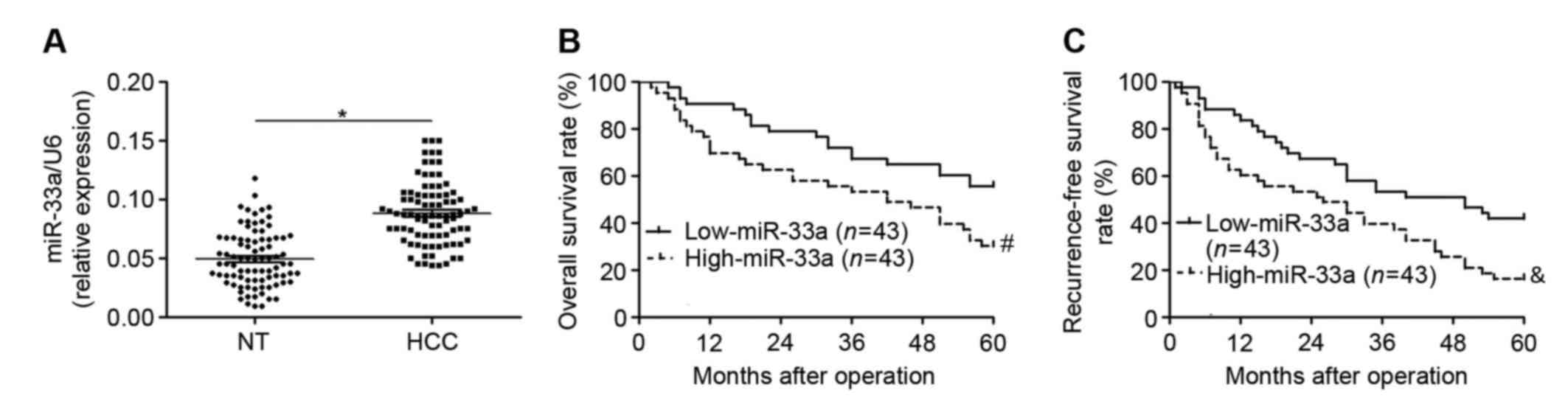
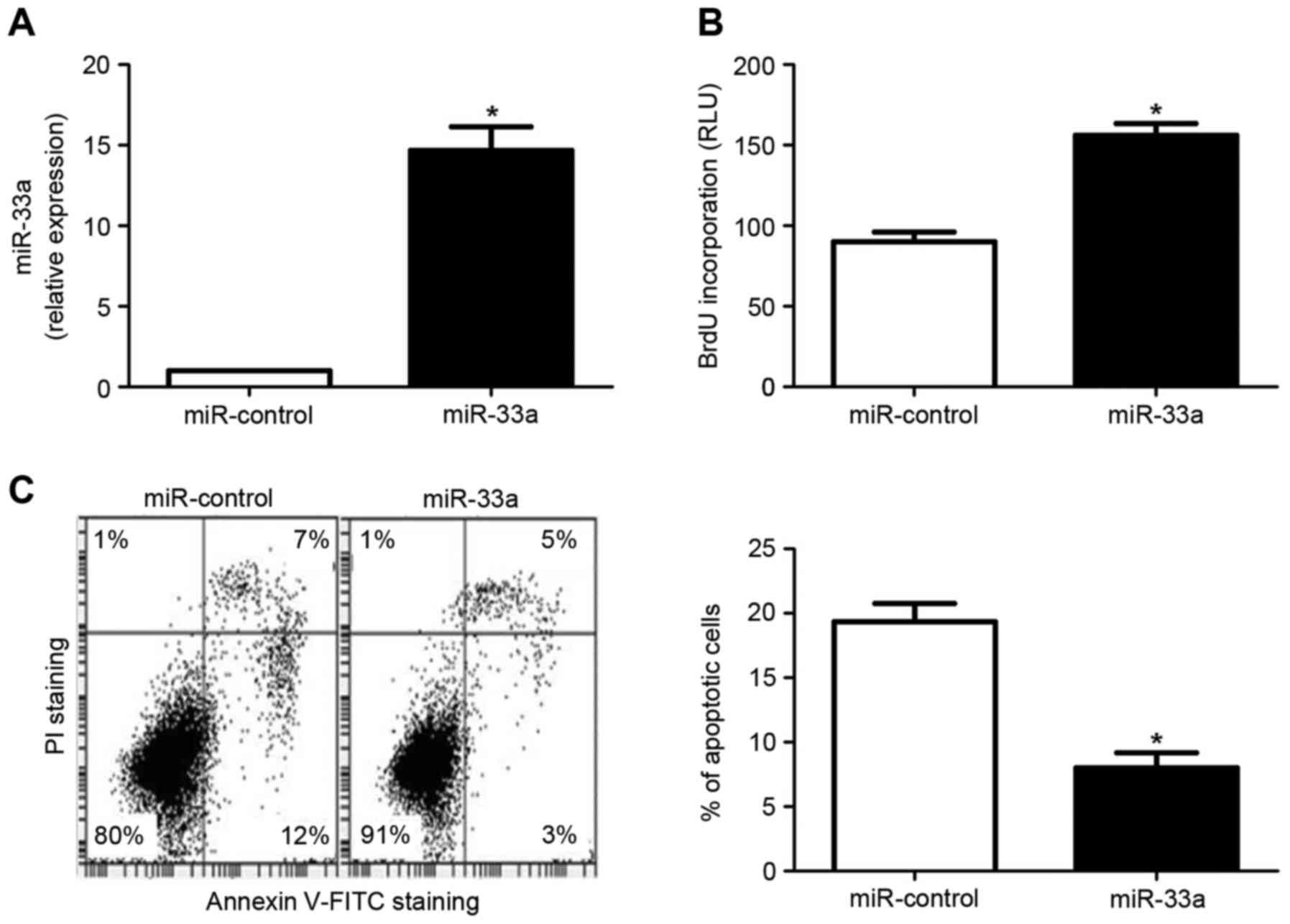
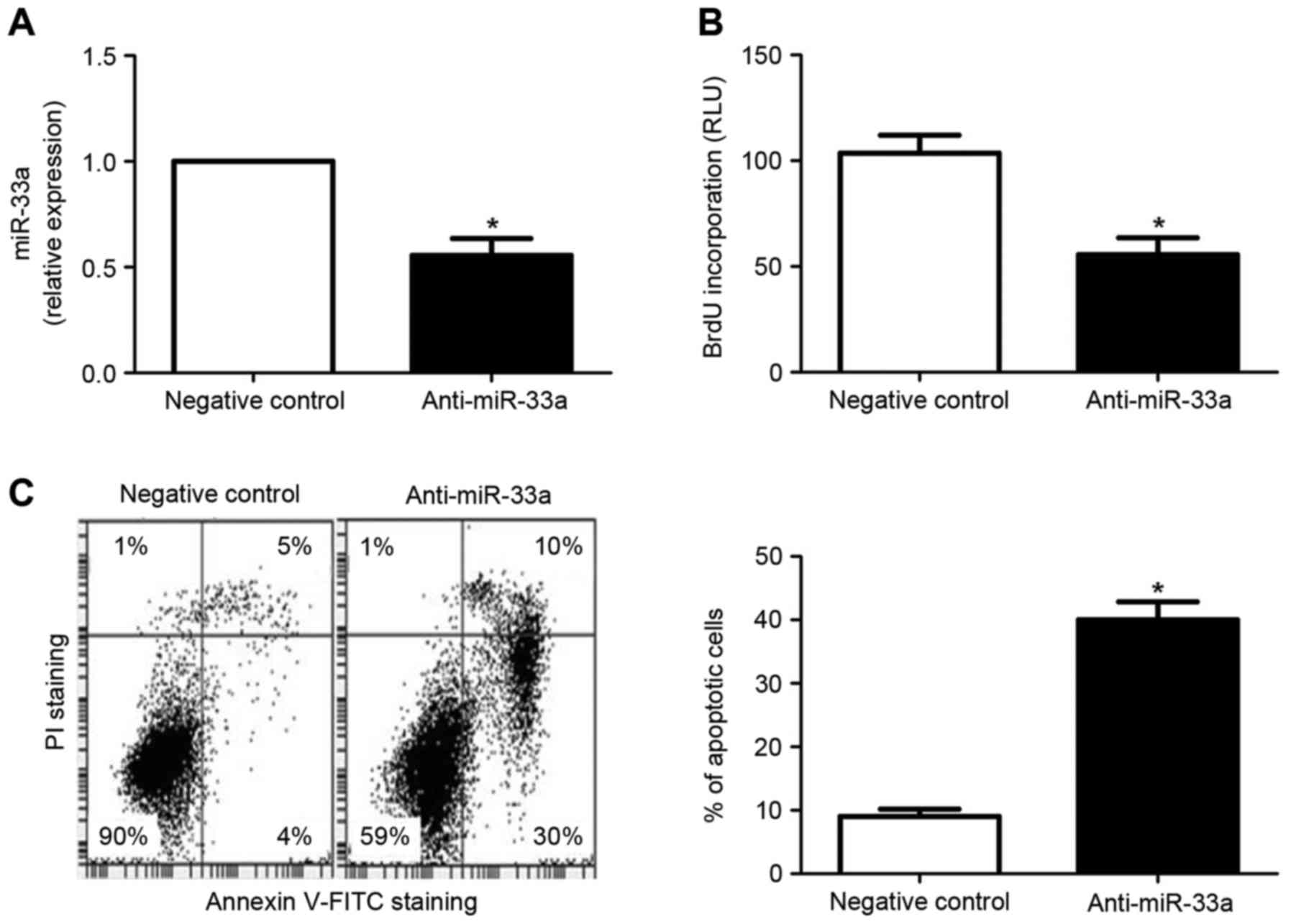
