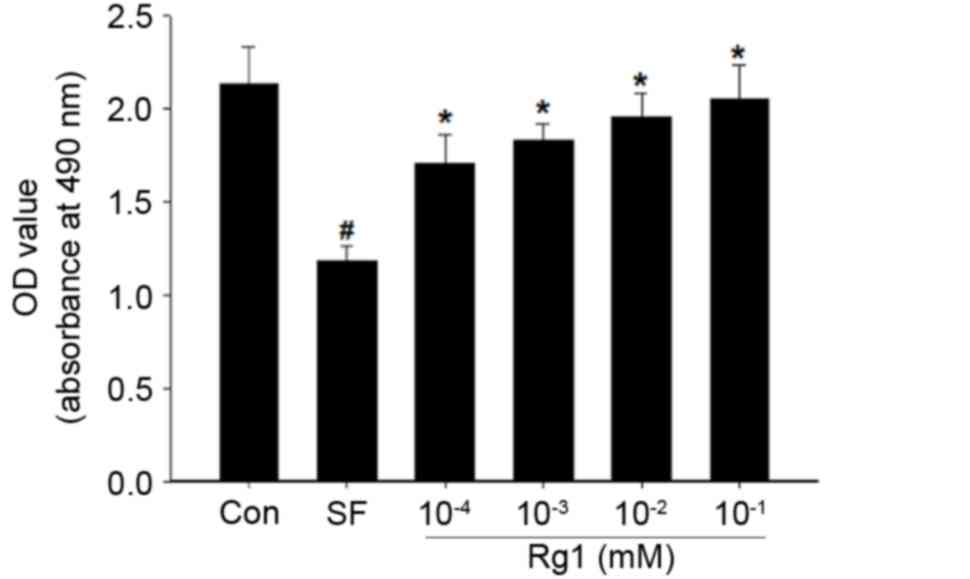
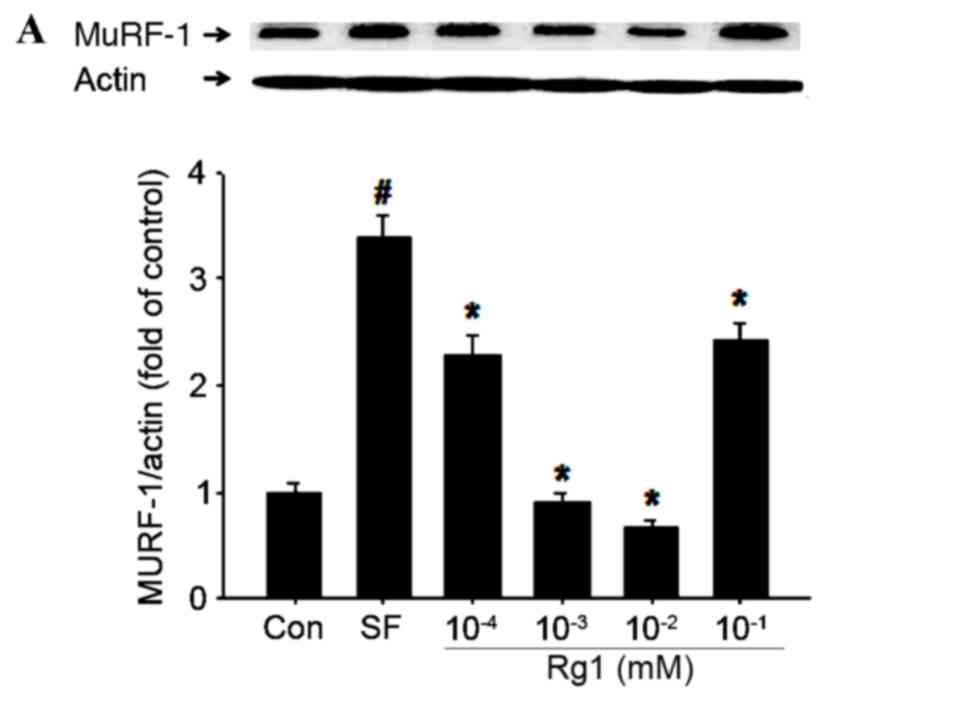
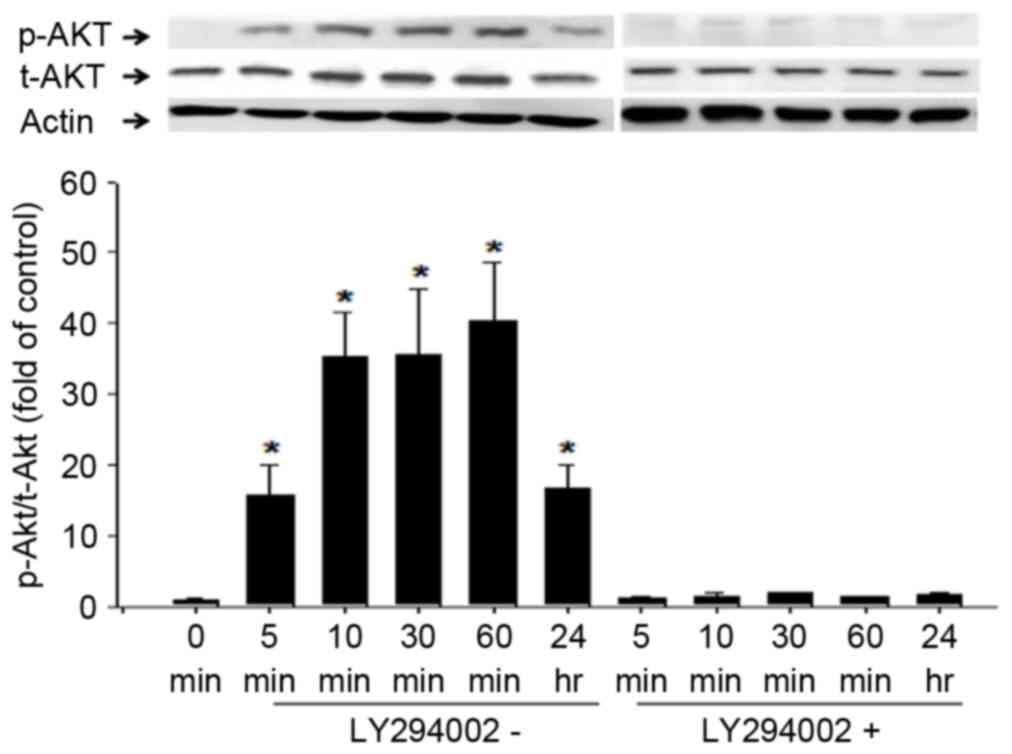
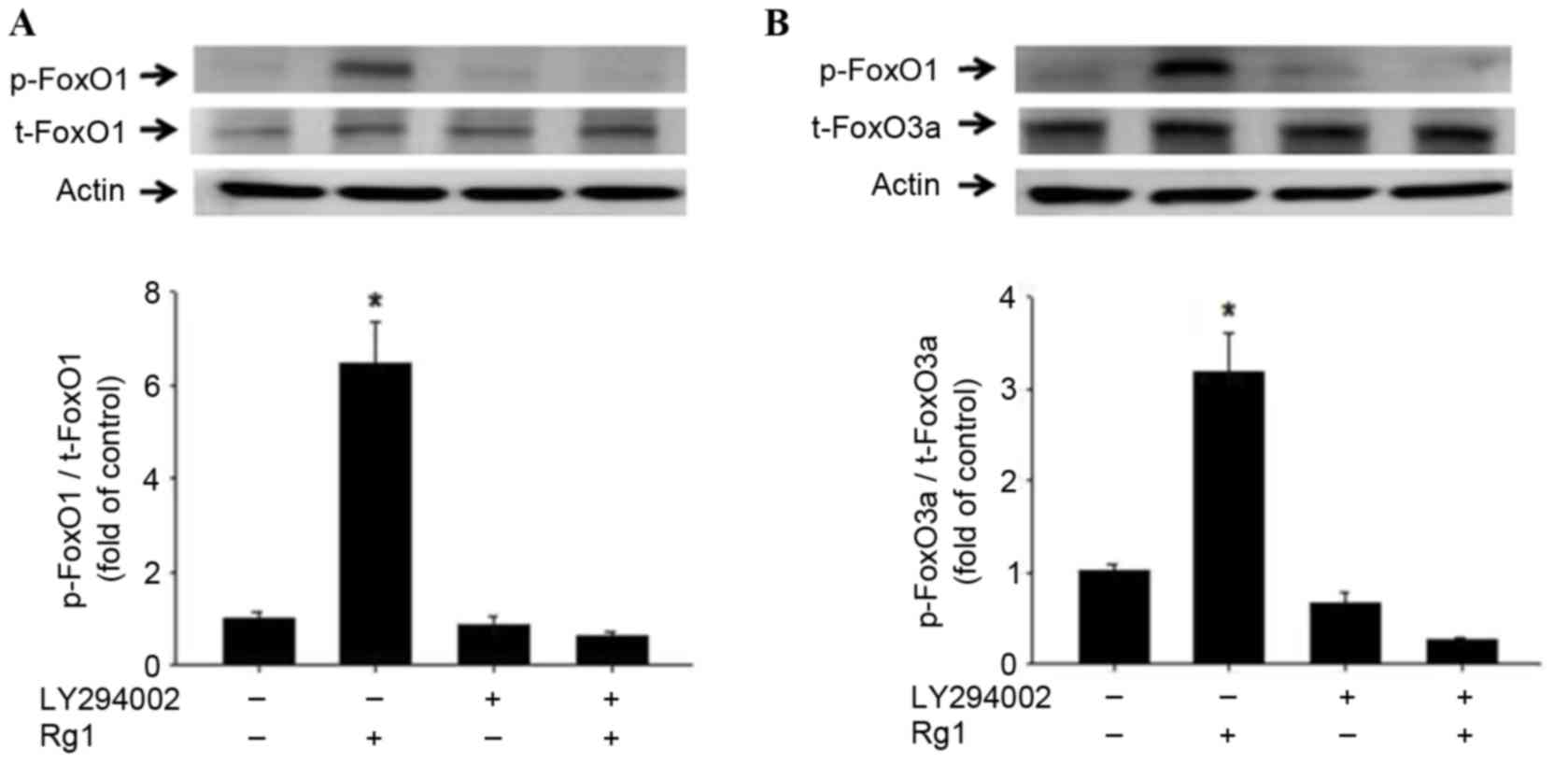
|
1
|
Kawai N, Hirasaka K, Maeda T, Haruna M,
Shiota C, Ochi A, Abe T, Kohno S, Ohno A, Teshima-Kondo S, et al:
Prevention of skeletal muscle atrophy in vitro using
anti-ubiquitination oligopeptide carried by atelocollagen. Biochim
Biophy Acta. 1853:873–880. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Langen RC, Gosker HR, Remels AH and Schols
AM: Triggers and mechanisms of skeletal muscle wasting in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2245–2256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Joassard OR, Durieux AC and Freyssenet DG:
β2-Adrenergic agonists and the treatment of skeletal muscle wasting
disorders. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2309–2321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang DT, Yin Y, Yang YJ, Lv PJ, Shi Y, Lu
L and Wei LB: Resveratrol prevents TNF-α-induced muscle atrophy via
