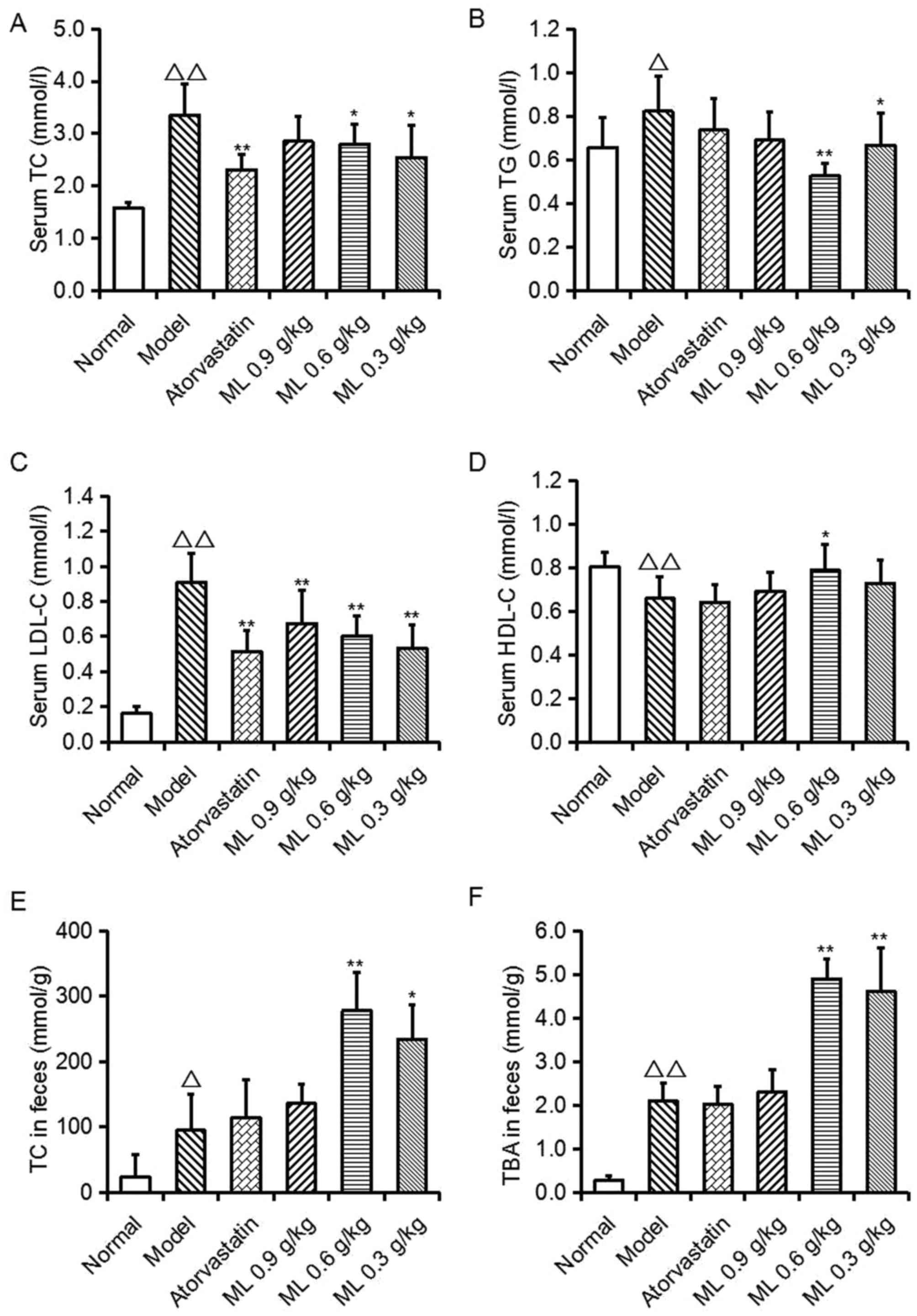
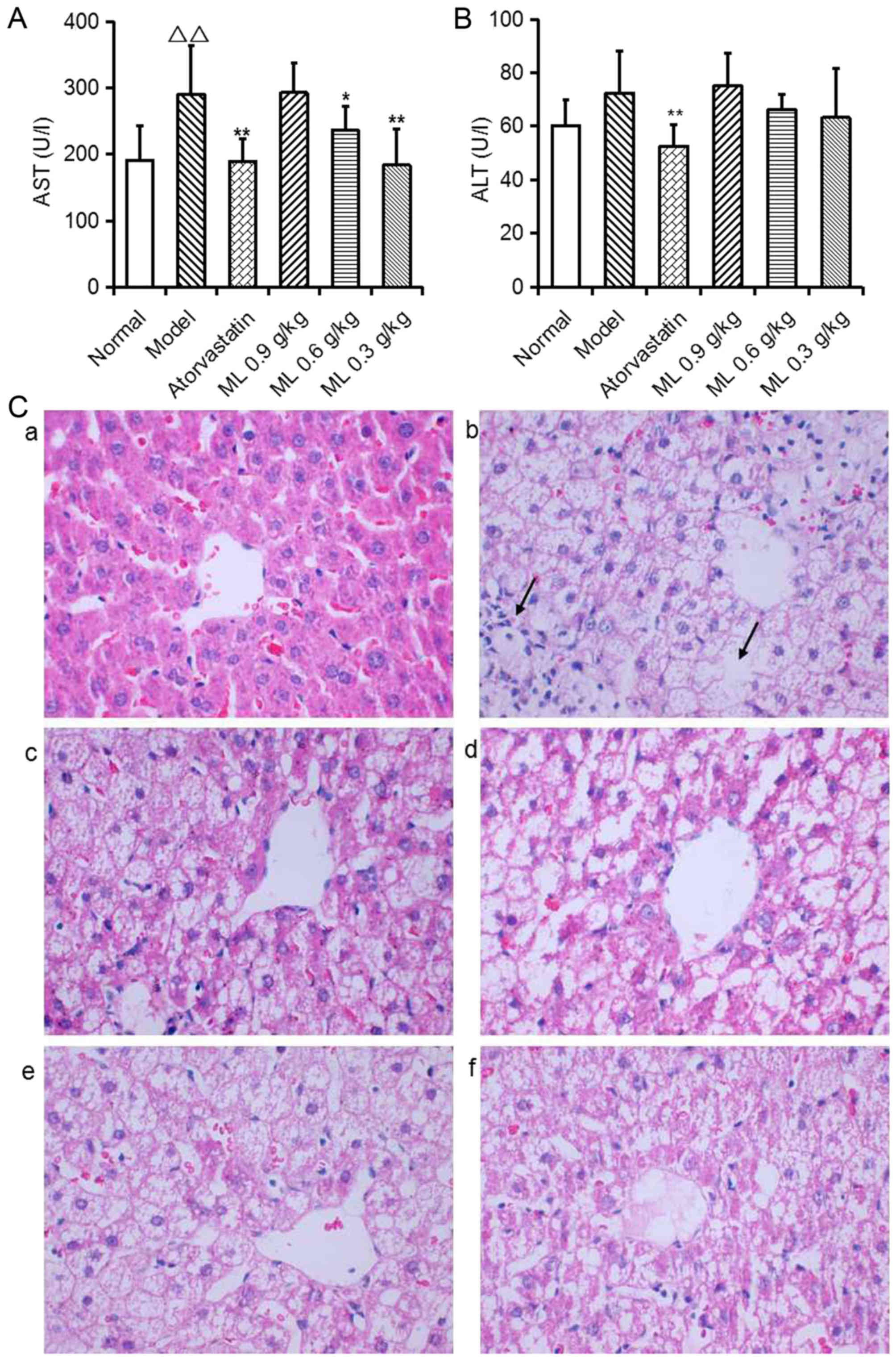
