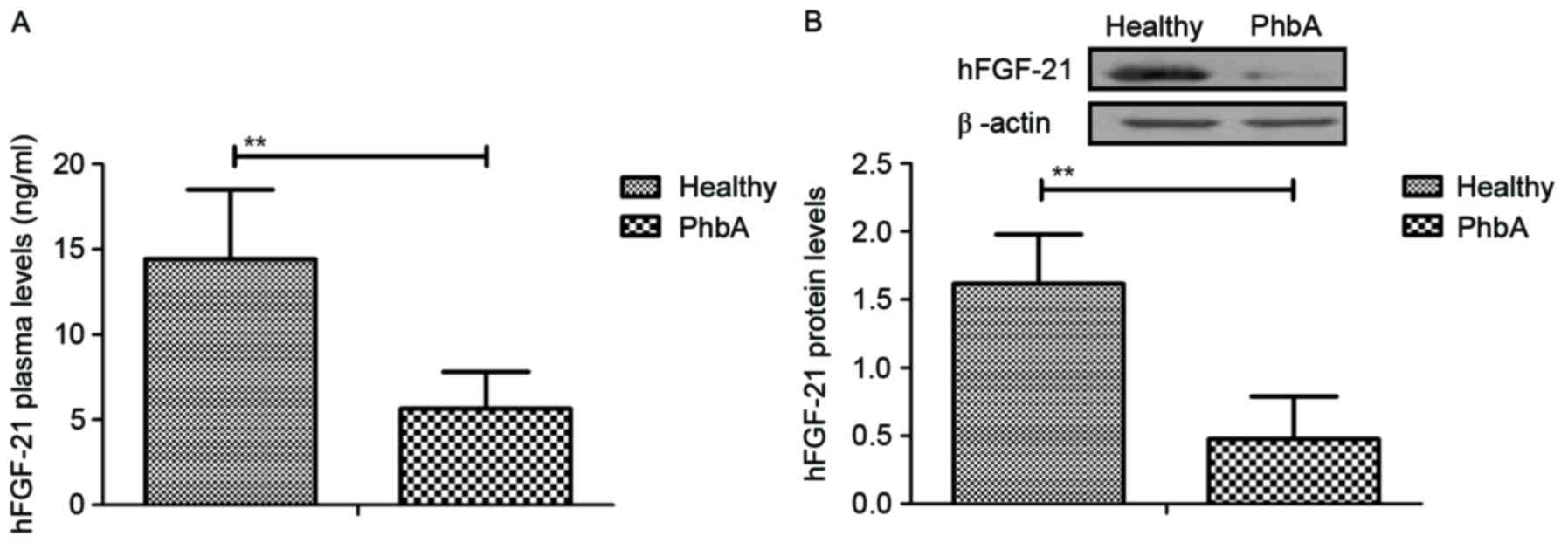
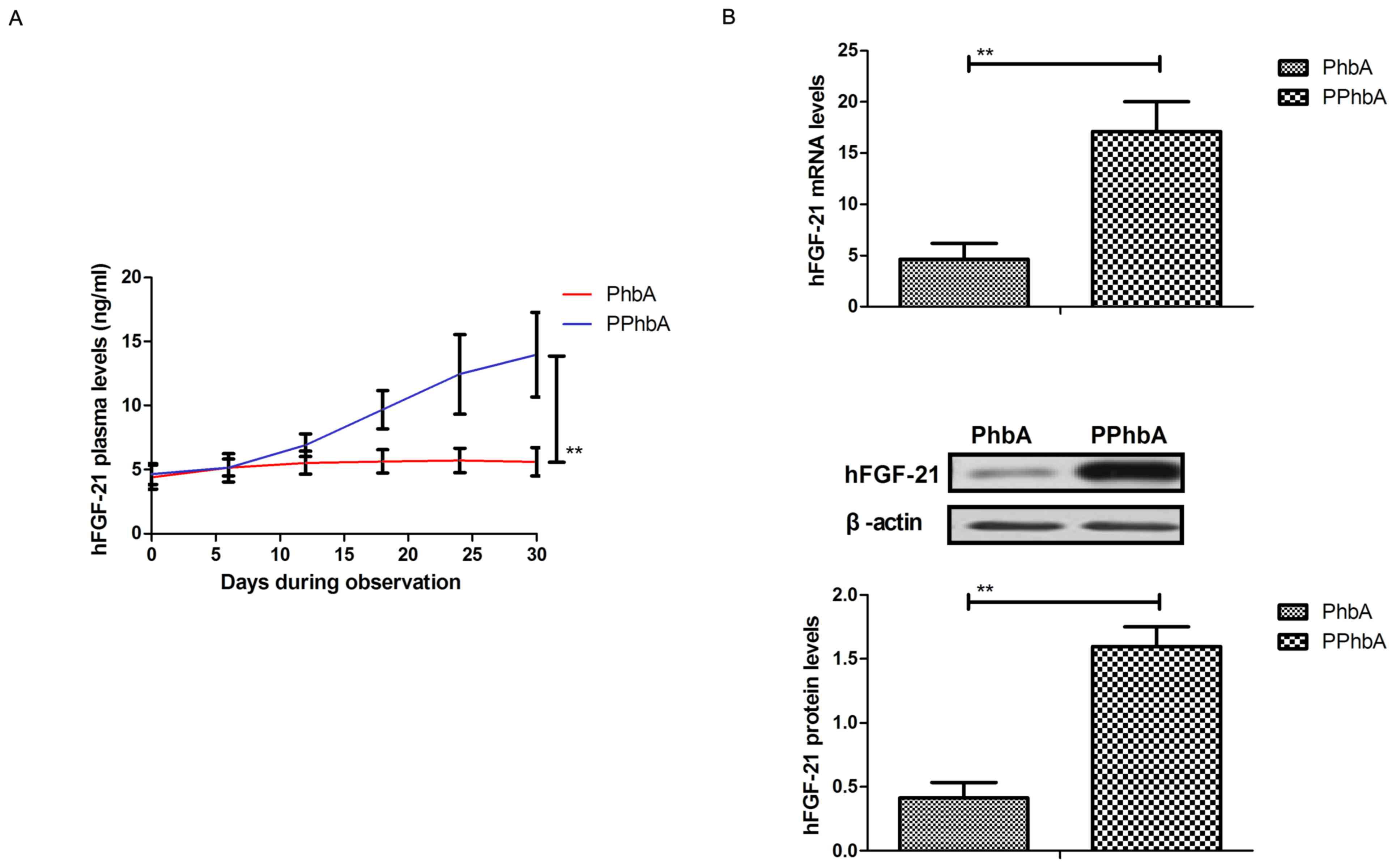
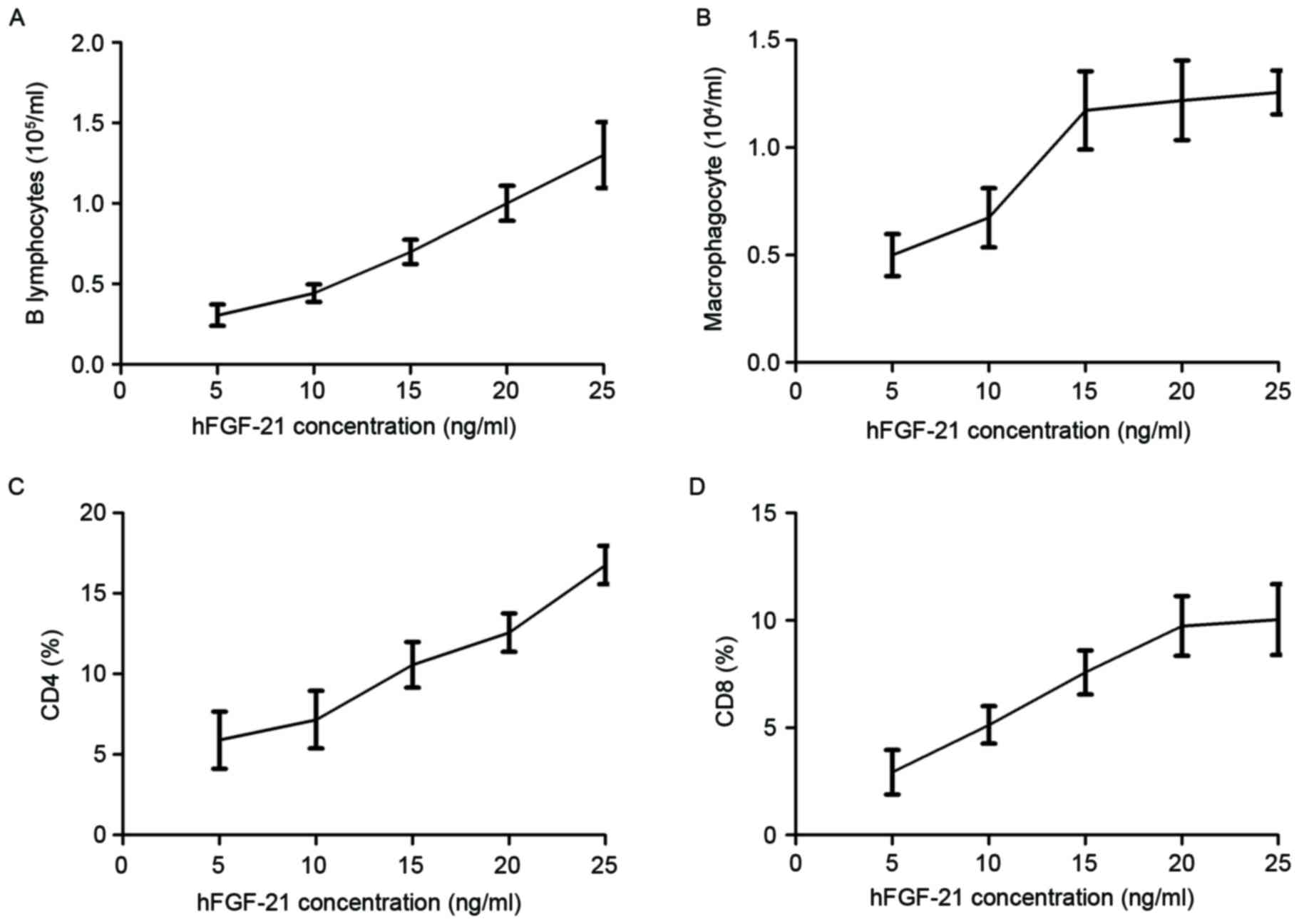
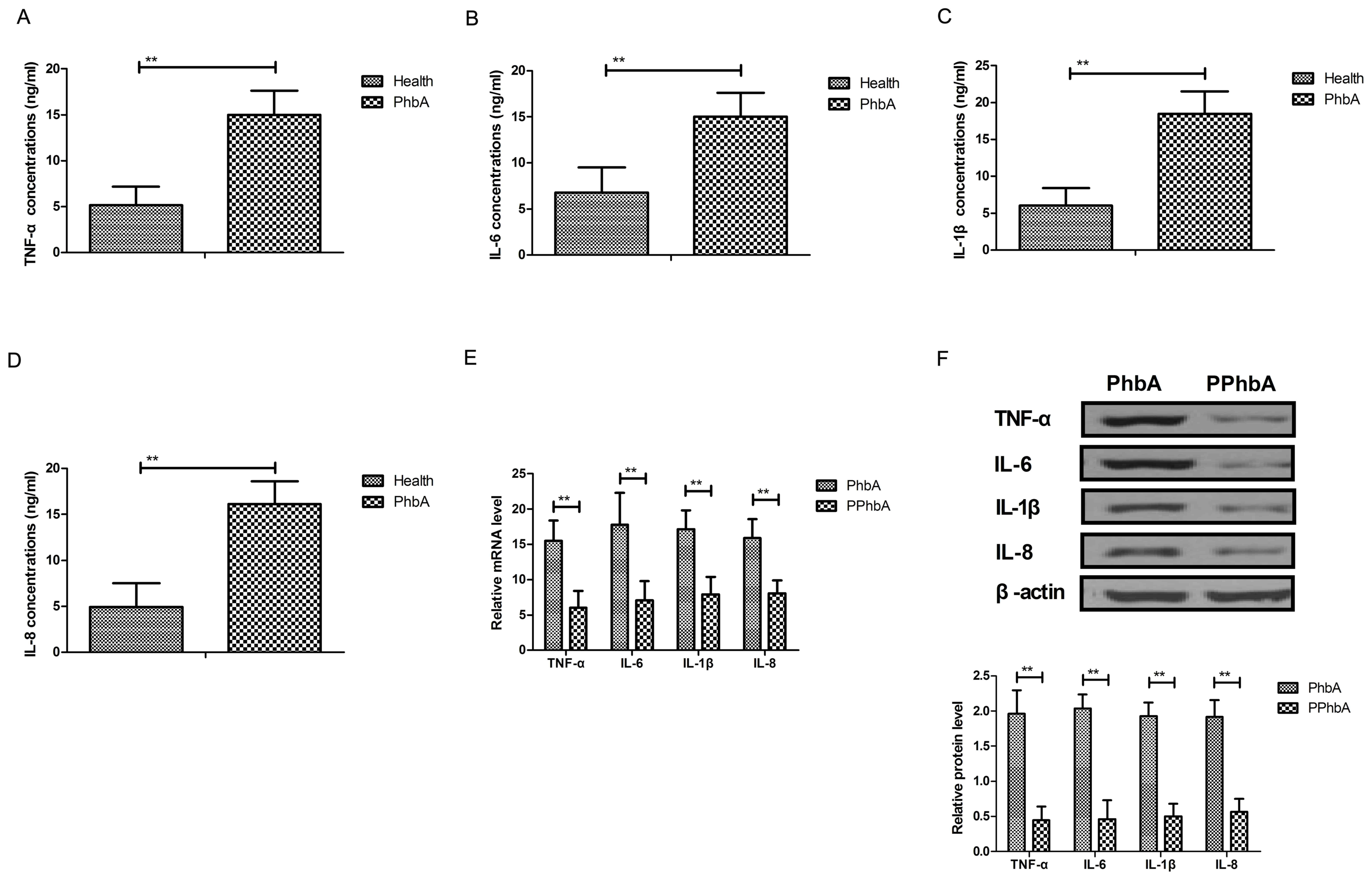
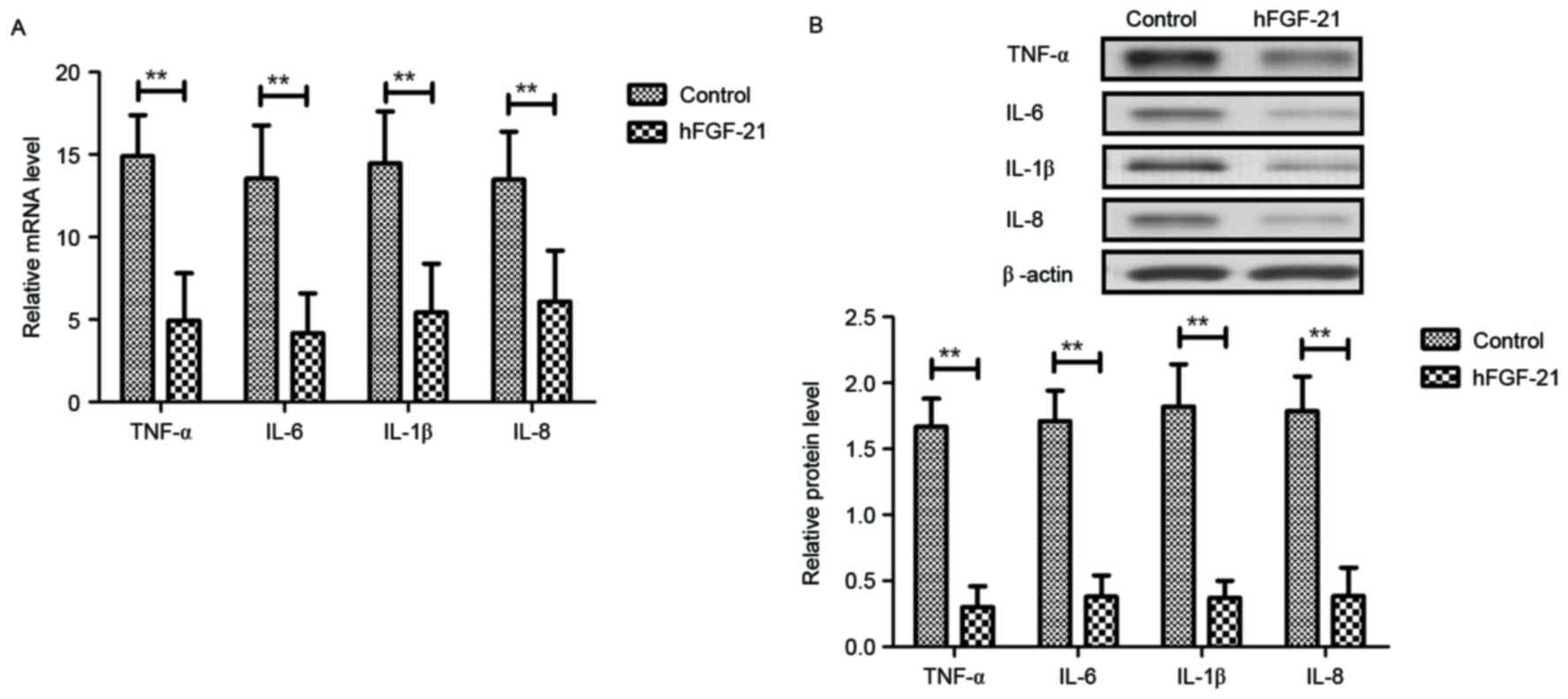
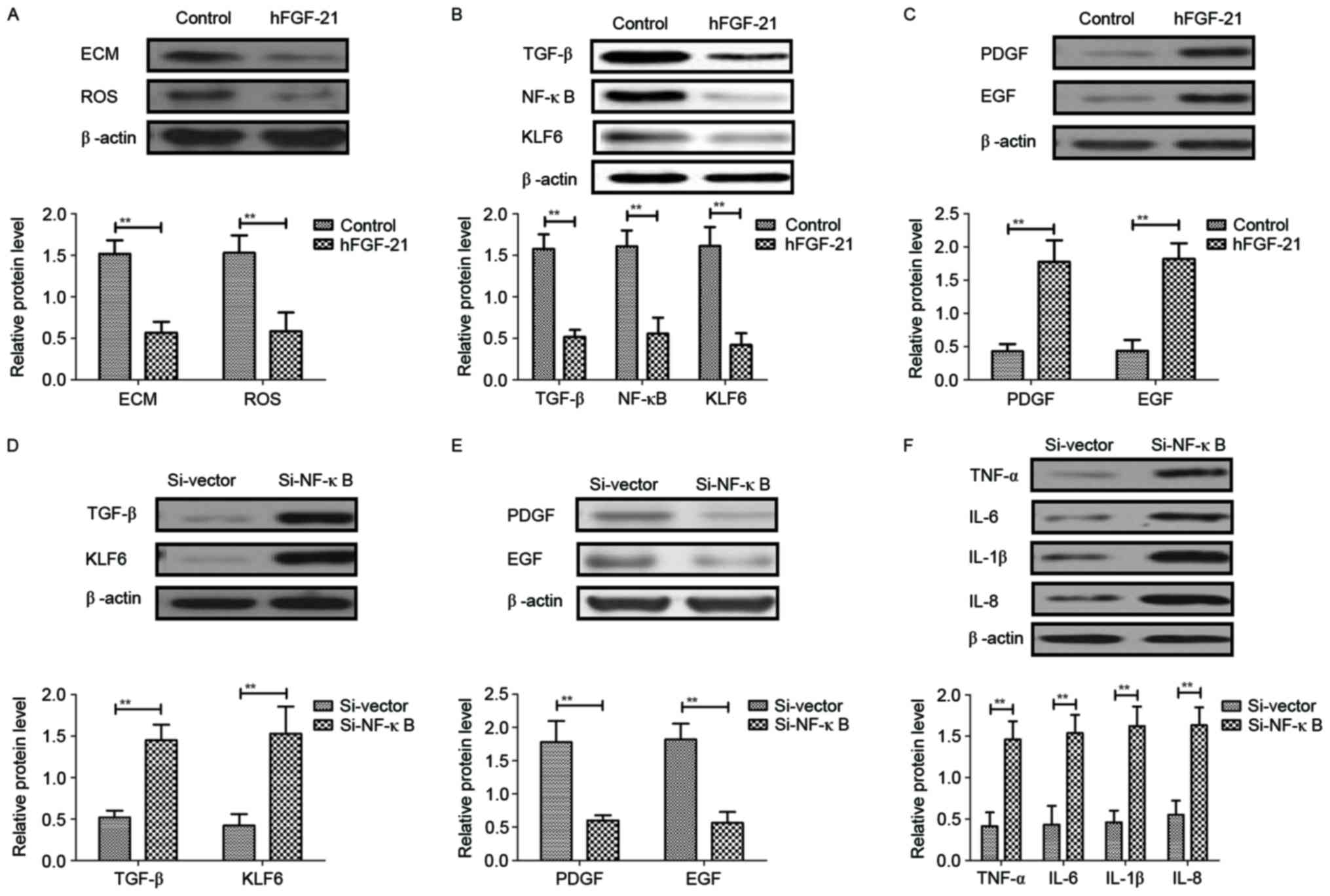
|
1
|
Acharya UR, Raghavendra U, Fujita H,
Hagiwara Y, Koh JE, Jen Hong T, Sudarshan VK, Vijayananthan A,
Yeong CH, Gudigar A and Ng KH: Automated characterization of fatty
