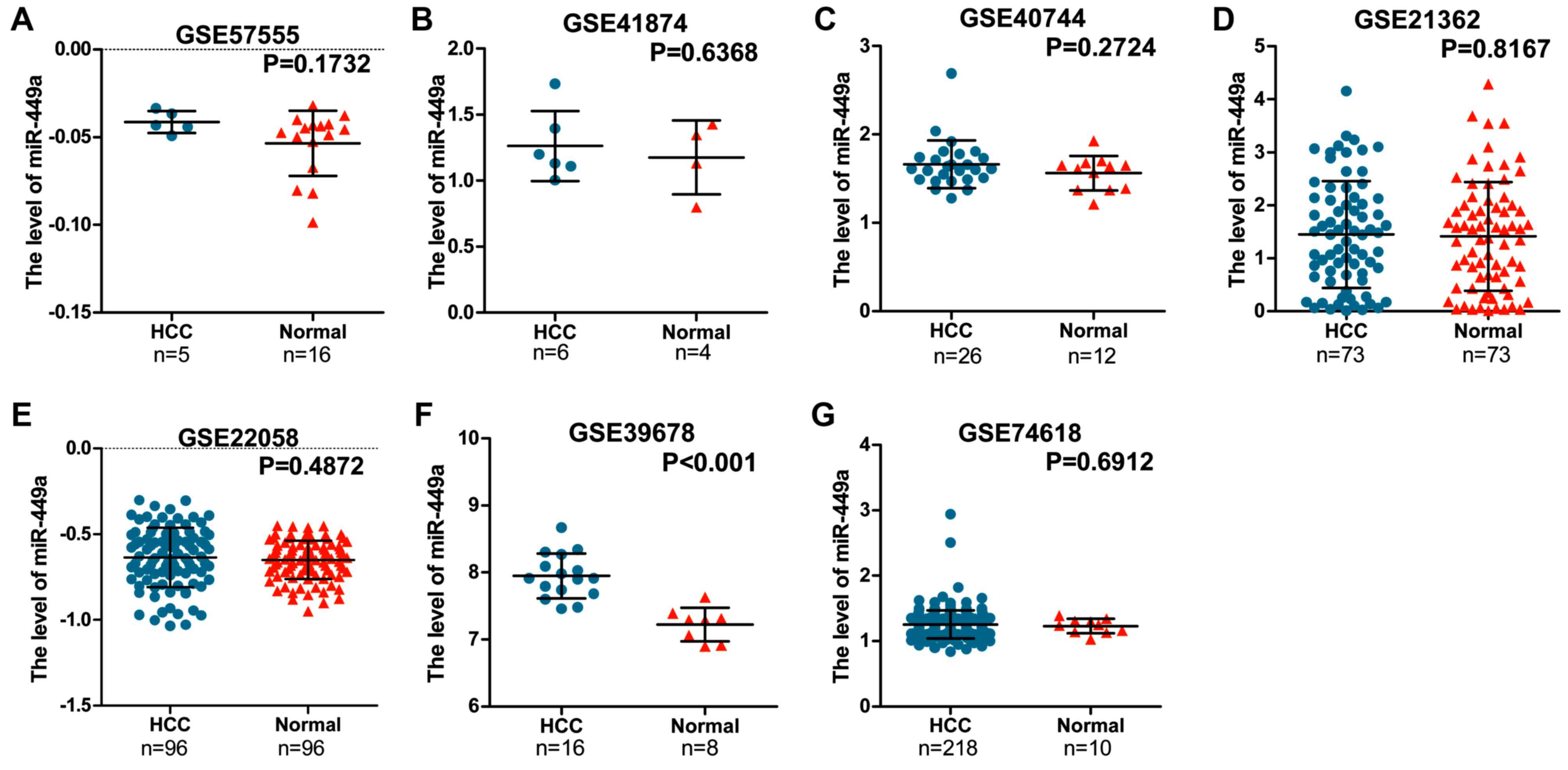
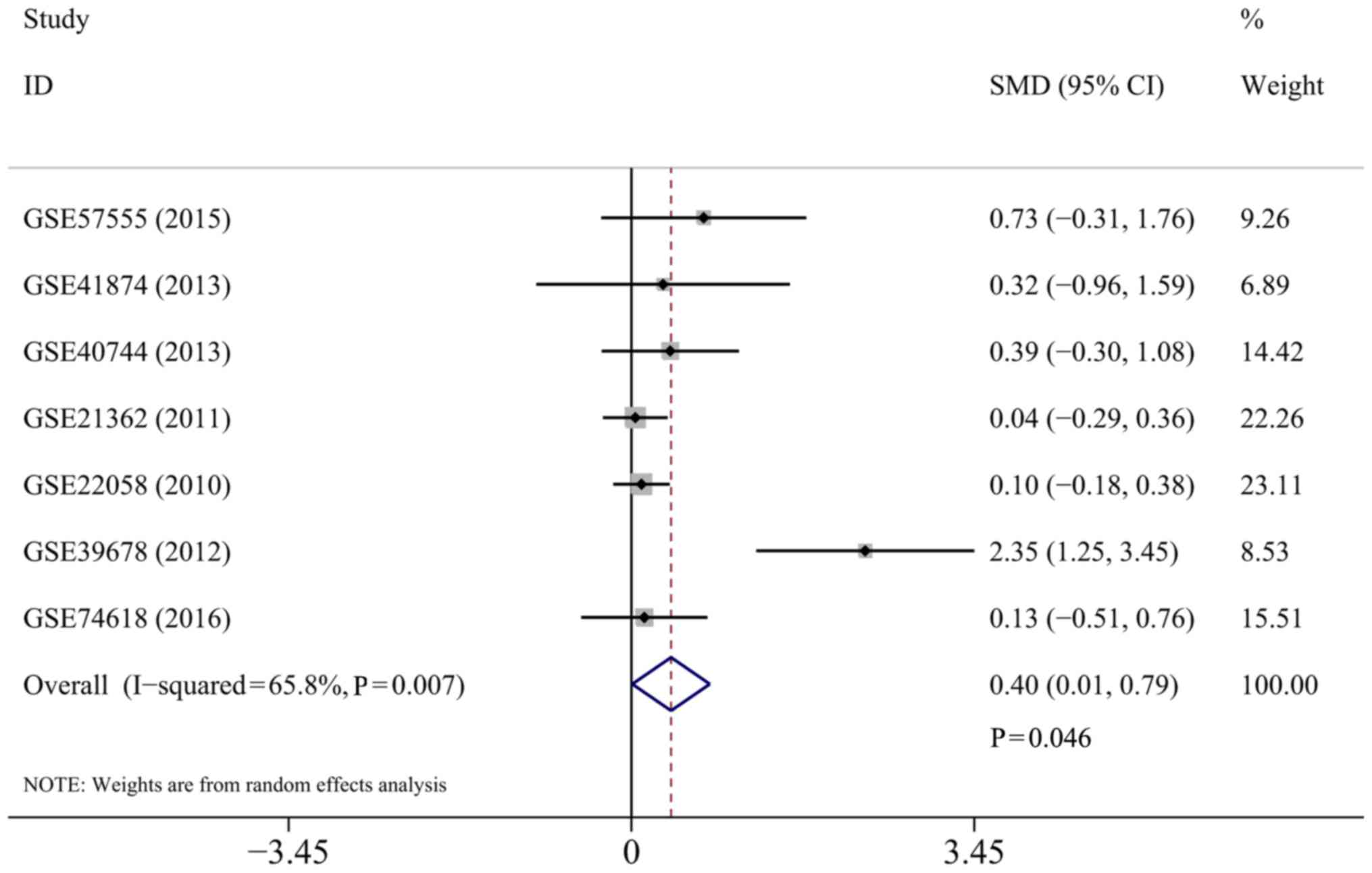
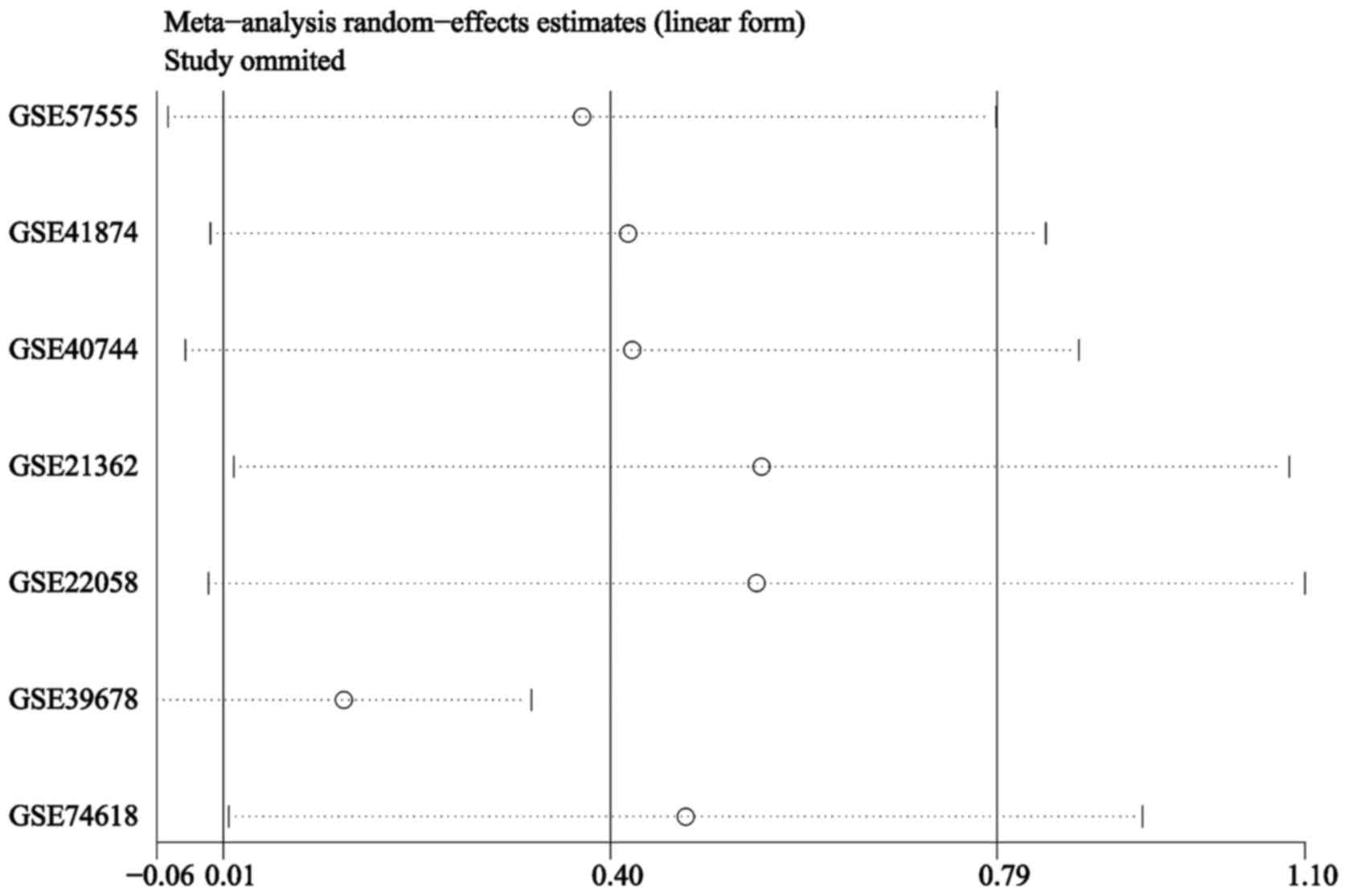
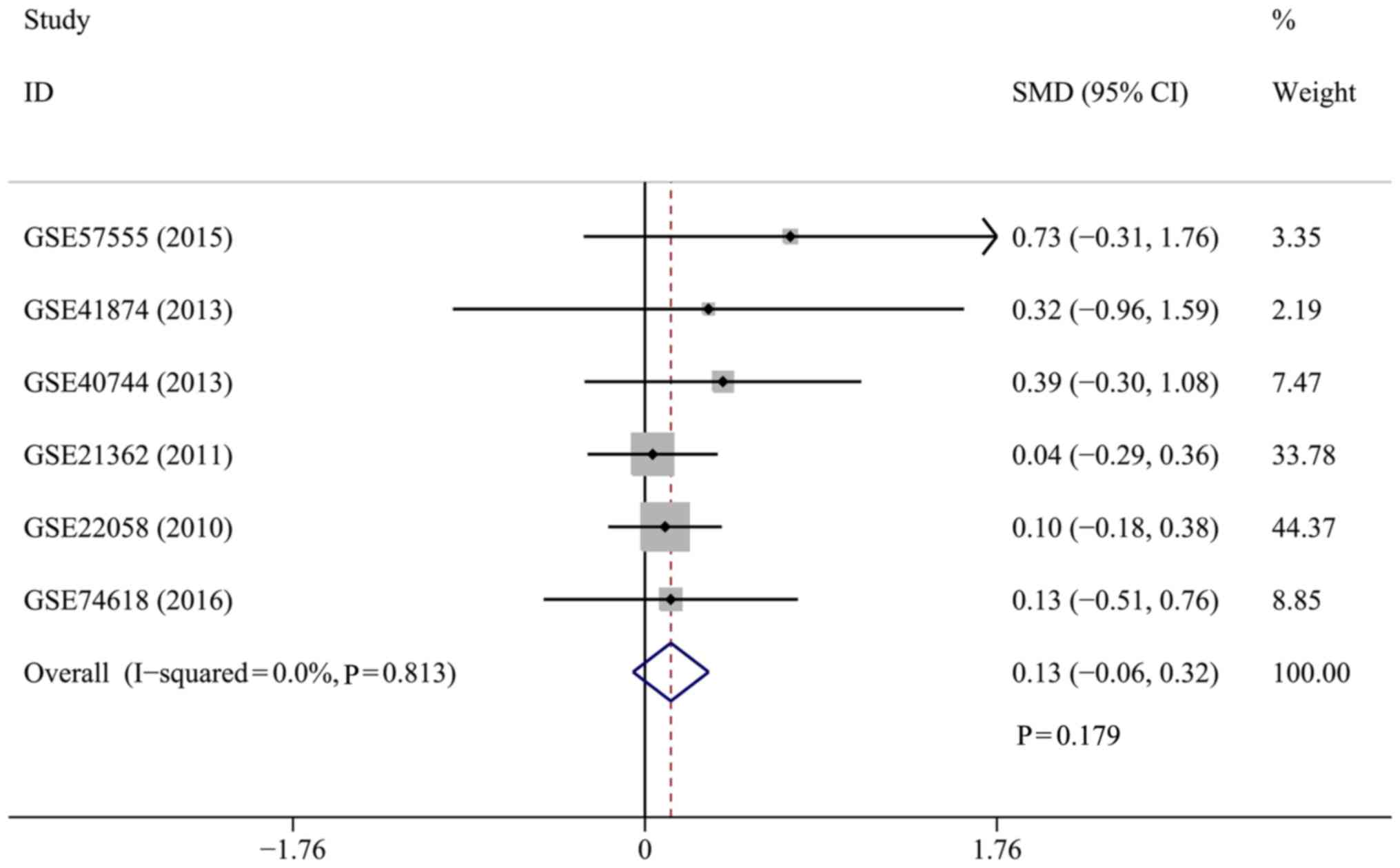
|
1
|
Wan LC, Wang F, Guo X, Lu S, Qiu Z, Zhao
Y, Zhang H and Lin J: Identification and characterization of small
non-coding RNAs from Chinese fir by high throughput sequencing. BMC
Plant Biol. 12:1462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bussotti G, Notredame C and Enright AJ:
Detecting and comparing non-coding RNAs in the high-throughput era.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:15423–15458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nat Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang H, Ke C, Ma X, Zhao Q, Yang M, Zhang
W and Wang J: MicroRNA-92 promotes invasion and chemoresistance by
targeting GSK3β and activating Wnt signaling in bladder cancer
cells. Tumour Biol. 37:16295–16304. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cech TR and Steitz JA: The noncoding RNA
revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 157:77–94.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dhamija S and Diederichs S: From junk to
master regulators of invasion: lncRNA functions in migration, EMT
and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 139:269–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu W, Liu S, Liang Y, Zhou Z and Liu X:
MiR-7 inhibits progression of hepatocarcinoma by targeting KLF-4
and promises a novel diagnostic biomarker. Cancer Cell Int.
