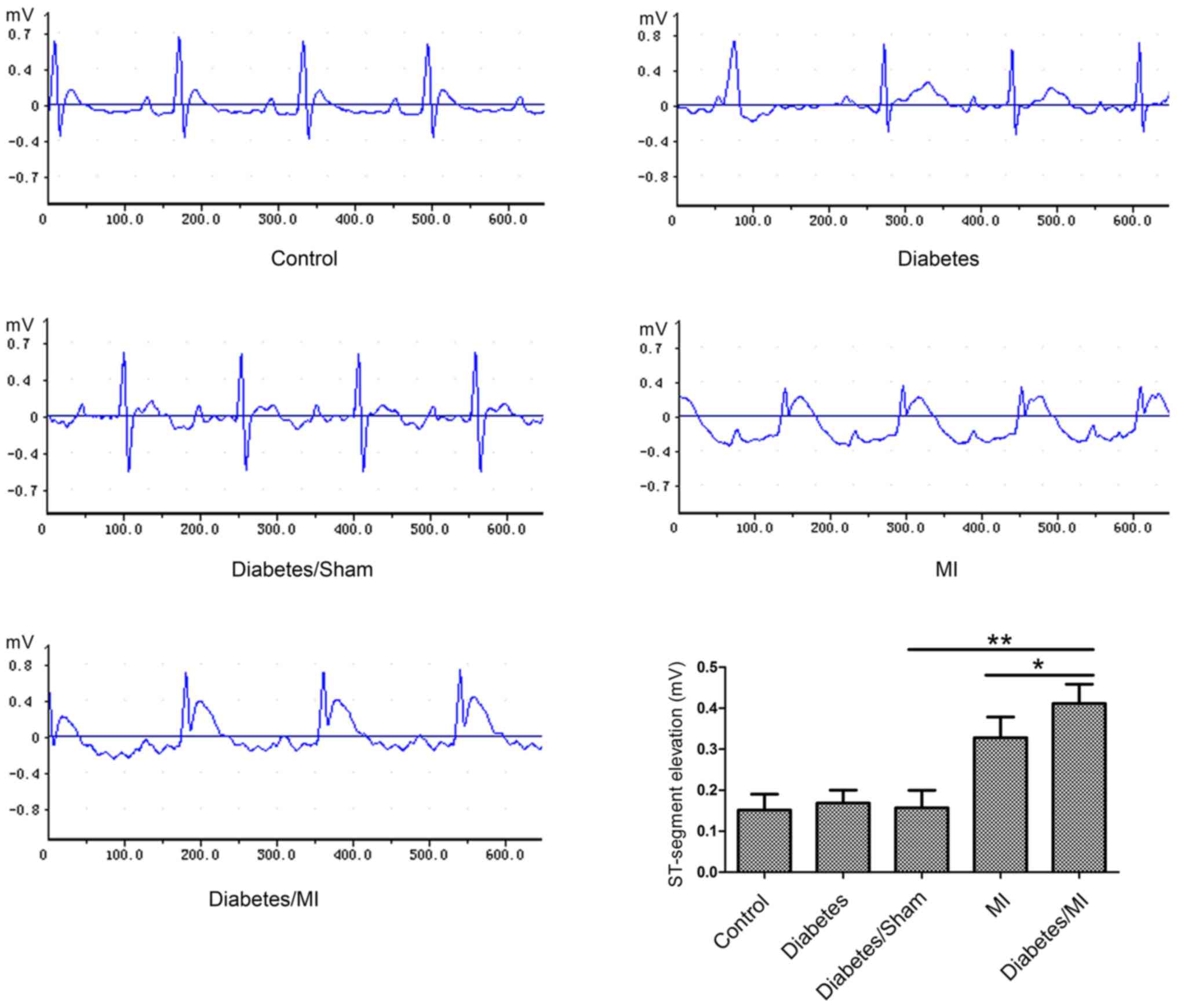
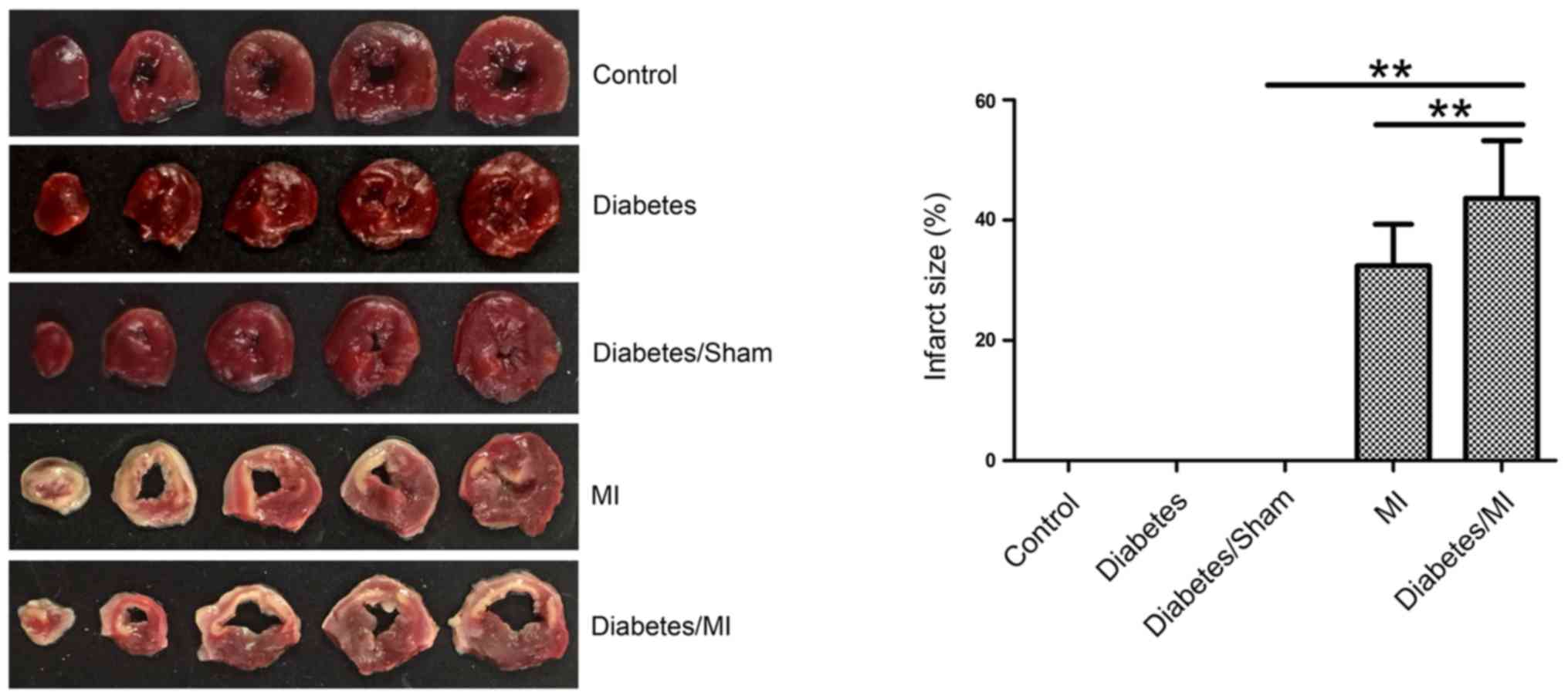
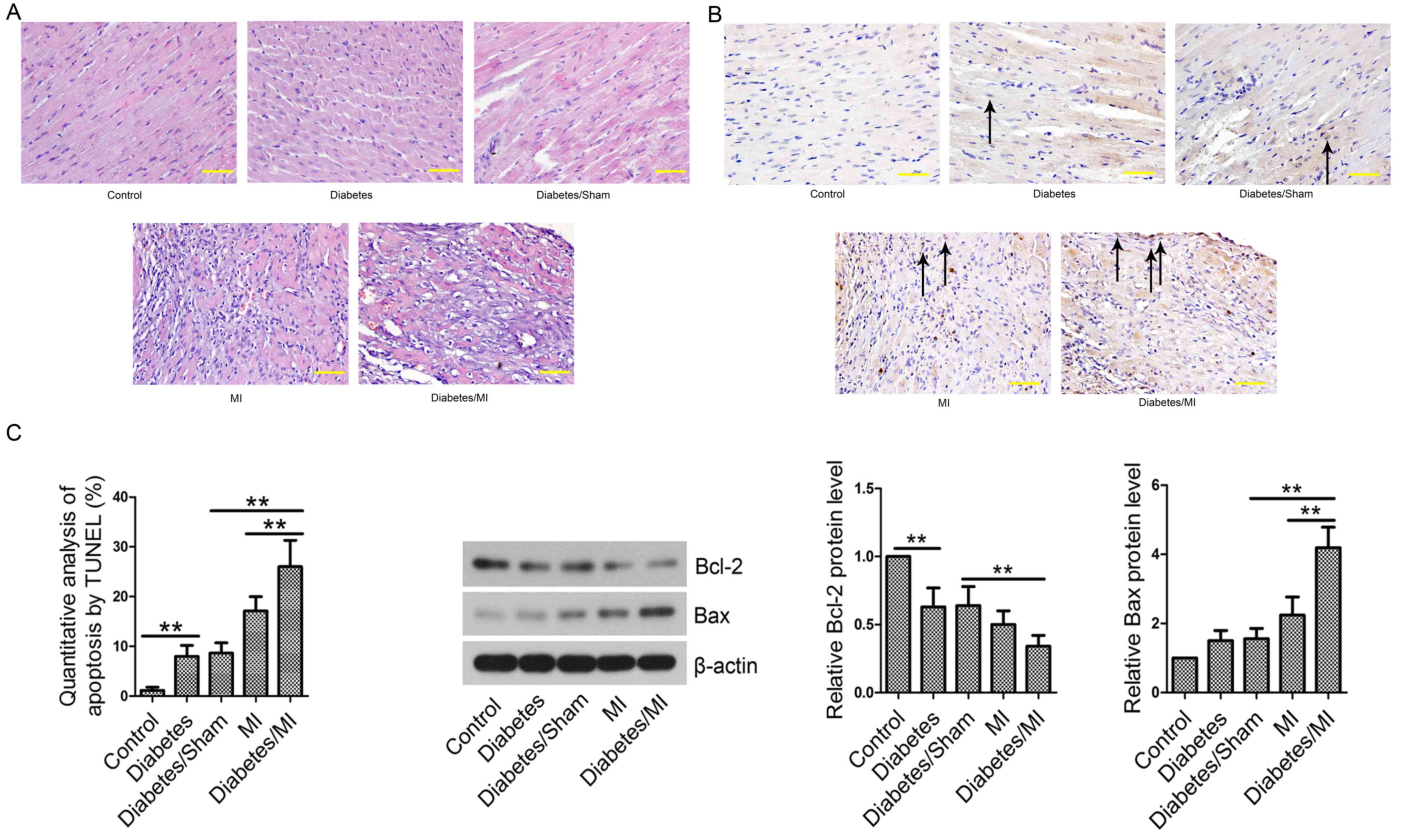
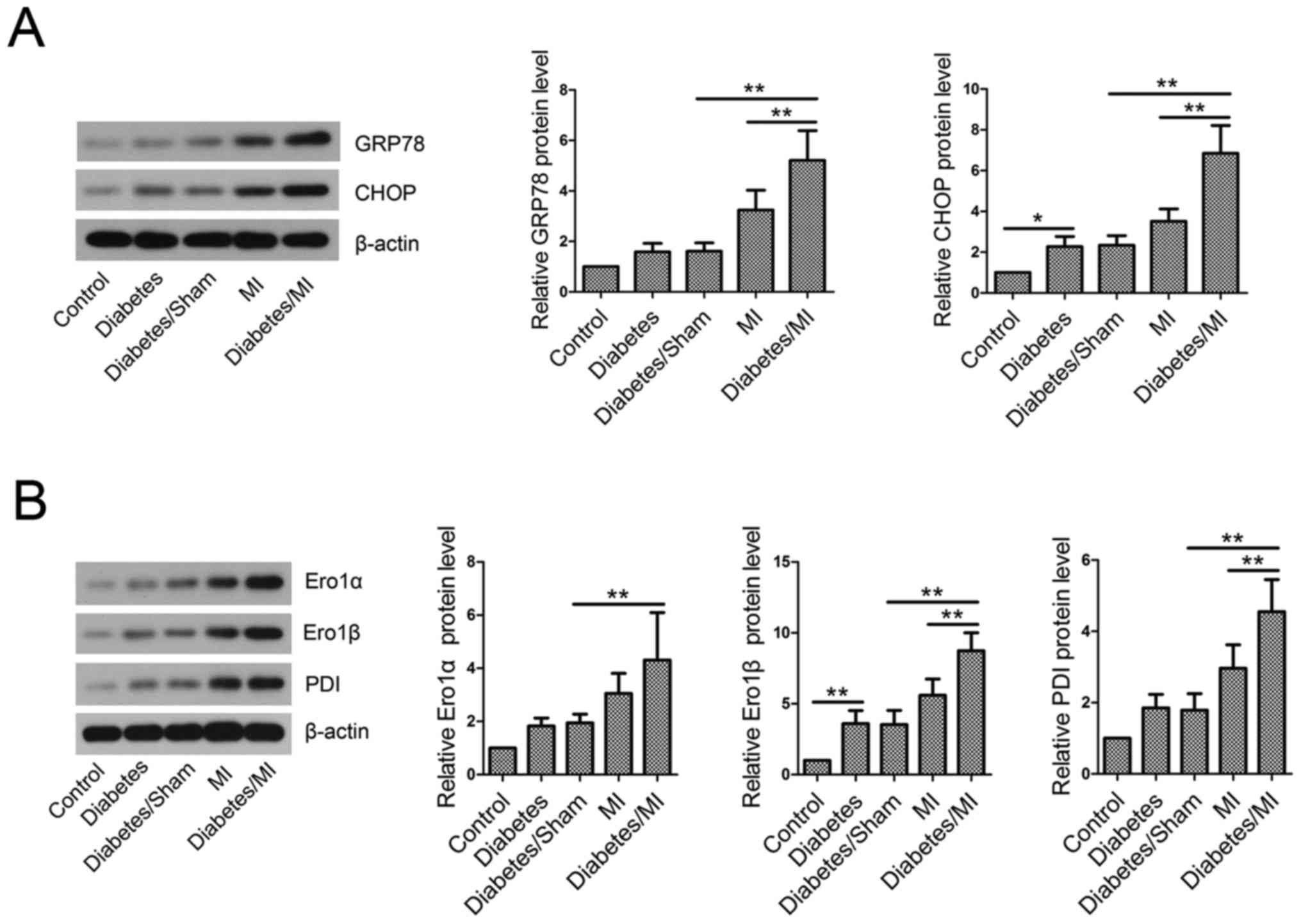
|
1
|
Bai Y, Wang X, Zhao S, Ma C, Cui J and
Zheng Y: Sulforaphane protects against cardiovascular disease via
Nrf2 activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:4075802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang ZH, Emma-Okon B and Remaley AT:
Dietary marine-derived long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids and
