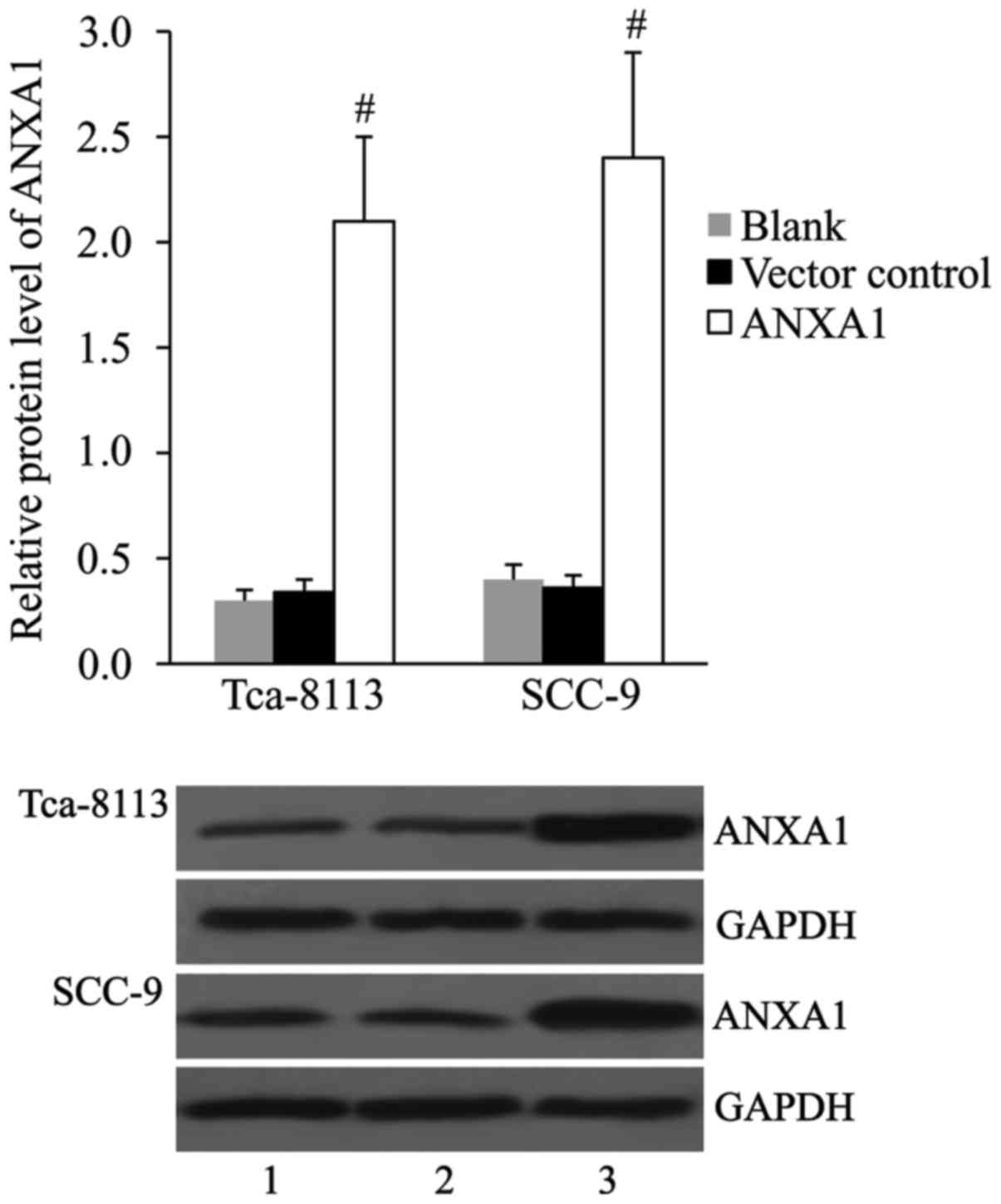
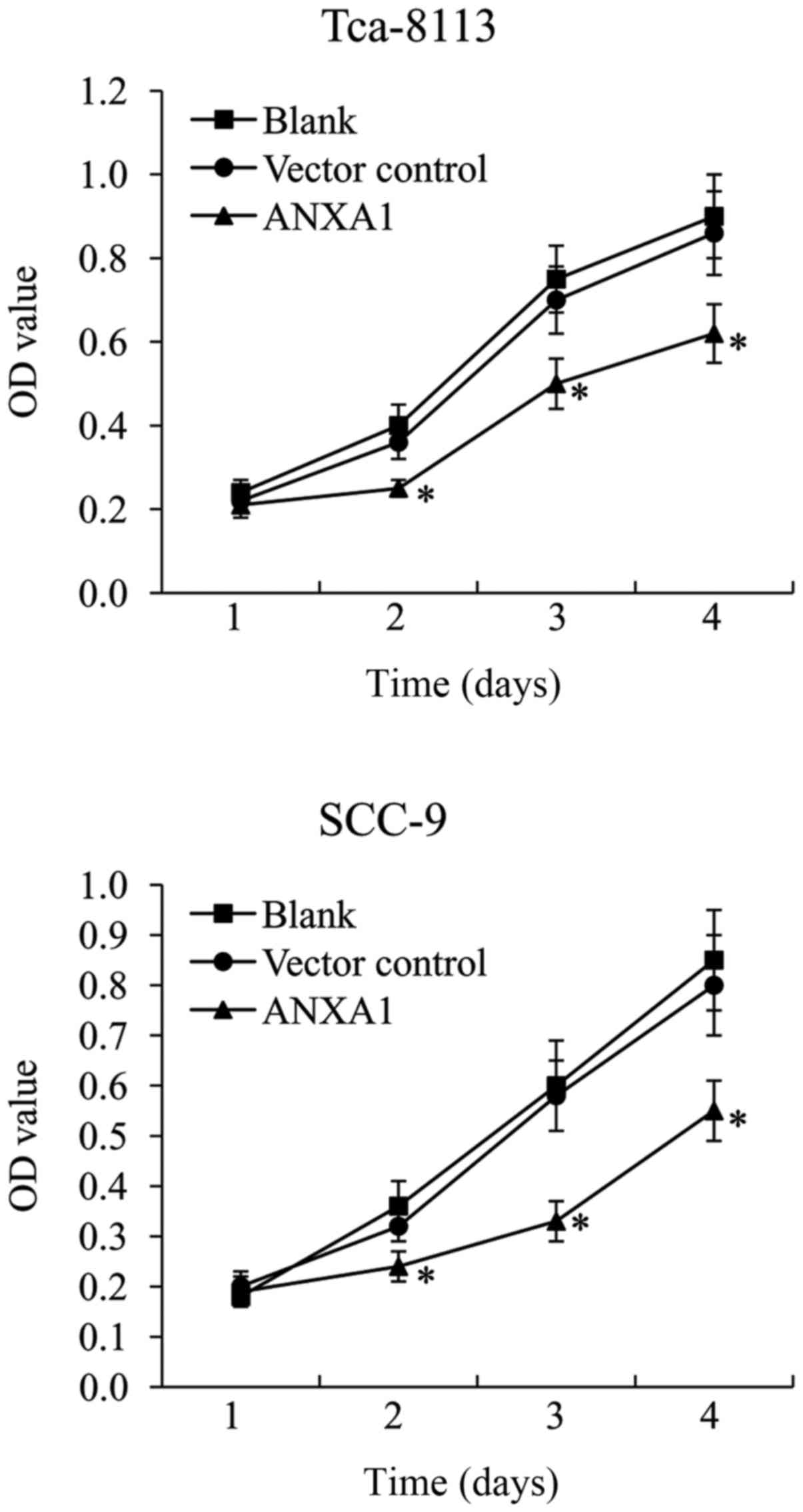
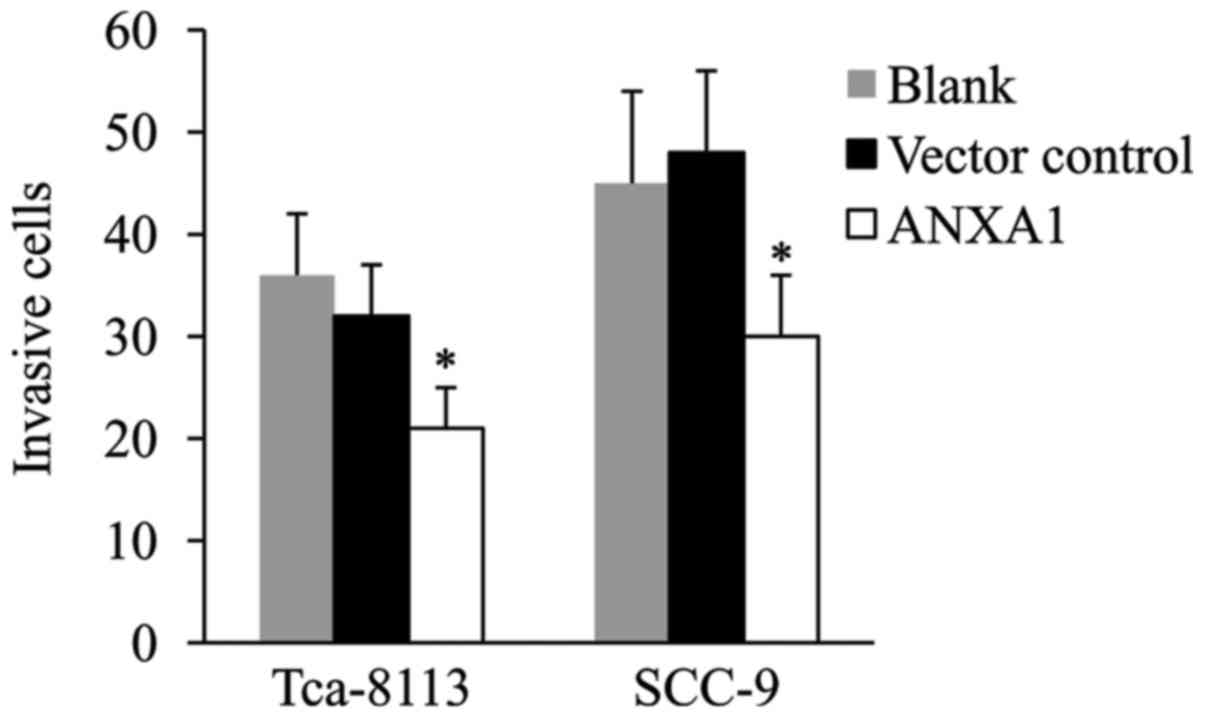
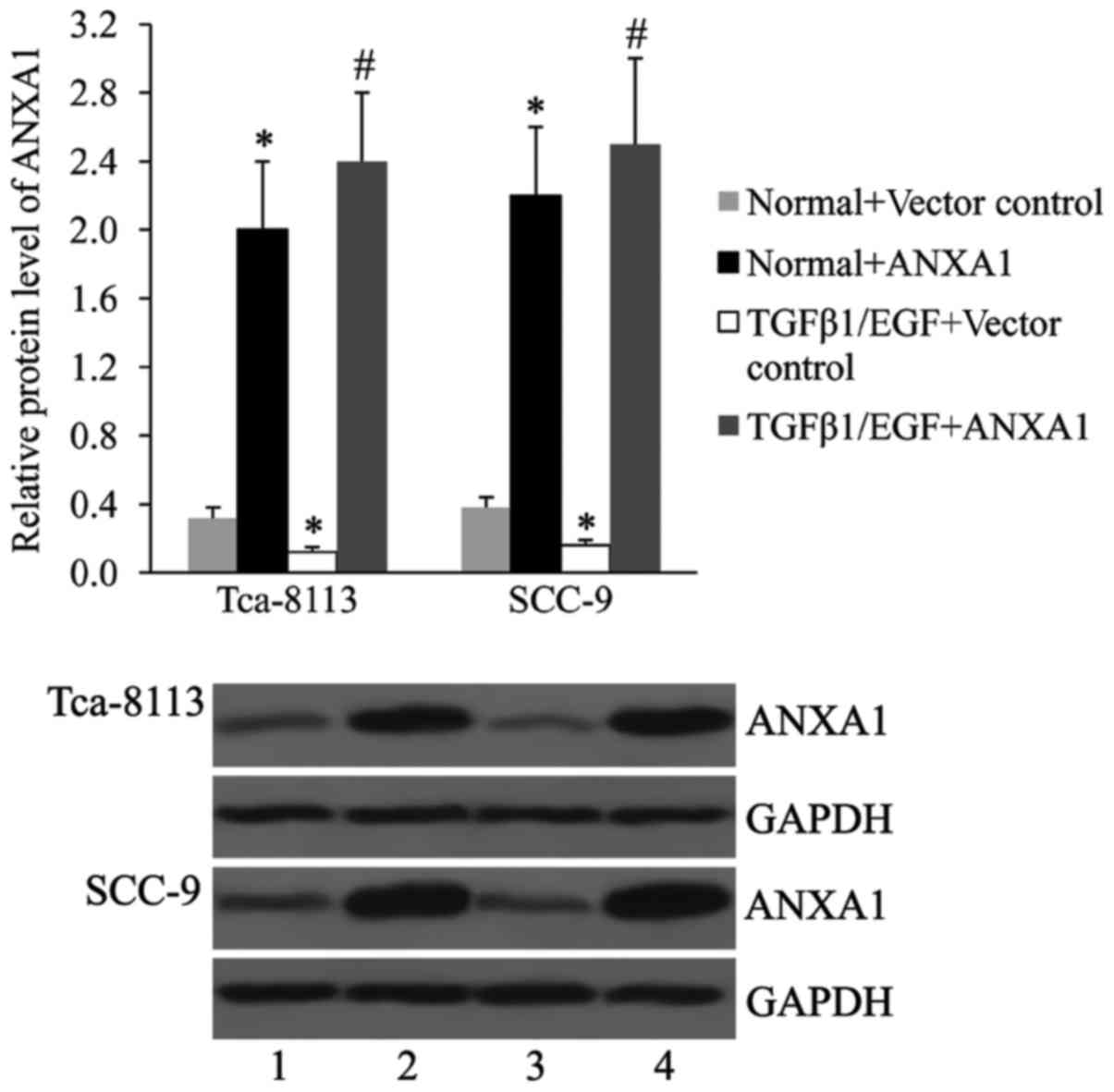
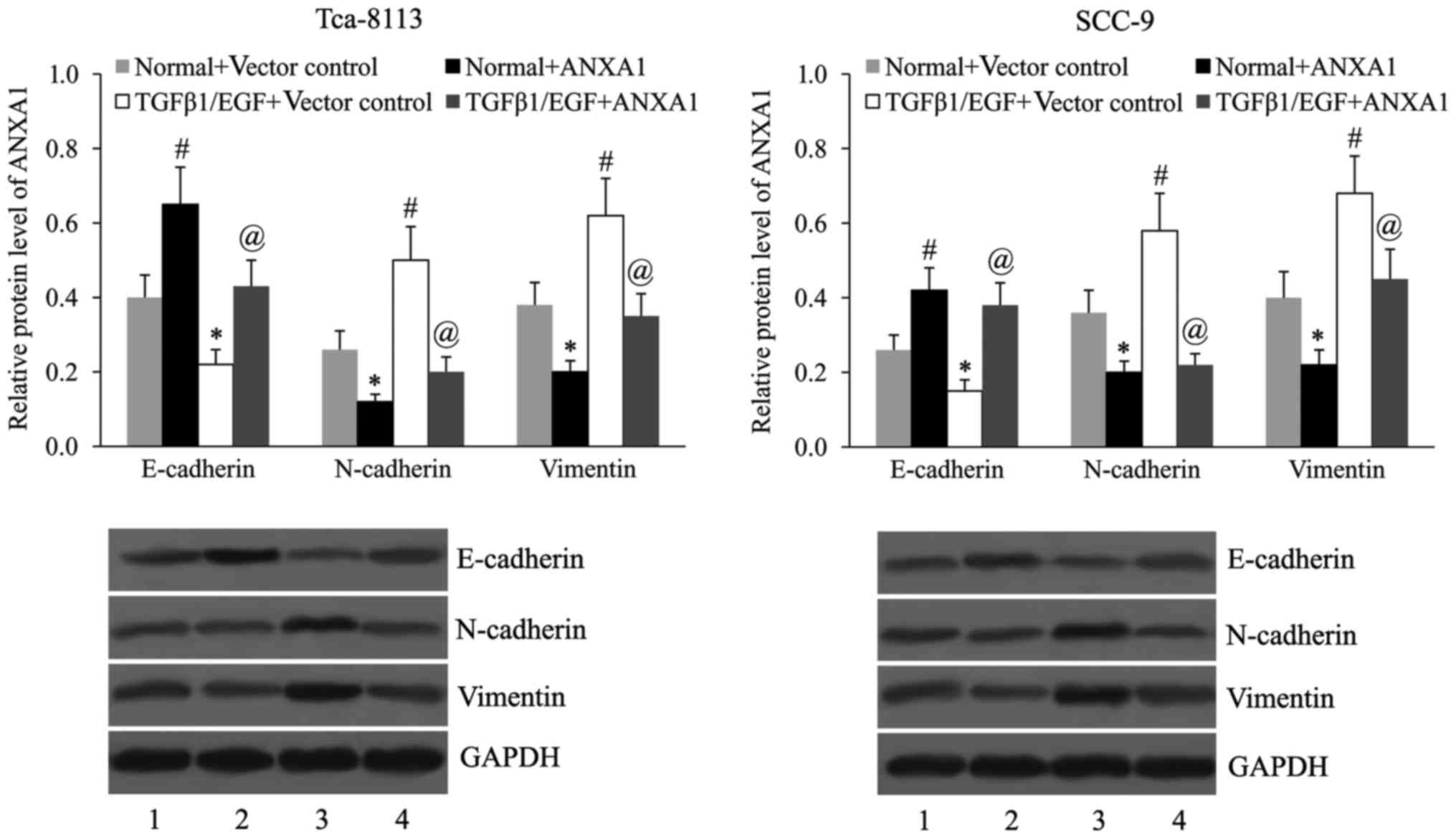
|
1
|
Liu W, Wang YF, Zhou HW, Shi P, Zhou ZT
and Tang GY: Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: A
retrospective cohort study of 218 Chinese patients. BMC Cancer.
10:6852010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Camargo Cancela M, Voti L, Guerra-Yi M,
Chapuis F, Mazuir M and Curado MP: Oral cavity cancer in developed
and in developing countries: Population-based incidence. Head Neck.
32:357–367. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hunter KD, Parkinson EK and Harrison PR:
