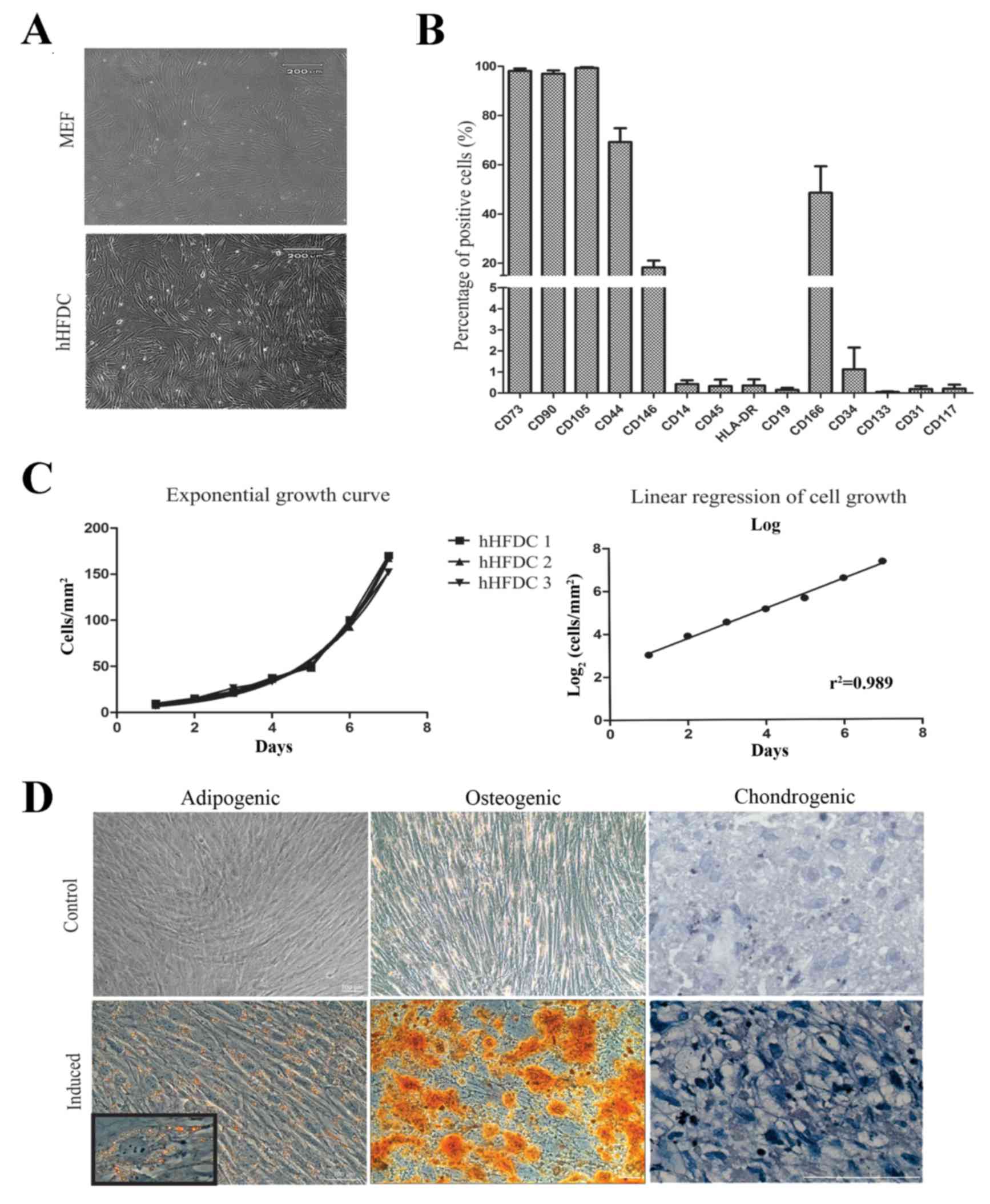
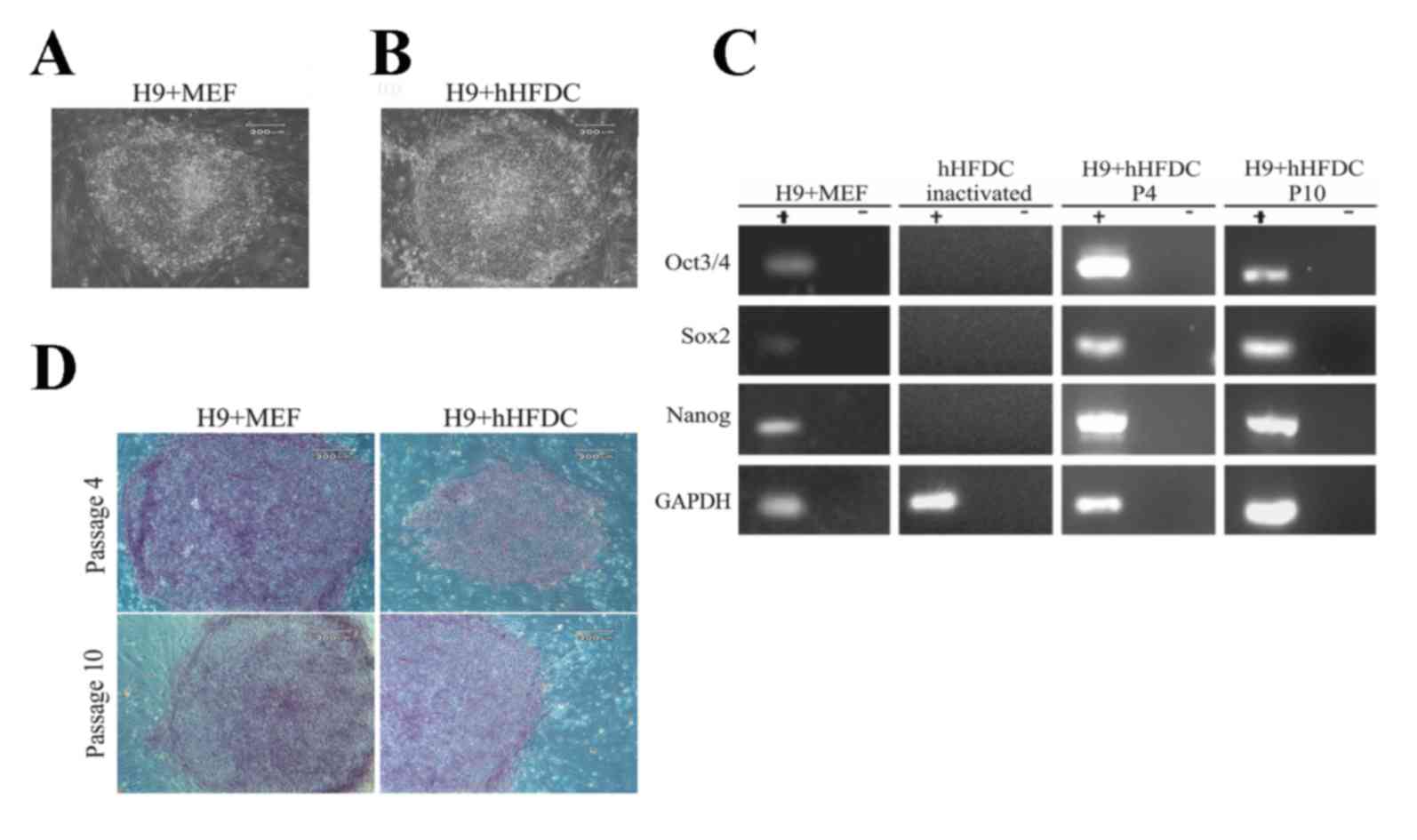
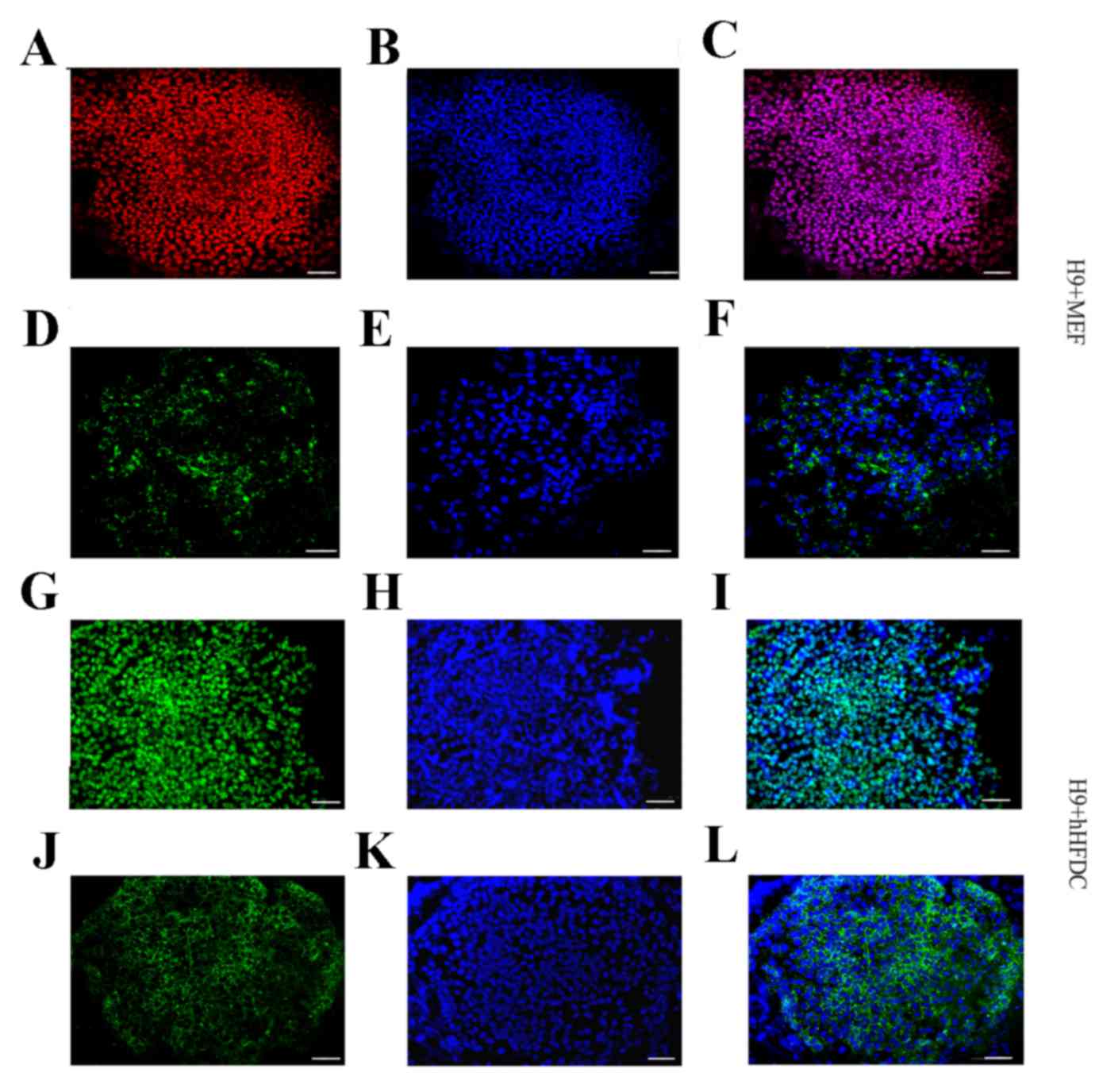
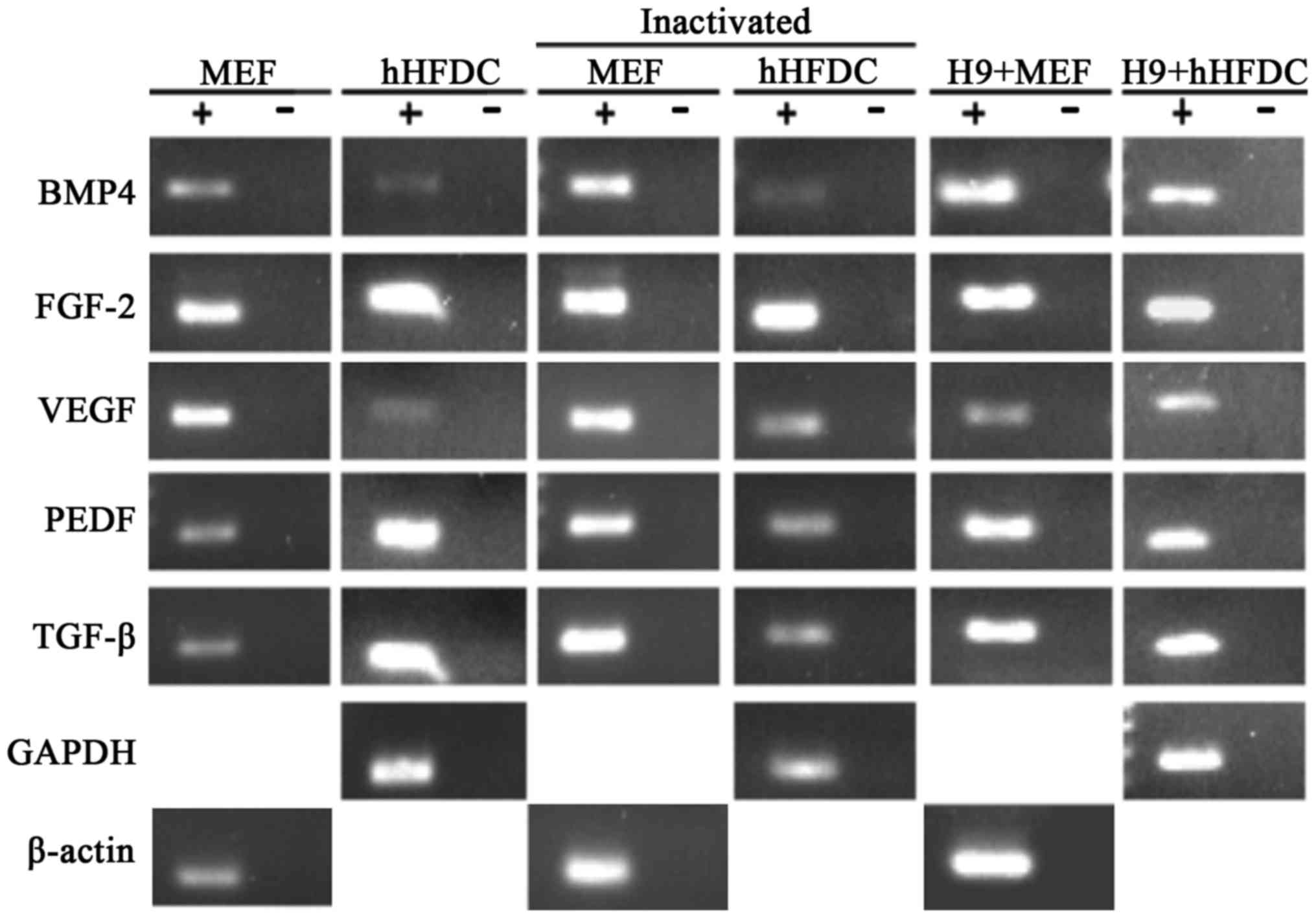
|
1
|
Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, Trounson A
and Bongso A: Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts:
Somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 18:399–404. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS,
Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS and Jones JM: Embryonic stem
cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 282:1145–1147.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakagawa M, Taniguchi Y, Senda S, Takizawa
N, Ichisaka T, Asano K, Morizane A, Doi D, Takahashi J, Nishizawa
M, et al: A novel efficient feeder-free culture system for the
derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep.