cardiovascular disease risk: A mini review. Lipids Health Dis.
15:2012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bernardi S, Michelli A, Zuolo G, Candido R
and Fabris B: Update on RAAS modulation for the treatment of
diabetic cardiovascular disease. J Diabetes Res. 2016:89175782016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lipes MA and Galderisi A: Cardiac
autoimmunity as a novel biomarker, mediator and therapeutic target
of heart disease in type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 15:302015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gregg EW, Cheng YJ, Saydah S, Cowie C,
Garfield S, Geiss L and Barker L: Trends in death rates among U.S.
adults with and without diabetes between 1997 and 2006: Findings
from the National Health Interview Survey. Diabetes Care.
35:1252–1257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JM: Nuclear receptors resolve
endoplasmic reticulum stress to improve hepatic insulin resistance.
Diabetes Metab J. 41:10–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Phillips MJ and Voeltz GK: Structure and
function of ER membrane contact sites with other organelles. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:69–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Tsai YH and Tseng SH: HDAC
inhibitors and RECK modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress in tumor
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:pii: E258. 2017.
|
|
9
|
Lee YT, Lin HY, Chan YW, Li KH, To OT, Yan
BP, Liu T, Li G, Wong WT, Keung W and Tse G: Mouse models of
atherosclerosis: A historical perspective and recent advances.
