|
1
|
Bakker R, Pierce S and Myers D: The role
of prostaglandins E1 and E2, dinoprostone, and misoprostol in
cervical ripening and the induction of labor: A mechanistic
approach. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 296:167–179. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim YM, Park JY, Sung JH, Choi SJ, Oh SY,
Roh CR and Kim JH: Predicting factors for success of vaginal
delivery in preterm induction with prostaglandin E2.
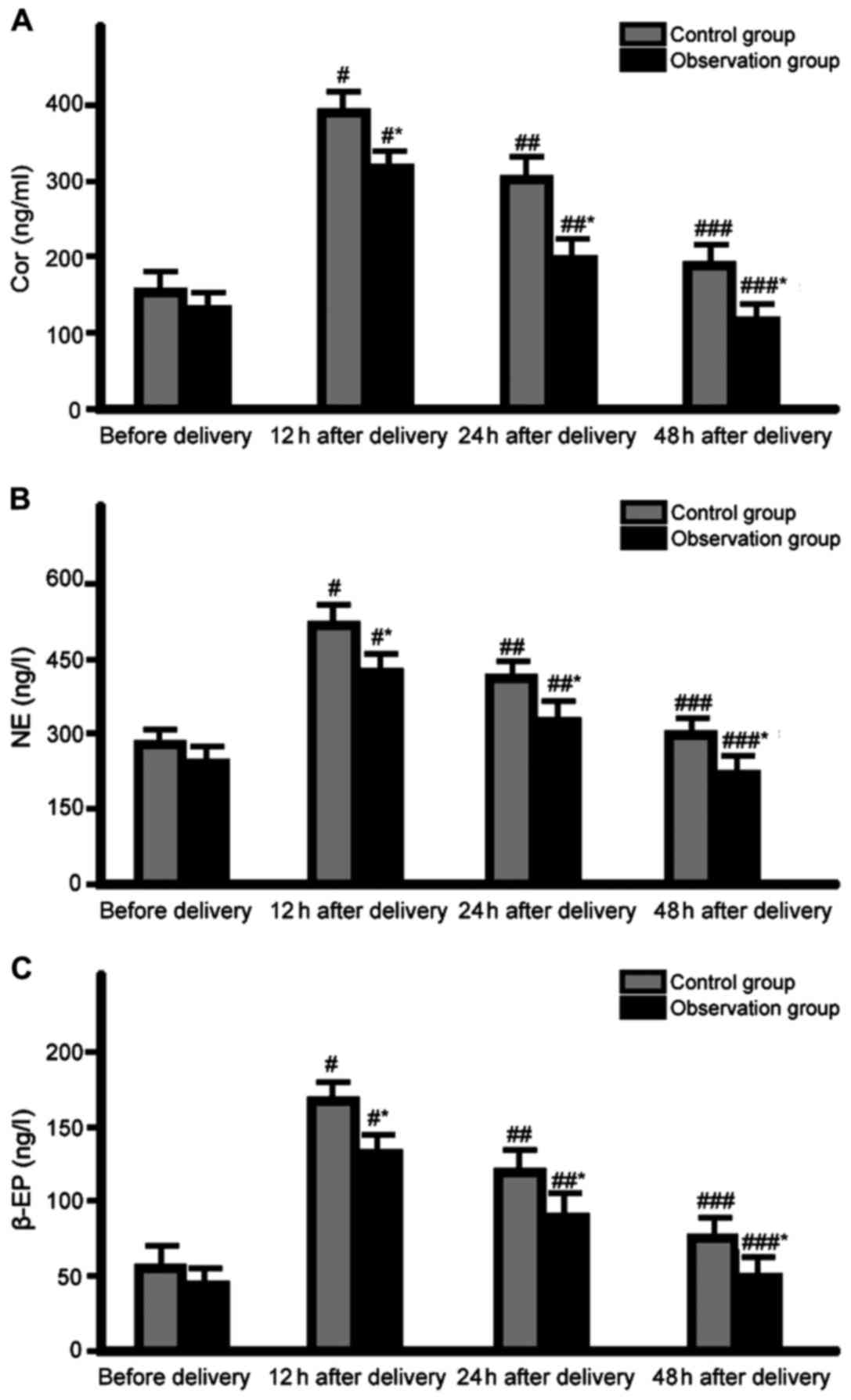
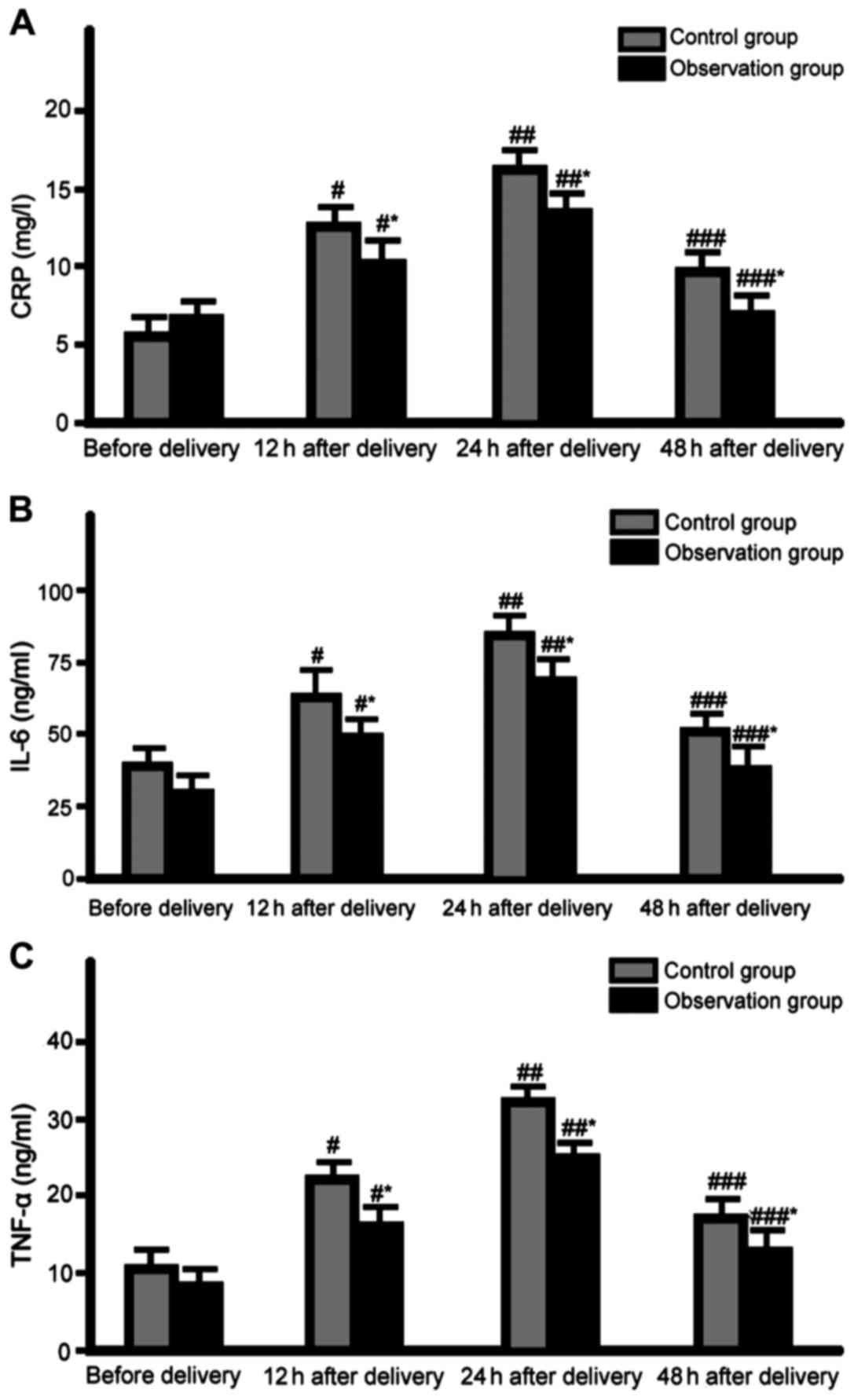
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 60:163–169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hiersch L, Borovich A, Gabbay-Benziv R,
Maimon-Cohen M, Aviram A, Yogev Y and Ashwal E: Can we predict
successful cervical ripening with prostaglandin E2
vaginal inserts? Arch Gynecol Obstet. 295:1–349. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sayed Ahmed WA, Ibrahim ZM, Ashor OE,
Mohamed ML, Ahmed MR and Elshahat AM: Use of the Foley catheter
versus a double balloon cervical ripening catheter in pre-induction
cervical ripening in postdate primigravidae. J Obstet Gynaecol Res.