Profiling early head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:127–135.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gobbetti T and Cooray SN: Annexin A1 and
resolution of inflammation: Tissue repairing properties and
signalling signature. Biol Chem. 397:981–993. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Swa HL, Blackstock WP, Lim LH and
Gunaratne J: Quantitative proteomics profiling of murine mammary
gland cells unravels impact of annexin-1 on DNA damage response,
cell adhesion, and migration. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:381–393.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guzmán-Aránguez A, Olmo N, Turnay J,
Lecona E, Pérez-Ramos P, de Silanes López I and Lizarbe MA:
Differentiation of human colon adenocarcinoma cells alters the
expression and intracellular localization of annexins A1, A2, and
A5. J Cell Biochem. 94:178–193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rohwer N, Bindel F, Grimm C, Lin SJ,
Wappler J, Klinger B, Blüthgen N, Bois Du I, Schmeck B, Lehrach H,
et al: Annexin A1 sustains tumor metabolism and cellular
proliferation upon stable loss of HIF1A. Oncotarget. 7:6693–6710.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fatimathas L and Moss SE: Annexins as
disease modifiers. Histol Histopathol. 25:527–532. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo C, Liu S and Sun MZ: Potential role of
Anxa1 in cancer. Future Oncol. 9:1773–1793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Y, Zhang C, Chen C, Sun S, Zheng H,
