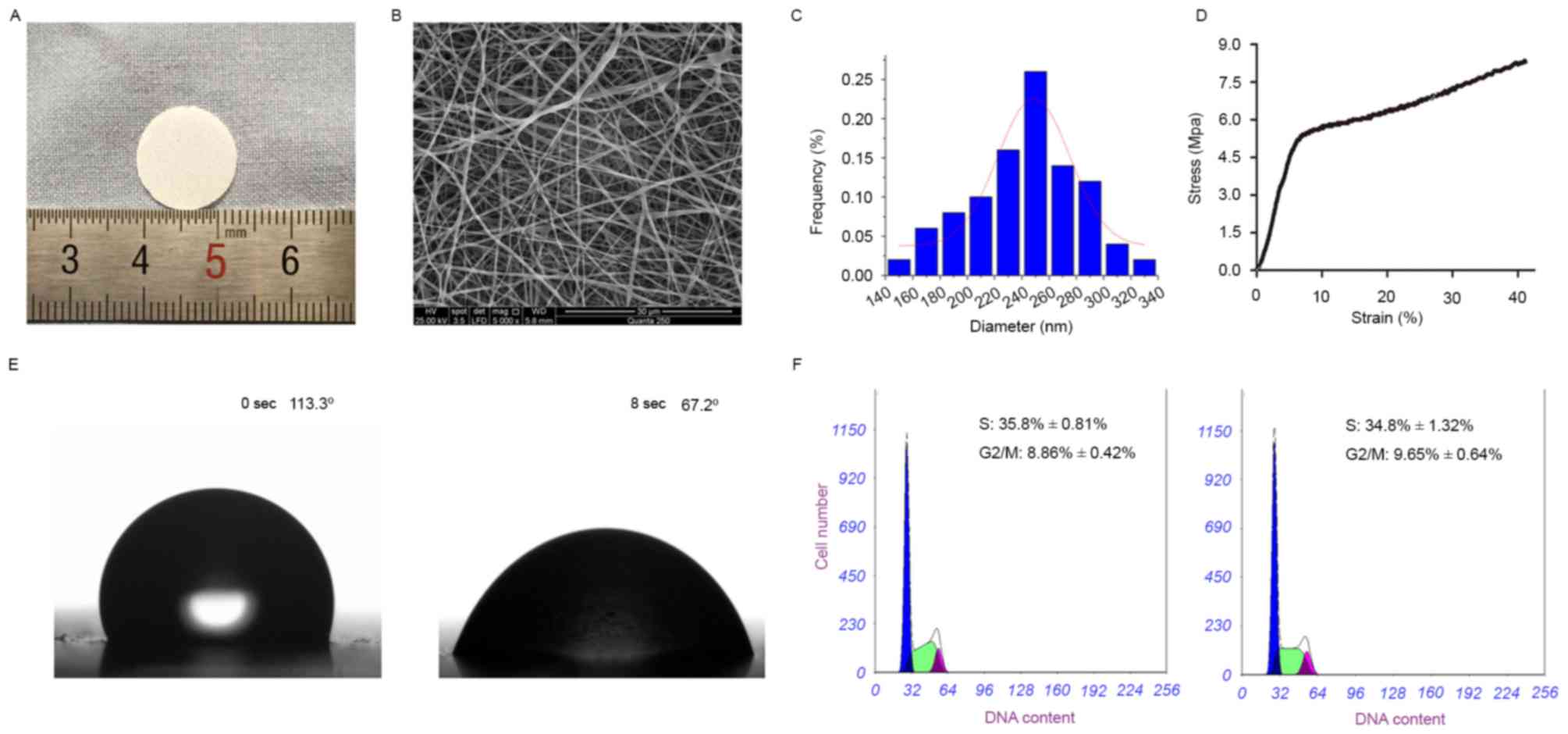
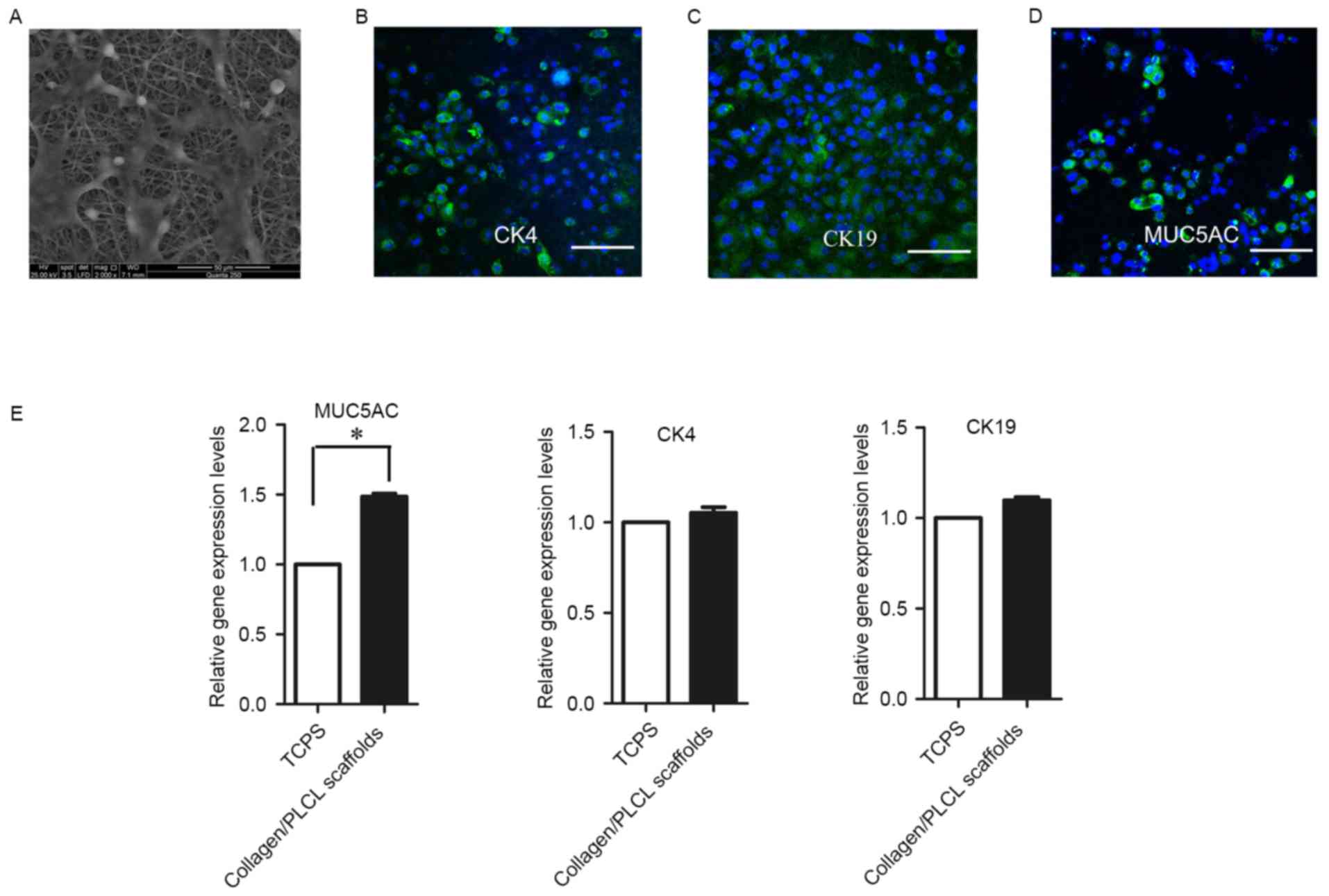
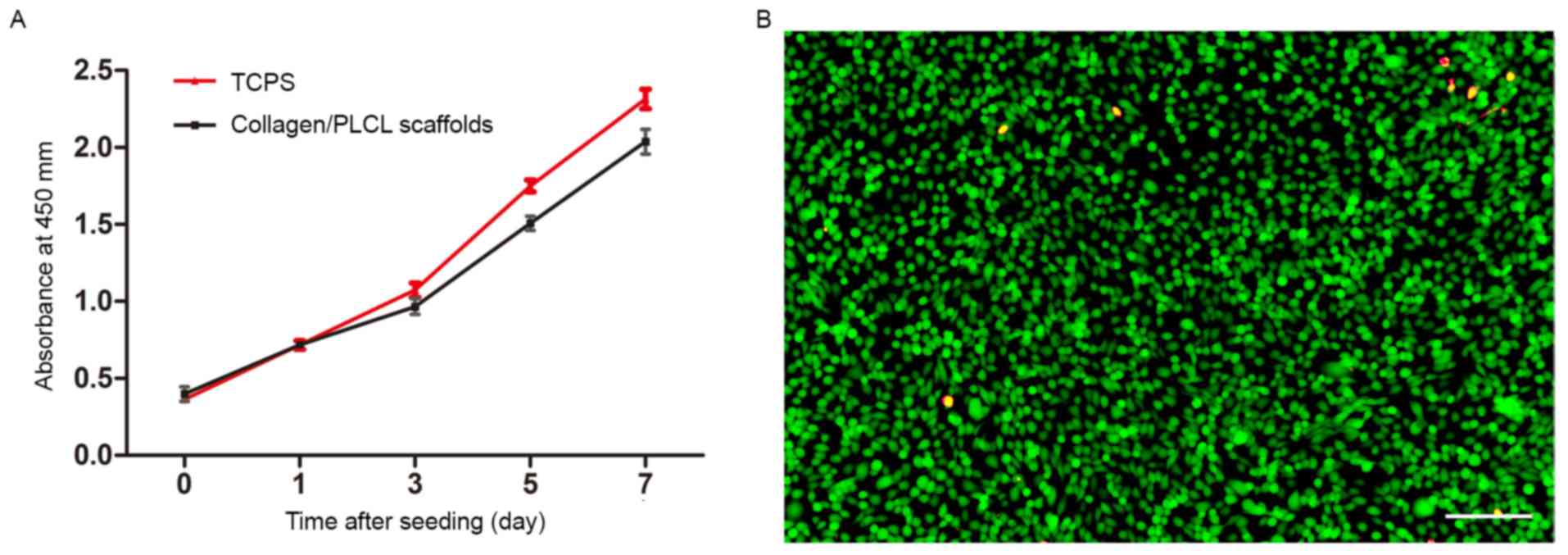
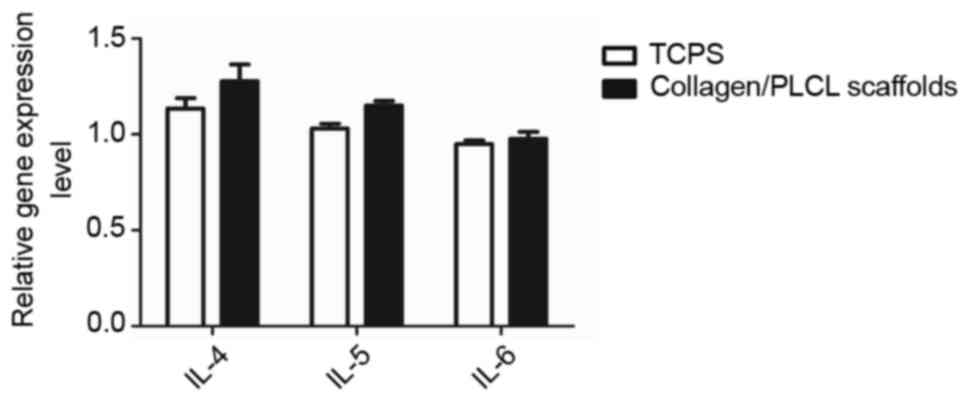
|
1
|
Eidet JR, Fostad IG, Shatos MA, Utheim TP,
Utheim ØA, Raeder S and Dartt DA: Effect of biopsy location and
size on proliferative capacity of ex vivo expanded conjunctival
tissue. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:2897–2903. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mason SL, Stewart RM, Kearns VR, Williams
RL and Sheridan CM: Ocular epithelial transplantation: Current uses
and future potential. Regen Med. 6:767–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
García-Posadas L, Arranz-Valsero I,
López-García A, Soriano-Romaní L and Diebold Y: A new human primary
epithelial cell culture model to study conjunctival inflammation.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:7143–7152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schrader S, Notara M, Beaconsfield M, Tuft
S, Geerling G and Daniels JT: Conjunctival epithelial cells
maintain stem cell properties after long-term culture and
cryopreservation. Regen Med. 4:677–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou H, Lu Q, Guo Q, Chae J, Fan X,
Elisseeff JH and Grant MP: Vitrified collagen-based conjunctival
equivalent for ocular surface reconstruction. Biomaterials.
35:7398–7406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schrader S, Notara M, Beaconsfield M, Tuft
SJ, Daniels JT and Geerling G: Tissue engineering for conjunctival
reconstruction: Established methods and future outlooks. Curr Eye
Res. 34:913–924. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Selvam S, Thomas PB and Yiu SC: Tissue
engineering: Current and future approaches to ocular surface
reconstruction. Ocul Surf. 4:120–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rama P, Bonini S, Lambiase A, Golisano O,
Paterna P, De Luca M and Pellegrini G: Autologous fibrin-cultured
limbal stem cells permanently restore the corneal surface of
patients with total limbal stem cell deficiency. Transplantation.
