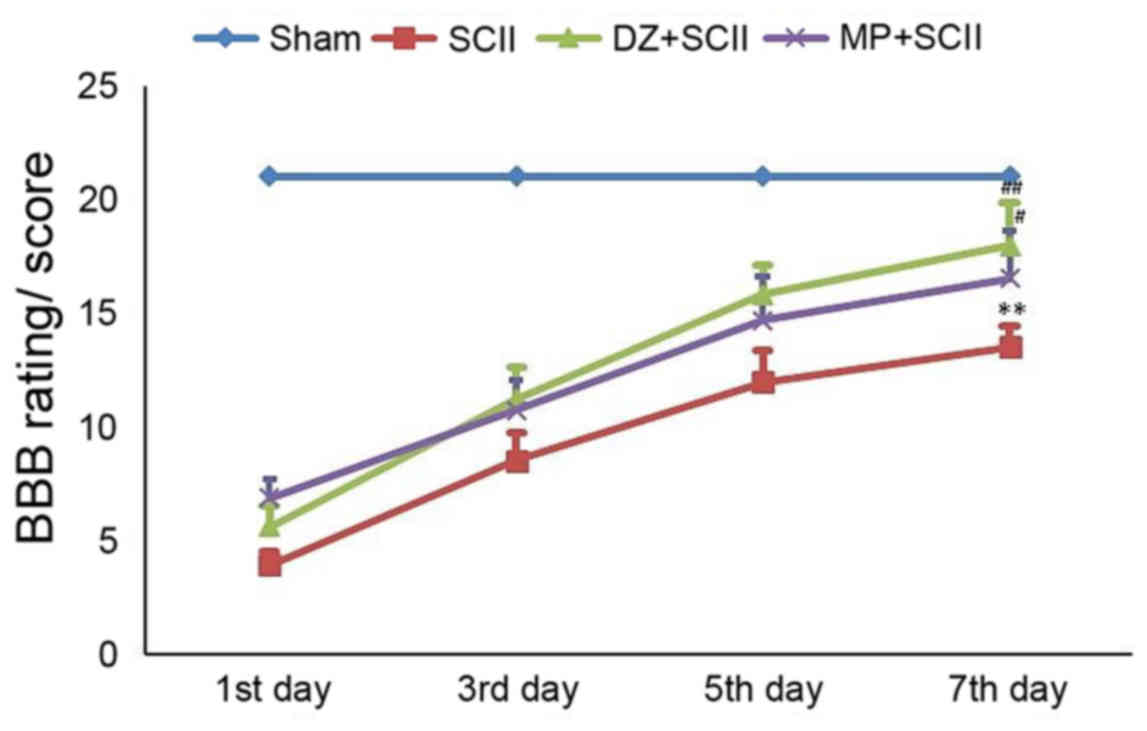
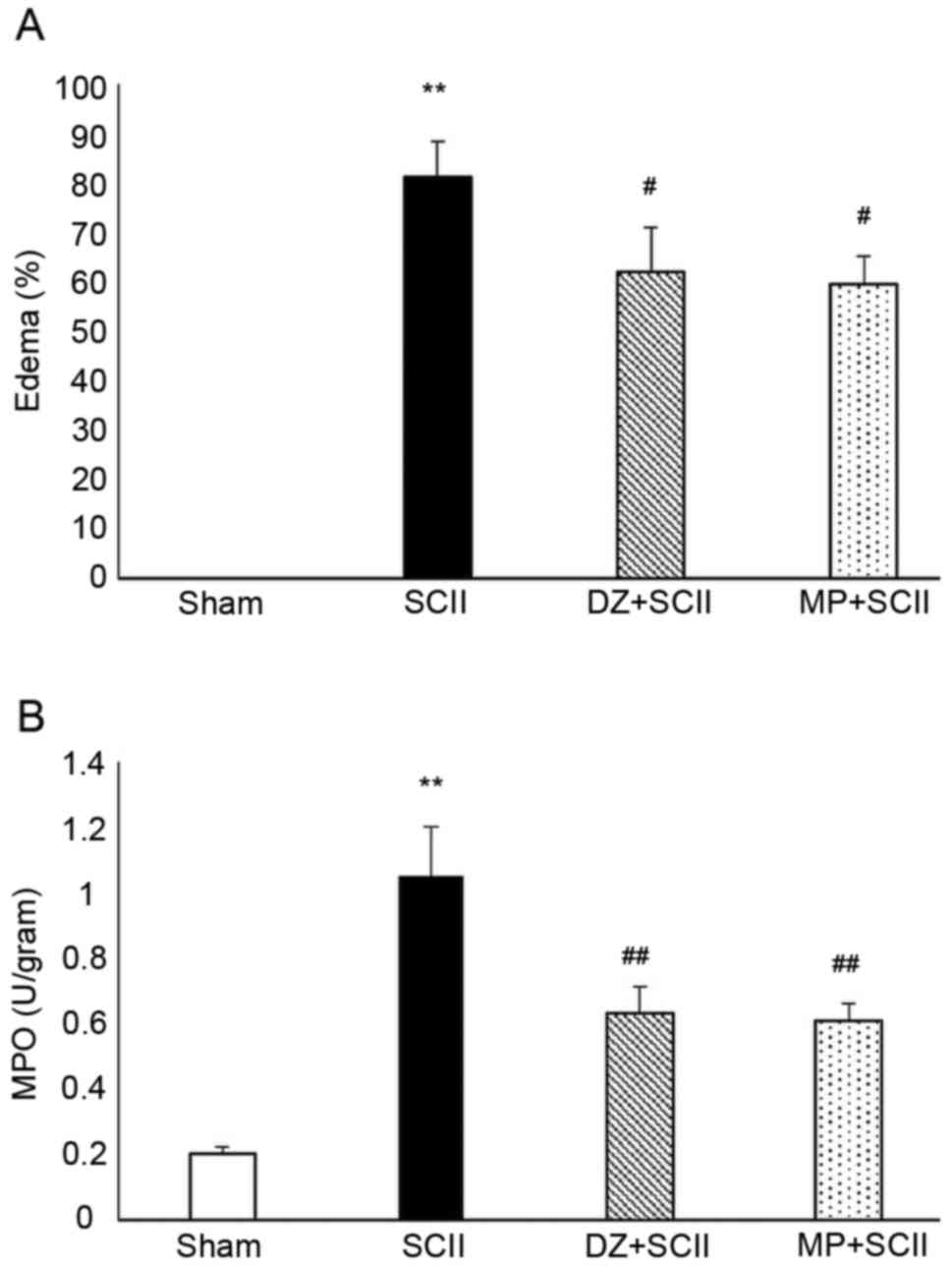
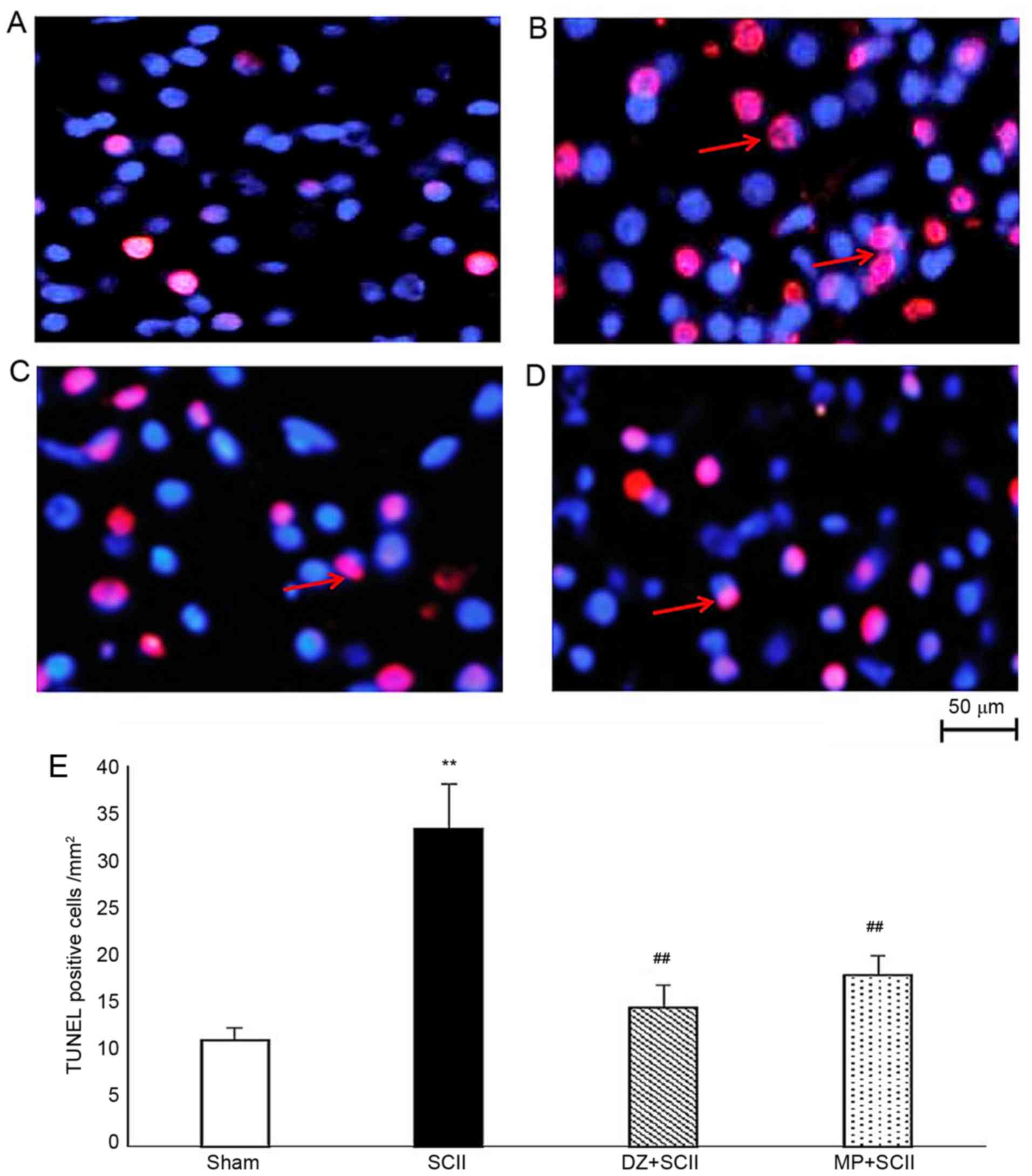
