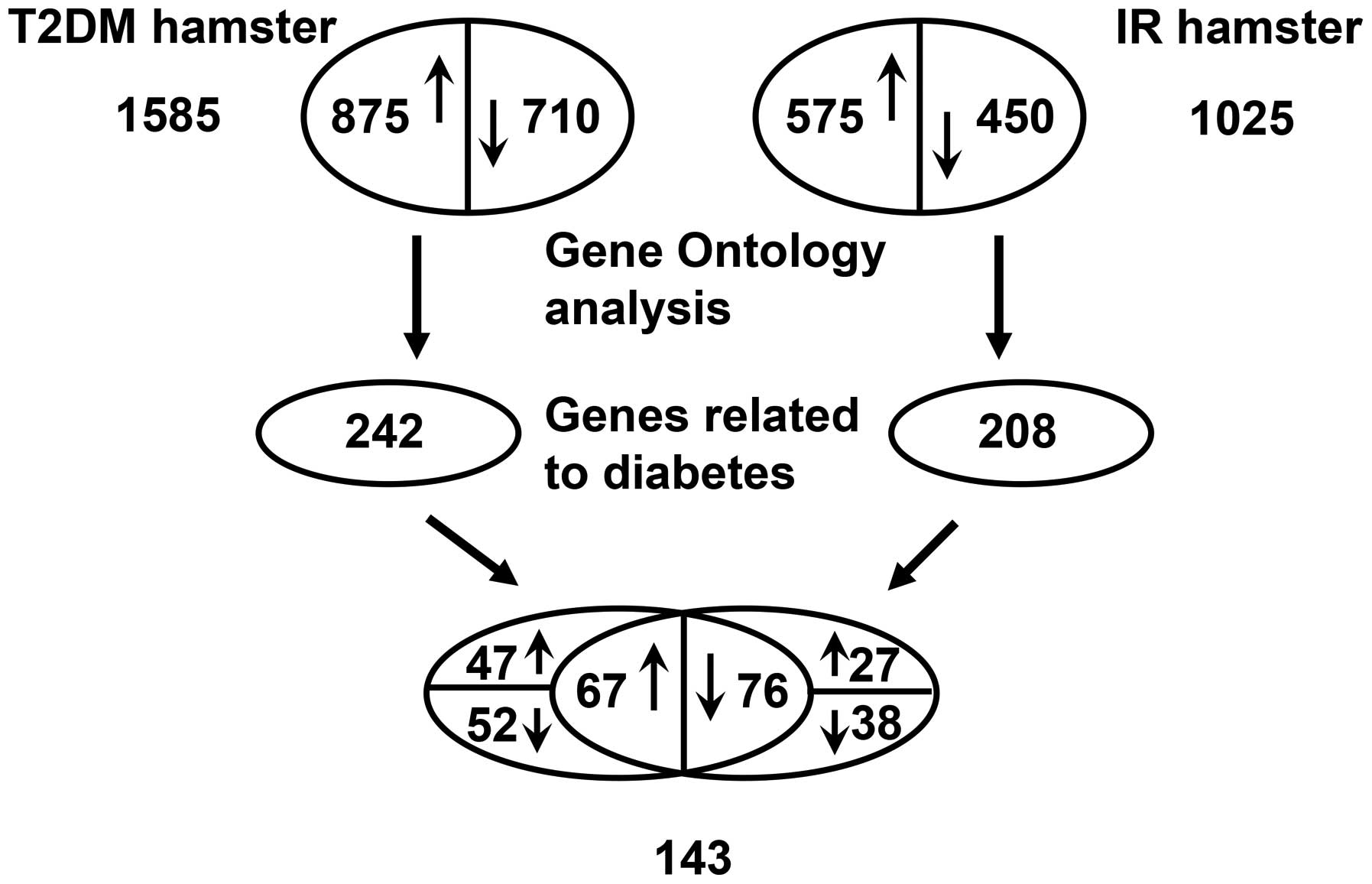
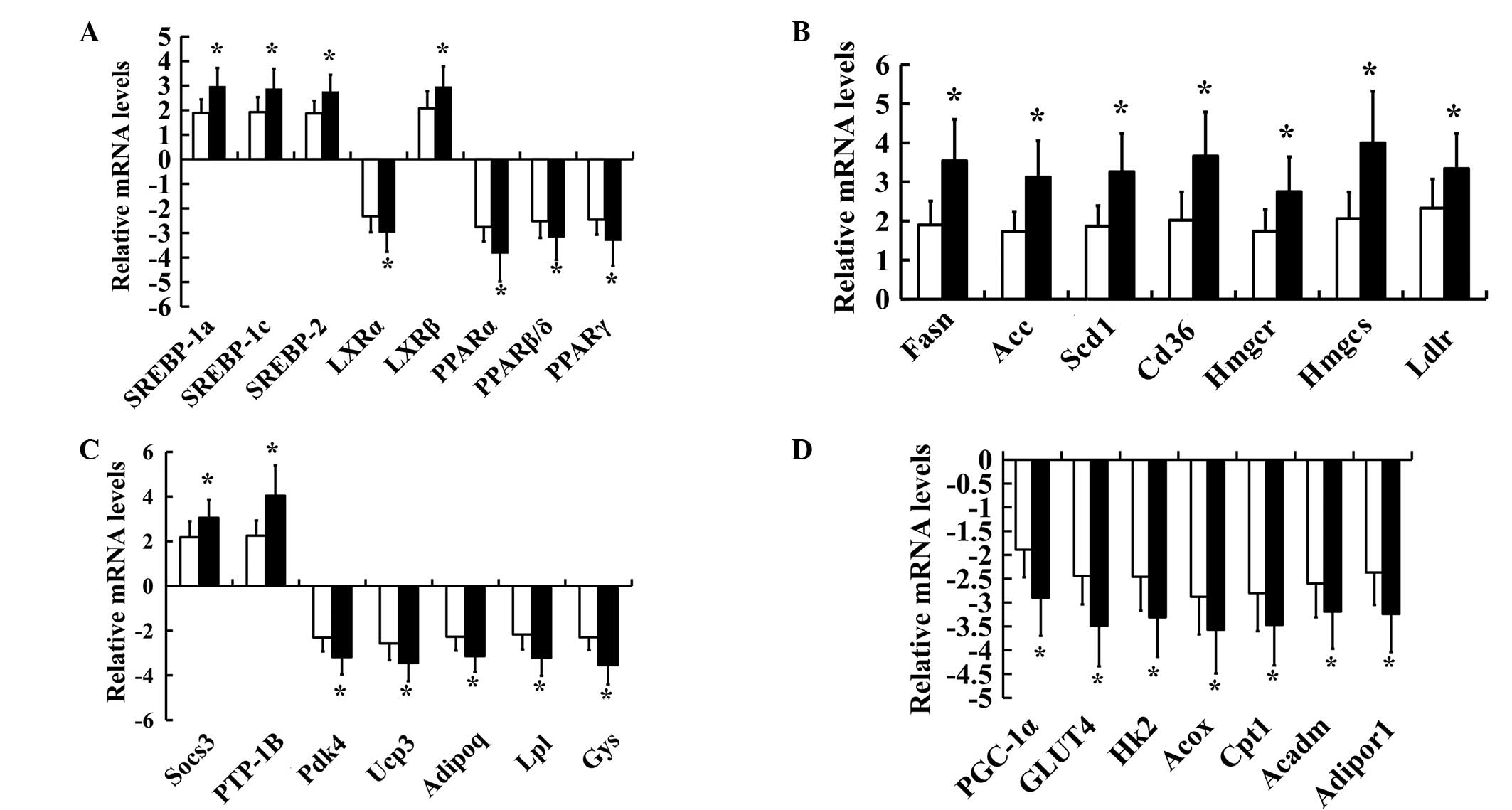
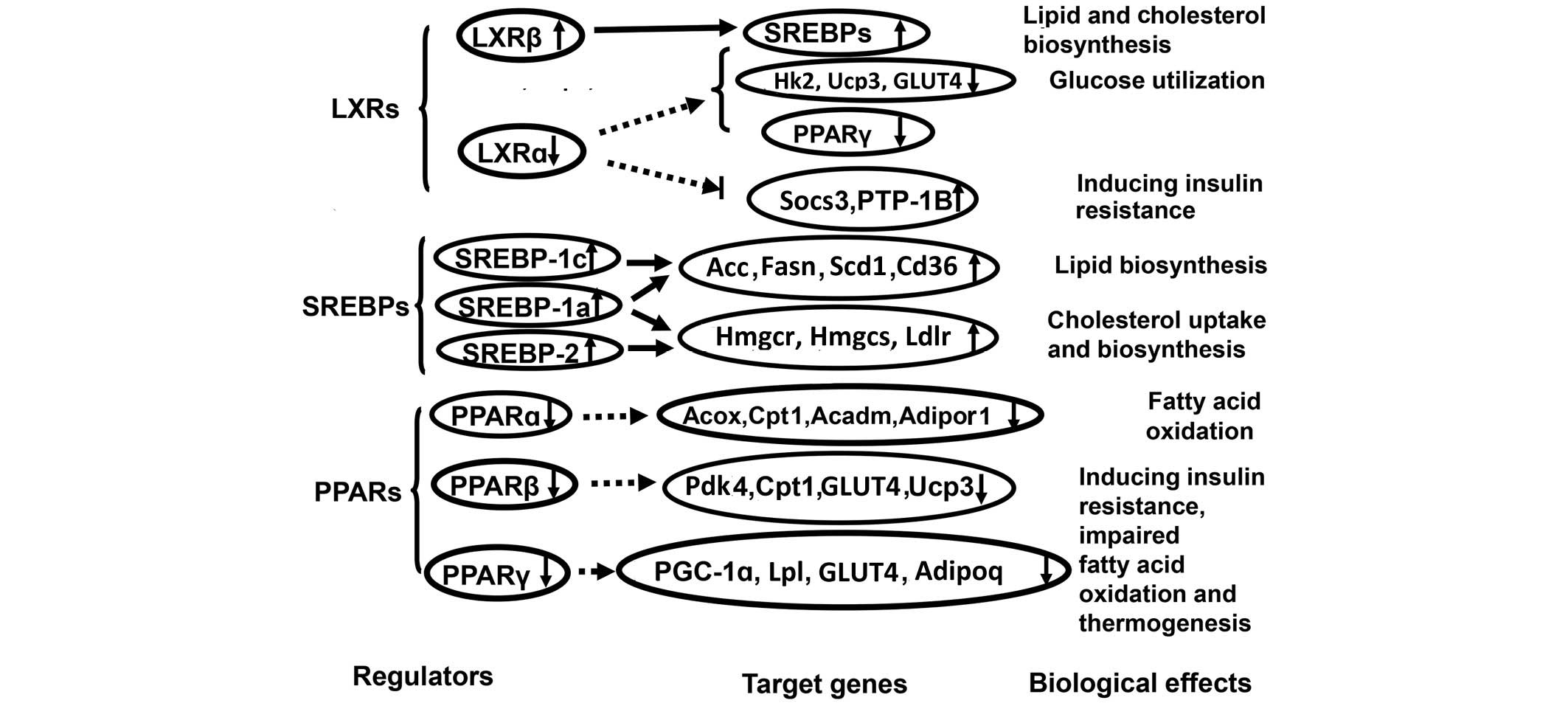
|
1
|
Anandharajan R, Sayyed SG, Doshi LS, Dixit
P, Chandak PG, Dixit AV, Brahma MK, Deshmukh NJ, Gupte R, Damre A,
et al: 18F9 (4-(3,6-bis (ethoxycarbonyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno
(2,3-c)pyridin-2-ylamino)-4-oxobutanoic acid) enhances
insulin-mediated glucose uptake in vitro and exhibits antidiabetic
activity in vivo in db/db mice. Metabolism. 58:1503–1516. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guri AJ, Hontecillas R and
Bassaganya-Riera J: Dietary modulators of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors: Implications for the prevention
and treatment of metabolic syndrome. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics.
