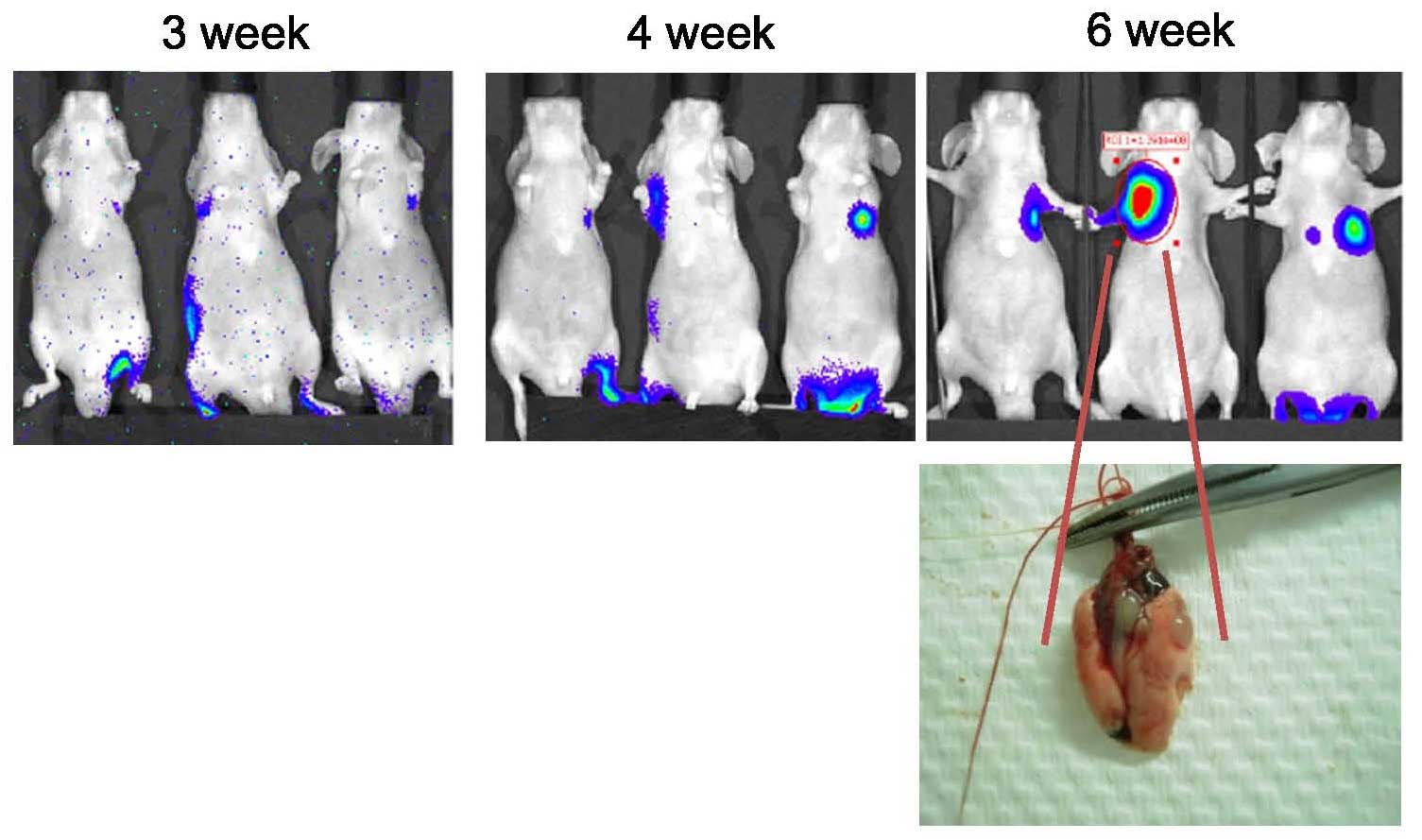
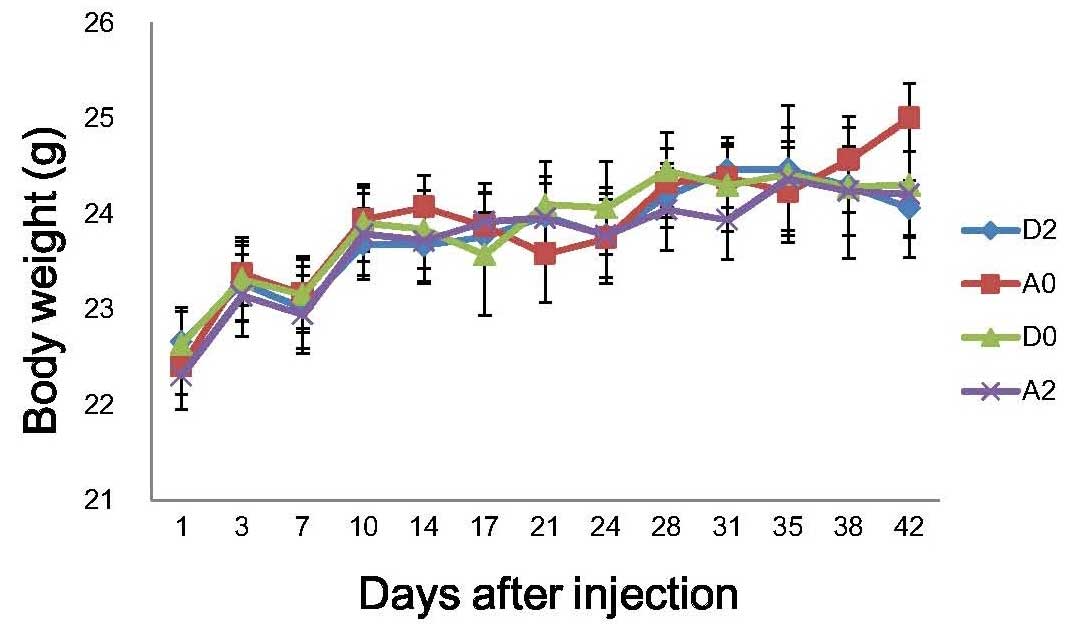
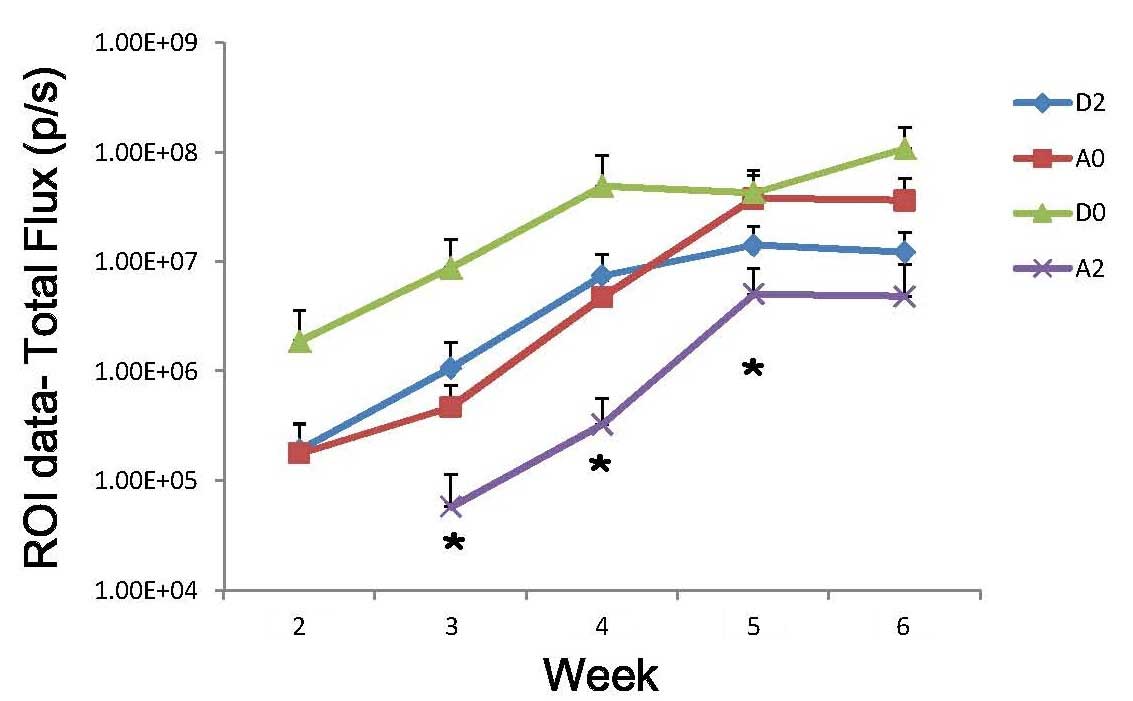
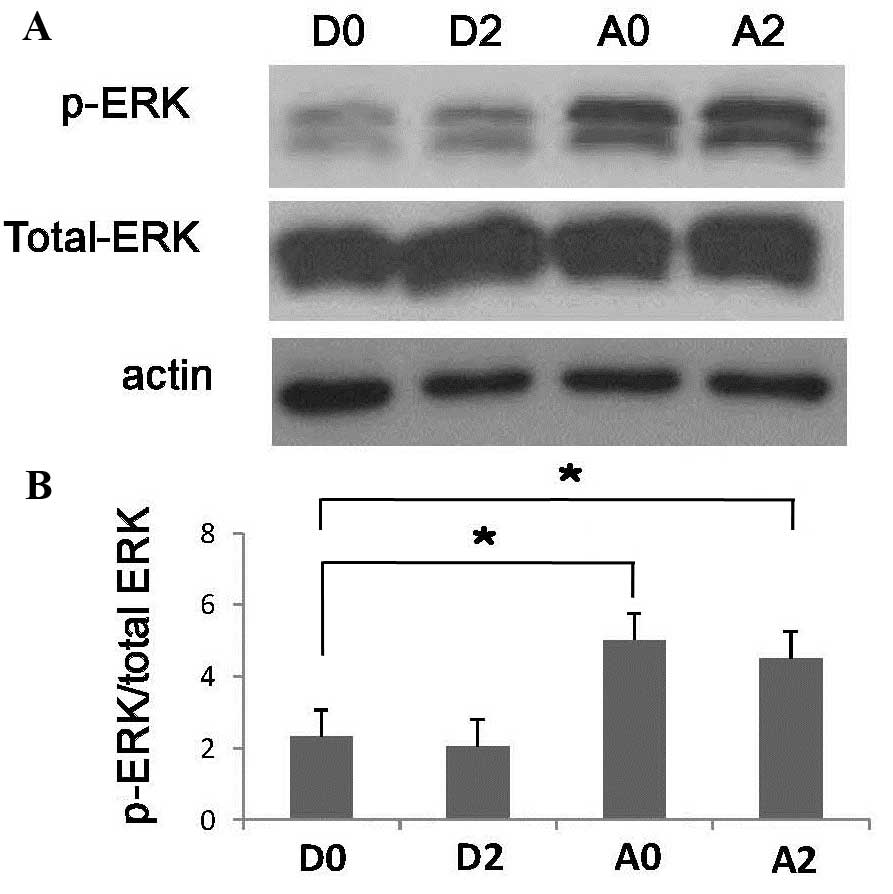
|
1
|
Meyer T and Hart IR: Mechanisms of tumour
metastasis. Eur J Cancer. 34:214–221. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang L, Gaskins K, Yu Z, Xiong Y, Merino
MJ and Kebebew E: An in vivo mouse model of metastatic human
thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 24:695–704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jin Y, Li F, Zheng C, Wang Y, Fang Z, Guo
C, Wang X, Liu H, Deng L, Li C, et al: NEDD9 promotes lung cancer
metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Cancer.
134:2294–2304. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu XG, Zhao L, Willingham MC and Cheng
SY: Thyroid hormone receptors are tumor suppressors in a mouse
model of metastatic follicular thyroid carcinoma. Oncogene.