Wan S, Meng Q, Chen Y and Wei J: Investigation of circulating
antibodies to ANXA1 in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:1233–1236.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin Y, Lin G, Fang W, Zhu H and Chu K:
Increased expression of annexin A1 predicts poor prognosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma and enhances cell malignant phenotype. Med
Oncol. 31:3272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boudhraa Z, Merle C, Mazzocut D, Chezal
JM, Chambon C, Miot-Noirault E, Theisen M, Bouchon B and Degoul F:
Characterization of pro-invasive mechanisms and N-terminal cleavage
of ANXA1 in melanoma. Arch Dermatol Res. 306:903–914. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boudhraa Z, Rondepierre F, Ouchchane L,
Kintossou R, Trzeciakiewicz A, Franck F, Kanitakis J, Labeille B,
Joubert-Zakeyh J, Bouchon B, et al: Annexin A1 in primary tumors
promotes melanoma dissemination. Clin Exp Metastasis. 31:749–760.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao Y, Chen Y, Xu D, Wang J and Yu G:
Differential expression of ANXA1 in benign human gastrointestinal
tissues and cancers. BMC Cancer. 14:5202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paweletz CP, Ornstein DK, Roth MJ, Bichsel
VE, Gillespie JW, Calvert VS, Vocke CD, Hewitt SM, Duray PH,
Herring J, et al: Loss of annexin 1 correlates with early onset of
tumorigenesis in esophageal and prostate carcinoma. Cancer Res.