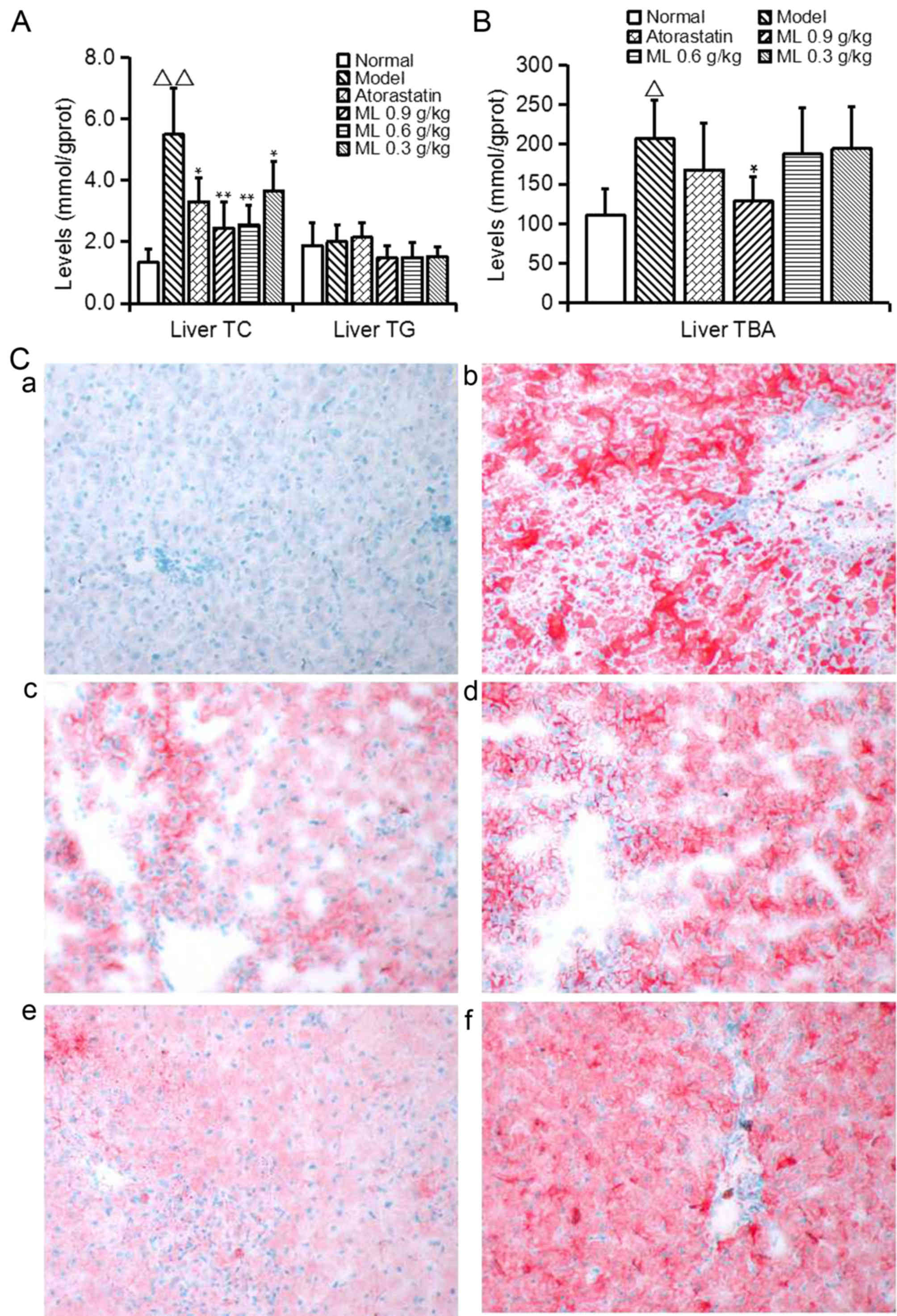
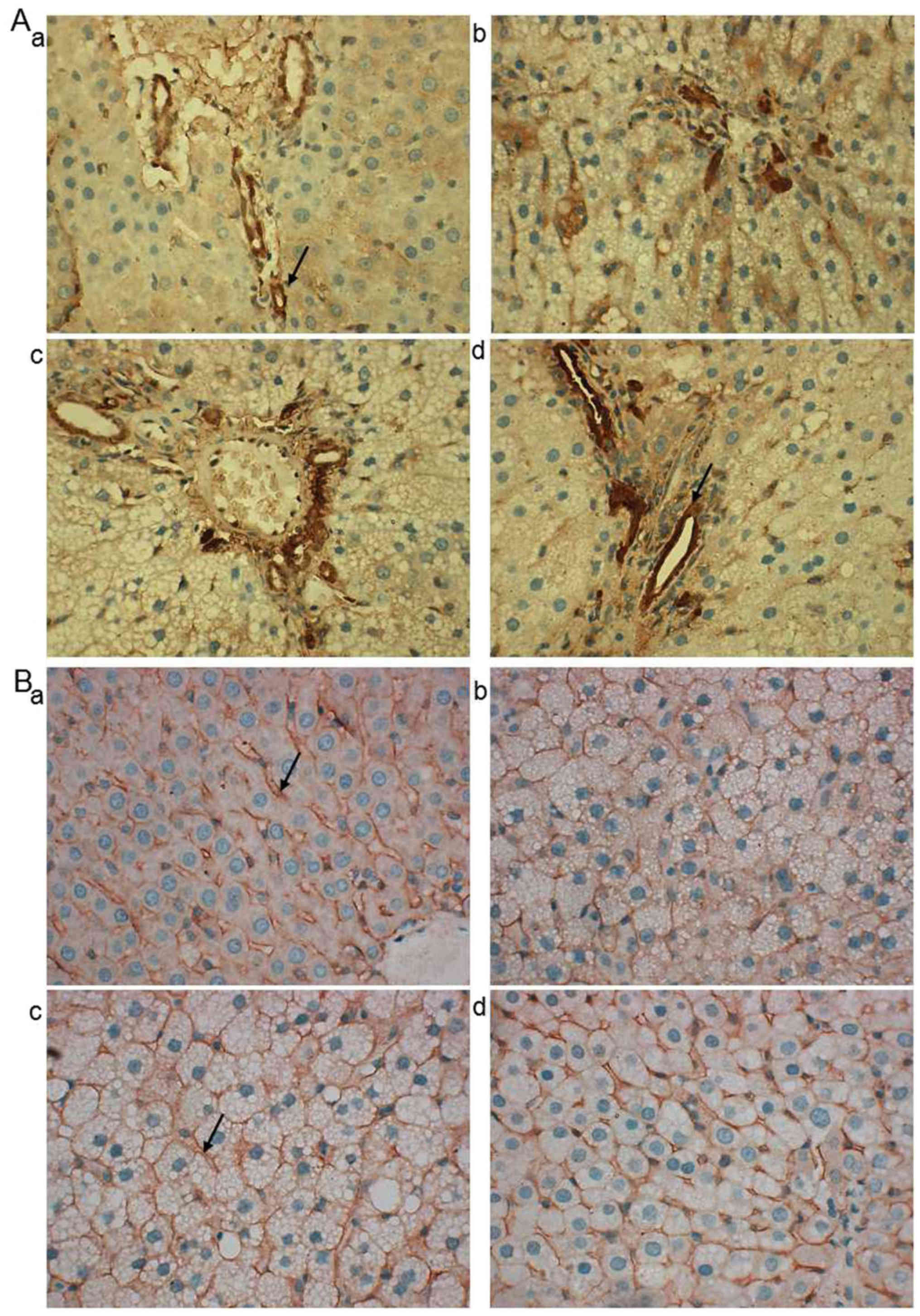