17:312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Morey C and Avner P: Employment
opportunities for non-coding RNAs. FEBS Lett. 567:27–34. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:847–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dehury B, Panda D, Sahu J, Sahu M, Sarma
K, Barooah M, Sen P and Modi M: In silico identification and
characterization of conserved miRNAs and their target genes in
sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) expressed sequence tags (ESTs).
Plant Signal Behav. 8:e265432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cong D, He M, Chen S, Liu X, Liu X and Sun
H: Expression profiles of pivotal microRNAs and targets in thyroid
papillary carcinoma: An analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:2271–2277. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Polioudakis D, Abell NS and Iyer VR:
MiR-191 regulates primary human fibroblast proliferation and
directly targets multiple oncogenes. PLoS One. 10:e01265352015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan S, Tang C, Zhang Y, Wu J, Bao J,
Zheng H, Xu C and Yan W: mir-34b/c and mir-449a/b/c are required
for spermatogenesis, but not for the first cleavage division in
mice. Biol Open. 4:212–223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumar P, Sharad S, Petrovics G, Mohamed A,
Dobi A, Sreenath TL, Srivastava S and Biswas R: Loss of miR-449a in
ERG-associated prostate cancer promotes the invasive phenotype by
inducing SIRT1. Oncotarget. 7:22791–22806. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi J, Liu Y, Liu J and Zhou J:
Hsa-miR-449a genetic variant is associated with risk of gastric
cancer in a Chinese population. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:13387–13392. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
You J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L
and Zhou Q: MiR-449a suppresses cell invasion by inhibiting MAP2K1
in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2730–2744.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo P, Huang ZL, Yu P and Li K: Trends in
cancer mortality in China: An update. Ann Oncol. 23:2755–2762.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Center MM and Jemal A: International
trends in liver cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 20:2362–2368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen CF, Hsu EC, Lin KT, Tu PH, Chang HW,
Lin CH, Chen YJ, Gu DL, Lin CH, Wu JY, et al: Overlapping
high-resolution copy number alterations in cancer genomes
identified putative cancer genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 52:1690–1701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takeshima N, Sozu T, Tajika A, Ogawa Y,
Hayasaka Y and Furukawa TA: Which is more generalizable, powerful
and interpretable in meta-analyses, mean difference or standardized
mean difference? BMC Med Res Methodol. 14:302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Valera EM, Faraone SV, Murray KE and
Seidman LJ: Meta-analysis of structural imaging findings in
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry.
61:1361–1369. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sandbothe M, Buurman R, Reich N, Greiwe L,
Vajen B, Gürlevik E, Schäffer V, Eilers M, Kühnel F, Vaquero A, et
al: The microRNA-449 family inhibits TGF-β-mediated liver cancer
cell migration by targeting SOX4. J Hepatol. 66:1012–1021. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Tang W, Chen G, Ren F, Liang H,
Dang Y and Rong M: An encapsulation of gene signatures for
hepatocellular carcinoma, MicroRNA-132 predicted target genes and
the corresponding overlaps. PLoS One. 11:e01594982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lau J, Ioannidis JP and Schmid CH:
Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med.