liver disease and cirrhosis using curvelet transform and entropy
features extracted from ultrasound images. Comput Biol Med.
79:250–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dezső K, Rókusz A, Bugyik E, Szücs A,
Szuák A, Dorogi B, Kiss M, Nemeskéri Á, Nagy P and Paku S: Human
liver regeneration in advanced cirrhosis is organized by the portal
tree. J Hepatol. 66:778–786. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aguirre Valadez JM, Rivera-Espinosa L,
Méndez-Guerrero O, Chávez-Pacheco JL, García Juárez I and Torre A:
Intestinal permeability in a patient with liver cirrhosis. Ther
Clin Risk Manag. 12:1729–1748. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ganai AA, Ganaie IA, Verma N and Farooqi
H: Regression of fibrosis/cirrhosis by Glycine
propionyl-l-carnitine treatment in d-Galactosamine induced chronic
liver damage. Chem Biol Interact. 260:117–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Askgaard G, Leon DA, Kjaer MS, Deleuran T,
Gerds TA and Tolstrup JS: Risk for alcoholic liver cirrhosis after
an initial hospital contact with alcohol problems: A nationwide
prospective cohort study. Hepatology. 65:929–937. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiriac S, Stanciu C and Trifan A:
Corticosteroid treatment in the setting of decompensated liver
cirrhosis with relative adrenal insufficiency: A case report and a
brief review of the literature. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi.
120:288–292. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Z, Sheng L, Yang Y, Yang F, Xiao X,
Hua J, Guo C, Wei Y, Tang R, Miao Q, et al: The management of
autoimmune hepatitis patients with decompensated cirrhosis:
Real-world experience and a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 52:424–435. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han Y, Zeng A, Liao H, Liu Y, Chen Y and
Ding H: The efficacy and safety comparison between tenofovir and
entecavir in treatment of chronic hepatitis B and HBV related
cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 42:168–175. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fialla AD, Israelsen M, Hamberg O, Krag A
and Gluud LL: Nutritional therapy in cirrhosis or alcoholic
hepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int.
