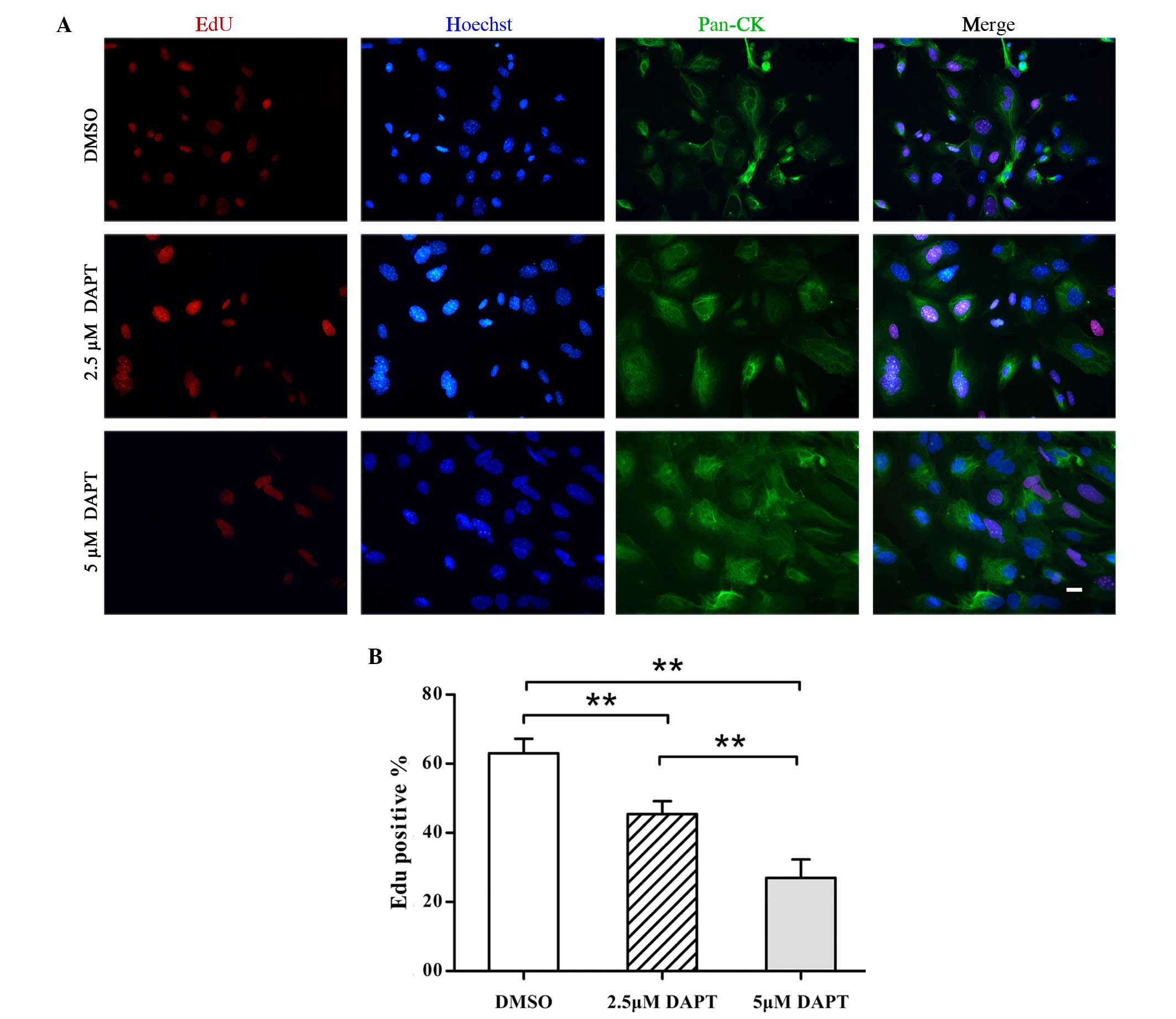
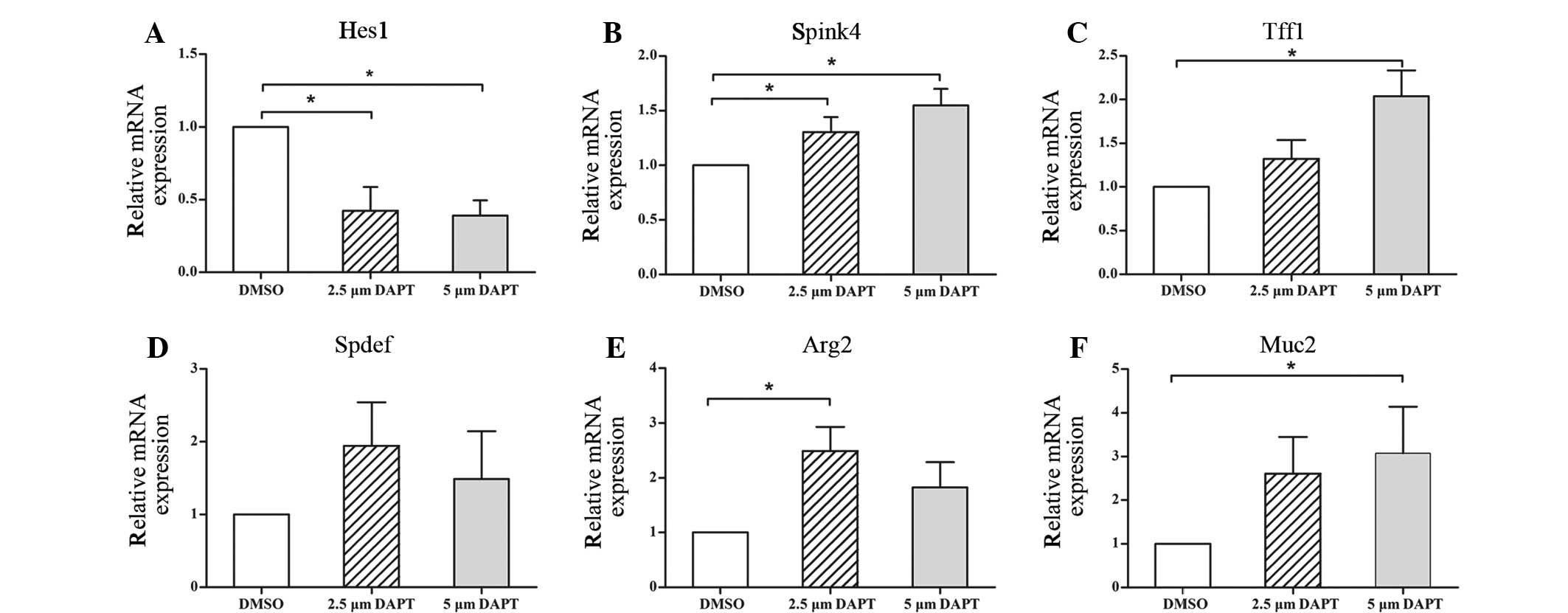
|
1
|
Teele DW, Klein JO and Rosner B:
Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life
in children in greater Boston: A prospective, cohort study. J
Infect Dis. 160:83–94. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Daly KA, Hoffman HJ, Kvaerner KJ, Kvestad
E, Casselbrant ML, Homoe P and Rovers MM: Epidemiology, natural
history, and risk factors: Panel report from the Ninth
International Research Conference on Otitis Media. Int J Pediatr
Otorhinolaryngol. 74:231–240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ting PJ, Lin CH, Huang FL, Lin MC, Hwang
KP, Huang YC, Chiu CH, Lin TY and Chen PY: Epidemiology of acute
otitis media among young children: A multiple database study in
Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 45:453–458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cayé-Thomasen Hermansson A, Bakaletz L,
Hellstrøm S, Kanzaki S, Kerschner J, Lim D, Lin J, Mason K and
Spratley J: Panel 3: Recent advances in anatomy, pathology, and
cell biology in relation to otitis media pathogenesis. Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 148(4 Suppl): E37–E51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kerschner JE, Li J, Tsushiya K and
Khampang P: Mucin gene expression and mouse middle ear epithelium.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 74:864–868. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Movahedan A, Majdi M, Afsharkhamseh N,
Sagha HM, Saadat NS, Shalileh K, Milani BY, Ying H and Djalilian
AR: Notch inhibition during corneal epithelial wound healing
promotes migration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:7476–7483. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma XB, Jia XS, Liu YL, Wang LL, Sun SL,
Song N, Wang EH and Li F: Expression and role of Notch signalling
in the regeneration of rat tracheal epithelium. Cell Prolif.
42:15–28. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kazanjian A, Noah T, Brown D, Burkart J
and Shroyer NF: Atonal homolog 1 is required for growth and
differentiation effects of notch/γ-secretase inhibitors on normal
and cancerous intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology.
139:918–928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fre S, Huyghe M, Mourikis P, Robine S,
