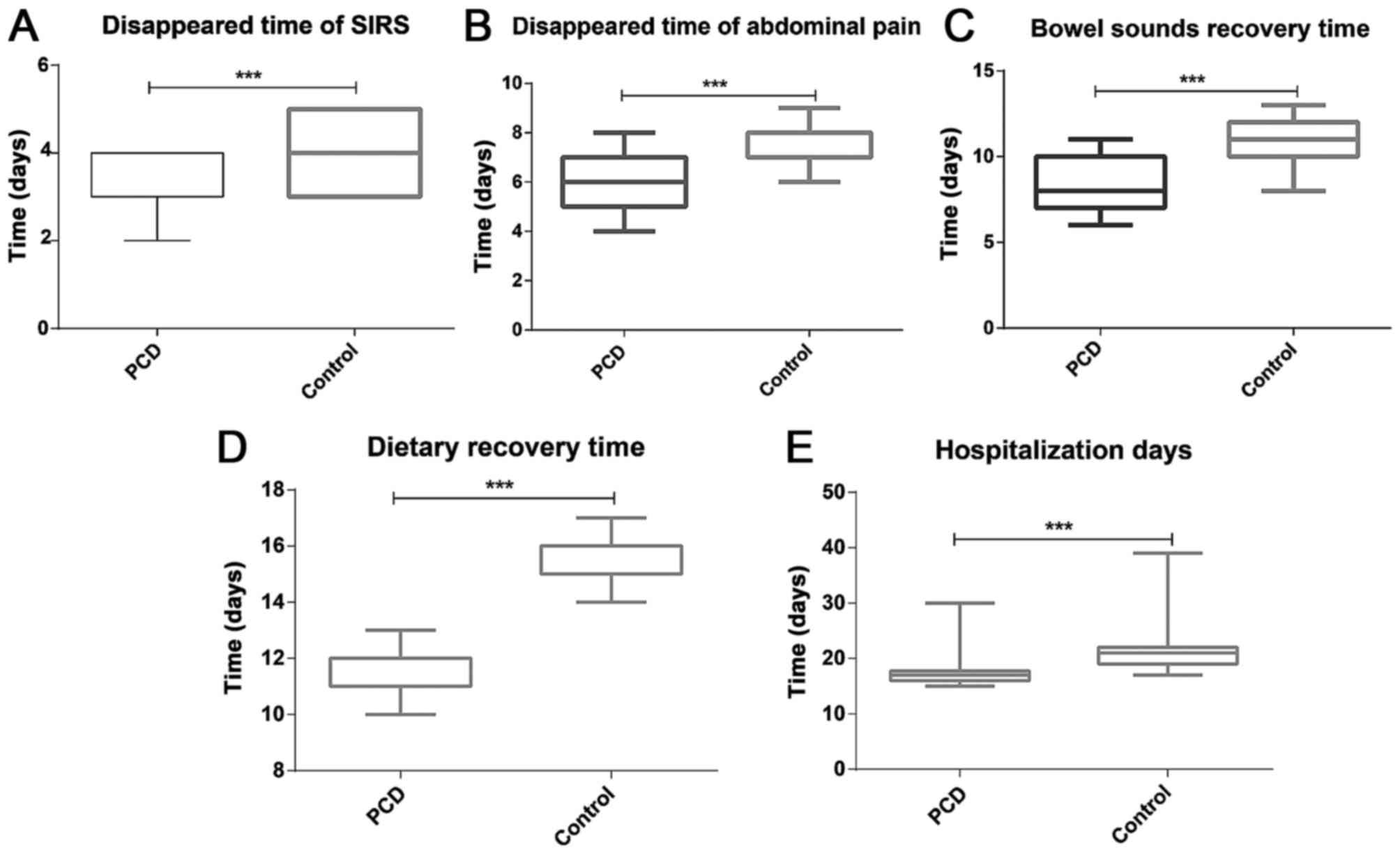
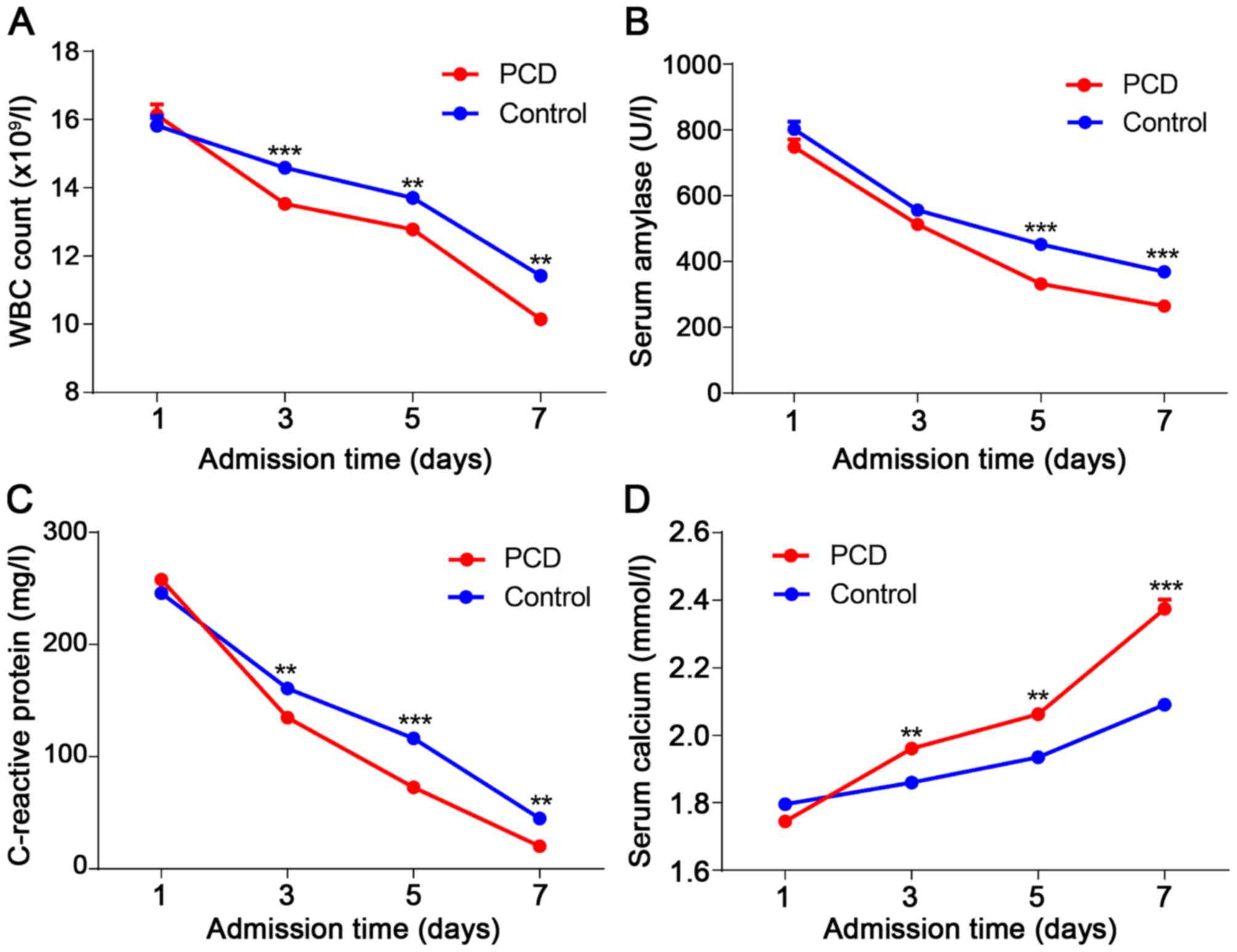
|
1
|
Bai Y, Liu Y, Jia L, Jiang H, Ji M, Lv N,
Huang K, Zou X, Li Y, Tang C, et al: Severe acute pancreatitis in
China: Etiology and mortality in 1976 patients. Pancreas.
35:232–237. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raraty MG, Connor S, Criddle DN, Sutton R
and Neoptolemos JP: Acute pancreatitis and organ failure:
Pathophysiology, natural history, and management strategies. Curr
Gastroenterol Rep. 6:99–103. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zerem E, Imamovic G, Omerović S and
Imširović B: Randomized controlled trial on sterile fluid
collections management in acute pancreatitis: Should they be
removed? Surg Endosc. 23:2770–2777. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vege SS, Gardner TB, Chari ST, Munukuti P,
Pearson RK, Clain JE, Petersen BT, Baron TH, Farnell MB and Sarr
MG: Low mortality and high morbidity in severe acute pancreatitis
without organ failure: A case for revising the Atlanta
classification to include ‘moderately severe acute pancreatitis’.
Am J Gastroenterol. 104:710–715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Babu RY, Gupta R, Kang M, Bhasin DK, Rana
SS and Singh R: Predictors of surgery in patients with severe acute
pancreatitis managed by the step-up approach. Ann Surg.
257:737–750. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ai XB, Qian XP, Pan WS, Xu J, Wu LQ, Zhang
WJ and Wang A: Ultrasound-guided percutaneous catheter drainage in
early treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Med.
1:45–48. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
La Greca A, Di Grezia M, Magalini S, Di
Giorgio A, Lodoli C, Di Flumeri G, Cozza V, Pepe G, Foco M, Bossola
M, et al: Comparison of cholecystectomy and percutaneous
cholecystostomy in acute cholecystitis: Results of a retrospective