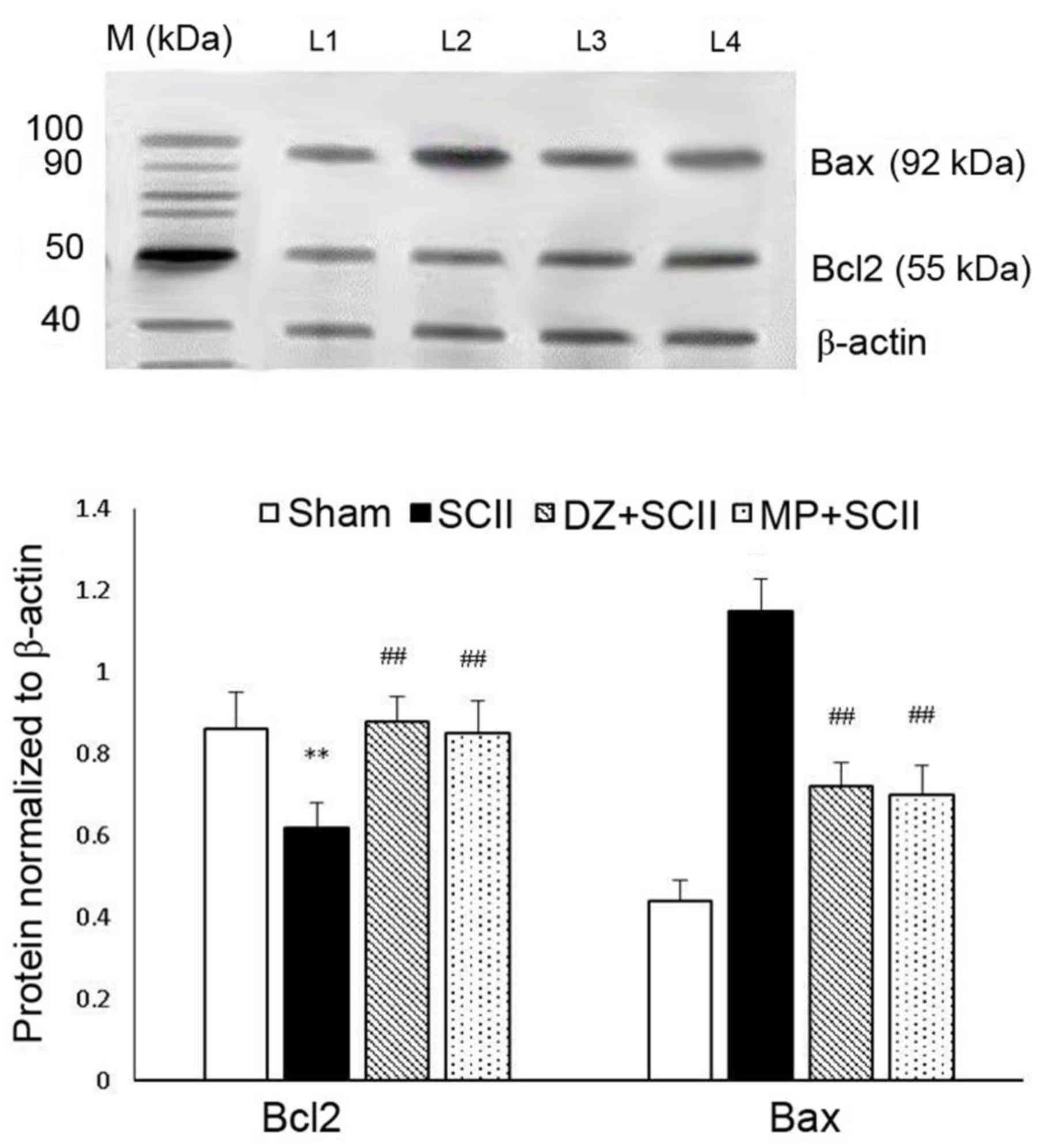
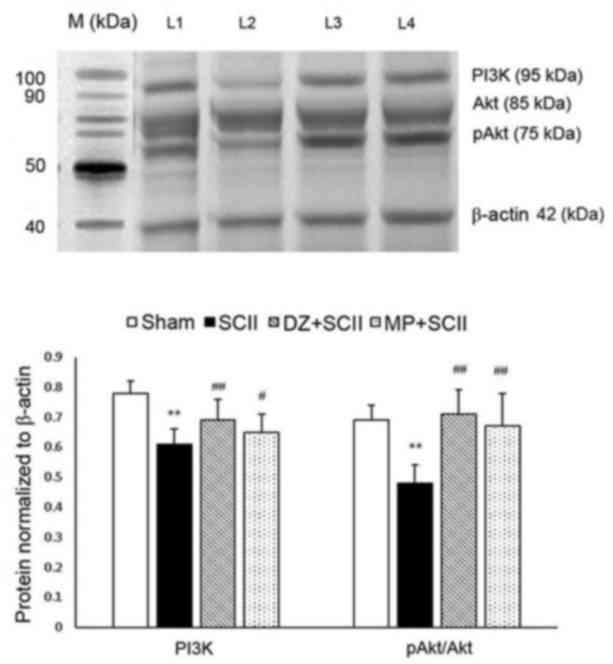
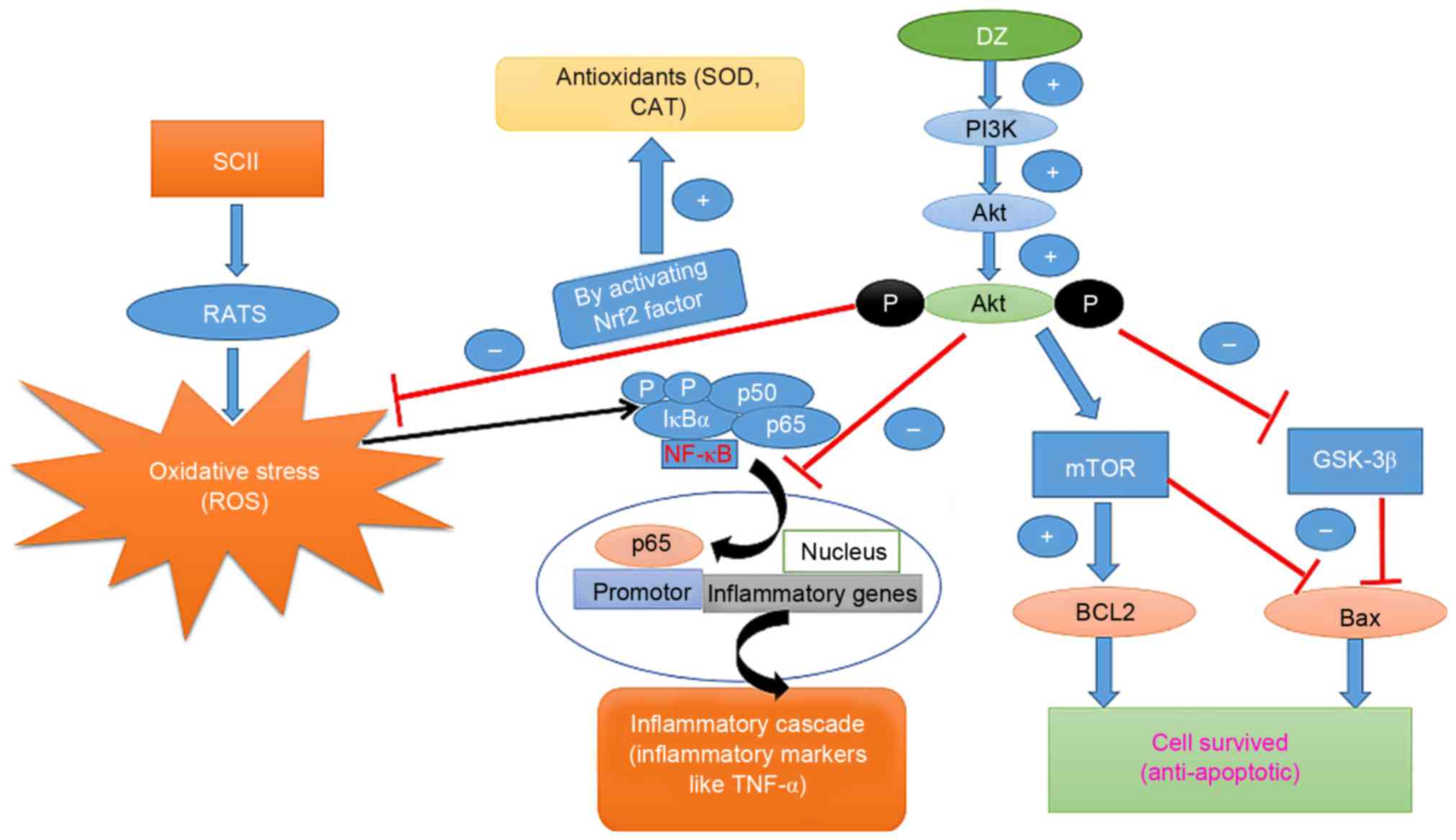
|
1
|
Wong DR, Coselli JS, Amerman K, Bozinovski
J, Carter SA, Vaughn WK and LeMaire SA: Delayed spinal cord
deficits after thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Thorac
Surg. 83:1345–1355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kanellopoulos GK, Xu XM, Hsu CY, Lu X,
Sundt TM and Kouchoukos NT: White matter injury in spinal cord
ischemia protection by AMPA/kainate glutamate receptor antagonism.