regulation of Akt/mTOR/FoxO1 signaling in C2C12 myotubes. Int
Immunopharmacol. 19:206–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Gilbert A, Gomes M,
Baracos V, Bailey J, Price SR, Mitch WE and Goldberg AL: Multiple
types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of
changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 18:39–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Langen RC, Gosker HR, Remels AH and Schols
AM: Triggers and mechanisms of skeletal muscle wasting in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2245–2256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feng W, Tu JC, Pouliquin P, Cabrales E,
Shen X, Dulhunty A, Worley PF, Allen PD and Pessah IN: Dynamic
regulation of ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1) channel activity by
Homer 1. Cell Calcium. 43:307–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Joassard OR, Amirouche A, Gallot YS,
Desgeorges MM, Castells J, Durieux AC, Berthon P and Freyssenet DG:
Regulation of Akt-mTOR, ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome
pathways in response to formoterol administration in rat skeletal
muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2444–2455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sandri M: Protein breakdown in muscle
wasting: Role of autophagy-lysosome and ubiquitin-proteasome. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2121–2129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kawai N, Hirasaka K, Maeda T, Haruna M,
Shiota C, Ochi A, Abe T, Kohno S, Ohno A, Teshima-Kondo S, et al:
Prevention of skeletal muscle atrophy in vitro using
anti-ubiquitination oligopeptide carried by atelocollagen. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1853:873–880. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kazi AA, Hong-Brown L, Lang SM and Lang
CH: Deptor knockdown enhances mTOR activity and protein synthesis
in myocytes and ameliorates disuse muscle atrophy. Mol Med.