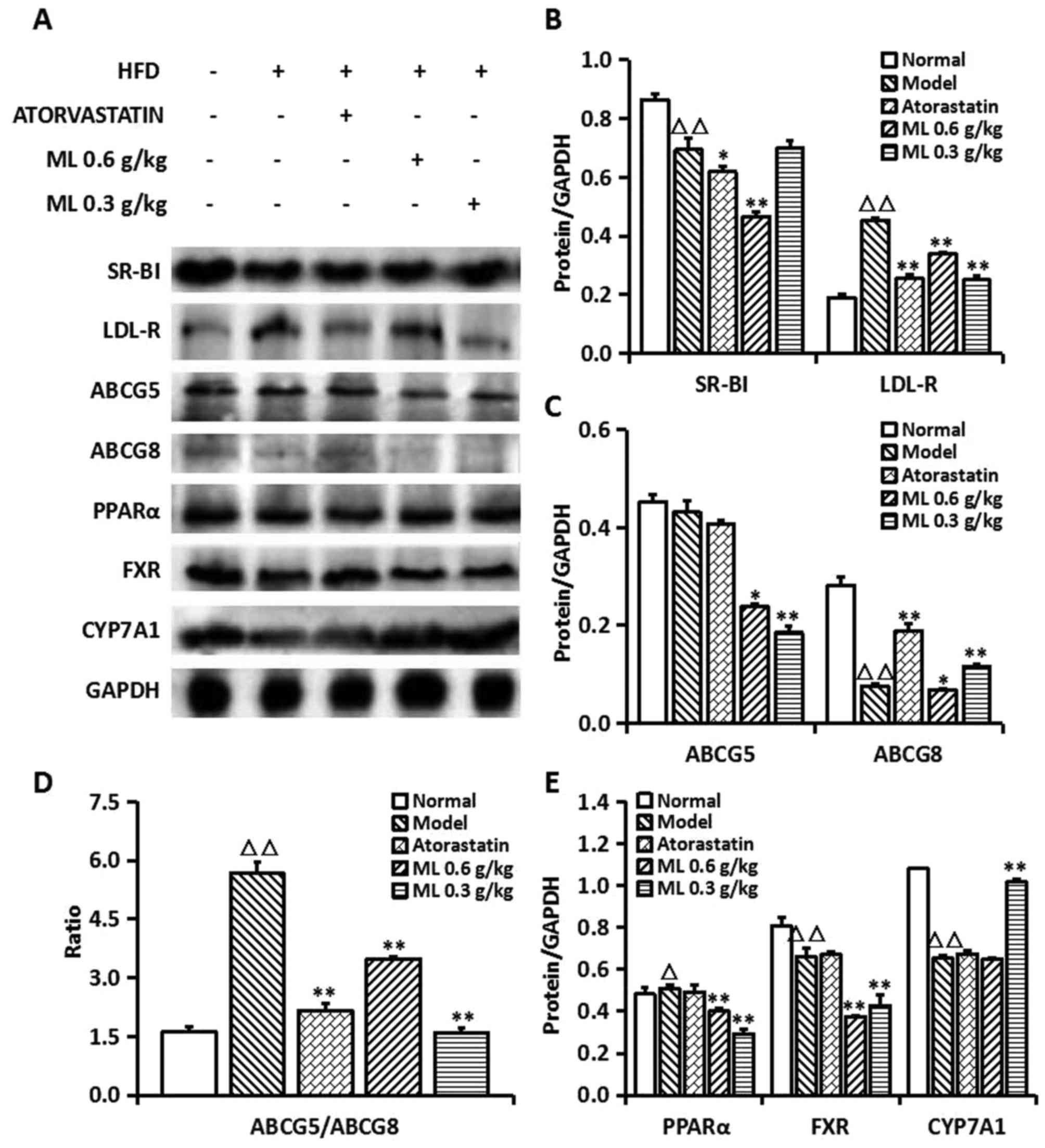
|
1
|
Navar-Boggan AM, Peterson ED, D'Agostino
RB Sr, Neely B, Sniderman AD and Pencina MJ: Hyperlipidemia in
early adulthood increases long-term risk of coronary heart disease.