4:35942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu HF, Chai C, Lim TC, Leong MF, Lim JK,
Gao S, Lim JK and Wan AC: A defined xeno-free and feeder-free
culture system for the derivation, expansion and direct
differentiation of transgene-free patient-specific induced
pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials. 35:2816–2826. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vuoristo S, Toivonen S, Weltner J, Mikkola
M, Ustinov J, Trokovic R, Palgi J, Lund R, Tuuri T and Otonkoski T:
A novel feeder-free culture system for human pluripotent stem cell
culture and induced pluripotent stem cell derivation. PLoS One.
8:e762052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jang M, Lee ST, Kim JW, Yang JH, Yoon JK,
Park JC, Ryoo HM, van der Vlies AJ, Ahn JY, Hubbell JA, et al: A
feeder-free, defined three-dimensional polyethylene glycol-based
extracellular matrix niche for culture of human embryonic stem
cells. Biomaterials. 34:3571–3580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scafetta G, Siciliano C, Frati G and De
Falco E: Culture of human limbal epithelial stem cells on tenon's
fibroblast feeder-layers: A translational approach. Methods Mol
Biol. 1283:187–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
dos Silva Santos D, de Coelho Oliveira VC,
Asensi KD, Vairo L, Carvalho AB, de Campos Carvalho AC and
Goldenberg RC: Human menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal cells as
new human feeder layer system for human embryonic stem cells. Cell
Med. 7:25–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma X, Li H, Xin S, Ma Y and Ouyang T:
Human amniotic fluid stem cells support undifferentiated
propagation and pluripotency of human embryonic stem cell without
b-FGF in a density dependent manner. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4661–4673. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Q, Qiu C, Huang Y, Jiang L, Huang Q,
Guo L and Liu T: Human amniotic epithelial cell feeder layers
maintain iPS cell pluripotency by inhibiting endogenous DNA
methyltransferase 1. Exp Ther Med. 6:1145–1154. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim ML, Jungebluth P, Sjöqvist S, Nikdin
H, Kjartansdóttir KR, Unger C, Vassliev I and Macchiarini P:
Decellularized feeders: An optimized method for culturing
pluripotent cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2:975–982. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abraham S, Sheridan SD, Miller B and Rao
RR: Stable propagation of human embryonic and induced pluripotent
stem cells on decellularized human substrates. Biotechnol Prog.