Louvard D and Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Notch signals control the fate
of immature progenitor cells in the intestine. Nature. 435:964–968.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Es JH, van Gijn ME, Riccio O, van den
Born M, Vooijs M, Begthel H, Cozijnsen M, Robine S, Winton DJ,
Radtke F and Clevers H: Notch/gamma-secretase inhibition turns
proliferative cells in intestinal crypts and adenomas into goblet
cells. Nature. 435:959–963. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma A, Boulton M, Zhao B, Connon C, Cai J
and Albon J: A role for notch signaling in human corneal epithelial
cell differentiation and proliferation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:3576–3585. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blanpain C, Lowry WE, Pasolli HA and Fuchs
E: Canonical notch signaling functions as a commitment switch in
the epidermal lineage. Genes Dev. 20:3022–3035. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Whitsett JA and Kalinichenko VV: Notch and
basal cells take center stage during airway epithelial
regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 8:597–598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bouras T, Pal B, Vaillant F, Harburg G,
Asselin-Labat ML, Oakes SR, Lindeman GJ and Visvader JE: Notch
signaling regulates mammary stem cell function and luminal
cell-fate commitment. Cell Stem Cell. 3:429–441. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thompson H and Tucker AS: Dual origin of
the epithelium of the mammalian middle ear. Science. 339:1453–1456.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsuchiya K, Kim Y, Ondrey FG and Lin J:
Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mouse middle ear
epithelial cell line. Acta Otolaryngol. 125:823–829. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakamura Y, Hamajima Y, Komori M, Yokota
M, Suzuki M and Lin J: The role of atoh1 in mucous cell metaplasia.
Int J Otolaryngol. 438609:2012.
|
|
20
|
Nakamura Y, Komori M, Yamakawa K, Hamajima
Y, Suzuki M, Kim Y and Lin J: Math1, retinoic acid, and TNF-α
synergistically promote the differentiation of mucous cells in
mouse middle ear epithelial cells in vitro. Pediatr Res.
74:259–265. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|