Circulation. 131:451–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garcia GH, Liu JN, Wong A, Cordasco F,
Dines DM, Dines JS, Gulotta LV and Warren R: Hyperlipidemia
increases the risk of retear after arthroscopic rotator cuff
repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 26:2086–2090. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bjornsson E, Jacobsen EI and Kalaitzakis
E: Hepatotoxicity associated with statins: Reports of idiosyncratic
liver injury post-marketing. J Hepatol. 56:374–380. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Graham DJ, Staffa JA, Shatin D, Andrade
SE, Schech SD, La Grenade L, Gurwitz JH, Chan KA, Goodman MJ and
Platt R: Incidence of hospitalized rhabdomyolysis in patients
treated with lipid-lowering drugs. JAMA. 292:2585–2590. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakamoto K, Honda T, Yokoya S, Waguri S
and Kimura J: Rab-small GTPases are involved in fluvastatin and
pravastatin-induced vacuolation in rat skeletal myofibers. FASEB J.
21:4087–4094. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chu SM, Shih WT, Yang YH, Chen PC and Chu
YH: Use of traditional Chinese medicine in patients with
hyperlipidemia: A population-based study in Taiwan. J
Ethnopharmacol. 168:129–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cai S, Sun W, Fan Y, Guo X, Xu G, Xu T,
Hou Y, Zhao B, Feng X and Liu T: Effect of mulberry leaf (Folium
Mori) on insulin resistance via IRS-1/PI3K/Glut-4 signalling
pathway in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Pharm Biol. 54:2685–2691.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salemi Z, Barzin Tond S, Fallah S, Shojaii
A and Seifi M: The effect of Morus alba leaves extract and powder
on resistin levels and liver transaminase enzymes activities in
diabetes. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand). 62:112–118.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Ren C, Lu G, Cui W, Mu Z, Gao H
and Wang Y: Purification, characterization and anti-diabetic
activity of a polysaccharide from mulberry leaf. Regul Toxicol
Pharmacol. 70:687–695. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khan MA, Rahman AA, Islam S, Khandokhar P,
Parvin S, Islam MB, Hossain M, Rashid M, Sadik G, Nasrin S, et al:
A comparative study on the antioxidant activity of methanolic
extracts from different parts of Morus alba L. (Moraceae). BMC Res
Notes. 6:242013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee YJ, Hsu JD, Lin WL, Kao SH and Wang
CJ: Upregulation of caveolin-1 by mulberry leaf extract and its
major components, chlorogenic acid derivatives, attenuates
alcoholic steatohepatitis via inhibition of oxidative stress. Food
Funct. 8:397–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeong JW, Lee HH, Lee KW, Kim KY, Kim SG,
Hong SH, Kim GY, Park C, Kim HK, Choi YW and Choi YH: Mori folium
inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix
metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the
activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in SW1353 human chondrocytes. Int
J Mol Med. 37:452–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ann JY, Eo H and Lim Y: Mulberry leaves
(Morus alba L.) ameliorate obesity-induced hepatic lipogenesis,
fibrosis, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-fed mice. Genes
Nutr. 10:462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sugimoto M, Arai H, Tamura Y, Murayama T,
Khaengkhan P, Nishio T, Ono K, Ariyasu H, Akamizu T, Ueda Y, et al:
Mulberry leaf ameliorates the expression profile of adipocytokines
by inhibiting oxidative stress in white adipose tissue in db/db
mice. Atherosclerosis. 204:388–394. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Enkhmaa B, Shiwaku K, Katsube T, Kitajima
K, Anuurad E, Yamasaki M and Yamane Y: Mulberry (Morus alba L.)
leaves and their major flavonol quercetin 3-(6-malonylglucoside)
attenuate atherosclerotic lesion development in LDL
receptor-deficient mice. J Nutr. 135:729–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aramwit P, Petcharat K and Supasyndh O:
Efficacy of mulberry leaf tablets in patients with mild
dyslipidemia. Phytother Res. 25:365–369. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aramwit P, Supasyndh O, Siritienthong T
and Bang N: Mulberry leaf reduces oxidation and C-reactive protein
level in patients with mild dyslipidemia. Biomed Res Int.