17:925–936. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng B, Ohkawa S, Li HY, Roberts-Wilson
TK and Price SR: FOXO3a mediates signaling crosstalk that
coordinates ubiquitin and atrogin-1/MAFbx expression during
glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. FASEB J.
24:2660–2669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
You JS, Lincoln HC, Kim CR, Frey JW,
Goodman CA, Zhong XP and Hornberger TA: The role of diacylglycerol
kinase ζ and phosphatidic acid in the mechanical activation of
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and skeletal muscle
hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 289:1551–1563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moylan JS, Smith JD, Chambers MA,
McLoughlin TJ and Reid MB: TNF induction of atrogin-1/MAFbx mRNA
depends on Foxo4 expression but not AKT-Foxo1/3 signaling. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C986–C993. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tisdale MJ: The ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway as a therapeutic target for muscle wasting. J Support
Oncol. 3:209–217. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Argiles JA, López-Soriano FJ and Busquets
S: Apoptosis signalling is essential and precedes protein
degradation in wasting skeletal muscle during catabolic conditions.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1674–1678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wray CJ, Mammen JM, Hershko DD and
Hasselgren PO: Sepsis upregulates the gene expression of multiple
ubiquitin ligases in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
35:698–705. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tong JF, Yan X, Zhu MJ and Du M:
AMP-activated protein kinase enhances the expression of
muscle-specific ubiquitin ligases despite its activation of
IGF-1/Akt signaling in C2C12 myotubes. J Cell Biochem. 108:458–468.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hershko A and Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin
system. Annu Rev Biochem. 67:425–479. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Argilés JM, López-Soriano FJ and Busquets
S: Apoptosis signalling is essential and precedes protein
degradation in wasting skeletal muscle during catabolic conditions.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1674–1678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, Panaro F,
Timofeyva Y, Kline WO, Gonzalez M, Yancopoulos GD and Glass DJ: The
IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle
atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription
factors. Mol Cell. 14:395–403. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C,
Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg
AL: Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin
ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell.
117:399–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baviera AM, Zanon NM, Navegantes LC and
Kettelhut IC: Involvement of cAMP/Epac/PI3K-dependent pathway in
the antiproteolytic effect of epinephrine on rat skeletal muscle.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 315:104–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sharp ZD and Bartke A: Evidence for
down-regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target
of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR)-dependent translation regulatory
signaling pathways in Ames dwarf mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med
Sci. 60:293–300. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goodman CA, Mayhew DL and Hornberger TA:
Recent progress toward understanding the molecular mechanisms that
regulate skeletal muscle mass. Cell Signal. 23:1896–1906. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kimura K, Cheng XW, Inoue A, Hu LN, Koike
T and Kuzuya M: β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate facilitates
PI3K/Akt-dependent mammalian target of rapamycin and FoxO1/3a
phosphorylations and alleviates tumor necrosis factor α/interferon
γ-induced MuRF-1 expression in C2C12 cells. Nutr Res. 34:368–374.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jia L, Li YF, Wu GF, Song ZY, Lu HZ, Song
CC, Zhang QL, Zhu JY, Yang GS and Shi XE: MiRNA-199a-3p regulates
C2C12 myoblast differentiation through IGF-1/AKT/ mTOR signal
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 15:296–308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Risson V, Mazelin L, Roceri M, Sanchez H,
Moncollin V, Corneloup C, Richard-Bulteau H, Vignaud A, Baas D,
Defour A, et al: Muscle inactivation of mTOR causes metabolic and
dystrophin defects leading to severe myopathy. J Cell Biol.
187:859–874. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sievenpiper JL, Arnason JT, Leiter LA and
Vuksan V: Variable effects of American ginseng: A batch of American
ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) with a depressed ginsenoside
profile does not affect postprandial glycemia. Eur J Clin Nutr.
57:243–248. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Um JY, Chung HS, Kim MS, Na HJ, Kwon HJ,
Kim JJ, Lee KM, Lee SJ, Lim JP, Do KR, et al: Molecular
authentication of Panax ginseng species by RAPD analysis and
PCR-RFLP. Biol Pharm Bull. 24:872–875. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hou CW, Lee SD, Kao CL, Cheng IS, Lin YN,
Chuang SJ, Chen CY, Ivy JL, Huang CY and Kuo CH: Improved
inflammatory balance of human skeletal muscle during exercise after
supplementations of the ginseng-based steroid Rg1. PLoS One.
