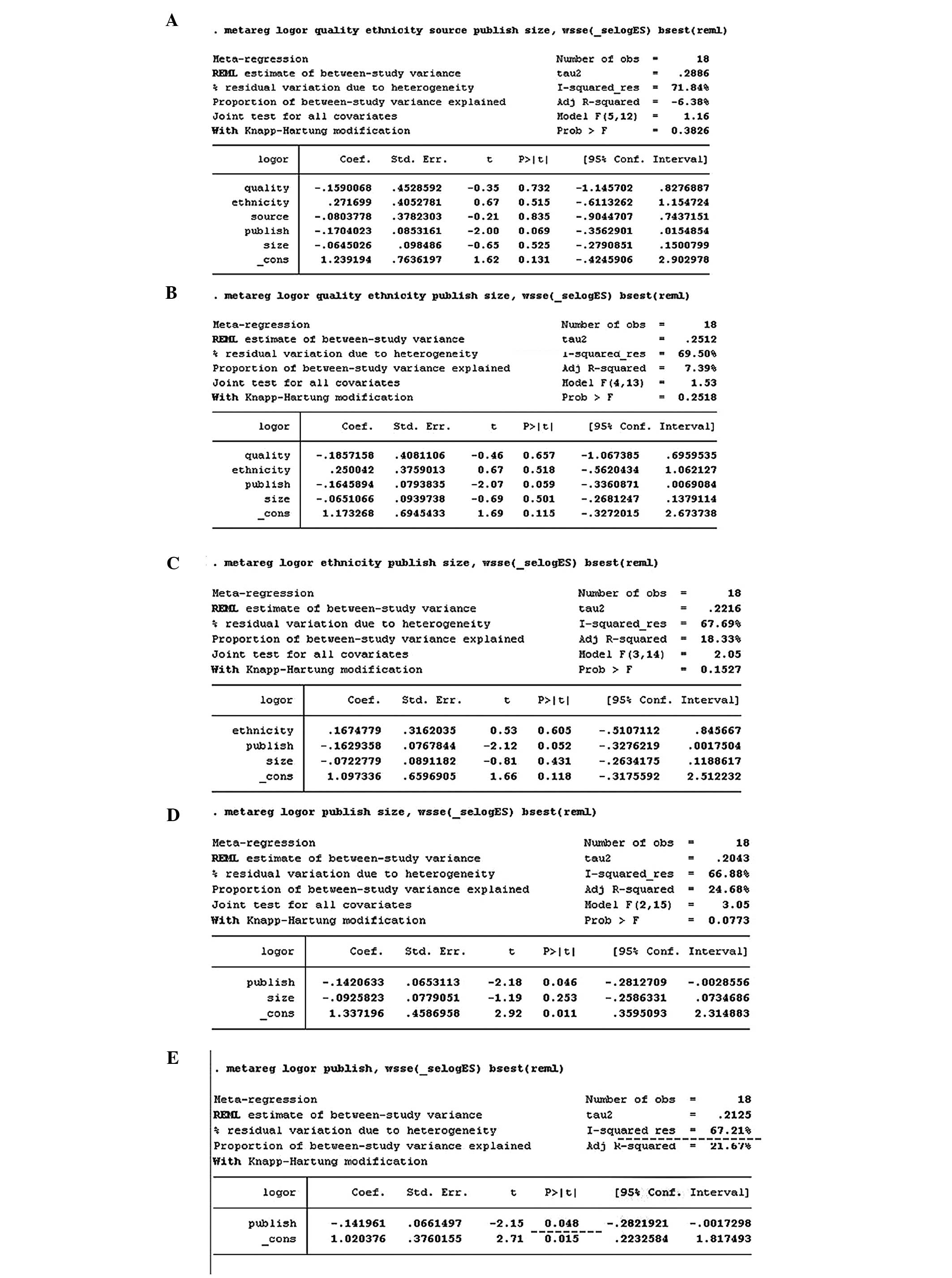
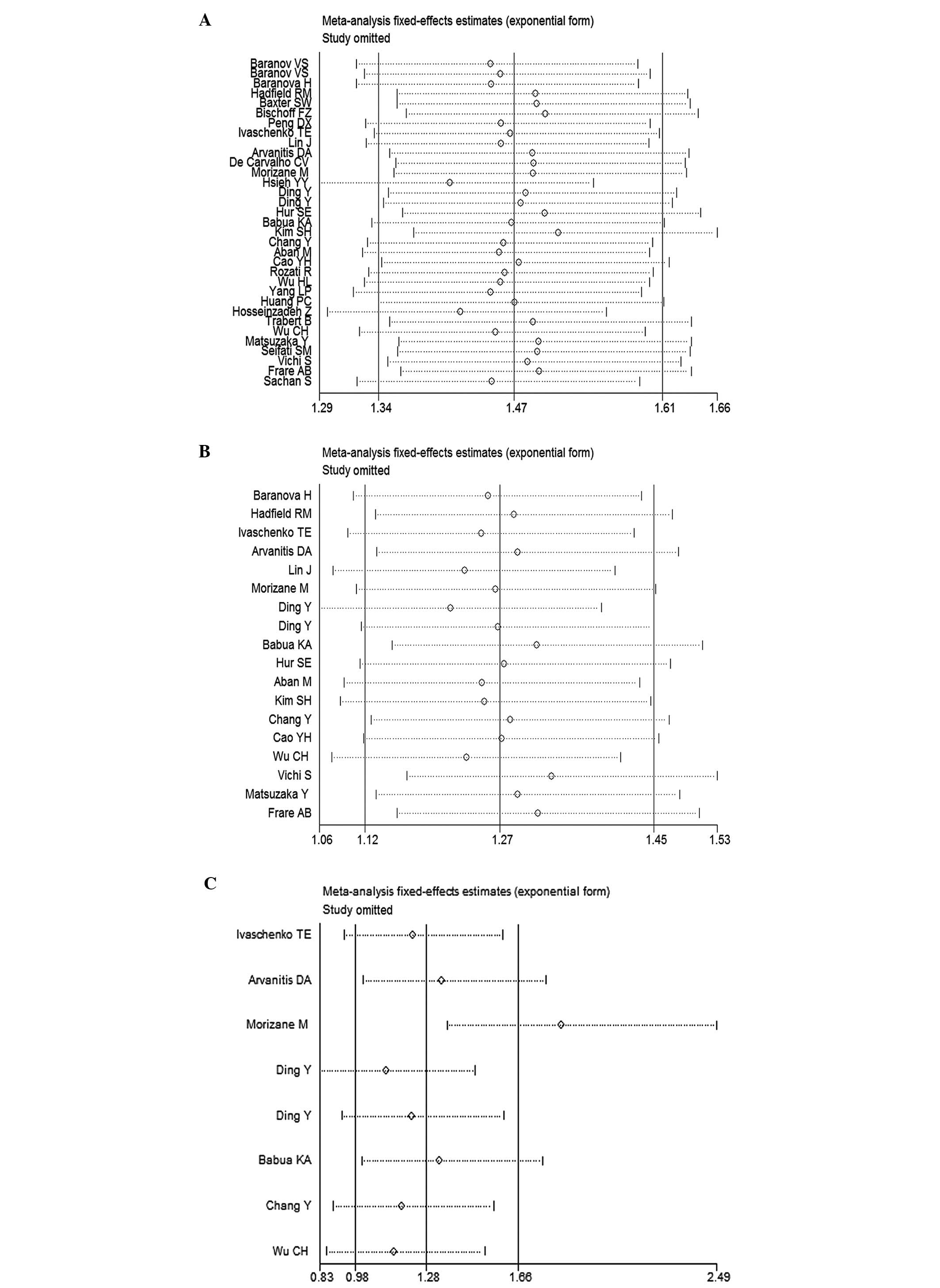
|
1
|
Viganò P, Parazzini F, Somigliana E and
Vercellini P: Endometriosis: Epidemiology and aetiological factors.
Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 18:177–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giudice LC, Tazuke SI and Swiersz L:
Status of current research on endometriosis. J Reprod Med.
43(Suppl): 252–262. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kennedy S: Is there a genetic basis to
endometriosis? Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 15:309–318. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mayani A, Barel S, Soback S and Almagor M:
Dioxin concentrations in women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod.
12:373–375. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eskenazi B, Mocarelli P, Warner M, Samuels
S, Vercellini P, Olive D, Needham LL, Patterson DG Jr, Brambilla P,
Gavoni N, et al: Serum dioxin concentrations and endometriosis: A
cohort study in Seveso, Italy. Environ Health Perspect.
110:629–634. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heilier JF, Nackers F, Verougstraete V,
Tonglet R, Lison D and Donnez J: Increased dioxin-like compounds in
the serum of women with peritoneal endometriosis and deep
endometriotic (adenomyotic) nodules. Fertil Steril. 84:305–312.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nebert DW and Vasiliou V: Analysis of the
glutathione S-transferase (GST) gene family. Hum Genomics.
1:460–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo SW: Glutathione S-transferases M1/T1
gene polymorphisms and endometriosis: A meta-analysis of genetic
association studies. Mol Hum Reprod. 11:729–743. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo SW: The association of endometriosis
risk and genetic polymorphisms involving dioxin detoxification
enzymes: A systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
124:134–143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hudelist G, Keckstein J and Wright JT: The
migrating adenomyoma: Past views on the etiology of adenomyosis and
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 92:1536–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ding Y, Chen ZF, Lin RY, Wang XF, Ding JB,
Ai XZ and Wen H: Relationship between endometriosis and glutathione
S-transferase M1, T1 genes of the Uygurs and Hans in Xinjiang.
Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 39:101–104. 2004.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rozati R, Baludu GS and Reddy BS: Possible
aggravating impact of gene polymorphism in women with
endometriosis. Indian J Med Res. 129:395–400. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang LP and An XF: Analysis on the
relationship between polymorphism of Exon7 situs in CYP1A1 gene,
GSTM1 gene and susceptibility of endometriosis in women of
Han nationality in Jilin City. Zhongguo Fu You Bao Jian.
24:2556–2564. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Peng DX, He YL, Qiu LW, Yang F and Lin JM:
Association between glutathione S-transferase M1 gene deletion and
genetic susceptibility to endometriosis. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue
Bao. 23:458–459, 462. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin J, Zhang X, Qian Y, et al: Glutathione
S-transferase M1 and T1 genotypes and endometriosis risk: A
case-controlled study. Chin Med J (Engl). 116:777–780.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morizane M, Yoshida S, Nakago S, Hamana S,
Maruo T and Kennedy S: No association of endometriosis with
glutathione S-transferase M1 and T1 null mutations in a Japanese
population. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 11:118–121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsieh YY, Chang CC, Tsai FJ, Lin CC, Chen
JM and Tsai CH: Glutathione S-transferase M1*null genotype but not
myeloperoxidase promoter G-463A polymorphism is associated with
higher susceptibility to endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 10:713–717.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Babu KA, Reddy NG, Deendayal M, Kennedy S
and Shivaji S: GSTM1, GSTT1 and CYP1A1 detoxification
gene polymorphisms and their relationship with advanced stages of
endometriosis in South Indian women. Pharmacogenet Genomics.
15:167–172. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hur SE, Lee JY, Moon HS and Chung HW:
Polymorphisms of the genes encoding the GSTM1, GSTT1
and GSTP1 in Korean women: No association with
endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 11:15–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aban M, Ertunc D, Tok EC, Tamer L, Arslan
M and Dilek S: Modulating interaction of glutathione-S-transferase
polymorphisms with smoking in endometriosis. J Reprod Med.
