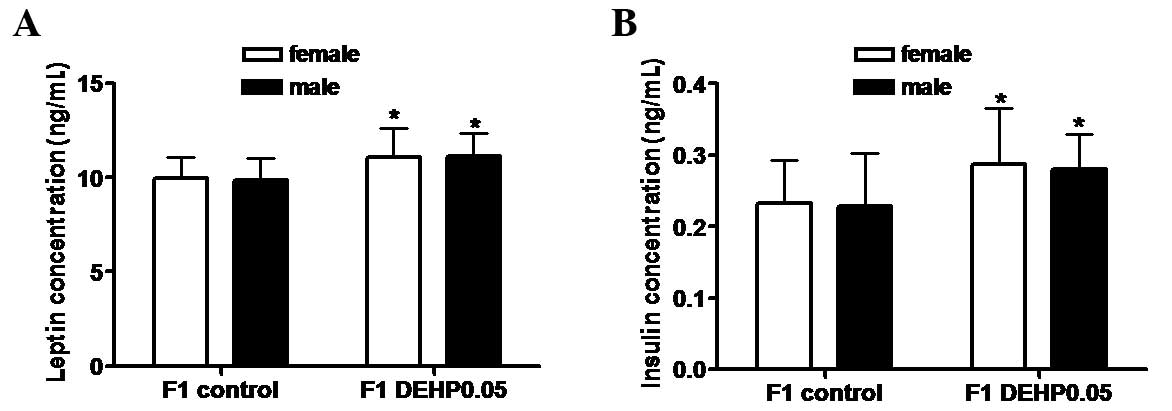
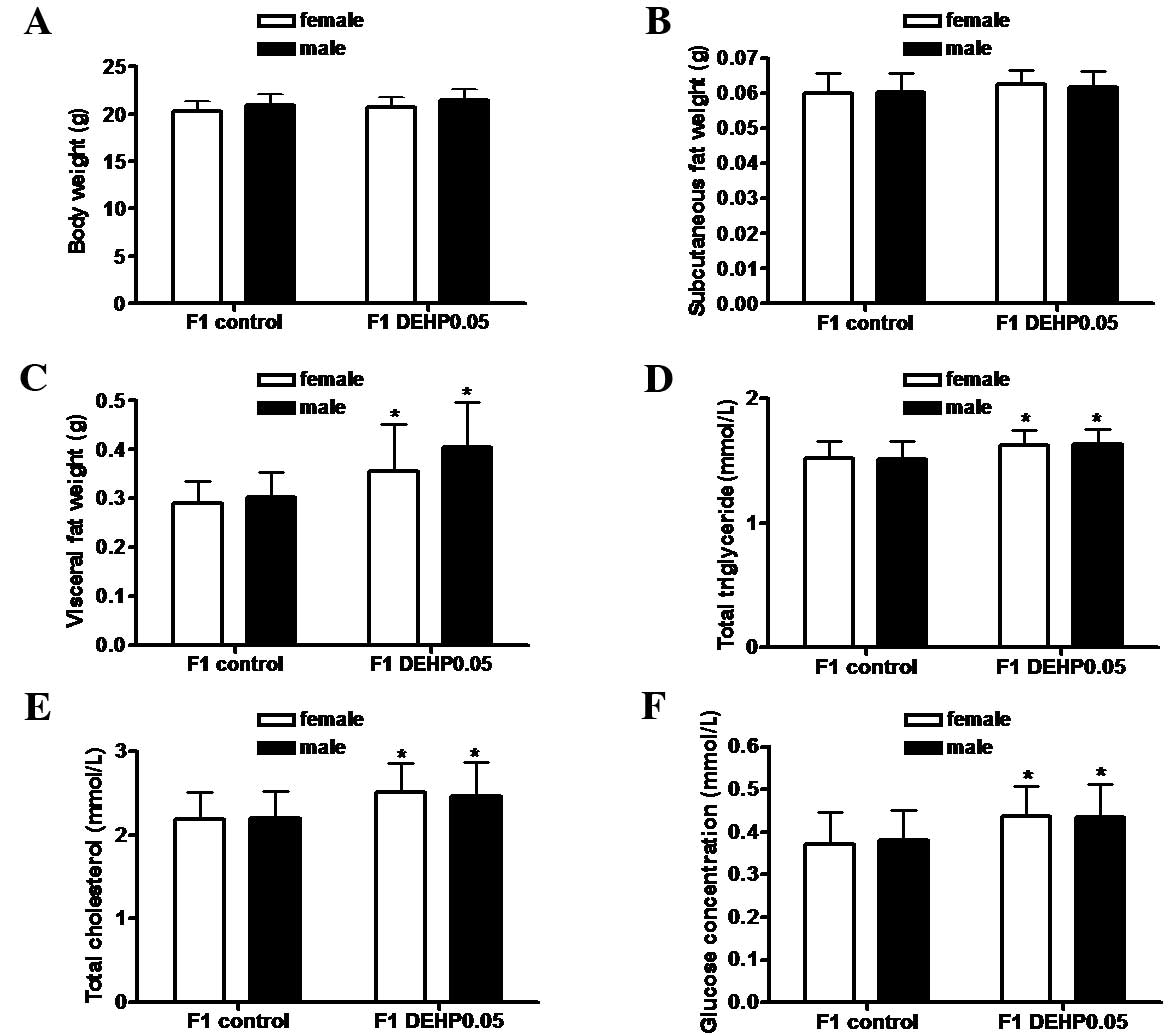
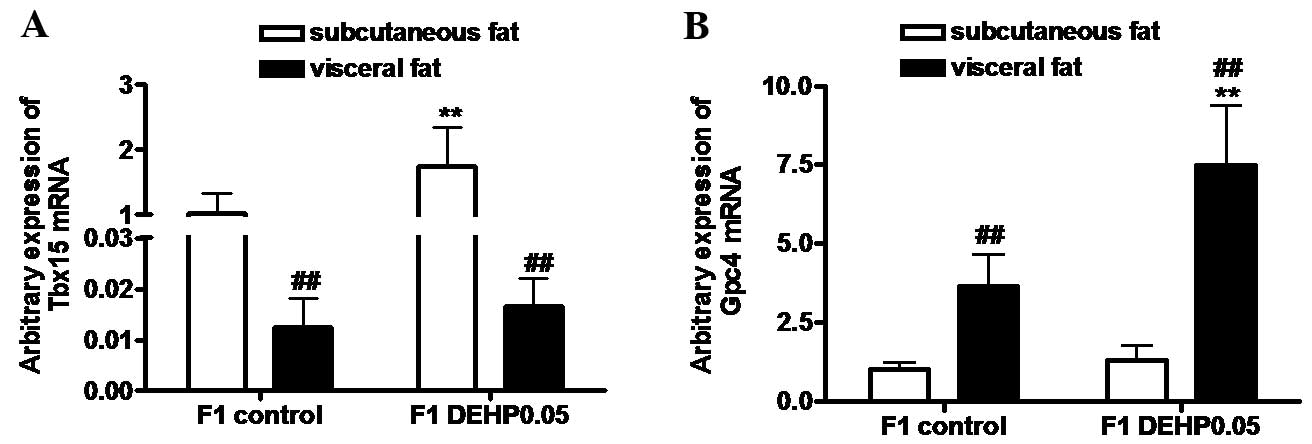
|
1
|
Kissebah AH and Krakower GR: Regional
adiposity and morbidity. Physiol Rev. 74:761–811. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grün F and Blumberg B: Perturbed nuclear
receptor signaling by environmental obesogens as emerging factors
in the obesity crisis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 8:161–171. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Casals-Casas C, Feige JN and Desvergne B:
Interference of pollutants with PPARs: Endocrine disruption meets
metabolism. Int J Obes (Lond). 32:(Suppl 6). S53–S61. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wittassek M, Wiesmüller GA, Koch HM,
Eckard R, Dobler L, Müller J, Angerer J and Schlüter C: Internal
phthalate exposure over the last two decades-a retrospective human
biomonitoring study. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 210:319–333. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wittassek M, Angerer J, Kolossa-Gehring M,
Schäfer SD, Klockenbusch W, Dobler L, Günsel AK, Müller A and
Wiesmüller GA: Fetal exposure to phthalates-a pilot study. Int J
Hyg Environ Health. 212:492–498. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Serrano SE, Braun J, Trasande L, Dills R
and Sathyanarayana S: Phthalates and diet: A review of the food
monitoring and epidemiology data. Environ Health. 13:432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stahlhut RW, van Wijngaarden E, Dye TD,
Cook S and Swan SH: Concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites
are associated with increased waist circumference and insulin
resistance in adult US males. Environ Health Perspect. 115:876–882.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hatch EE, Nelson JW, Qureshi MM, Weinberg
J, Moore LL, Singer M and Webster TF: Association of urinary
phthalate metabolite concentrations with body mass index and waist
circumference: A cross-sectional study of NHANES data, 1999–2002.