35:2072–2078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Manne V, Akhtar E and Saab S: Cirrhosis
regression in patients with viral hepatitis B and C: A systematic
review. J Clin Gastroenterol. 48:e76–e84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eto K: FGF-21, a newcomer in the field of
hypertension research. J Hum Hypertens. 27:343–344. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reinehr T, Woelfle J, Wunsch R and Roth
CL: Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) and its relation to
obesity, metabolic syndrome, and nonalcoholic fatty liver in
children: A longitudinal analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
97:2143–2150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dushay J, Chui PC, Gopalakrishnan GS,
Varela-Rey M, Crawley M, Fisher FM, Badman MK, Martinez-Chantar ML
and Maratos-Flier E: Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in
obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology.
139:456–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hotta Y, Nakamura H, Konishi M, Murata Y,
Takagi H, Matsumura S, Inoue K, Fushiki T and Itoh N: Fibroblast
growth factor 21 regulates lipolysis in white adipose tissue but is
not required for ketogenesis and triglyceride clearance in liver.
Endocrinology. 150:4625–4633. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang R, Yi X, Li X and Jiang X: Fibroblast
growth factor-21 is positively associated with atrial fibrosis in
atrial fibrillation patients with rheumatic heart disease. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14901–14908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cariello M and Moschetta A: Fibroblast
growth factor 21: A new liver safeguard. Hepatology. 60:792–794.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suomalainen A, Elo JM, Pietiläinen KH,
Hakonen AH, Sevastianova K, Korpela M, Isohanni P, Marjavaara SK,
Tyni T, Kiuru-Enari S, et al: FGF-21 as a biomarker for
muscle-manifesting mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies: A
diagnostic study. Lancet Neurol. 10:806–818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin Z, Wu Z, Yin X, Liu Y, Yan X, Lin S,
Xiao J, Wang X, Feng W and Li X: Serum levels of FGF-21 are
increased in coronary heart disease patients and are independently
associated with adverse lipid profile. PLoS One. 5:e155342010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kamada Y, Yoshida Y, Saji Y, Fukushima J,
Tamura S, Kiso S and Hayashi N: Transplantation of basic fibroblast
growth factor-pretreated adipose tissue-derived stromal cells
enhances regression of liver fibrosis in mice. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G157–G167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsuzaki K, Murata M, Yoshida K, Sekimoto
G, Uemura Y, Sakaida N, Kaibori M, Kamiyama Y, Nishizawa M,
Fujisawa J, et al: Chronic inflammation associated with hepatitis C
virus infection perturbs hepatic transforming growth factor beta
signaling, promoting cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 46:48–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aldaba-Muruato LR, Moreno MG, Shibayama M,
Tsutsumi V and Muriel P: Protective effects of allopurinol against
acute liver damage and cirrhosis induced by carbon tetrachloride:
Modulation of NF-κB, cytokine production and oxidative stress.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:65–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Lédinghen V, Douvin C, Kettaneh A, Ziol
M, Roulot D, Marcellin P, Dhumeaux D and Beaugrand M: Diagnosis of
hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis by transient elastography in
HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic
Syndr. 41:175–179. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Matsui Y, Fujiwara H,
Sakurai J, Masaoka Y, Gobara H and Kanazawa S: CT
fluoroscopy-guided renal tumour cutting needle biopsy:
Retrospective evaluation of diagnostic yield, safety, and risk
factors for diagnostic failure. Eur Radiol. 28:283–290. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Almeida Mde A, Pizzini CV, Damasceno LS,
Muniz Mde M, Almeida-Paes R, Peralta RH, Peralta JM, Oliveira Rde
V, Vizzoni AG, de Andrade CL and Zancopé-Oliveira RM: Validation of
western blot for Histoplasma capsulatum antibody detection assay.