52:715–721. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim SH, Choi YM, Lee GH, Hong MA, Lee KS,
Lee BS, Kim JG and Moon SY: Association between susceptibility to
advanced stage endometriosis and the genetic polymorphisms of aryl
hydrocarbon receptor repressor and glutathione-S-transferase T1
genes. Hum Reprod. 22:1866–1870. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao YH, Yao L, Wang D and Han P:
Relationship between endometriosis and glutathione S-transferase
Nl, T1 and P1 genetic polymorphism. Maternal and Child Health Care
of China. 24:805–814. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Wu HL, Feng D and Liu PX: Relationship
between glutathione S-transferase M1 gene polymorphism and
susceptibility to endometriosis. Yi Xue Lin Chuang Yan Jiu.
26:764–766. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Huang PC, Tsai EM, Li WF, Liao PC, Chung
MC, Wang YH and Wang SL: Association between phthalate exposure and
glutathione S-transferase M1 polymorphism in adenomyosis, leiomyoma
and endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 25:986–994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hosseinzadeh Z, Mashayekhi F and Sorouri
ZZ: Association between GSTM1 gene polymorphism in Iranian
patients with endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 27:185–189. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu CH, Guo CY, Yang JG, Tsai HD, Chang YJ,
Tsai PC, Hsu CC and Kuo PL: Polymorphisms of dioxin receptor
complex components and detoxification-related genes jointly confer
susceptibility to advanced-stage endometriosis in the Taiwanese Han
population. Am J Reprod Immunol. 67:160–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seifati SM, Parivar K, Aflatoonian A,
Firouzabadi Dehghani R and Sheikhha MH: No association of
GSTM1 null polymorphism with endometriosis in women from
central and southern Iran. Iran J Reprod Med. 10:23–28.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsuzaka Y, Kikuti YY, Goya K, Suzuki T,
Cai LY, Oka A, Inoko H, Kulski JK, Izumi S and Kimura M: Lack of an
association human dioxin detoxification gene polymorphisms with
endometriosis in Japanese women: Results of a pilot study. Environ
Health Prev Med. 17:512–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chang Y: Association studies of the
relationship between GSTM1, GSTT1 gene polymorphism
and susceptibility to endometriosis in women of Han nationality in
Hunan province. Masters thesis, Central South University.
2007.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-2007172085.htm(In
Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Sachan S, Nair RR, Khanna A and Singh K:
CYP1A1 and GSTM1 genes polymorphism and its association with
endometriosis: A pilot study. Asian Pacific Journal of
Reproduction. 2:297–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Baranova H, Canis M, Ivaschenko T,
Albuisson E, Bothorishvilli R, Baranov V, Malet P and Bruhat MA:
Possible involvement of arylamine N-acetyltransferase 2,
glutathione S-transferases M1 and T1 genes in the development of
endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 5:636–641. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baranov VS, Ivaschenko T, Bakay B, Aseev
M, Belotserkovskaya R, Baranova H, Malet P, Perriot J, Mouraire P
and Baskakov VN: Proportion of the GSTM1 0/0 genotype in
some Slavic populations and its correlation with cystic fibrosis
and some multifactorial diseases. Hum Genet. 97:516–520. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baranov VS, Ivashchenko TE, Shved NIU,
Iarmolinskata MI, Sel'kov SA, Gorbushin SM, Savitskiĭ GA, Malet P,
Kanis M, Bruhat M and Baranova E: Genetic factors of predisposition
to endometriosis and response to its treatment. Genetika.