2013:7879812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi Y, Miyazawa M, Kamei A, Abe K
and Kojima T: Ameliorative effects of mulberry (Morus alba L.)
leaves on hyperlipidemia in rats fed a high-fat diet: Induction of
fatty acid oxidation, inhibition of lipogenesis, and suppression of
oxidative stress. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:2385–2395. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lou Z, Zhang G, Su J, Xia B, Yu J and Yan
M: Effect of green tea and mulberry leaf powder on serum lipid
profile in rats with hyperlipidemia. Zhongchengyao. 38:1594–1597.
2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Trimarco V, Izzo R, Stabile E, Rozza F,
Santoro M, Manzi MV, Serino F, Schiattarella GG, Esposito G and
Trimarco B: Effects of a new combination of nutraceuticals with
Morus alba on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity and endotelial
function in dyslipidemic subjects. A cross-over, randomized,
double-blind trial. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 22:149–154.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Valacchi G, Belmonte G, Miracco C, Eo H
and Lim Y: Effect of combined mulberry leaf and fruit extract on
liver and skin cholesterol transporters in high fat diet-induced
obese mice. Nutr Res Pract. 8:20–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Riwanto M and Landmesser U: High density
lipoproteins and endothelial functions: Mechanistic insights and
alterations in cardiovascular disease. J Lipid Res. 54:3227–3243.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van der Velde AE, Vrins CL, van den Oever
K, Seemann I, Oude Elferink RP, van Eck M, Kuipers F and Groen AK:
Regulation of direct transintestinal cholesterol excretion in mice.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 295:G203–G208. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
The State Science and Technology
Commission of China: Regulations on the management of laboratory
animals. Shiyong Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 4:66–67. 2016.(In
Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Ministry of Science and Technology of the
People's Republic of China: 2018, Methods for managing experimental
animal licenses (trial). [online] Available at:. http://www.most.gov.cn/fggw/zfwj/zfwj2001/zf01yw/zf01kjjh/200312/t20031209_31332.htmJuly
30–2015
|
|
26
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: A
receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science.
232:34–47. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huby T, Doucet C, Dachet C, Ouzilleau B,
Ueda Y, Afzal V, Rubin E, Chapman MJ and Lesnik P: Knockdown
expression and hepatic deficiency reveal an atheroprotective role
for SR-BI in liver and peripheral tissues. J Clin Invest.
116:2767–2776. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Braamskamp MJ, Hutten BA and Wiegman A:
Early initiation of statin treatment in children with familial
hypercholesterolaemia. Curr Opin Lipidol. 26:236–239. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yakushiji E, Ayaori M, Nishida T, Shiotani
K, Takiguchi S, Nakaya K, Uto-Kondo H, Ogura M, Sasaki M, Yogo M,
et al: Probucol-oxidized products, spiroquinone and diphenoquinone,
promote reverse cholesterol transport in mice. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 36:591–597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang DQ: Regulation of intestinal
cholesterol absorption. Annu Rev Physiol. 69:221–248. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Orsoni A, Villard EF, Bruckert E,
Robillard P, Carrie A, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Chapman MJ,
Dallinga-Thie GM, Le Goff W and Guerin M: Impact of LDL apheresis
on atheroprotective reverse cholesterol transport pathway in
familial hypercholesterolemia. J Lipid Res. 53:767–775. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Si Y, Zhai L, Guo S, Zhao J, Sang
H, Pang X, Zhang X, Chen A and Qin S: Celastrus orbiculatus thunb.
Reduces lipid accumulation by promoting reverse cholesterol
transport in hyperlipidemic mice. Lipids. 51:677–692. 2016.