Stroke. 31:1945–1952. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang P, Zhang L, Zhu L, Chen F, Zhou S,
Tian T, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Li X, Zhang C and Xu L: The change
tendency of PI3K/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury. Am J Transl
Res. 7:2223–2232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maniar HS, Sundt TM III, Prasad SM, Chu
CM, Camillo CJ, Moon MR, Rubin BG and Sicard GA: Delayed paraplegia
after thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair: A continuing
risk. Ann Thorac Surg. 75:113–119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Zhang C, Hong Z, Chen H, Chen W
and Chen G: C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) mediates neuronal
apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 5:107–111.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gokce EC, Kahveci R, Gokce A, Sargon MF,
Kisa U, Aksoy N, Cemil B and Erdogan B: Curcumin attenuates
inflammation, oxidative stress, and ultrastructural damage induced
by spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Stroke
Cerebrovasc Dis. 25:1196–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lafci G, Gedik HS, Korkmaz K, Erdem H,
Cicek OF, Nacar OA, Yildirim L, Kaya E and Ankarali H: Efficacy of
iloprost and montelukast combination on spinal cord
ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model. J Cardiothorac Surg.
8:642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burguete MC, Torregrosa G, Pérez-Asensio
FJ, Castelló-Ruiz M, Salom JB, Gil JV and Alborch E: Dietary
phytoestrogens improve stroke outcome after transient focal
cerebral ischemia in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 23:703–710. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rivera P, Pérez-Martín M, Pavón FJ,
Serrano A, Crespillo A, Cifuentes M, López-Ávalos MD, Grondona JM,
Vida M and Fernández-Llebrez P: Pharmacological administration of
the isoflavone daidzein enhances cell proliferation and reduces
high fat diet-induced apoptosis and gliosis in the rat hippocampus.
PLoS One. 8:e647502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aras AB, Guven M, Akman T, Ozkan A, Sen
HM, Duz U, Kalkan Y, Silan C and Cosar M: Neuroprotective effects
of daidzein on focal cerebral ischemia injury in rats. Neural
Regener Res. 10:146–152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ma Y, Sullivan JC and Schreihofer DA:
Dietary genistein and equol (4′,7 isoflavandiol) reduce oxidative
stress and protect rats against focal cerebral ischemia. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 299:R871–R877. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu J, Oka J, Ezaki J, Ohtomo T, Ueno T,
Uchiyama S, Toda T, Uehara M and Ishimi Y: Possible role of equol
status in the effects of isoflavone on bone and fat mass in
postmenopausal Japanese women: A double-blind, randomized,
controlled trial. Menopause. 14:866–874. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prossnitz ER and Barton M: Estrogen
biology: New insights into GPER function and clinical
opportunities. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 389:71–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu SZ, Zhong W, Ghavideldarestani M,
Saurabh R, Lindow SW and Atkin SL: Multiple mechanisms of soy
isoflavones against oxidative stress-induced endothelium injury.
Free Radic Biol Med. 47:167–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lovekamp-Swan T, Glendenning M and
Schreihofer DA: A high soy diet reduces programmed cell death and
enhances bcl-xl expression in experimental stroke. Neuroscience.
148:644–652. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pettiford JN, Bikhchandani J, Ostlie DJ,
St Peter SD, Sharp RJ and Juang D: A review: The role of high dose
methylprednisolone in spinal cord trauma in children. Pediatr Surg
Int. 28:287–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Deng Z, Liao J, Song C, Liang C,
Xue H, Wang L, Zhang K and Yan G: Leptin attenuates cerebral
ischemia injury through the promotion of energy metabolism via the
PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:567–574. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang P, Zhang L, Zhu L, Chen F, Zhou S,
Tian T, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Li X and Zhang C: The change tendency of
PI3K/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res.