42:1489–1494. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kehl S, Weiss C and Rath W: Balloon
catheters for induction of labor at term after previous cesarean
section: A systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
204:44–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salim R, Zafran N, Nachum Z, Garmi G,
Kraiem N and Shalev E: Single-balloon compared with double-balloon
catheters for induction of labor: A randomized controlled trial.
Obstet Gynecol. 118:79–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alfirevic Z, Keeney E, Dowswell T, Welton
NJ, Medley N, Dias S, Jones LV, Gyte G and Caldwell DM: Which
method is best for the induction of labour? A systematic review,
network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health
Technol Assess. 20:1–584. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jozwiak M, Bloemenkamp KW, Kelly AJ, Mol
BW, Irion O and Boulvain M: Mechanical methods for induction of
labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Mar 14–2012.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Husain S, Husain S and Izhar R: Oral
misoprostol alone versus oral misoprostol and Foley's catheter for
induction of labor: A randomized controlled trial. J Obstet
Gynaecol Res. 43:1270–1277. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Policiano C, Pimenta M, Martins D and
Clode N: Efficacy and safety of foley catheter balloon for cervix
priming in term pregnancy. Acta Med Port. 30:281–284. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duro Gómez J, Garrido Oyarzún MF,
Rodríguez Marín AB, de la Torre González AJ, Arjona Berral JE and
Castelo-Branco C: Vaginal misoprostol and cervical ripening balloon
for induction of labor in late-term pregnancies. J Obstet Gynaecol
Res. 43:87–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vrachnis N, Malamas FM, Sifakis S,
Tsikouras P and Iliodromiti Z: Immune aspects and myometrial
actions of progesterone and CRH in labor. Clin Dev Immunol.
2012:9376182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li YY, Yin ZY, Li S, Xu H, Zhang XP, Cheng
H, Du L, Zhou XY and Zhang B: Comparison of transvaginal surgery
and methotrexate/mifepristone-combined transcervical resection in
the treatment of cesarean scar pregnancy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:2957–2963. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Florio P, Romero R, Chaiworapongsa T,
Kusanovic JP, Torricelli M, Lowry PJ and Petraglia F: Amniotic
fluid and umbilical cord plasma corticotropin-releasing factor
(CRF), CRF-binding protein, adrenocorticotropin, and cortisol
concentrations in intraamniotic infection and inflammation at term.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 93:3604–3609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jagielska I, Kazdepka-Ziemińska A, Janicki
R, Fórmaniak J, Walentowicz-Sadłecka M and Grabiec M: Evaluation of
the efficacy and safety of Foley catheter pre-induction of labor.
Ginekol Pol. 84:180–185. 2013.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eleje GU, Ezugwu EC, Eke AC, Eleje LI,
Ikechebelu JI, Ezebialu IU, Obiora CC, Nwosu BO, Ezeama CO, Udigwe
GO, et al: Accuracy of a combined insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein-1/interleukin-6 test (Premaquick) in
predicting delivery in women with threatened preterm labor. J
Perinat Med. Feb 25–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Castillo-Castrejon M, Meraz-Cruz N,
Gomez-Lopez N, Flores-Pliego A, Beltrán-Montoya J, Viveros-Alcaráz
M and Vadillo-Ortega F: Choriodecidual cells from term human
pregnancies show distinctive functional properties related to the
induction of labor. Am J Reprod Immunol. 71:86–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bollapragada S, Youssef R, Jordan F, Greer
I, Norman J and Nelson S: Term labor is associated with a core
inflammatory response in human fetal membranes, myometrium, and
cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 200:104.e1–104.e11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|