10:e01163872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu SH, Huang HY, Korivi M, Hsu MF, Huang
CY, Hou CW, Chen CY, Kao CL, Lee RP, Lee SD and Kuo CH: Oral Rg1
supplementation strengthens antioxidant defense system against
exercise-induced oxidative stress in rat skeletal muscles. J Int
Soc Sport Nutr. 9:232012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang XD, Yang YY, Ouyang DS and Yang GP: A
review of biotransformation and pharmacology of ginsenoside
compound K. Fitoterapia. 100:208–220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu QF, Deng ZY, Ye JM, He AL and Li SS:
Ginsenoside Rg1 protects chronic cyclosporin a nephropathy from
tubular cell apoptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
in rats. Transplant Proc. 47:pp. 566–569. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim WK, Song SY, Oh WK, Kaewsuwan S, Tran
TL, Kim WS and Sung JH: Wound-healing effect of ginsenoside Rd from
leaves of Panax ginseng via cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase
pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 702:285–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qi B, Liu L, Zhang H, Zhou GX, Wang S,
Duan XZ, Bai XY, Wang SM and Zhao DQ: Anti-fatigue effects of
proteins isolated from Panax quinquefolium. J Ethnopharmacol.
153:430–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhuang CL, Mao XY, Liu S, Chen WZ, Huang
DD, Zhang CJ, Chen BC, Shen X and Yu Z: Ginsenoside Rb1 improves
postoperative fatigue syndrome by reducing skeletal muscle
oxidative stress through activation of the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway in
aged rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 740:480–487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wei HJ, Yang HH, Chen CH, Lin WW, Chen SC,
Lai PH, Chang Y and Sung HW: Gelatin microspheres encapsulated with
a nonpeptide angiogenic agent, ginsenoside Rg1, for intramyocardial
injection in a rat model with infarcted myocardium. J Control
Release. 120:27–34. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sato S, Ogura Y and Kumar A: TWEAK/Fn14
signaling axis mediates skeletal muscle atrophy and metabolic
dysfunction. Front Immunol. 5:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Argilés JM, López-Soriano FJ and Busquets
S: Apoptosis signalling is essential and precedes protein
degradation in wasting skeletal muscle during catabolic conditions.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1674–1678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thomas MP, Mills J and Engelbrecht AM:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) activity decreases in C2C12
myotubes during acute simulated ischemia at a cost to their
survival. Life Sci. 91:44–53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Giresi PG, Stevenson EJ, Theilhaber J,
Koncarevic A, Parkington J, Fielding RA and Kandarian SC:
Identification of a molecular signature of sarcopenia. Physiol
Genomics. 21:253–263. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kandarian SC and Jackman RW: Intracellular
signaling during skeletal muscle atrophy. Muscle Nerve. 33:155–165.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schulze PC, Fang J, Kassik KA, Gannon J,
Cupesi M, MacGillivray C, Lee RT and Rosenthal N: Transgenic
overexpression of locally acting insulin-like growth factor-1
inhibits ubiquitin-mediated muscle atrophy in chronic
left-ventricular dysfunction. Circ Res. 97:418–426. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim WK, Song SY, Oh WK, Kaewsuwan S, Tran
TL, Kim WS and Sung JH: Wound-healing effect of ginsenoside Rd from
leaves of Panax ginseng via cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase
pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 702:285–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Attele AS, Wu JA and Yuan CS: Ginseng
pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem
Pharmacol. 58:1685–1693. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen X: Cardiovascular protection by
ginsenosides and their nitric oxide releasing action. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 23:728–732. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gillis CN: Panax ginseng pharmacology: A
nitric oxide link? Biochem Pharmacol. 54:1–8. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nag SA, Qin JJ, Wang W, Wang MH, Wang H
and Zhang R: Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: In vitro and in
vivo activities, structure-activity relationships and molecular
mechanisms of action. Front Pharmacol. 3:252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xie JT, Mehendale S and Yuan CS: Ginseng
and diabetes. Am J Chin Med. 33:397–404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hwang JT, Kim SH, Lee MS, Kim SH, Yang HJ,
Kim MJ, Kim HS, Ha J, Kim MS and Kwon DY: Anti-obesity effects of
ginsenoside Rh2 are associated with the activation of AMPK
signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
364:1002–1008. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cho WC, Chung WS, Lee SK, Leung AW, Cheng
CH and Yue KK: Ginsenoside Re of Panax ginseng possesses
significant antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic efficacies in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 550:173–179.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shang W, Yang Y, Zhou L, Jiang B, Jin H
and Chen M: Ginsenoside Rb1 stimulates glucose uptake through
insulin-like signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Endocrinol.