127:820–826. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
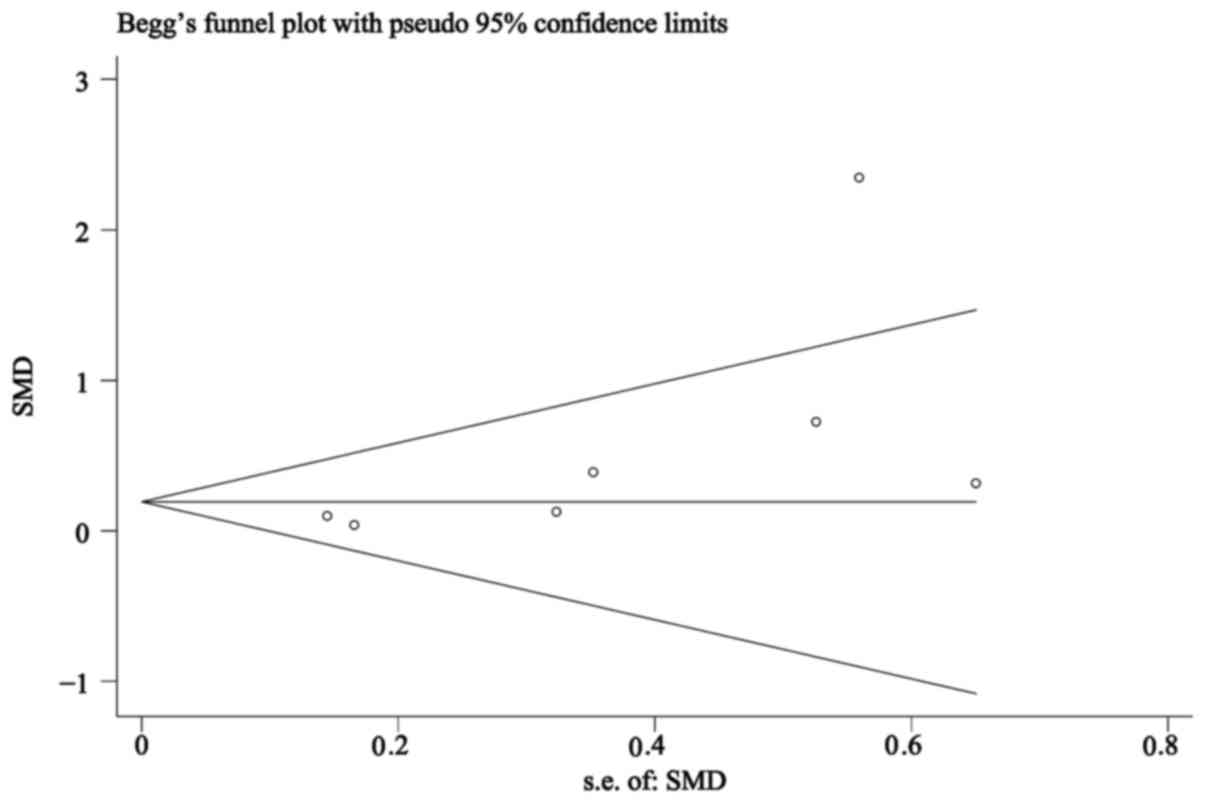
Begg CB and Mazumdar M: Operating
characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias.
Biometrics. 50:1088–1101. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Q, Huang CS, Yu W, et al:
MicroRNA-449a suppresses liver cancer migration and invasion
through targeting CXC chemokine ligand 5. Chin J Exp Surg.
34:228–230. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Liu S, Liu K, Zhang W, Wang Y, Jin Z, Jia
B and Liu Y: miR-449a inhibits proliferation and invasion by
regulating ADAM10 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res.
8:2609–2619. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen SP, Liu BX, Xu J, Pei XF, Liao YJ,
Yuan F and Zheng F: MiR-449a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by multiple
targets. BMC Cancer. 15:7062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Wang Y, Sun X, Mei C, Wang L, Li Z
and Zha X: miR-449a promotes liver cancer cell apoptosis by
downregulation of Calpain 6 and POU2F1. Oncotarget. 7:13491–13501.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Liu H, Xie Z, Deng W, Wu C, Qin
B, Hou J and Lu M: Epigenetically regulated miR-449a enhances
hepatitis B virus replication by targeting cAMP-responsive element
binding protein 5 and modulating hepatocytes phenotype. Sci Rep.