72:1478–1485. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu WC, Spilker MH, Yannas IV and Rubin
PA: Inhibition of conjunctival scarring and contraction by a porous
collagen-glycosaminoglycan implant. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
41:2404–2411. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ye J, Shi X, Chen X, Xie J, Wang C, Yao K,
Gao C and Gou Z: Chitosan-modified, collagen-based biomimetic
nanofibrous membranes as selective cell adhering wound dressings in
the treatment of chemically burned corneas. J Mater Chem B.
2:4226–4236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen H, Fan X, Xia J, Chen P, Zhou X,
Huang J, Yu J and Gu P: Electrospun chitosan-graft-poly
(ε-caprolactone)/poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffolds for
retinal tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:453–461.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang K, Wang H, Huang C, Su Y, Mo X and
Ikada Y: Fabrication of silk fibroin blended P(LLA-CL) nanofibrous
scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 93:984–993.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Freyria AM, Ronzière MC, Cortial D, Galois
L, Hartmann D, Herbage D and Mallein-Gerin F: Comparative
phenotypic analysis of articular chondrocytes cultured within type
I or type II collagen scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A. 15:1233–1245.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He X, Fu W, Feng B, Wang H, Liu Z, Yin M,
Wang W and Zheng J: Electrospun collagen-poly(L-lactic
acid-co-ε-caprolactone) membranes for cartilage tissue engineering.
Regen Med. 8:425–436. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim BS and Mooney DJ: Development of
biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue
engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 16:224–230. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu W, Liu Z, Feng B, Hu R, He X, Wang H,
Yin M, Huang H, Zhang H and Wang W: Electrospun gelatin/PCL and
collagen/PLCL scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Int J
Nanomedicine. 9:2335–2344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yin A, Zhang K, McClure MJ, Huang C, Wu J,
Fang J, Mo X, Bowlin GL, Al-Deyab SS and El-Newehy M:
Electrospinning collagen/chitosan/poly(L-lactic
acid-co-epsilon-caprolactone) to form a vascular graft: Mechanical
and biological characterization. J Biomed Mater Res A.
101:1292–1301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Yan C, Zhu M, Yao Q, Shao C, Lu W,
Wang J, Mo X, Gu P, Fu Y and Fan X: Electrospun nanofibrous
SF/P(LLA-CL) membrane: A potential substratum for endothelial
keratoplasty. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:3337–3350. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao Q, Zhu M, Chen J, Shao C, Yan C, Wang
Z, Fan X, Gu P and Fu Y: Reconstruction of conjunctival
epithelium-like tissue using a temperature-responsive culture dish.
Mol Vis. 21:1113–1121. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang D, Ni N, Chen J, Yao Q, Shen B,
Zhang Y, Zhu M, Wang Z, Ruan J, Wang J, et al: Electrospun SF/PLCL
nanofibrous membrane: A potential scaffold for retinal progenitor
cell proliferation and differentiation. Sci Rep. 5:143262015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gipson IK: The ocular surface: The
challenge to enable and protect vision: The Friedenwald lecture.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 48:4390–4398. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elisseeff J, Ferran A, Hwang S, Varghese S
and Zhang Z: The role of biomaterials in stem cell differentiation:
Applications in the musculoskeletal system. Stem Cells Dev.
15:295–303. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vasita R and Katti DS: Nanofibers and
their applications in tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine.
1:15–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian L, Qu M, Wang Y, Duan H, Di G, Xie L
and Zhou Q: Inductive differentiation of conjunctival goblet cells
by γ-secretase inhibitor and construction of recombinant
conjunctival epithelium. Exp Eye Res. 123:37–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dogru M, Okada N, Asano-Kato N, Tanaka M,
Igarashi A, Takano Y, Fukagawa K, Shimazaki J, Tsubota K and
Fujishima H: Atopic ocular surface disease: Implications on tear
function and ocular surface mucins. Cornea. 24 (8 Suppl):S18–S23.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng X, Ma P, de Paiva CS, Cunningham MA,
Hwang CS, Pflugfelder SC and Li DQ: TSLP and downstream molecules
in experimental mouse allergic conjunctivitis. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 51:3076–3082. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Barisani-Asenbauer T, Inic-Kanada A, Belij
S, Marinkovic E, Stojicevic I, Montanaro J, Stein E, Bintner N and
Stojanovic M: The ocular conjunctiva as a mucosal immunization
route: A profile of the immune response to the model antigen
tetanus toxoid. PLoS One. 8:e606822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|