198:561–569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Song Z, Moser C, Wu H, Faber V, Kharazmi A
and Høiby N: Cytokine modulating effect of ginseng treatment in a
mouse model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. J Cyst
Fibros. 2:112–119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee E, Ko E, Lee J, Rho S, Ko S, Shin MK,
Min BI, Hong MC, Kim SY and Bae H: Ginsenoside Rg1 enhances CD4(+)
T-cell activities and modulates Th1/Th2 differentiation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 4:235–244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Foletta VC, White LJ, Larsen AE, Léger B
and Russell AP: The role and regulation of MAFbx/atrogin-1 and
MuRF1 in skeletal muscle atrophy. Pflugers Arch. 461:325–335. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jagoe RT and Goldberg AL: What do we
really know about the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in muscle
atrophy? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 4:183–190. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wray CJ, Mammen JM, Hershko DD and
Hasselgren PO: Sepsis upregulates the gene expression of multiple
ubiquitin ligases in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
35:698–705. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hershko A: The ubiquitin system. Springer
US; 1998
|
|
60
|
Krawiec BJ, Nystrom GJ, Frost RA,
Jefferson LS and Lang CH: AMP-activated protein kinase agonists
increase mRNA content of the muscle-specific ubiquitin ligases
MAFbx and MuRF1 in C2C12 cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
292:E1555–E1567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Baehr LM, Furlow JD and Bodine SC: Muscle
sparing in muscle RING finger 1 null mice: Response to synthetic
glucocorticoids. J Physiol. 589:4759–4776. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cong H, Sun L, Liu C and Tien P:
Inhibition of atrogin-1/MAFbx expression by adenovirus-delivered
small hairpin RNAs attenuates muscle atrophy in fasting mice. Hum
Gene Ther. 22:313–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Polge C, Heng AE, Jarzaguet M, Ventadour
S, Claustre A, Combaret L, Béchet D, Matondo M, Uttenweiler-Joseph
S, Monsarrat B, et al: Muscle actin is polyubiquitinylated in vitro
and in vivo and targeted for breakdown by the E3 ligase MuRF1.
FASEB J. 25:3790–3802. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Clarke BA, Drujan D, Willis MS, Murphy LO,
Corpina RA, Burova E, Rakhilin SV, Stitt TN, Patterson C, Latres E
and Glass DJ: The E3 Ligase MuRF1 degrades myosin heavy chain
protein in dexamethasone-treated skeletal muscle. Cell Metab.
6:376–385. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fielitz J, Kim MS, Shelton JM, Latif S,
Spencer JA, Glass DJ, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN:
Myosin accumulation and striated muscle myopathy result from the
loss of muscle RING finger 1 and 3. J Clin Invest. 117:2486–2495.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kedar V, McDonough H, Arya R, Li HH,
Rockman HA and Patterson C: Muscle-specific RING finger 1 is a bona
fide ubiquitin ligase that degrades cardiac troponin I. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:pp. 18135–18140. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cohen S, Brault JJ, Gygi SP, Glass DJ,
Valenzuela DM, Gartner C, Latres E and Goldberg AL: During muscle
atrophy, thick, but not thin, filaments components are degraded by
MuRF1-dependent ubiquitylation. J Cell Biol. 185:1083–1095. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Csibi A, Cornille K, Leibovitch MP, Poupon
A, Tintignac LA, Sanchez AM and Leibovitch SA: The translation
regulatory subunit eIF3f controls the kinase-dependent mTOR
signaling required for muscle differentiation and hypertrophy in
mouse. PLoS One. 5:e89942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tintignac LA, Lagirand J, Batonnet S,
Sirri V, Leibovitch MP and Leibovitch SA: Degradation of MyoD
mediated by the SCF (MAFbx) ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem.
280:2847–2856. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Du J, Wang X, Miereles C, Bailey JL,
Debigare R, Zheng B, Price SR and Mitch WE: Activation of caspase-3
is an initial step triggering accelerated muscle proteolysis in
catabolic conditions. J Clin Invest. 113:115–123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|