7:2223–2232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung SY, Kim DY, Yune TY, Shin DH, Baek SB
and Kim CJ: Treadmill exercise reduces spinal cord injury-induced
apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in rats. Exp Ther Med.
7:587–593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hwang JY, Min SW, Jeon YT, Hwang JW, Park
SH, Kim JH and Han SH: Effect of coenzyme Q10 on spinal cord
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Neurosurg Spine. 22:432–438. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mdzinarishvili A, Kiewert C, Kumar V,
Hillert M and Klein J: Bilobalide prevents ischemia-induced edema
formation in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience. 144:217–222. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Atkinson C, Frankenfeld CL and Lampe JW:
Gut bacterial metabolism of the soy isoflavone daidzein: Exploring
the relevance to human health. Exp Biol Med. 230:155–170. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Zhang T, Liang X, Shi L, Wang L, Chen J,
Kang C, Zhu J and Mi M: Estrogen receptor and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway involvement in S-(−)equol-induced activation of Nrf2/ARE in
endothelial cells. PLoS One. 8:e790752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Palencia G, Medrano JÁ, Ortiz-Plata A,
Farfán DJ, Sotelo J, Sánchez A and Trejo-Solís C: Anti-apoptotic,
anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of thalidomide on
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neurol Sci.
351:78–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JW, Jin YC, Kim YM, Rhie S, Kim HJ,
Seo HG, Lee JH, Ha YL and Chang KC: Daidzein administration in vivo
reduces myocardial injury in a rat ischemia/reperfusion model by
inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Life Sci. 84:227–234. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hwang L, Choi IY, Kim SE, Ko IG, Shin MS,
Kim CJ, Kim SH, Jin JJ, Chung JY and Yi JW: Dexmedetomidine
ameliorates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced memory impairment by
inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic
factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Int J Mol Med.
31:1047–1056. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sung YH, Kim SC, Hong HP, Park CY, Shin
MS, Kim CJ, Seo JH, Kim DY, Kim DJ and Cho HJ: Treadmill exercise
ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal loss through suppressing
microglial activation in Parkinson's disease mice. Life Sci.
91:1309–1316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rami A: Ischemic neuronal death in the rat
hippocampus: The calpain-calpastatin-caspase hypothesis. Neurobiol
Dis. 13:75–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Okuno S, Saito A, Hayashi T and Chan PH:
The c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway mediates Bax
activation and subsequent neuronal apoptosis through interaction
with Bim after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci.
24:7879–7887. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen MH, Ren QX, Yang WF, Chen XL, Lu C
and Sun J: Influences of HIF-lα on Bax/Bcl-2 and VEGF expressions
in rats with spinal cord injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
6:2312–2322. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Gu J, Liu Y, Long H, Wang G, Yin G
and Fan J: iNOS participates in apoptosis of spinal cord neurons
via p-BAD dephosphorylation following ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)
injury in rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 545:117–122. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mao Z, Zheng YL, Zhang YQ, Han BP, Zhu XW,
Chang Q and Hu XB: The anti-apoptosis effects of daidzein in the
brain of D-galactose treated mice. Molecules. 12:1455–1470. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han BJ, Li W, Jiang GB, Lai SH, Zhang C,
Zeng CC and Liu YJ: Effects of daidzein in regards to cytotoxicity
in vitro, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species level, cell cycle
arrest and the expression of caspase and Bcl-2 family proteins.
Oncol Rep. 34:1115–1120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chakrabarti M, Das A, Samantaray S, Smith
JA, Banik NL, Haque A and Ray SK: Molecular mechanisms of estrogen
for neuroprotection in spinal cord injury and traumatic brain
injury. Rev Neurosci. 27:271–281. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu F, Sugawara T, Maier CM, Hsieh LB and
Chan PH: Akt/Bad signaling and motor neuron survival after spinal
cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 20:491–499. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim MH, Park JS, Seo MS, Jung JW, Lee YS
and Kang KS: Genistein and daidzein repress adipogenic
differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem
cells via Wnt/β-catenin signalling or lipolysis. Cell Prolif.
43:594–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|