1:126–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Unger RH and Orci L: Lipotoxic diseases of
nonadipose tissues in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord.
24(Suppl 4): S28–S32. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith AG and Muscat GE: Skeletal muscle
and nuclear hormone receptors: Implications for cardiovascular and
metabolic disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:2047–2063. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li G, Liu X, Zhu H, Huang L, Liu Y, Ma C
and Qin C: Insulin resistance in insulin-resistant and diabetic
hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) is associated with abnormal
hepatic expression of genes involved in lipid and glucose
metabolism. Comp Med. 59:449–458. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brown MS, Faust JR and Goldstein JL: Role
of the low density lipoprotein receptor in regulating the content
of free and esterified cholesterol in human fibroblasts. J Clin
Invest. 55:783–793. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patti ME, Butte AJ, Crunkhorn S, Cusi K,
Berria R, Kashyap S, Miyazaki Y, Kohane I, Costello M, Saccone R,
et al: Coordinated reduction of genes of oxidative metabolism in
humans with insulin resistance and diabetes: Potential role of PGC1
and NRF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8466–8471. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dumas JF, Simard G, Flamment M, Ducluzeau
PH and Ritz P: Is skeletal muscle mitochondrial dysfunction a cause
or an indirect consequence of insulin resistance in humans?
Diabetes Metab. 35:159–167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mullen KL, Pritchard J, Ritchie I, Snook
LA, Chabowski A, Bonen A, Wright D and Dyck DJ: Adiponectin
resistance precedes the accumulation of skeletal muscle lipids and
insulin resistance in high-fat-fed rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 296:R243–R251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mauvais-Jarvis F, Clegg DJ and Hevener AL:
The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose
homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 34:309–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi CS, Fillmore JJ, Kim JK, Liu ZX, Kim
S, Collier EF, Kulkarni A, Distefano A, Hwang YJ, Kahn M, et al:
Overexpression of uncoupling protein 3 in skeletal muscle protects
against fat-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest.
117:1995–2003. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nieto-Vazquez I, Fernández-Veledo S, de
Alvaro C and Lorenzo M: Dual role of interleukin-6 in regulating
insulin sensitivity in murine skeletal muscle. Diabetes.
57:3211–3221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsou RC and Bence KK: The genetics of
PTPN1 and obesity: Insights from mouse models of tissue-specific
PTP1B deficiency. J Obes. 2012:9268572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heikkinen S, Suppola S, Malkki M, Deeb SS,
Jänne J and Laakso M: Mouse hexokinase II gene: Structure, cDNA,
promoter analysis and expression pattern. Mamm Genome. 11:91–96.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Norris AW, Hirshman MF, Yao J, Jessen N,
Musi N, Chen L, Sivitz WI, Goodyear LJ and Kahn CR: Endogenous
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma augments fatty
acid uptake in oxidative muscle. Endocrinology. 149:5374–5383.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hessvik NP, Boekschoten MV, Baltzersen MA,
Kersten S, Xu X, Andersén H, Rustan AC and Thoresen GH: LXR{beta}
is the dominant LXR subtype in skeletal muscle regulating
lipogenesis and cholesterol efflux. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
298:E602–E613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu R, Ou Z, Ruan X and Gong J: Role of
liver X receptors in cholesterol efflux and inflammatory signaling.