Environ Health. 7:272008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buser MC, Murray HE and Scinicariello F:
Age and sex differences in childhood and adulthood obesity
association with phthalates: Analyses of NHANES 2007–2010. Int J
Hyg Environ Health. 217:687–694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Meng X, Chen L, Li D, Zhao L,
Zhao Y, Li L and Shi H: Age and sex-specific relationships between
phthalate exposures and obesity in Chinese children at puberty.
PLoS One. 9:e1048522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feige JN, Gerber A, Casals-Casas C, Yang
Q, Winkler C, Bedu E, Bueno M, Gelman L, Auwerx J, Gonzalez FJ and
Desvergne B: The pollutant diethylhexyl phthalate regulates hepatic
energy metabolism via species-specific PPARalpha-dependent
mechanisms. Environ Health Perspect. 118:234–241. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smerieri A, Testa C, Lazzeroni P, Nuti F,
Grossi E, Cesari S, Montanini L, Latini G, Bernasconi S, Papini AM
and Street ME: Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate metabolites in urine
show age-related changes and associations with adiposity and
parameters of insulin sensitivity in childhood. PLoS One.
10:e01178312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao C, Cheng X, Guo J, Xia H and Ma X:
Perinatal exposure to diethyl-hexyl-phthalate induces obesity in
mice. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 5:725–733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schmidt JS, Schaedlich K, Fiandanese N,
Pocar P and Fischer B: Effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP)
on female fertility and adipogenesis in C3H/N mice. Environ Health
Perspect. 120:1123–1129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gesta S, Blüher M, Yamamoto Y, Norris AW,
Berndt J, Kralisch S, Boucher J, Lewis C and Kahn CR: Evidence for
a role of developmental genes in the origin of obesity and body fat
distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:6676–6681. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto Y, Gesta S, Lee KY, Tran TT,
Saadatirad P and Kahn CR: Adipose depots possess unique
developmental gene signatures. Obesity (Silver Spring). 18:872–878.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hatch EE, Nelson JW, Stahlhut RW and
Webster TF: Association of endocrine disruptors and obesity:
Perspectives from epidemiological studies. Int J Androl.
33:324–332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lott JA and Turner K: Evaluation of
Trinder's glucose oxidase method for measuring glucose in serum and
urine. Clin Chem. 21:1754–1760. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu L, Gu H, Yang J, Ma S, Yu F, Ren Y and
An L: Adipogenic differentiation is not influenced by
lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting the SOCS3 gene in
adipose-derived stromal cells. Mol Biol Rep. 37:2455–2462. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Naville D, Pinteur C, Vega N, Menade Y,
Vigier M, Le Bourdais A, Labaronne E, Debard C, Luquain-Costaz C,
Bégeot M, et al: Low-dose food contaminants trigger sex-specific,
hepatic metabolic changes in the progeny of obese mice. FASEB J.
