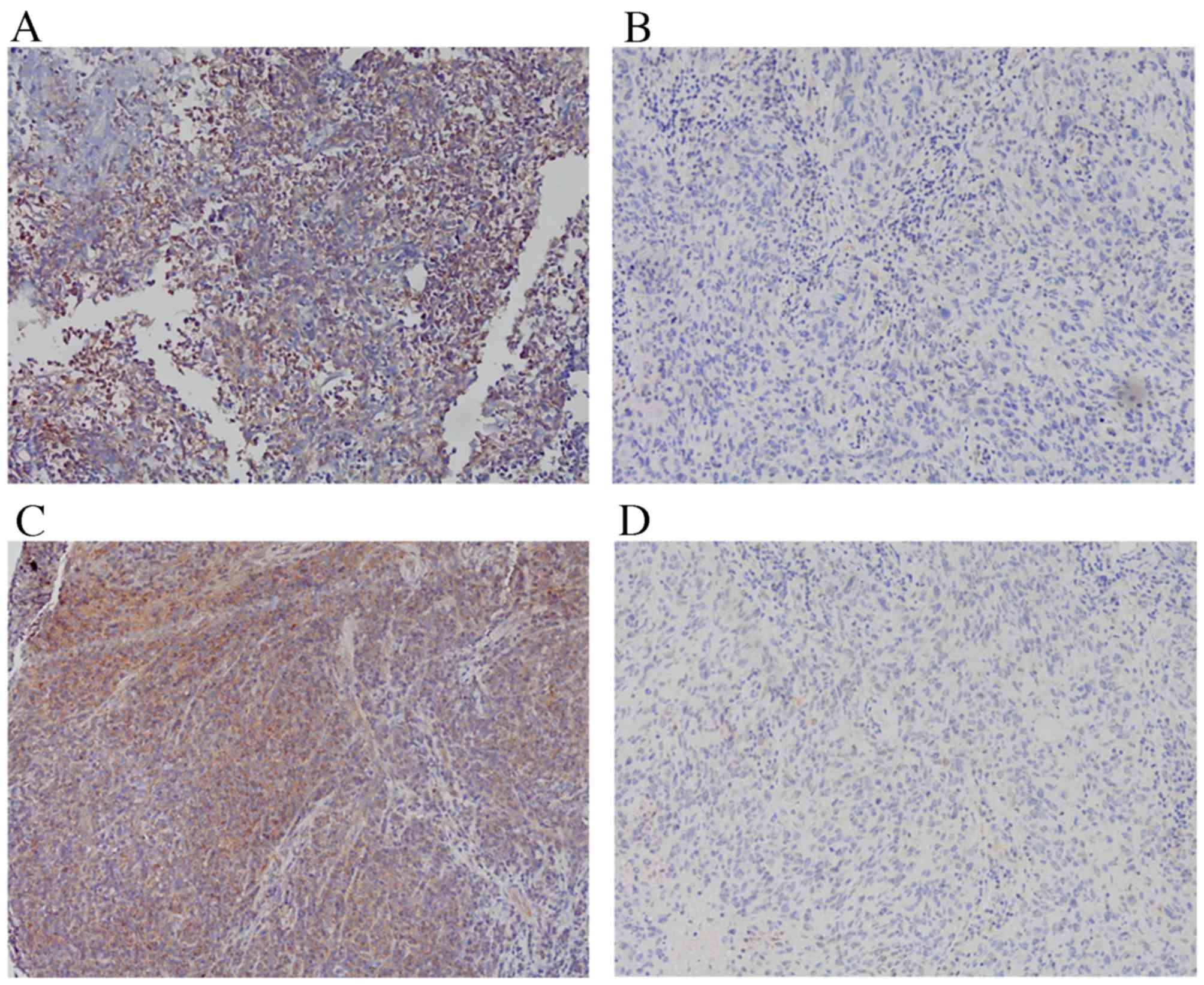
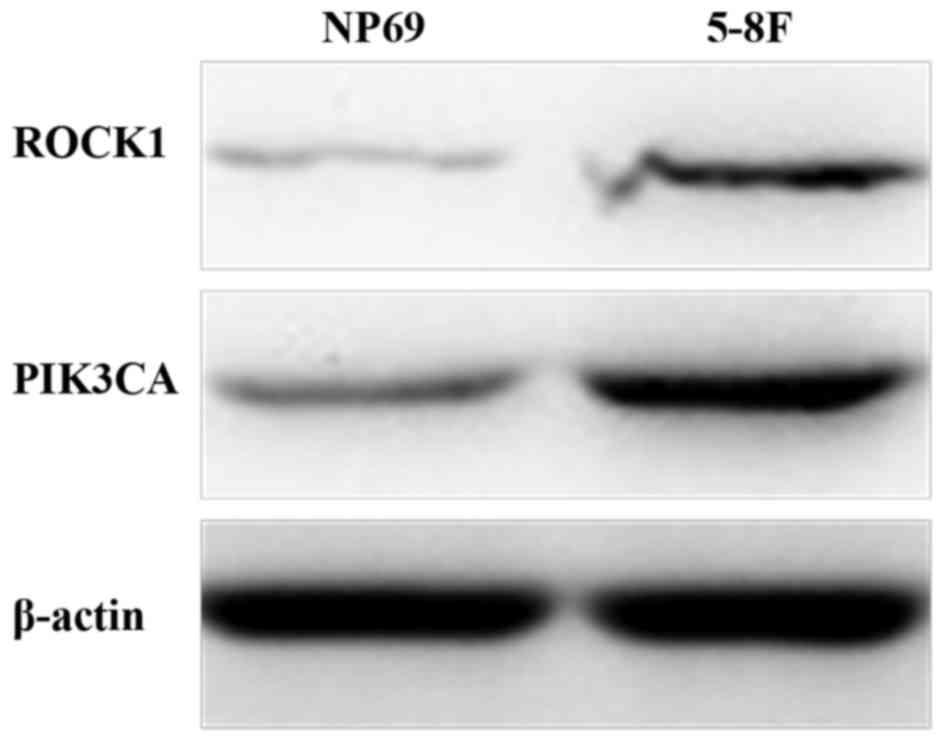
|
1
|
Chang ET and Adami HO: The enigmatic
epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 15:1765–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perri F, Dell'Oca I, Muto P, Schiavone C,
Aversa C, Fulciniti F, Solla R, Scarpati GD, Buonerba C, Di Lorenzo
G and Caponigro F: Optimal management of a patient with recurrent
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. World J Clin Cases. 2:297–300. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang T, Riaz N, Cheng S, Lu J and Lee N:
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
A review. J Radiat Oncol. 1:129–146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jin Y, Cai XY, Cai YC, Cao Y, Xia Q, Tan
YT, Jiang WQ and Shi YX: To build a prognostic score model
containing indispensible tumor markers for metastatic
nasopharyngeal carcinoma in an epidemic area. Eur J Cancer.
48:882–888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan YH, Sze H, Chan C and
Lam TH: The battle against nasopharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol.
104:272–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang W, Zeng Z, Wei F, Chen P, Schmitt
DC, Fan S, Guo X, Liang F, Shi L, Liu Z, et al: SPLUNC1 is
associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma prognosis and plays an
important role in all-trans-retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition
and differentiation in nasopharyngeal cancer cells. FEBS J.
281:4815–4829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li M, Li C, Li D, Xie Y, Shi J, Li G, Guan
Y, Li M, Zhang P, Peng F, et al: Periostin, a stroma-associated
protein, correlates with tumor invasiveness and progression in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:865–877. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Newell-Litwa KA, Badoual M, Asmussen H,
Patel H, Whitmore L and Horwitz AR: ROCK1 and 2 differentially
regulate actomyosin organization to drive cell and synaptic
polarity. J Cell Biol. 210:225–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi Y, Pontrello CG, DeFea KA, Reichardt
LF and Ethell IM: Focal adhesion kinase acts downstream of EphB
receptors to maintain mature dendritic spines by regulating cofilin
activity. J Neurosci. 29:8129–8142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lai K, Killingsworth MC and Lee CS: Gene
of the month: PIK3CA. J Clin Pathol. 68:253–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Q, Zhang B, Shao Y, Chen L, Wang X,
Zhang Z, Shu Y and Guo R: Correlation between the expression levels
of miR-1 and PIK3CA in non-small-cell lung cancer and their
relationship with clinical characteristics and prognosis. Future
Oncol. 10:49–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene F and Trotti A: Pharynx. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th.