BMC Infect Dis. 16:872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mattheolabakis G, Ling D, Ahmad G and
Amiji M: Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of lipid-modified platinum
derivatives in combination with survivin silencing siRNA in
resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Pharm Res. 33:2943–2953.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiao S, Chen H, Wang Y, Zhu J, Tan J and
Gao J: Splenectomy versus partial splenic embolization for massive
splenomegaly secondary to hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis: A
case-control study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016:34716262016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maan R, van Tilborg M, Deterding K, Ramji
A, van der Meer AJ, Wong F, Fung S, Sherman M, Manns MP, Cornberg
M, et al: Safety and effectiveness of direct-acting antiviral
agents for treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C virus
infection and cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:1821–1830.e6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Artigas A, Wernerman J, Arroyo V, Vincent
JL and Levy M: Role of albumin in diseases associated with severe
systemic inflammation: Pathophysiologic and clinical evidence in
sepsis and in decompensated cirrhosis. J Crit Care. 33:62–70. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen X, Shi C, Meng X, Zhang K, Li X, Wang
C, Xiang Z, Hu K and Han X: Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
suppresses bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by attenuating the
expression of TGF-β1 and FGF-2. Exp Mol Pathol. 101:22–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohno T, Tanaka Y, Sugauchi F, Orito E,
Hasegawa I, Nukaya H, Kato A, Matunaga S, Endo M, Tanaka Y, et al:
Suppressive effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino
acid granules on oxidative stress and inflammation in HCV-positive
patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 38:683–688. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Prystupa A, Kiciński P, Sak J,
Boguszewska-Czubara A, Toruń-Jurkowska A and Załuska W:
Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1α, IL-6) and hepatocyte growth
factor in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterol
Res Pract. 2015:5326152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ganji SH, Kashyap ML and Kamanna VS:
Niacin inhibits fat accumulation, oxidative stress, and
inflammatory cytokine IL-8 in cultured hepatocytes: Impact on
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 64:982–990. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cesaratto L, Codarin E, Vascotto C,
Leonardi A, Kelley MR, Tiribelli C and Tell G: Specific inhibition
of the redox activity of ape1/ref-1 by e3330 blocks tnf-α-induced
activation of IL-8 production in liver cancer cell lines. PLoS One.
8:e709092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park K, Hong SW, Hur W, Lee MY, Yang JA,
Kim SW, Yoon SK and Hahn SK: Target specific systemic delivery of
TGF-β siRNA/(PEI-SS)-g-HA complex for the treatment of liver
cirrhosis. Biomaterials. 32:4951–4958. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chávez E, Castro-Sánchez L, Shibayama M,
Tsutsumi V, Moreno MG and Muriel P: Sulfasalazine prevents the
increase in TGF-β, COX-2, nuclear NFκB translocation and fibrosis
in CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis in the rat. Hum Exp Toxicol.
31:913–920. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Salehi MH, Kamalidehghan B, Houshmand M,
Aryani O, Sadeghizadeh M and Mossalaeie MM: Association of
fibroblast growth factor (FGF-21) as a biomarker with primary
mitochondrial disorders, but not with secondary mitochondrial
disorders (Friedreich Ataxia). Mol Biol Rep. 40:6495–6499. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gahete MD, Córdoba-Chacón J, Luque RM and
Kineman RD: The rise in growth hormone during starvation does not
serve to maintain glucose levels or lean mass but is required for
appropriate adipose tissue response in female mice. Endocrinology.
154:263–269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu D, Sun CY, Sun GP, Ren GP, Ye XL, Zhu
SL, Wang WF, Xu PF, Li SJ, Wu Q, et al: The synergistic effect of
FGF-21 and insulin on regulating glucose metabolism and its
mechanism. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 49:977–984. 2014.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ren G, Yin J, Wang W, Li L and Li D:
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-21 signals through both FGF
receptor-1 and 2. Sci China Life Sci. 53:1000–1008. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kharitonenkov A, Dunbar JD, Bina HA,
Bright S, Moyers JS, Zhang C, Ding L, Micanovic R, Mehrbod SF,
Knierman MD, et al: FGF-21/FGF-21 receptor interaction and
activation is determined by betaKlotho. J Cell Physiol. 215:1–7.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A,
Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers
JS, Owens RA, et al: FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin
Invest. 115:1627–1635. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|