Lipids Health Dis. 16:122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oyadomari S, Koizumi A, Takeda K, Gotoh T,
Akira S, Araki E and Mori M: Targeted disruption of the Chop gene
delays endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated diabetes. J Clin
Invest. 109:525–532. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi ZY, Liu Y, Dong L, Zhang B, Zhao M,
Liu WX, Zhang X and Yin XH: Cortistatin improves cardiac function
after acute myocardial infarction in rats by suppressing myocardial
apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
Ther: pii: 1074248416644988. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Rao J, Zhang C, Wang P, Lu L, Qian X, Qin
J, Pan X, Li G, Wang X and Zhang F: C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP)
contributes to hepatocyte death via the promotion of ERO1α
signalling in acute liver failure. Biochem J. 466:369–378. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takada A, Miki T, Kuno A, Kouzu H, Sunaga
D, Itoh T, Tanno M, Yano T, Sato T, Ishikawa S and Miura T: Role of
ER stress in ventricular contractile dysfunction in type 2
diabetes. PLoS One. 7:e398932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barr LA, Shimizu Y, Lambert JP, Nicholson
CK and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates high fat
diet-induced cardiac dysfunction via the suppression of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Nitric Oxide. 46:145–156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rawal S, Manning P and Katare R:
Cardiovascular microRNAs: As modulators and diagnostic biomarkers
of diabetic heart disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 13:442014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuusisto J and Laakso M: Update on type 2
diabetes as a cardiovascular disease risk equivalent. Curr Cardiol
Rep. 15:3312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu SF, Huang Y, Wang N, Shen WX, Fu SP, Li
Q, Yu ML, Liu WX, Chen X, Jing XY and Zhu BM: Cardioprotective
effect of electroacupuncture pretreatment on myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via antiapoptotic signaling. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2016:46097842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tiwari RP, Jain A, Khan Z, Kohli V,
Bharmal RN, Kartikeyan S and Bisen PS: Cardiac troponins I and T:
Molecular markers for early diagnosis, prognosis and accurate
triaging of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Mol Diagn
Ther. 16:371–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Yu P, Chen M, Peng Q, Wang Z and
Dong N: Remote ischaemic preconditioning and sevoflurane
postconditioning synergistically protect rats from myocardial
injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion partly via inhibition
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:22–32.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ding M, Lei J, Han H, Li W, Qu Y, Fu E, Fu
F and Wang X: SIRT1 protects against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating eNOS in diabetic rats.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:1432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu J, Wang N, Xie F, Sun LH, Chen QX, Ye
JH, Cai BZ, Yang BF and Ai J: Blockage of peripheral NPY Y1 and Y2
receptors modulates barorefex sensitivity of diabetic rats. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 31:421–431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang R, Li Y, Yang X, Yue Y, Dou L, Wang
Y, Zhang W and Li X: Protective role of deoxyschizandrin and
schisantherin A against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats. PLoS One. 8:e615902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xie F, Sun L, Su X, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhang
R, Wang N, Zhao J, Ban T, Niu H and Ai J: Neuropeptide Y reverses
chronic stress-induced baroreflex hypersensitivity in rats. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 29:463–474. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Agrawal YO, Sharma PK, Shrivastava B, Arya
DS and Goyal SN: Hesperidin blunts streptozotocin-isoproternol
induced myocardial toxicity in rats by altering of PPAR-γ receptor.
Chem Biol Interact. 219:211–220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bussani R, Abbate A, Biondi-Zoccai GG,
Dobrina A, Leone AM, Camilot D, Di Marino MP, Baldi F, Silvestri F,
Biasucci LM and Baldi A: Right ventricular dilatation after left
ventricular acute myocardial infarction is predictive of extremely
high peri-infarctual apoptosis at postmortem examination in humans.
J Clin Pathol. 56:672–676. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Wang Q, Guo W and Zhu YZ: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates cardiac dysfunction in a rat model of heart
failure: A mechanism through cardiac mitochondrial protection.
