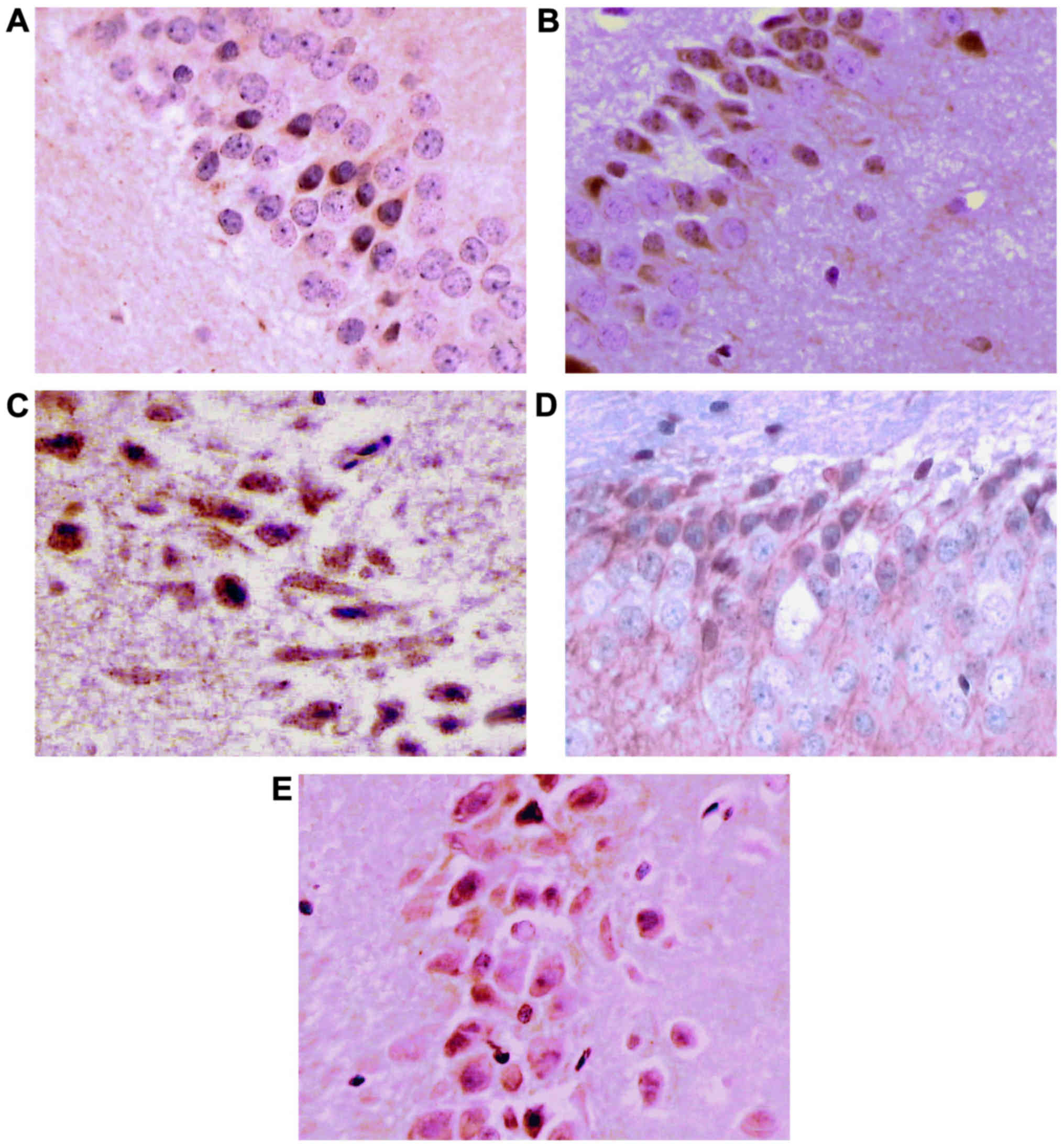
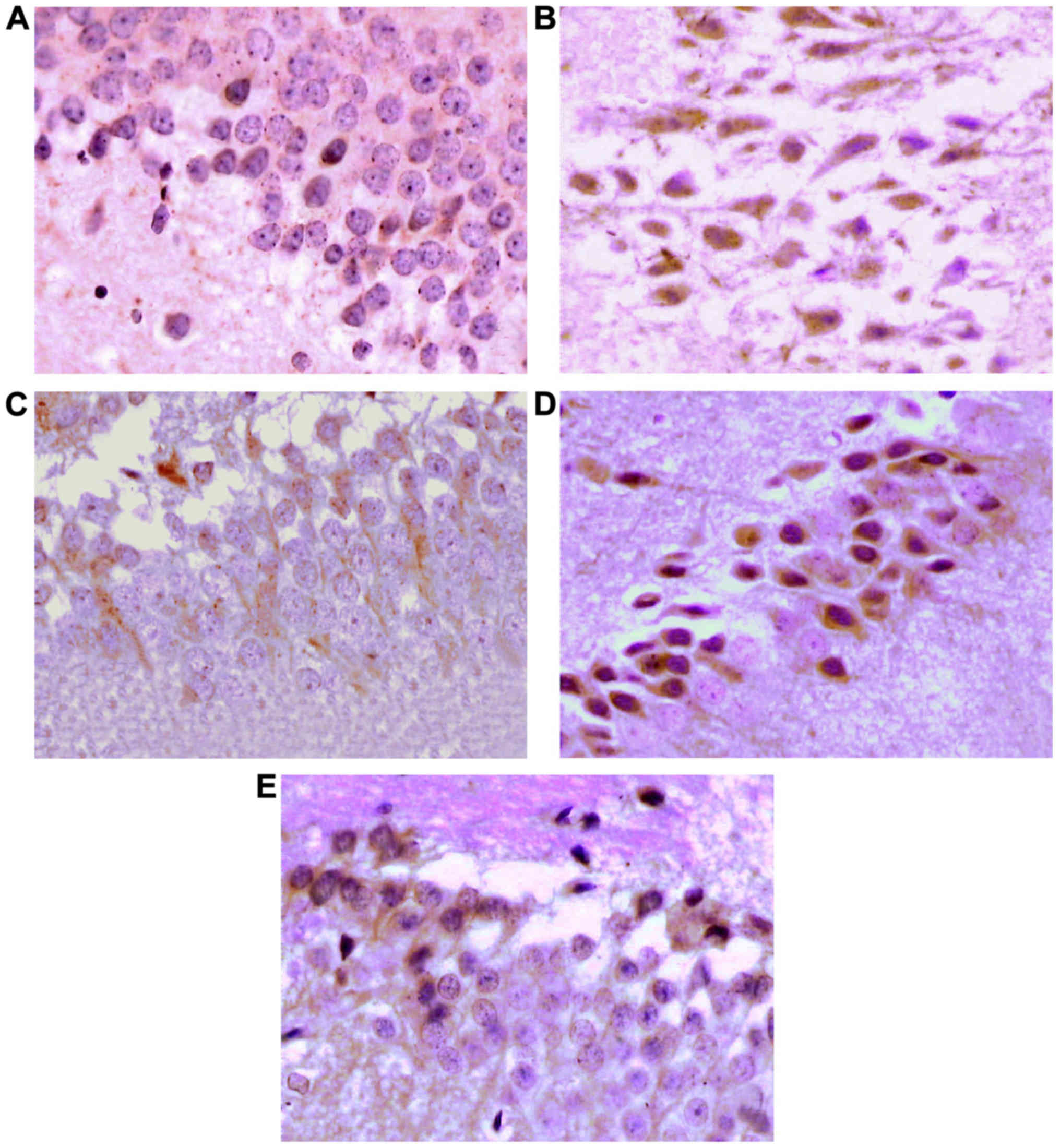
|
1
|
Wang C, Xie N, Wang Y, Li Y, Ge X and Wang
M: Role of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter in rat hippocampal
neuronal death after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus.
