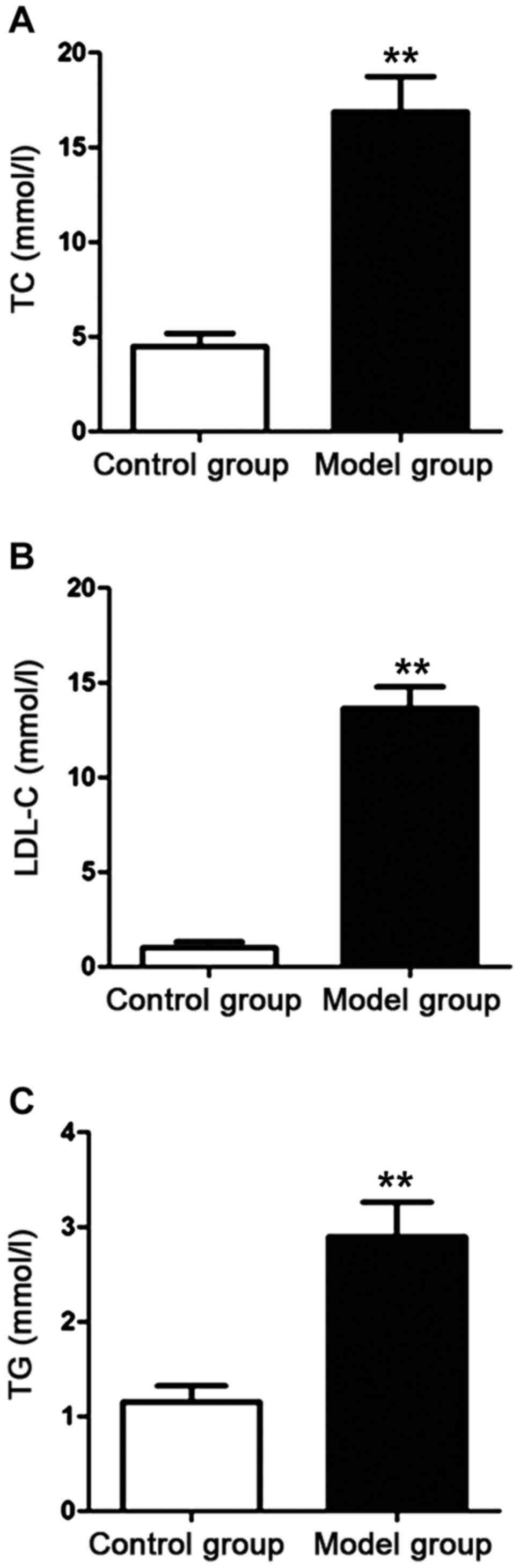
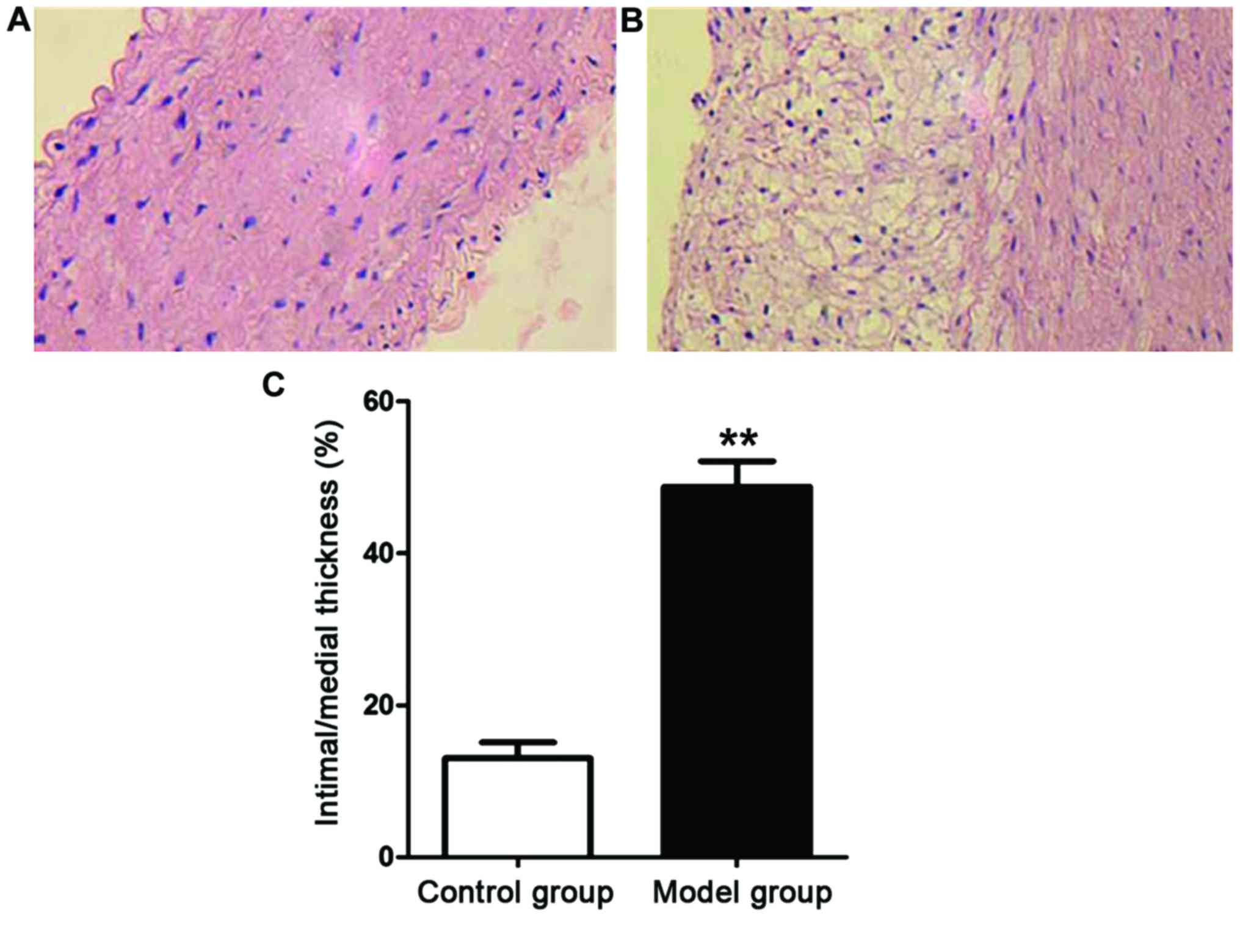
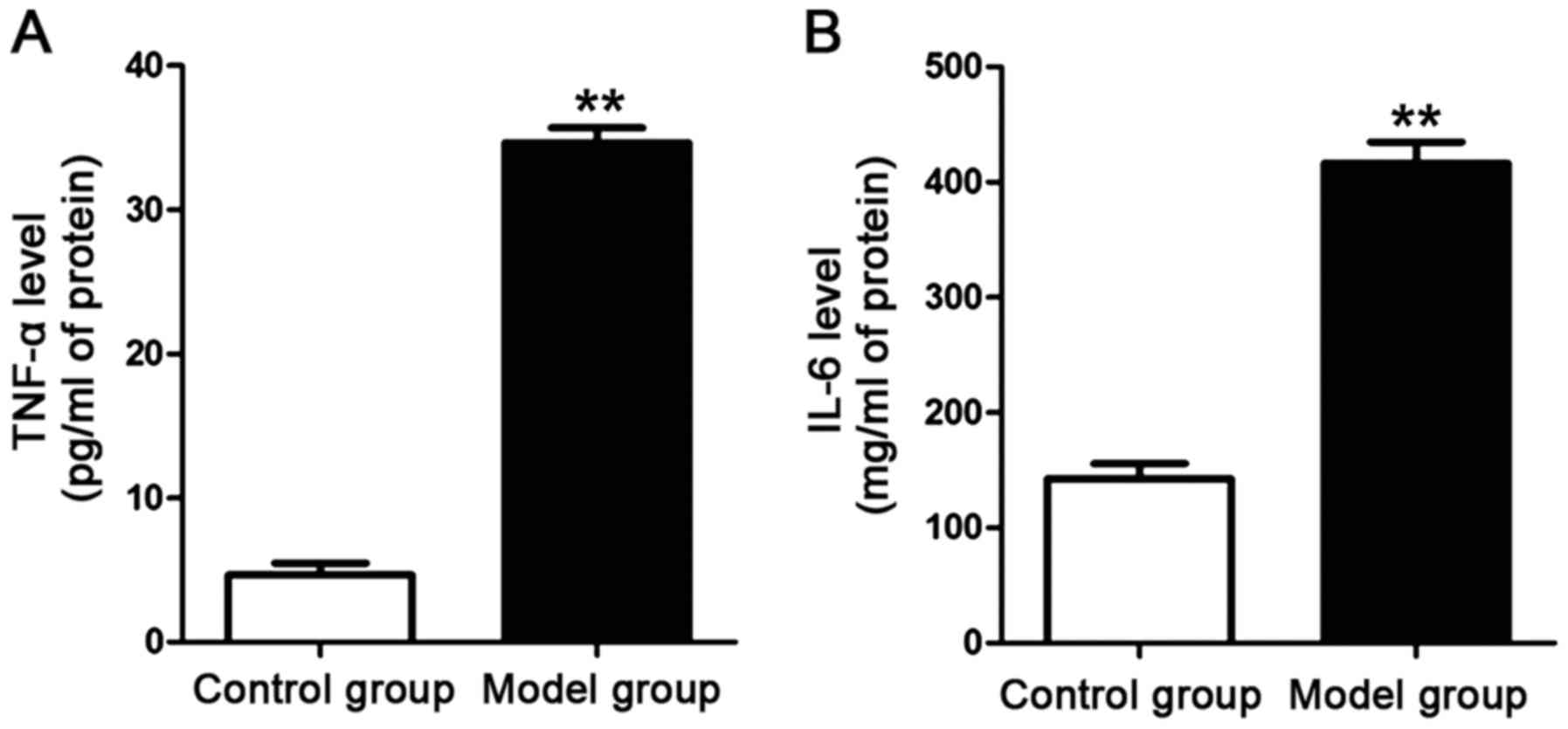
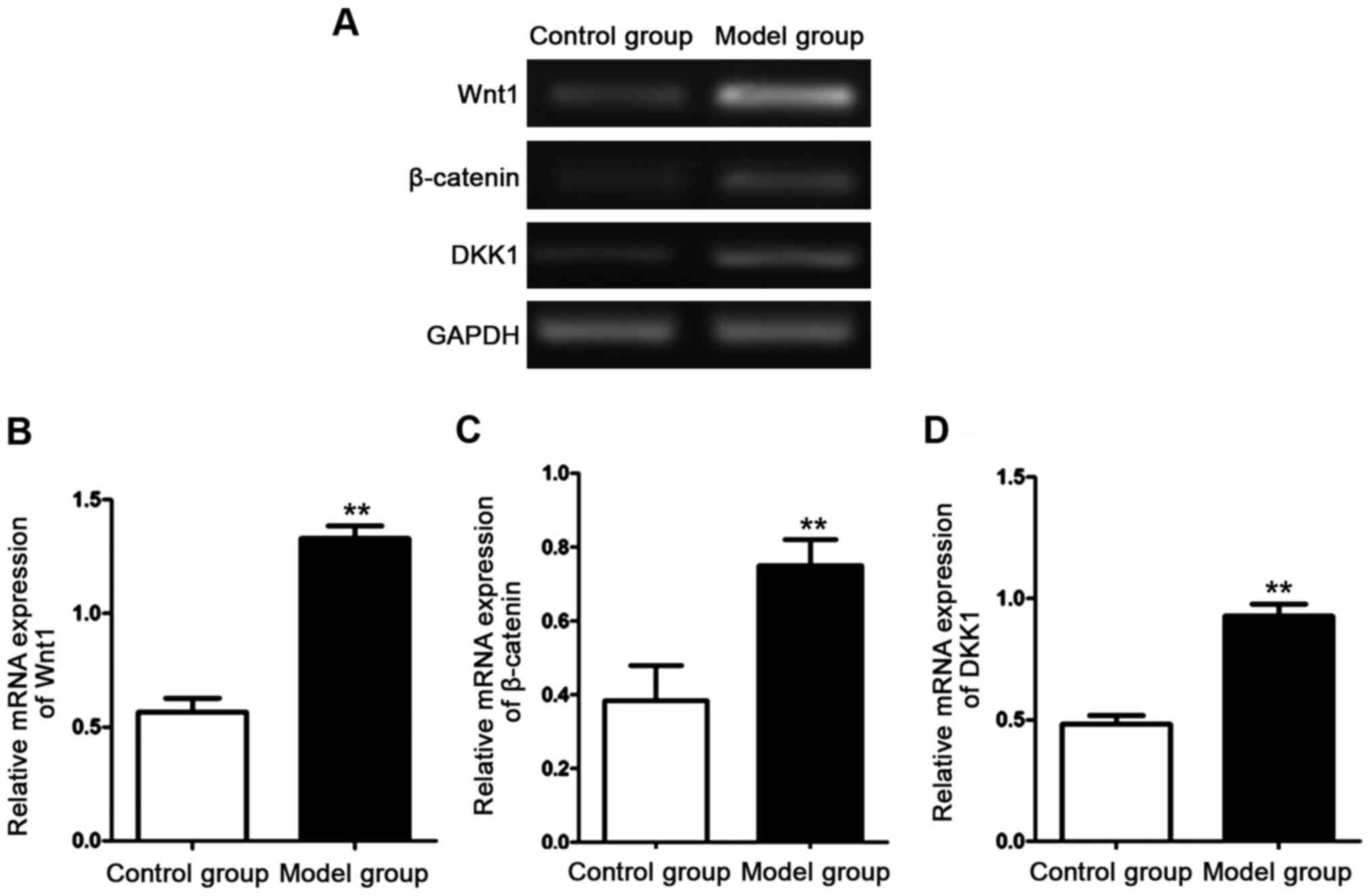
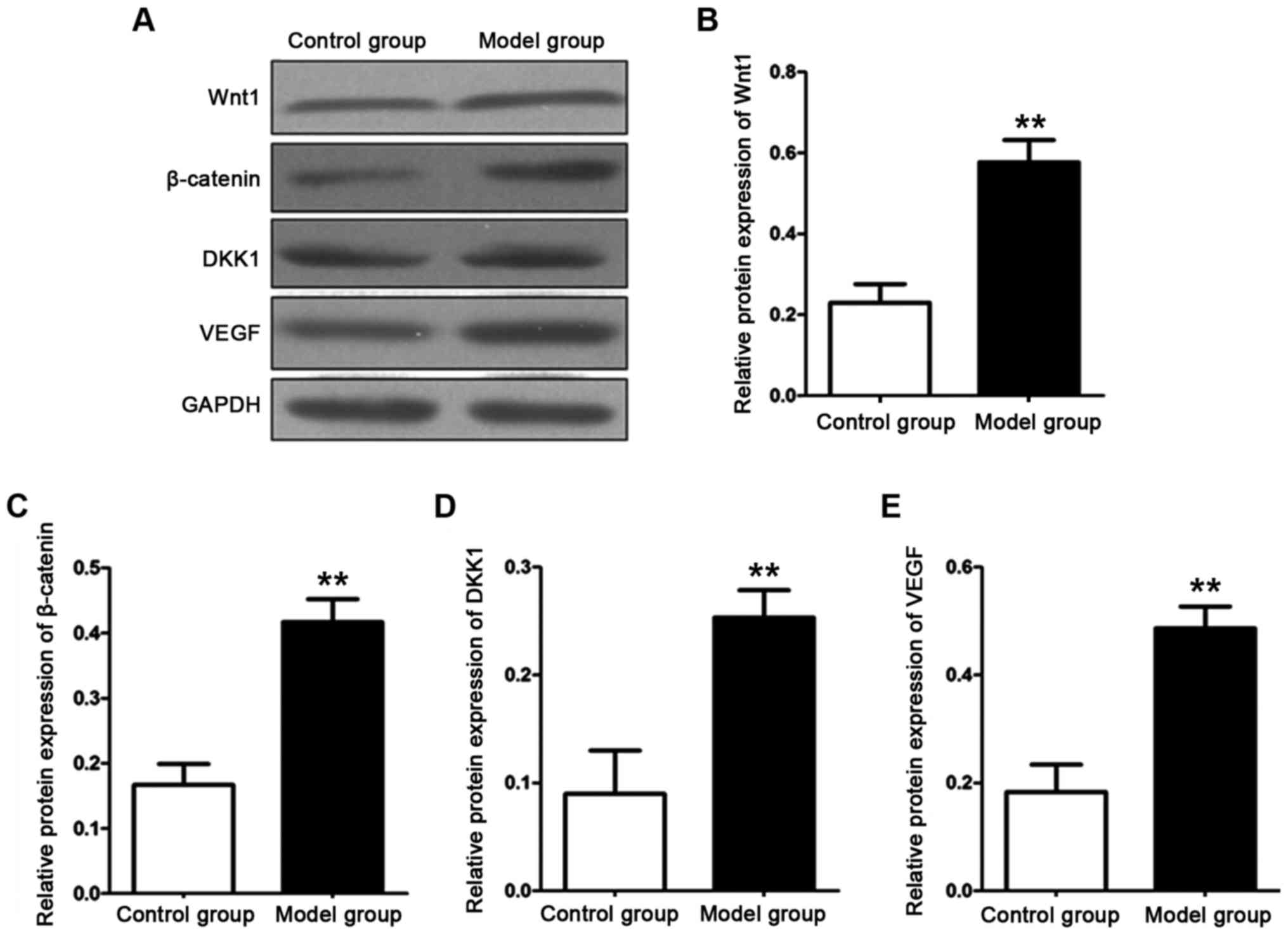
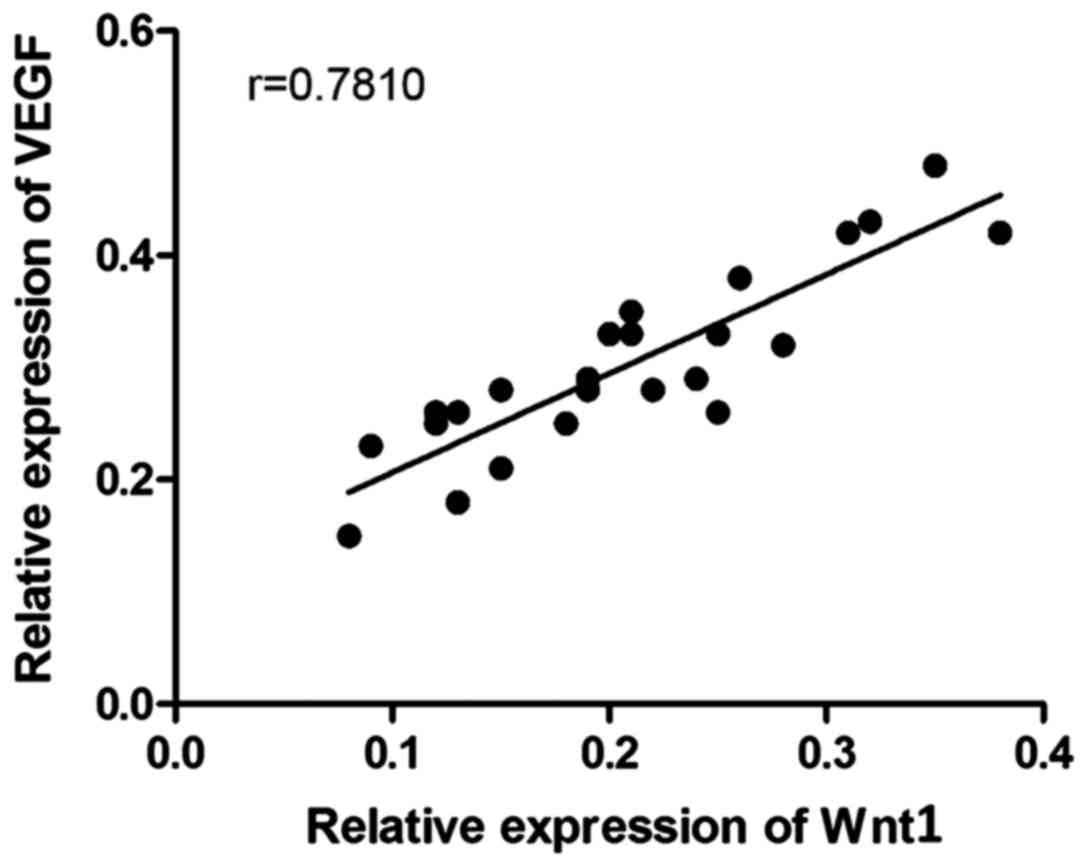
|
1
|
Dolan H, Crain B, Troncoso J, Resnick SM,
Zonderman AB and Obrien RJ: Atherosclerosis, dementia, and
Alzheimer disease in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging
cohort. Ann Neurol. 68:231–240. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamamoto S, Zhong J, Yancey PG, Zuo Y,
Linton MF, Fazio S, Yang H, Narita I and Kon V: Atherosclerosis
following renal injury is ameliorated by pioglitazone and losartan
via macrophage phenotype. Atherosclerosis. 242:56–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rose H, Low H, Dewar E, Bukrinsky M, Hoy
J, Dart A and Sviridov D: The effect of HIV infection on
atherosclerosis and lipoprotein metabolism: A one year prospective
study. Atherosclerosis. 229:206–211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alberts-Grill N, Denning TL, Rezvan A and
Jo H: The role of the vascular dendritic cell network in
atherosclerosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 305:C1–C21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bauer AJ and Martin KA: Coordinating
regulation of gene expression in cardiovascular disease:
Interactions between chromatin modifiers and transcription factors.