35:243–248. 1999.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hadfield RM, Manek S, Weeks DE, Mardon HJ,
Barlow DH and Kennedy SH: OXEGENE Collaborative Group: Linkage and
association studies of the relationship between endometriosis and
genes encoding the detoxification enzymes GSTM1,
GSTT1 and CYP1A1. Mol Hum Reprod. 7:1073–1078. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baxter SW, Thomas EJ and Campbell IG:
GSTM1 null polymorphism and susceptibility to endometriosis
and ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis. 22:63–65. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ivashchenko TE, Shved NIU, Kramareva NA,
Aĭlamazian EK and Baranov VS: Analysis of the polymorphic alleles
of genes encoding phase 1 and phase 2 detoxication enzymes in
patients with endometriosis. Genetika. 39:525–529. 2003.(In
Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Arvanitis DA, Koumantakis GE, Goumenou AG,
Matalliotakis IM, Koumantakis EE and Spandidos DA: CYP1A1, CYP19,
and GSTM1 polymorphisms increase the risk of endometriosis.
Fertil Steril. 79(Suppl 1): 702–709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vichi S, Medda E, Ingelido AM, Ferro A,
Resta S, Porpora MG, Abballe A, Nisticò L, De Felip E, Gemma S and
Testai E: Glutathione transferase polymorphisms and risk of
endometriosis associated with polychlorinated biphenyls exposure in
Italian women: A gene-environment interaction. Fertil Steril.
97:1143–1151.e3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bischoff FZ, Marquez-Do D, Dang D, Carson
SA, Buster JE and Simpson JL: NAT2 and GSTM1 DNA
polymorphisms: Increased GSTM1 (active) genotypes in
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 77(Suppl 1): S172002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Trabert B, Schwartz SM, Peters U, De Roos
AJ, Chen C, Scholes D and Holt VL: Genetic variation in the sex
hormone metabolic pathway and endometriosis risk: An evaluation of
candidate genes. Fertil Steril. 96:1401–1406.e3. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
De Carvalho CV, D'Amora P, Schor E,
Baracat EC, Girão MJC and Da Silva IDG: GSTM1 polymorphism
analysis in patients with mild and severe endometriosis. Fertil
Steril. 82(Suppl 2): S2912004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Frare AB, Barbosa AM, Costa IR, Souza SR,
Silva RC, Bordin BM, Ribeiro Júnior CL and Moura KK: GSTM1
and GSTT1 polymorphisms in endometriosis in women from
Goiás, Brazil. Genet Mol Res. 12:2764–2770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Arvanitis DA, Goumenou AG, Matalliotakis
IM, Koumantakis EE and Spandidos DA: Low-penetrance genes are
associated with increased susceptibility to endometriosis. Fertil
Steril. 76:1202–1206. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Y and Xu LZ: Meta-analysis of
association between GSTM1 gene polymorphism and cervical
cancer. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 5:480–484. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sergentanis TN and Economopoulos KP:
GSTT1 and GSTP1 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk:
A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 121:195–202. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
García-Closas M, Malats N, Silverman D,
Dosemeci M, Kogevinas M, Hein DW, Tardón A, Serra C, Carrato A,
García-Closas R, et al: NAT2 slow acetylation, GSTM1 null
genotype, and risk of bladder cancer: results from the Spanish
Bladder Cancer Study and meta-analyses. Lancet. 366:649–659. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen B, Cao L, Zhou Y, Yang P, Wan HW, Jia
GQ, Liu L and Wu XT: Glutathione S-transferase T1 (GSTT1)
gene polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility: A
meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Dig Dis Sci. 55:1831–1838.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang H, Zhou Y, Zhuang W, Yin YQ, Liu GJ,
Wu TX, Yao X, Du L, Wei ML and Wu XT: Glutathione S-transferase M1
null genotype associated with gastric cancer among Asians. Dig Dis
Sci. 55:1824–1830. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Das P, Shaik AP and Bammidi VK:
Meta-analysis study of glutathione-S-transferases (GSTM1,
GSTP1, and GSTT1) gene polymorphisms and risk of
acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 50:1345–1351. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nelson HH, Wiencke JK, Christiani DC,
Cheng TJ, Zuo ZF, Schwartz BS, Lee BK, Spitz MR, Wang M, Xu X, et
al: Ethnic differences in the prevalence of the homozygous deleted
genotype of glutathione S-transferase theta. Carcinogenesis.
16:l243–1245. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|