|
|
33
|
Zhu RG, Sun YD, Hou YT, Fan JG, Chen G and
Li TP: Pectin penta-oligogalacturonide reduces cholesterol
accumulation by promoting bile acid biosynthesis and excretion in
high-cholesterol-fed mice. Chem Biol Interact. 272:153–159. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maxwell KN, Fisher EA and Breslow JL:
Overexpression of PCSK9 accelerates the degradation of the LDLR in
a post-endoplasmic reticulum compartment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:2069–2074. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zelcer N, Hong C, Boyadjian R and Tontonoz
P: LXR regulates cholesterol uptake through Idol-dependent
ubiquitination of the LDL receptor. Science. 325:100–104. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kosenko T, Golder M, Leblond G, Weng W and
Lagace TA: Low density lipoprotein binds to proprotein convertase
subtilisin/kexin type-9 (PCSK9) in human plasma and inhibits
PCSK9-mediated low density lipoprotein receptor degradation. J Biol
Chem. 288:8279–8288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ji Y, Wang N, Ramakrishnan R, Sehayek E,
Huszar D, Breslow JL and Tall AR: Hepatic scavenger receptor BI
promotes rapid clearance of high density lipoprotein free
cholesterol and its transport into bile. J Biol Chem.
274:33398–33402. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Braun A, Zhang S, Miettinen HE, Ebrahim S,
Holm TM, Vasile E, Post MJ, Yoerger DM, Picard MH, Krieger JL, et
al: Probucol prevents early coronary heart disease and death in the
high-density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI/apolipoprotein E double
knockout mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7283–7288. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chulsky S, Paland N, Lazarovich A and
Fuhrman B: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) decreases
hepatic SR-BI expression and impairs HDL-mediated reverse
cholesterol transport. Atherosclerosis. 233:11–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Berge KE, Tian H, Graf GA, Yu L, Grishin
NV, Schultz J, Kwiterovich P, Shan B, Barnes R and Hobbs HH:
Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by
mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science. 290:1771–1775.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Mitsche MA, Lutjohann D, Cohen JC,
Xie XS and Hobbs HH: Relative roles of ABCG5/ABCG8 in liver and
intestine. J Lipid Res. 56:319–330. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van der Veen JN, van Dijk TH, Vrins CL,
van Meer H, Havinga R, Bijsterveld K, Tietge UJ, Groen AK and
Kuipers F: Activation of the liver X receptor stimulates
trans-intestinal excretion of plasma cholesterol. J Biol Chem.
284:19211–19219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dikkers A, Freak de Boer J, Annema W,
Groen AK and Tietge UJ: Scavenger receptor BI and ABCG5/G8
differentially impact biliary sterol secretion and reverse
cholesterol transport in mice. Hepatology. 58:293–303. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cao Y, Bei W, Hu Y, Cao L, Huang L, Wang
L, Luo D, Chen Y, Yao X, He W, et al: Hypocholesterolemia of
Rhizoma Coptidis alkaloids is related to the bile acid by
up-regulated CYP7A1 in hyperlipidemic rats. Phytomedicine.
19:686–692. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li T, Matozel M, Boehme S, Kong B, Nilsson
LM, Guo G, Ellis E and Chiang JY: Overexpression of cholesterol
7alpha-hydroxylase promotes hepatic bile acid synthesis and
secretion and maintains cholesterol homeostasis. Hepatology.
53:996–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM,
Lambert G and Gonzalez FJ: Targeted disruption of the nuclear
receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell.
102:731–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cai SY, He H, Nguyen T, Mennone A and
Boyer JL: Retinoic acid represses CYP7A1 expression in human
hepatocytes and HepG2 cells by FXR/RXR-dependent and independent
mechanisms. J Lipid Res. 51:2265–2274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kojima Y, Kimura T, Nakagawa K, Asai A,
Hasumi K, Oikawa S and Miyazawa T: Effects of mulberry leaf extract
rich in 1-deoxynojirimycin on blood lipid profiles in humans. J
Clin Biochem Nutr. 47:155–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chan KC, Yang MY, Lin MC, Lee YJ, Chang WC
and Wang CJ: Mulberry leaf extract inhibits the development of
atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits and in cultured aortic
vascular smooth muscle cells. J Agric Food Chem. 61:2780–2788.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He X, Fang J, Ruan Y, Wang X, Sun Y, Wu N,
Zhao Z, Chang Y, Ning N, Guo H and Huang L: Structures,
bioactivities and future prospective of polysaccharides from Morus
alba (white mulberry): A review. Food Chem. 245:899–910. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|