60:6293–6297. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang JS, Calvo BF, Maygarden SJ, Caskey
LS, Mohler JL and Ornstein DK: Dysregulation of annexin I protein
expression in high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:117–123. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Faria PC, Sena AA, Nascimento R, Carvalho
WJ, Loyola AM, Silva SJ, Durighetto AF, Oliveira AD, Oliani SM and
Goulart LR: Expression of annexin A1 mRNA in peripheral blood from
oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oral Oncol. 46:25–30. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nomura H, Uzawa K, Yamano Y, Fushimi K,
Nakashima D, Kouzu Y, Kasamatsu A, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Bukawa H,
et al: Down-regulation of plasma membranous Annexin A1 protein
expression in premalignant and malignant lesions of the oral
cavity: Correlation with epithelial differentiation. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 135:943–949. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng TY, Wu MS, Lin JT, Lin MT, Shun CT,
Huang HY, Hua KT and Kuo ML: Annexin A1 is associated with gastric
cancer survival and promotes gastric cancer cell invasiveness
through the formyl peptide receptor/extracellular signal-regulated
kinase/integrin beta-1-binding protein 1 pathway. Cancer.
118:5757–5767. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Babbin BA, Lee WY, Parkos CA, Winfree LM,
Akyildiz A, Perretti M and Nusrat A: Annexin I regulates SKCO-15
cell invasion by signaling through formyl peptide receptors. J Biol
Chem. 281:19588–19599. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fang Y, Guan X, Cai T, Long J, Wang H, Xie
X and Zhang Y: Knockdown of ANXA1 suppresses the biological
behavior of human NSCLC cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 13:3858–3866.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maschler S, Gebeshuber CA, Wiedemann EM,
Alacakaptan M, Schreiber M, Custic I and Beug H: Annexin A1
attenuates EMT and metastatic potential in breast cancer. EMBO Mol
Med. 2:401–414. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu DW, Liu Y, Yang X, Yang CZ, Ma J, Yang
X, Qiao JK, Wang LZ, Li J, Zhang CP, et al: Low Annexin A1
expression predicts benefit from induction chemotherapy in oral
cancer patients with moderate or poor pathologic differentiation
grade. BMC Cancer. 13:3012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu DW, Yang X, Yang CZ, Ma J, Liu Y, Yan
M, Wang LZ, Li J, Zhang CP, Zhang ZY and Zhong LP: Annexin A1
down-regulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma correlates to
pathological differentiation grade. Oral Oncol. 49:542–550. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Yang X, Zhong LP, Zhou XJ, Pan
HY, Wei KJ, Li J, Chen WT and Zhang ZY: Decreased expression of
Annexin A1 correlates with pathologic differentiation grade in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:362–370. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Przybyla L, Muncie JM and Weaver VM:
Mechanical control of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transitions in
development and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 32:527–554. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diepenbruck M and Christofori G:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis: Yes, no,
maybe?t. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 43:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin CY, Jeng YM, Chou HY, Hsu HC, Yuan RH,
Chiang CP and Kuo MY: Nuclear localization of annexin A1 is a
prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol.
97:544–550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Richter P, Umbreit C, Franz M and Berndt
A, Grimm S, Uecker A, Böhmer FD, Kosmehl H and Berndt A: EGF/TGFβ1
co-stimulation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells causes an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition cell phenotype expressing laminin
332. J Oral Pathol Med. 40:46–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Diamond ME, Sun L, Ottaviano AJ, Joseph MJ
and Munshi HG: Differential growth factor regulation of N-cadherin
expression and motility in normal and malignant oral epithelium. J
Cell Sci. 121:2197–2207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|