6:253892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sarma NJ, Tiriveedhi V, Subramanian V,
Shenoy S, Crippin JS, Chapman WC and Mohanakumar T: Hepatitis C
virus mediated changes in miRNA-449a modulates inflammatory
biomarker YKL40 through components of the NOTCH signaling pathway.
PLoS One. 7:e508262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
El-Serag HB, Kramer J, Duan Z and Kanwal
F: Racial differences in the progression to cirrhosis and
hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV-infected veterans. Am J
Gastroenterol. 109:1427–1435. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Buurman R, Gürlevik E, Schäffer V, Eilers
M, Sandbothe M, Kreipe H, Wilkens L, Schlegelberger B, Kühnel F and
Skawran B: Histone deacetylases activate hepatocyte growth factor
signaling by repressing microRNA-449 in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Gastroenterology. 143:811–820.e15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murakami Y, Kubo S, Tamori A, Itami S,
Kawamura E, Iwaisako K, Ikeda K, Kawada N, Ochiya T and Taguchi YH:
Comprehensive analysis of transcriptome and metabolome analysis in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 5:162942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Morita K, Shirabe K, Taketomi A, Soejima
Y, Yoshizumi T, Uchiyama H, Ikegami T, Yamashita Y, Sugimachi K,
Harimoto N, et al: Relevance of microRNA-18a and microRNA-199a-5p
to hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after living donor liver
transplantation. Liver Transpl. 22:665–676. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Diaz G, Melis M, Tice A, Kleiner DE,
Mishra L, Zamboni F and Farci P: Identification of microRNAs
specifically expressed in hepatitis C virus-associated
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 133:816–824. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sato F, Hatano E, Kitamura K, Myomoto A,
Fujiwara T, Takizawa S, Tsuchiya S, Tsujimoto G, Uemoto S and
Shimizu K: MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan Criteria.
PLoS One. 6:e164352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu AM, Yao TJ, Wang W, Wong KF, Lee NP,
Fan ST, Poon RT, Gao C and Luk JM: Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b
in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular
carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2:e0008252012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Noh JH, Chang YG, Kim MG, Jung KH, Kim JK,
Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Kim SJ, Kwon SH, et al: MiR-145 functions
as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2
in liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 335:455–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Martinez-Quetglas I, Pinyol R, Dauch D,
Torrecilla S, Tovar V, Moeini A, Alsinet C, Portela A,
Rodriguez-Carunchio L, Solé M, et al: IGF2 Is Up-regulated by
epigenetic mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinomas and is an
actionable oncogene product in experimental models.
Gastroenterology. 151:1192–1205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Petrovic N, Ergün S and Isenovic ER:
Levels of MicroRNA heterogeneity in cancer biology. Mol Diagn Ther.
21:511–523. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luo LJ, Zhang LP, Duan CY, Wang B, He NN,
Abulimiti P and Lin Y: The inhibition role of miR-22 in
hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion via targeting
CD147. Cancer Cell Int. 17:172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xia W, Zhou J, Luo H, Liu Y, Peng C, Zheng
W and Ma W: MicroRNA-32 promotes cell proliferation, migration and
suppresses apoptosis in breast cancer cells by targeting FBXW7.
Cancer Cell Int. 17:142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu C, Li G, Yang N, Su Z, Zhang S, Deng
T, Ren S, Lu S, Tian Y, Liu Y and Qiu Y: miR-324-3p suppresses
migration and invasion by targeting WNT2B in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Cell International. 17:22017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Towler BP, Jones CI and Newbury SF:
Mechanisms of regulation of mature miRNAs. Biochem Soc Trans.
43:1208–1214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tacke F, Zimmermann HW, Trautwein C and
Schnabl B: CXCL5 plasma levels decrease in patients with chronic
liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:523–529. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang MH, Chen CL, Chau GY, Chiou SH, Su
CW, Chou TY, Peng WL and Wu JC: Comprehensive analysis of the
independent effect of twist and snail in promoting metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 50:1464–1474. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Curtil C, Enache LS, Radreau P, Dron AG,
Scholtès C, Deloire A, Roche D, Lotteau V, André P and Ramière C:
The metabolic sensors FXRα, PGC-1α, and SIRT1 cooperatively
regulate hepatitis B virus transcription. FASEB J. 28:1454–1463.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schulze K, Imbeaud S, Letouze E,
Alexandrov LB, Calderaro J, Rebouissou S, Couchy G, Meiller C,
Shinde J, Soysouvanh F, et al: Exome sequencing of hepatocellular
carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential
therapeutic targets. Nat Genet. 47:505–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
ClinicalTrials.gov: A multicenter phase I
study of MRX34, microRNA miR-RX34 liposomal injection, NCT01829971.