Front Cardiovasc Med. 4:192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gajjala PR, Sanati M and Jankowski J:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of chronic kidney disease with
diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases as its comorbidities.
Front Immunol. 6:3402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garcia-Martín A, Reyes-Garcia R,
García-Fontana B, Morales-Santana S, Coto-Montes A, Muñoz-Garach M,
Rozas-Moreno P and Muñoz-Torres M: Relationship of Dickkopf1 (DKK1)
with cardiovascular disease and bone metabolism in Caucasian type 2
diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 9:e1117032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Register TC, Hruska KA, Divers J, Bowden
DW, Palmer ND, Carr JJ, Wagenknecht LE, Hightower RC, Xu J, Smith
SC, et al: Plasma Dickkopf1 (DKK1) concentrations negatively
associate with atherosclerotic calcified plaque in
African-Americans with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:E60–E65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Witztum JL and Lichtman AH: The influence
of innate and adaptive immune responses on atherosclerosis. Annu
Rev Pathol. 9:73–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Geng YJ and Jonasson L: Linking immunity
to atherosclerosis: Implications for vascular pharmacology - a
tribute to Göran K. Hansson. Vascul Pharmacol. 56:29–33. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taghavie-Moghadam PL, Butcher MJ and
Galkina EV: The dynamic lives of macrophage and dendritic cell
subsets in atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1319:19–37. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Patel KM, Strong A, Tohyama J, Jin X,
Morales CR, Billheimer J, Millar J, Kruth H and Rader DJ:
Macrophage sortilin promotes LDL uptake, foam cell formation, and
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 116:789–796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fontes JA, Rose NR and Čiháková D: The
varying faces of IL-6: From cardiac protection to cardiac failure.
Cytokine. 74:62–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Orbay H, Hong H, Zhang Y and Cai W:
PET/SPECT imaging of hindlimb ischemia: Focusing on angiogenesis
and blood flow. Angiogenesis. 16:279–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bogdanovich S, Kim Y, Mizutani T, Yasuma
R, Tudisco L, Cicatiello V, Bastos-Carvalho A, Kerur N, Hirano Y,
Baffi JZ, et al: Human IgG1 antibodies suppress angiogenesis in a
target-independent manner. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 1:458–463.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xu Y, Chen B, George SK and Liu B:
Downregulation of MicroRNA-152 contributes to high expression of
DKK1 in multiple myeloma. RNA Biol. 12:1314–1322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mozos I and Marginean O: Links between
vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular diseases. BioMed Res Int.
2015:1092752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taghavie-Moghadam PL, Gjurich BN, Jabeen
R, Krishnamurthy P, Kaplan MH, Dobrian AD, Nadler JL and Galkina
EV: STAT4 deficiency reduces the development of atherosclerosis in
mice. Atherosclerosis. 243:169–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caliceti C, Nigro P, Rizzo P and Ferrari
R: ROS, Notch, and Wnt signaling pathways: Crosstalk between three
major regulators of cardiovascular biology. BioMed Res Int.
2014:3187142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou H, Binmadi NO, Yang YH, Proia P and
Basile JR: Semaphorin 4D cooperates with VEGF to promote
angiogenesis and tumor progression. Angiogenesis. 15:391–407. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|