Biosci Rep. 31:87–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han Q, Zhang HY, Zhong BL, Zhang B and
Chen H: Antiapoptotic effect of recombinant HMGB1 A-box protein via
regulation of microRNA-21 in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
model in rats. DNA Cell Biol. 35:192–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Ni M, Lee B, Barron E, Hinton DR and
Lee AS: The unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP is
required for endoplasmic reticulum integrity and stress-induced
autophagy in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ. 15:1460–1471.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu H, Zhen J, Yang Y, Gu J, Wu S and Liu
Q: Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy by
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in a
streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model. J Cell Mol Med.
20:623–631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bennett HL, Fleming JT, O'Prey J, Ryan KM
and Leung HY: Androgens modulate autophagy and cell death via
regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone glucose-regulated
protein 78/BiP in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 1:e722010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
DeGracia DJ and Montie HL: Cerebral
ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem. 91:1–8.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang M, Yu LM, Zhao H, Zhou XX, Yang Q,
Song F, Yan L, Zhai ME, Li BY, Zhang B, et al:
2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside protects murine
hearts against ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating
Notch1/Hes1 signaling and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:317–330. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu
J, Yankner BA and Yuan J: Caspase-12 mediates
endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by
amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H and Ichijo H:
Survival and apoptosis signals in ER stress: The role of protein
kinases. J Chem Neuroanat. 28:93–100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X, Batchvarova
N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL and Ron D: CHOP is
implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired
function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 12:982–995. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gross A: BCL-2 family proteins as
regulators of mitochondria metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1857:1243–1246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fu HY, Okada K, Liao Y, Tsukamoto O,
Isomura T, Asai M, Sawada T, Okuda K, Asano Y, Sanada S, et al:
Ablation of C/EBP homologous protein attenuates endoplasmic
reticulum-mediated apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction induced by
pressure overload. Circulation. 122:361–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Inaba K, Masui S, Iida H, Vavassori S,
Sitia R and Suzuki M: Crystal structures of human Ero1alpha reveal
the mechanisms of regulated and targeted oxidation of PDI. EMBO J.
29:3330–3343. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dias-Gunasekara S, Gubbens J, van Lith M,
Dunne C, Williams JA, Kataky R, Scoones D, Lapthorn A, Bulleid NJ,
Benham AM, et al: Tissue-specific expression and dimerization of
the endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase Ero1beta. J Biol Chem.
280:33066–33075. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kozlov G, Määttänen P, Thomas DY and
Gehring K: A structural overview of the PDI family of proteins.
FEBS J. 277:3924–3936. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Andreu CI, Woehlbier U, Torres M and Hetz
C: Protein disulfide isomerases in neurodegeneration: From disease
mechanisms to biomedical applications. FEBS Lett. 586:2826–2834.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Swiatkowska M, Padula G, Michalec L,
Stasiak M, Skurzynski S and Cierniewski CS: Ero1alpha is expressed
on blood platelets in association with protein-disulfide isomerase
and contributes to redox-controlled remodeling of alphaIIbbeta3. J
Biol Chem. 285:29874–29883. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scull CM and Tabas I: Mechanisms of ER
stress-induced apoptosis in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 31:2792–2797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Su D, Ma J, Yang J, Kang Y, Lv M and Li Y:
Monosialotetrahexosy-1 ganglioside attenuates diabetes-associated
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through suppression of the
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Clin Neurosci.
41:54–59. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu L, Li S, Tang X, Li Z, Zhang J, Xue X,
Han J, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, et al: Diallyl trisulfide
ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing
oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated
apoptosis in type 1 diabetic rats: Role of SIRT1 activation.
Apoptosis. 22:942–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Woo YJ, Panlilio CM, Cheng RK, Liao GP,
Atluri P, Hsu VM, Cohen JE and Chaudhry HW: Therapeutic delivery of
cyclin A2 induces myocardial regeneration and enhances cardiac
function in ischemic heart failure. Circulation. 114 1
Suppl:I206–I213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pasumarthi KB, Nakajima H, Nakajima HO,
Soonpaa MH and Field LJ: Targeted expression of cyclin D2 results
in cardiomyocyte DNA synthesis and infarct regression in transgenic
mice. Circ Res. 96:110–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|