Mol Med Rep. 5:895–900. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guillet-Deniau I, Pichard AL, Koné A,
Esnous C, Nieruchalski M, Girard J and Prip-Buus C: Glucose induces
de novo lipogenesis in rat muscle satellite cells through a
sterol-regulatory-element-bnding-protein-1c-dependent pathway. J
Cell Sci. 117:1937–1944. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yahagi N, Shimano H, Hasty AH, Matsuzaka
T, Ide T, Yoshikawa T, Amemiya-Kudo M, Tomita S, Okazaki H, Tamura
Y, et al: Absence of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1
(SREBP-1) ameliorates fatty livers but not obesity or insulin
resistance in Lep(ob)/Lep(ob) mice. J Biol Chem. 277:19353–19357.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thompson AL and Cooney GJ: Acyl-CoA
inhibition of hexokinase in rat and human skeletal muscle is a
potential mechanism of lipid-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes.
49:1761–1765. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yen CF, Jiang YN, Shen TF, Wong IM, Chen
CC, Chen KC, Chang WC, Tsao YK and Ding ST: Cloning and expression
of the genes associated with lipid metabolism in Tsaiya ducks.
Poult Sci. 84:67–74. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang G, Yang J, Horton JD, Hammer RE,
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Diminished hepatic response to
fasting/refeeding and liver X receptor agonists in mice with
selective deficiency of sterol regulatory element-binding
protein-1c. J Biol Chem. 277:9520–9528. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kruszynska YT, Mulford MI, Baloga J, Yu JG
and Olefsky JM: Regulation of skeletal muscle hexokinase II by
insulin in nondiabetic and NIDDM subjects. Diabetes. 47:1107–1113.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gosmain Y, Lefai E, Ryser S, Roques M and
Vidal H: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 mediates the
effect of insulin on hexokinase II gene expression in human muscle
cells. Diabetes. 53:321–329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Whitehead JP, Richards AA, Hickman IJ,
Macdonald GA and Prins JB: Adiponectin - a key adipokine in the
metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes Metab. 8:264–280. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Almabouada F, Diaz-Ruiz A, Rabanal-Ruiz Y,
Peinado JR, Vazquez-Martinez R and Malagon MM: Adiponectin
receptors form homomers and heteromers exhibiting distinct ligand
binding and intracellular signaling properties. J Biol Chem.
288:3112–3125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamauchi T and Kadowaki T: Physiological
and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin
receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and
cardiovascular diseases. Int J Obes (Lond). 32(Suppl 7): S13–S18.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Muscat GE and Dressel U: Cardiovascular
disease and PPARdelta: Targeting the risk factors. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 6:887–894. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chung SS, Kim M, Youn BS, Lee NS, Park JW,
Lee IK, Lee YS, Kim JB, Cho YM, Lee HK and Park KS: Glutathione
peroxidase 3 mediates the antioxidant effect of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human skeletal muscle
cells. Mol Cell Biol. 29:20–30. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Knaub LA, Jensen DR, Young Jung D,
Hong EG, Ko HJ, Coates AM, Goldberg IJ, de la Houssaye BA, Janssen
RC, et al: Skeletal muscle-specific deletion of lipoprotein lipase
enhances insulin signaling in skeletal muscle but causes insulin
resistance in liver and other tissues. Diabetes. 58:116–124. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi CS, Befroy DE, Codella R, Kim S,
Reznick RM, Hwang YJ, Liu ZX, Lee HY, Distefano A, Samuel VT, et
al: Paradoxical effects of increased expression of PGC-1alpha on
muscle mitochondrial function and insulin-stimulated muscle glucose
metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19926–19931. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kadowaki T and Yamauchi T: Adiponectin and
adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev. 26:439–451. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Awazawa M, Ueki K, Inabe K, Yamauchi T,
Kaneko K, Okazaki Y, Bardeesy N, Ohnishi S, Nagai R and Kadowaki T:
Adiponectin suppresses hepatic SREBP1c expression in an
AdipoR1/LKB1/AMPK dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
382:51–56. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|