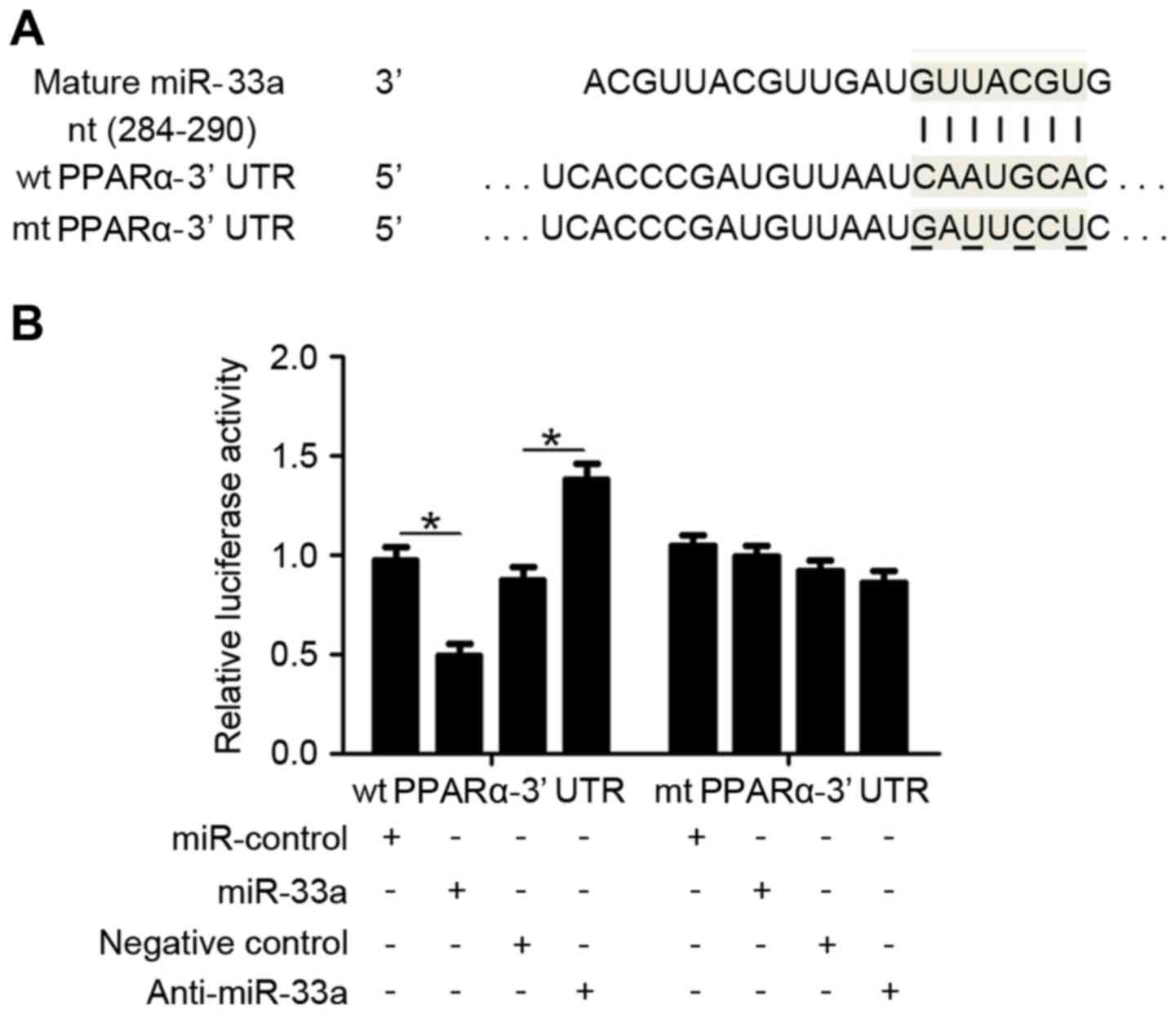
|
1
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJ: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Osman A: MicroRNAs in health and
disease-basic science and clinical applications. Clin Lab.