Neurochem Res. 40:1739–1746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buckmaster PS, Wen X, Toyoda I, Gulland FM
and van Bonn W: Hippocampal neuropathology of domoic acid-induced
epilepsy in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). J Comp
Neurol. 522:1691–1706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wassink G, Davidson JO, Dhillon SK, Fraser
M, Galinsky R, Bennet L and Gunn AJ: Partial white and grey matter
protection with prolonged infusion of recombinant human
erythropoietin after asphyxia in preterm fetal sheep. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 37:1080–1094. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang M, Yan W, Liu Y, Hu H, Sun Q, Chen X,
Zang W and Chen L: Erythropoietin ameliorates diabetes-associated
cognitive dysfunction in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 7:28012017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vinberg M, Miskowiak K, Hoejman P,
Pedersen M and Kessing LV: The effect of recombinant erythropoietin
on plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in patients with
affective disorders: A randomised controlled study. PLoS One.
10:e01276292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bahçekapılı N, Akgün-Dar K, Albeniz I,
Kapucu A, Kandil A, Yağız O and Üzüm G: Erythropoietin pretreatment
suppresses seizures and prevents the increase in inflammatory
mediators during pentylenetetrazole-induced generalized seizures.
Int J Neurosci. 124:762–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ugurluer G, Cebi A, Mert H, Mert N, Serin
M and Erkal HS: Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin against
oxidant injury following brain irradiation: An experimental study.
Arch Med Sci. 12:1348–1353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Si Z, Li S, Huang Z, He Y, Zhang T
and Wang A: The calcineurin inhibitor FK506 prevents cognitive
impairment by inhibiting reactive astrogliosis in
pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus rats. Front Cell Neurosci.
11:4282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mikati MA, Abi-Habib RJ, El Sabban ME,
Dbaibo GS, Kurdi RM, Kobeissi M, Farhat F and Asaad W: Hippocampal
programmed cell death after status epilepticus: Evidence for
NMDA-receptor and ceramide-mediated mechanisms. Epilepsia.
44:282–291. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Henshall DC, Araki T, Schindler CK, Lan
J-Q, Tiekoter KL, Taki W and Simon RP: Activation of
Bcl-2-associated death protein and counter-response of Akt within
cell populations during seizure-induced neuronal death. J Neurosci.
22:8458–8465. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meller R, Schindler CK, Chu XP, Xiong ZG,
Cameron JA, Simon RP and Henshall DC: Seizure-like activity leads
to the release of BAD from 14-3-3 protein and cell death in
hippocampal neurons in vitro. Cell Death Differ. 10:539–547. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Genc S, Koroglu TF and Genc K:
Erythropoietin as a novel neuroprotectant. Restor Neurol Neurosci.
22:105–119. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Kang T, Qi B, Kong L, Jiao Y, Cao Y,
Zhang J and Yang J: Neuroprotective effects of ginseng protein on
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hippocampus of D-galactose/AlCl3
inducing rats model of Alzheimer's disease. J Ethnopharmacol.
179:162–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uzüm G, Sarper Diler A, Bahçekapili N and
Ziya Ziylan Y: Erythropoietin prevents the increase in blood-brain
barrier permeability during pentylentetrazol induced seizures. Life
Sci. 78:2571–2576. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fu Z, Yang J, Wei Y and Li J: Effects of
piceatannol and pterostilbene against β-amyloid-induced apoptosis
on the PI3K/Akt/Bad signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Food Funct.
7:1014–1023. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang X, Dong L,
Xing Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Chen L, Qiao H, et al: Protection by silibinin
against experimental ischemic stroke: Up-regulated pAkt, pmTOR,
HIF-1α and Bcl-2, down-regulated Bax, NF-κB expression. Neurosci
Lett. 529:45–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miao J, Wang L, Zhang X, Zhu C, Cui L, Ji
H, Liu Y and Wang X: Protective effect of aliskiren in experimental
ischemic stroke: Up-regulated p-PI3K, p-AKT, Bcl-2 expression,
Attenuated Bax Expression. Neurochem Res. 41:2300–2310. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kong J, Ren G, Jia N, Wang Y, Zhang H,
Zhang W, Chen B and Cao Y: Effects of nicorandil in neuroprotective
activation of PI3K/AKT pathways in a cellular model of Alzheimer's
disease. Eur Neurol. 70:233–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiao Z, Peng J, Yang L, Kong H and Yin F:
Interleukin-1β plays a role in the pathogenesis of mesial temporal
lobe epilepsy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in
hippocampal neurons. J Neuroimmunol. 282:110–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|