27:3860–3870. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moore RW, Rudy TA, Lin TM, Ko K and
Peterson RE: Abnormalities of sexual development in male rats with
in utero and lactational exposure to the antiandrogenic plasticizer
Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Environ Health Perspect. 109:229–237.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lamb JC IV, Chapin RE, Teague J, Lawton AD
and Reel JR: Reproductive effects of four phthalic acid esters in
the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 88:255–269. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Niermann S, Rattan S, Brehm E and Flaws
JA: Prenatal exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) affects
reproductive outcomes in female mice. Reprod Toxicol. 53:23–32.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alonso-Magdalena P, Quesada I and Nadal Á:
Prenatal Exposure to BPA and offspring outcomes: The diabesogenic
behavior of BPA. Dose Response. 13:1559325815590395. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vaiserman A: Early-life exposure to
endocrine disrupting chemicals and later-life health outcomes: An
epigenetic bridge? Aging Dis. 5:419–429. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boberg J, Metzdorff S, Wortziger R,
Axelstad M, Brokken L, Vinggaard AM, Dalgaard M and Nellemann C:
Impact of diisobutyl phthalate and other PPAR agonists on
steroidogenesis and plasma insulin and leptin levels in fetal rats.
Toxicology. 250:75–81. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Holemans K, Aerts L and Van Assche FA:
Lifetime consequences of abnormal fetal pancreatic development. J
Physiol. 547:11–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rajesh P and Balasubramanian K:
Gestational exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) impairs
pancreatic β-cell function in F1 rat offspring. Toxicol Lett.
232:46–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Martinelli MI, Mocchiutti NO and Bernal
CA: Effect of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) on lipolysis and
lipoprotein lipase activities in adipose tissue of rats. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 29:739–745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Newbold RR: Impact of environmental
endocrine disrupting chemicals on the development of obesity.
Hormones (Athens). 9:206–217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gesta S, Bezy O, Mori MA, Macotela Y, Lee
KY and Kahn CR: Mesodermal developmental gene Tbx15 impairs
adipocyte differentiation and mitochondrial respiration. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:2771–2776. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tumova S, Woods A and Couchman JR: Heparan
sulfate proteoglycans on the cell surface: Versatile coordinators
of cellular functions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 32:269–288. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li H, Melford K, Judson A and Bensadoun A:
Murine glypican-4 gene structure and expression; Sp1 and Sp3 play a
major role in glypican-4 expression in 3T3-F442A cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1679:141–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chelbi ST, Doridot L, Mondon F, Dussour C,
Rebourcet R, Busato F, Gascoin-Lachambre G, Barbaux S, Rigourd V,
Mignot TM, et al: Combination of promoter hypomethylation and PDX1
overexpression leads to TBX15 decrease in vascular IUGR placentas.
Epigenetics. 6:247–255. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li L, Zhang T, Qin XS, Ge W, Ma HG, Sun
LL, Hou ZM, Chen H, Chen P, Qin GQ, et al: Exposure to diethylhexyl
phthalate (DEHP) results in a heritable modification of imprint
genes DNA methylation in mouse oocytes. Mol Biol Rep. 41:1227–1235.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu L, Gu H, Zhao Y, An L and Yang J:
Glypican 4 may be involved in the adipose tissue redistribution in
high-fat feeding C57BL/6J mice with peroxisome
proliferators-activated receptor γ agonist rosiglitazone treatment.
Exp Ther Med. 8:1813–1818. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sassa Y, Hata Y, Aiello LP, Taniguchi Y,
Kohno K and Ishibashi T: Bifunctional properties of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 in KDR gene regulation
mediated via interaction with both Sp1 and Sp3. Diabetes.
53:1222–1229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sugawara A, Uruno A, Kudo M, Ikeda Y, Sato
K, Taniyama Y, Ito S and Takeuchi K: Transcription suppression of
thromboxane receptor gene by peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma via an interaction with Sp1 in vascular smooth
muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 277:9676–9683. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huber WW, Grasl-Kraupp B and
Schulte-Hermann R: Hepatocarcinogenic potential of di(2-ethylhexyl)
phthalate in rodents and its implications on human risk. Crit Rev
Toxicol. 26:365–481. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Feige JN, Gelman L, Rossi D, Zoete V,
Métivier R, Tudor C, Anghel SI, Grosdidier A, Lathion C,
Engelborghs Y, et al: The endocrine disruptor
monoethyl-hexyl-phthalate is a selective peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator that promotes
adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 282:19152–19166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hao C, Cheng X, Xia H and Ma X: The
endocrine disruptor mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate promotes
adipocyte differentiation and induces obesity in mice. Biosci Rep.
32:619–629. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|