58:393–402. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rottiers V and Näär AM: MicroRNAs in
metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
13:239–250. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA and Ray SD:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: New perspectives on
therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:62–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dhanasekaran R, Limaye A and Cabrera R:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current trends in worldwide epidemiology,
risk factors, diagnosis, and therapeutics. Hepat Med. 4:19–37.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ and Cressman EN:
Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
48:2047–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tanaka S and Arii S: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 39:486–492.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cirera-Salinas D, Pauta M, Allen RM,
Salerno AG, Ramírez CM, Chamorro-Jorganes A, Wanschel AC, Lasuncion
MA, Morales-Ruiz M, Suarez Y, et al: Mir-33 regulates cell
proliferation and cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle. 11:922–933.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li T, Francl JM, Boehme S and Chiang JY:
Regulation of cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis by the
cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase/steroid response element-binding protein
2/microRNA-33a axis in mice. Hepatology. 58:1111–1121. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo F, Li Y,
Shioda T, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE and Näär AM: MicroRNA-33 and the
SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis.
Science. 328:1566–1569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ramírez CM, Goedeke L, Rotllan N, Yoon JH,
Cirera-Salinas D, Mattison JA, Suárez Y, de Cabo R, Gorospe M and
Fernández-Hernando C: MicroRNA 33 regulates glucose metabolism. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:2891–2902. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang C, Yu XJ, Guo XZ, Sun MH, Wang Z,
Song Y, Ni QX, Li HY, Mukaida N and Li YY: MicroRNA-33a-mediated
downregulation of Pim-3 kinase expression renders human pancreatic
cancer cells sensitivity to gemcitabine. Oncotarget. 6:14440–14455.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang C, Wang Z, Li YY, Yu BH, Zhang F and
Li HY: miR-33a suppresses the nuclear translocation of β-catenin to
enhance gemcitabine sensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 36:9395–9403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuo PL, Liao SH, Hung JY, Huang MS and Hsu
YL: MicroRNA-33a functions as a bone metastasis suppressor in lung
cancer by targeting parathyroid hormone related protein. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:3756–3766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang H, Sun T, Hu J, Zhang R, Rao Y, Wang
S, Chen R, McLendon RE, Friedman AH, Keir ST, et al: miR-33a
promotes glioma-initiating cell self-renewal via PKA and NOTCH
pathways. J Clin Invest. 124:4489–4502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang T, Han G, Wang Y, Chen K and Sun Y:
MicroRNA expression profiles in supraglottic carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
31:2029–2034. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Huang Z, Wu S, Zang X, Liu M and
Shi J: miR-33a is up-regulated in chemoresistant osteosarcoma and
promotes osteosarcoma cell resistance to cisplatin by
down-regulating TWIST. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lendvai G, Jármay K, Karácsony G, Halász
T, Kovalszky I, Baghy K, Wittmann T, Schaff Z and Kiss A: Elevated
miR-33a and miR-224 in steatotic chronic hepatitis C liver
biopsies. World J Gastroenterol. 20:15343–15350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang CF, Sun CC, Zhao F, Zhang YD and Li
DJ: miR-33a levels in hepatic and serum after chronic HBV-induced
fibrosis. J Gastroenterol. 50:480–490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
World Medical Association, . World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, Lobo N,
Dalerba P, Qian D, Diehn M, Liu H, Panula SP, Chiao E, et al:
Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with
normal stem cells. Cell. 138:592–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang N, Chu ES, Zhang J, Li X, Liang Q,
Chen J, Chen M, Teoh N, Farrell G, Sung JJ and Yu J: Peroxisome
proliferator activated receptor alpha inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis
through mediating NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 5:8330–8340.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lujambio A and Lowe SW: The microcosmos of
cancer. Nature. 482:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cho WC: MicroRNAs: Potential biomarkers
for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and targets for therapy. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1273–1281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dávalos A, Goedeke L, Smibert P, Ramírez
CM, Warrier NP, Andreo U, Cirera-Salinas D, Rayner K, Suresh U,
Pastor-Pareja JC, et al: miR-33a/b contribute to the regulation of
fatty acid metabolism and insulin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:9232–9237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou Y, Huang ZF, Wu S, Zang XF, Liu M and
Shi J: miR-33a is up-regulated in chemoresistant osteosarcoma and
promotes osteosarcoma cell resistance to cisplatin by
down-regulating TWIST. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 33:122014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M,
Grünweller A, Hartmann RK and Aigner A: MicroRNA replacement
therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:5214–5224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lefebvre P, Chinetti G, Fruchart JC and
Staels B: Sorting out the roles of PPAR alpha in energy metabolism
and vascular homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 116:571–580. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grau R, Punzón C, Fresno M and Iñiguez MA:
Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonists inhibit
cyclo-oxygenase 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor
transcriptional activation in human colorectal carcinoma cells via
inhibition of activator protein-1. Biochem J. 395:81–88. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yokoyama Y, Xin B, Shigeto T, Umemoto M,
Kasai-Sakamoto A, Futagami M, Tsuchida S, Al-Mulla F and Mizunuma
H: Clofibric acid, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
alpha ligand, inhibits growth of human ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:1379–1386. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|