26:1126–1134. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bajpai VK, Mistriotis P and Andreadis ST:
Clonal multipotency and effect of long-term in vitro expansion on
differentiation potential of human hair follicle derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 8:74–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th. The National Academies
Press; Washington, DC: pp. 1–220. 2011
|
|
16
|
Pasolli HA: The hair follicle bulge: A
niche for adult stem cells. Microsc Microanal. 17:513–519. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Driskell RR, Clavel C, Rendi M and Watt
FM: Hair follicle dermal papilla cells at a glance. J Cell Sci.
124:1179–1182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu JY, Peng HF, Gopinath S, Tian J and
Andreadis ST: Derivation of functional smooth muscle cells from
multipotent human hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng
Part A. 16:2553–2564. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hoogduijn MJ, Gorjup E and Genever PG:
Comparative characterization of hair follicle dermal stem cells and
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 15:49–60. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jahoda CA, Whitehouse J, Reynolds AJ and
Hole N: Hair follicle dermal cells differentiate into adipogenic
and osteogenic lineages. Exp Dermatol. 12:849–859. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop DJ and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Buhring HJ, Treml S, Cerabona F, de Zwart
P, Kanz L and Sobiesiak M: Phenotypic characterization of distinct
human bone marrow derived MSC subsets. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1176:124–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA, Robey
PG, Storms RW and Gimble JM: Surface protein characterization of
human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. J Cell Physiol.
189:54–63. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Hung S, Peng S, Huang C, Wei H,
Guo Y, Fu YS, Lai MC and Chen CC: Mesenchymal stem cells in the
wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells.
22:1330–1337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Na GY, Paek SH, Park BC, Kim DW, Lee WJ,
Kim MK and Kim JC: Isolation and characterization of outer root
sheath melanocytes of human hair follicles. Br J Dermatol.
155:902–909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Asensi KD, Fortunato RS, dos Santos DS,
Pacheco TS, de Rezende DF, Rodrigues DC, Mesquita FC,
Kasai-Brunswick TH, de Carvalho AC and Goldenberg RC: Reprogramming
to pluripotent state modifies mesenchymal stem cell resistance to
oxidative stress. J Cell Mol Med. 18:824–831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patel AN, Park E, Kuzman M, Benetti F,
Silva FJ and Allickson JG: Multipotent menstrual blood stromal stem
cells: Isolation, characterization, and differentiation. Cell
Transplant. 17:303–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nekanti U, Dastidar S, Venugopal P, Totey
S and Ta M: Increased proliferation and analysis of differential
gene expression in human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal
stromal cells under hipoxya. Int J Biol Sci. 9:499–512. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee CH, Park JH, Lee JH, Ahn JY, Park JH,
Lee BR, Kim DY and Lim JM: Replacement of mouse embryonic
fibroblasts with bone marrow stromal cells for use in establishing
and maintaining embryonic stem cells in mice. Cell Biol Int.
36:537–543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amit M, Margulets V, Segev H, Sharik K,
Laevsky I, Coleman R and Itskovitz-Eldor J: Human feeder layers for
human embryonic stem cells. Biol Reprod. 68:2150–2156. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cheng L, Hammond H, Ye Z, Zhan X and
Dravid G: Human adult marrow cells support prolonged expansion of
human embryonic stem cells in culture. Stem Cells. 21:131–142.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhan X, Hill C, Brayton CF and Shamblott
MJ: Cells derived from human umbilical cord blood support the
long-term growth of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells.
Cloning Stem Cells. 10:513–522. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee JB, Song JM, Lee JE, Park JH, Kim SJ,
Kang SM, Know JN, Kim MK, Roh SI and Yoon HS: Available human
feeder cells for the maintenance of human embryonic stem cells.