29:1909–1919. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim WG, Guigon CJ, Fozzatti L, Park JW, Lu
C, Willingham MC and Cheng SY: SKI-606, an Src inhibitor, reduces
tumor growth, invasion, and distant metastasis in a mouse model of
thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1281–1290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lim JC, Chan TK, Ng DS, Sagineedu SR,
Stanslas J and Wong WS: Andrographolide and its analogues:
Versatile bioactive molecules for combating inflammation and
cancer. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 39:300–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hung SK, Hung LC, Kuo CD, Lee KY, Lee MS,
Lin HY, Chen YJ and Fu SL: Andrographolide sensitizes
Ras-transformed cells to radiation in vitro and in vivo. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 77:1232–1239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qiao M, Sheng S and Pardee AB: Metastasis
and AKT activation. Cell Cycle. 7:2991–2996. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huber MA, Azoitei N, Baumann B, Grünert S,
Sommer A, Pehamberger H, Kraut N, Beug H and Wirth T: NF-kappaB is
essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in a
model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 114:569–581.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu SL, Huang YJ, Liang FP, Huang YF,
Chuang CF, Wang SW and Yao JW: Malignant transformation of an
epithelial cell by v-Src via tv-a-mediated retroviral infection: A
new cell model for studying carcinogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 338:830–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim E, Modi KD and Kim J: In vivo
bioluminescent imaging of mammary tumors using IVIS spectrum. J Vis
Exp. pii:12102009.
|
|
12
|
Ruan K, Song G and Ouyang G: Role of
hypoxia in the hallmarks of human cancer. J Cell Biochem.
107:1053–1062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ji LL, Wang Z, Dong F, Zhang WB and Wang
ZT: Andrograpanin, a compound isolated from anti-inflammatory
traditional Chinese medicine Andrographis paniculata, enhances
chemokine SDF-1alpha-induced leukocytes chemotaxis. J Cell Biochem.
95:970–978. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wiart C, Kumar K, Yusof MY, Hamimah H,
Fauzi ZM and Sulaiman M: Antiviral properties of ent-labdene
diterpenes of Andrographis paniculata nees, inhibitors of herpes
simplex virus type 1. Phytother Res. 19:1069–1070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang FP, Lin CH, Kuo CD, Chao HP and Fu
SL: Suppression of v-Src transformation by andrographolide via
degradation of the v-Src protein and attenuation of the Erk
signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 283:5023–5033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie SR, Wang Y, Liu CW, Luo K and Cai YQ:
Liquiritigenin inhibits serum-induced HIF-1α and VEGF expression
via the AKT/mTOR-p70S6K signalling pathway in HeLa cells. Phytother
Res. 26:1133–1141. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang H, Duan L, Zou Z, Li H, Yuan S, Chen
X, Zhang Y, Li X, Sun H, Zha H, et al: Activation of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway is involved in S100A4-induced
viability and migration in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Med Sci.
11:841–849. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gavert N, Ben-Shmuel A, Lemmon V, Brabletz
T and Ben-Ze'ev A: Nuclear factor-kappaB signaling and ezrin are
essential for L1-mediated metastasis of colon cancer cells. J Cell
Sci. 123:2135–2143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramos JW: The regulation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 40:2707–2719. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Balmanno K and Cook SJ: Tumour cell
survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ.
16:368–377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martin P and Pognonec P: ERK and cell
death: Cadmium toxicity, sustained ERK activation and cell death.
FEBS J. 277:39–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Watabe M, Masuda Y, Nakajo S, Yoshida T,
Kuroiwa Y and Nakaya K: The cooperative interaction of two
different signaling pathways in response to bufalin induces
apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells. J Biol Chem.
271:14067–14072. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim YH, Lee DH, Jeong JH, Guo ZS and Lee
YJ: Quercetin augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death: Involvement
of the ERK signal transduction pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
75:1946–1958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sinha D, Bannergee S, Schwartz JH,
Lieberthal W and Levine JS: Inhibition of ligand-independent ERK1/2
activity in kidney proximal tubular cells deprived of soluble
survival factors up-regulates Akt and prevents apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 279:10962–10972. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
von Degenfeld G, Wehrman TS and Blau HM:
Imaging beta-galactosidase activity in vivo using sequential
reporter-enzyme luminescence. Methods Mol Biol. 574:249–259. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|