2013.
|
|
54
|
Veals SA, Schindler C, Leonard D, Fu XY,
Aebersold R, Darnell JE Jr and Levy DE: Subunit of an
alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to
interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA-binding
proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 12:3315–3324. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang H, Huang ZZ, Wang J and Lu SC: The
role of c-Myb and Sp1 in the up-regulation of methionine
adenosyltransferase 2A gene expression in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. FASEB J. 15:1507–1516. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wan Z, Zhi N, Wong S, Keyvanfar K, Liu D,
Raghavachari N, Munson PJ, Su S, Malide D, Kajigaya S and Young NS:
Human parvovirus B19 causes cell cycle arrest of human erythroid
progenitors via deregulation of the E2F family of transcription
factors. J Clin Invest. 120:3530–3544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen HZ, Tsai SY and Leone G: Emerging
roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:785–797. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jiang Y, Yim SH, Xu HD, Jung SH, Yang SY,
Hu HJ, Jung CK and Chung YJ: A potential oncogenic role of the
commonly observed E2F5 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma.
World J Gastroenterol. 17:470–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Suryadinata R, Sadowski M and Sarcevic B:
Control of cell cycle progression by phosphorylation of
cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) substrates. Biosci Rep. 30:243–255.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Iyirhiaro GO, Im DS, Boonying W, Callaghan
SM, During MJ, Slack RS and Park DS: Cdc25A Is a critical mediator
of ischemic neuronal death in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci.
37:6729–6740. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shi Y, Qian ZR, Zhang S, Li W, Masugi Y,
Li T, Chan JA, Yang J, Da Silva A, Gu M, et al: Cell cycle protein
expression in neuroendocrine tumors: Association of CDK4/CDK6,
CCND1, and phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein with proliferative
index. Pancreas. 46:1347–1353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shang A, Lu WY, Yang M, Zhou C, Zhang H,
Cai ZX, Wang WW, Wang WX and Wu GQ: miR-9 induces cell arrest and
apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma via CDK 4/6 pathway.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lulla AR, Slifker MJ, Zhou Y, Lev A,
Einarson MB, Dicker DT and El-Deiry WS: miR-6883 family miRNAs
target CDK4/6 to induce G1 phase cell cycle arrest in colon cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 77:6902–6913. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dall'Acqua A, Sonego M, Pellizzari I,
Pellarin I, Canzonieri V, D'Andrea S, Benevol S, Sorio R, Giorda G,
Califano D, et al: CDK6 protects epithelial ovarian cancer from
platinum-induced death via FOXO3 regulation. EMBO Mol Med.
9:1415–1433. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhu H, Wang G, Zhou X, Song X, Gao H, Ma
C, Chang H, Li H, Liu FF, Lu J and Ma J: miR-1299 suppresses cell
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by targeting CDK6.
Biomed Pharmacother. 83:792–797. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu H, Tao J, Li X, Zhang T, Zhao L, Wang
Y, Zhang L, Xiong J, Zeng Z, Zhan N, et al: MicroRNA-206 prevents
the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating
expression of met proto-oncogene and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 in
mice. Hepatology. 66:1952–1967. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zou X, Tsutsui T, Ray D, Blomquist JF,
Ichijo H, Ucker DS and Kiyokawa H: The cell cycle-regulatory CDC25A
phosphatase inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell
Biol. 21:4818–4828. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sur S and Agrawal DK: Phosphatases and
kinases regulating CDC25 activity in the cell cycle: Clinical
implications of CDC25 overexpression and potential treatment
strategies. Mol Cell Biochem. 416:33–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|