Reproduction. 128:727–735. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Richards M, Tan S, Fong CY, Biswas A, Chan
WK and Bongso A: Comparative evaluation of various human feeders
for prolonged undifferentiated growth of human embryonic stem
cells. Stem Cells. 21:546–556. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hoffman LM and Carpenter MK:
Characterization and culture of human embryonic stem cells. Nat
Biotechnol. 23:699–708. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baker DE, Harrison NJ, Maltby E, Smith K,
Moore HD, Shaw PJ, Heath PR, Holden H and Andrews PW: Adaptation to
culture of human embryonic stem cells and oncogenesis in vivo. Nat
Biotechnol. 25:207–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mitalipova MM, Rao RR, Hoyer DM, Johnson
JA, Meisner LF, Jones KL, Dalton S and Stice SL: Preserving the
genetic integrity of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol.
23:19–20. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brimble SN, Zeng X, Weiler DA, Luo Y, Liu
Y, Lyons IG, Freed WJ, Robins AJ, Rao MS and Schulz TC: Karyotypic
stability, genotyping, differentiation, feeder-free maintenance and
gene expression sampling in three human embryonic stem cell lines
derived prior to August 9, 2001. Stem Cells Dev. 13:585–597. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Draper JS, Smith K, Gokhale P, Moore HD,
Maltby E, Johnson J, Meisner L, Zwaka TP, Thomson JA and Andrews
PW: Recurrent gain of chromosomes 17q and 12 in cultured human
embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 22:53–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cho M, Lee EJ, Nam H, Yang JH, Cho J, Lim
JM and Lee G: Human feeder layer system derived from umbilical cord
stromal cells for human embryonic stem cells. Fertil Steril.
93:2525–2531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Villa-Diaz LG, Pacut C, Slawny NA, Ding J,
O'shea KS and Smith GD: Analysis of the factors that limit the
ability of feeder cells to maintain the undifferentiated state of
human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 18:641–651. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pekkanen-Mattila M, Ojala M, Kerkelä E,
Rajala K, Skottman H and Aalto-Setälä K: The effect of human and
mouse fibroblast feeder cells on cardiac differentiation of human
pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2012:8750592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hovatta O, Mikkola M, Gertow K, Strömberg
AM, Inzunza J, Hreinsson J, Rozell B, Blennow E, Andäng M and
Ahrlund-Richter L: A culture system using human foreskin
fibroblasts as feeder cells allows production of human embryonic
stem cells. Hum Reprod. 18:1404–1409. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sánchez L, Gutierrez-Aranda I, Ligero G,
Martín M, Ayllón V, Real PJ, Ramos-Mejía V, Bueno C and Menendez P:
Maintenance of human embryonic stem cells in media conditioned by
human mesenchymal stem cells obviates the requirement of exogenous
basic fibroblast growth factor supplementation. Tissue Eng Part C
Methods. 18:387–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Anisimov SV, Christophersen NS, Correia
AS, Hall VJ, Sandelin I, Li JY and Brundin P: Identification of
molecules derived from human fibroblast feeder cells that support
the proliferation of human embryonic stem cells. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 16:79–88. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xi J, Wang Y, Zhang P, He L, Nan X, Yue W
and Pei X: Human fetal liver stromal cells that overexpress bFGF
support growth and maintenance of human embryonic stem cells. PLoS
One. 5:1–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kumar N, Pethe P and Bhartiya D: Role of
TGFbeta and myofibroblasts in supporting the propagation of human
embryonic stem cells in vitro. Int J Dev Biol. 54:1329–1336. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eiselleova L, Peterkova I, Neradil J,
Slaninova I, Hampl A and Dvorak P: Comparative study of mouse and
human feeder cells for human embryonic stem cells. Int J Dev Biol.
52:353–363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Amand MM, Hanover JA and Shiloach J: A
comparison of strategies for immortalizating mouse embryonic
fibroblasts. J Biol Methods. 3:e412016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Paus R and Foitzik K: In search of the
hair ‘hair cycle clock’: A guided tour. Differentiation.
72:489–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Stenn KS and Paus R: Controls of hair
follicle cycling. Physiol Rev. 81:449–494. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tong X and Coulombe PA: Keratin 17
modulates hair follicle cycling in a TNF alpha-dependent fahion.
Genes Dev. 20:1353–1364. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Weiner L, Han R, Scichitano BM, Li J,
Hasegawa K, Grossi M, Lee D and Brissette JL: Dedicated ephitelial
recipient cells determine pigmentation patterns. Cell. 130:932–942.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mckay TR, Camarasa MV, Iskender B, Ye J,
Bates N, Miller D, Fitzsimmons JC, Foxler D, Mee M, Sharp TV, et
al: Human feeder cell line for derivation and culture of
hESCs/hiPSc. Stem Cell Res. 7:154–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|