Springer Science & Business Media LLC; NY: pp. 41–49. 2010
|
|
13
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng Z, Huang H, Zhang W, Xiang B, Zhou M,
Zhou Y, Ma J, Yi M, Li X, Li X, et al: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Advances in genomics and molecular genetics. Sci China Life Sci.
54:966–975. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vigil D, Kim TY, Plachco A, Garton AJ,
Castaldo L, Pachter JA, Dong H, Chen X, Tokar B, Campbell SL and
Der CJ: ROCK1 and ROCK2 are required for non-small cell lung cancer
anchorage-independent growth and invasion. Cancer Res.
72:5338–5347. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Ye L, Zhang L and Jiang WG:
Placenta growth factor, PLGF, influences the motility of lung
cancer cells, the role of Rho associated kinase, Rock1. J Cell
Biochem. 105:313–320. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tripathi V, Popescu NC and Zimonjic DB:
DLC1 induces expression of E-cadherin in prostate cancer cells
through Rho pathway and suppresses invasion. Oncogene. 33:724–733.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Croft DR, Crighton D, Samuel MS, Lourenco
FC, Munro J, Wood J, Bensaad K, Vousden KH, Sansom OJ, Ryan KM and
Olson MF: p53-mediated transcriptional regulation and activation of
the actin cytoskeleton regulatory RhoC to LIMK2 signaling pathway
promotes cell survival. Cell Res. 21:666–682. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, He X, Ma Y, Liu Y, Shi H, Guo W
and Liu L: Overexpression of ROCK1 and ROCK2 inhibits human
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:244–251. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang C, Zhang S, Zhang Z, He J, Xu Y and
Liu S: ROCK has a crucial role in regulating prostate tumor growth
through interaction with c-Myc. Oncogene. 33:5582–5591. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen KW, Wang WY, Liang WM, Twu CW, Chao
JY, Liang KL, Wu CT, Jiang RS, Shih YT and Lin JC: The volume of
retropharyngeal nodes predicts distant metastasis in patients with
advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47:1171–1175. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Psyrri A, Seiwert TY and Jimeno A:
Molecular pathways in head and neck cancer: EGFR, PI3K and more. Am
Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 246–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang YS, Hsu HT, Ko YC, Yeh KT, Chang SJ,
Lin CY and Chang JG: Combined mutational analysis of RAS, BRAF,
PIK3CA, and TP53 genes in Taiwanese patients with oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.
118:110–116.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiu W, Tong GX, Manolidis S, Close LG,
Assaad AM and Su GH: Novel mutant-enriched sequencing identified
high frequency of PIK3CA mutations in pharyngeal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 122:1189–1194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barault L, Veyrie N, Jooste V, Lecorre D,
Chapusot C, Ferraz JM, Lièvre A, Cortet M, Bouvier AM, Rat P, et
al: Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH
kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a
population-based series of colon cancers. Int J Cancer.
122:2255–2259. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kalinsky K, Jacks LM, Heguy A, Patil S,
Drobnjak M, Bhanot UK, Hedvat CV, Traina TA, Solit D, Gerald W and
Moynahan ME: PIK3CA mutation associates with improved outcome in
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5049–5059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ehrenschwender M, Siegmund D, Wicovsky A,
Kracht M, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Spindler V, Waschke J, Kalthoff H,
Trauzold A and Wajant H: Mutant PIK3CA licenses TRAIL and CD95L to
induce non-apoptotic caspase-8-mediated ROCK activation. Cell Death
Differ. 17:1435–1447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|