study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:4668–4674. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mortelé KJ, Girshman J, Szejnfeld D,
Ashley SW, Erturk SM, Banks PA and Silverman SG: CT-guided
percutaneous catheter drainage of acute necrotizing pancreatitis:
Clinical experience and observations in patients with sterile and
infected necrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 192:110–116. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Freeny PC, Hauptmann E, Althaus SJ,
Traverso LW and Sinanan M: Percutaneous CT-guided catheter drainage
of infected acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Techniques and results.
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 170:969–975. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen
HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG and Vege SS: Acute Pancreatitis
Classification Working Group: Classification of acute pancreatitis
- 2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by
international consensus. Gut. 62:102–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walser EM, Nealon WH, Marroquin S, Raza S,
Hernandez JA and Vasek J: Sterile fluid collections in acute
pancreatitis: Catheter drainage versus simple aspiration.
Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 29:102–107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hookey LC, Debroux S, Delhaye M,
Arvanitakis M, Le Moine O and Devière J: Endoscopic drainage of
pancreatic-fluid collections in 116 patients: A comparison of
etiologies, drainage techniques, and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc.
63:635–643. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Banks PA and Freeman ML: Practice
Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology:
Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol.
101:2379–2400. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Navalho M, Pires F, Duarte A, Gonçalves A,
Alexandrino P and Távora I: Percutaneous drainage of infected
pancreatic fluid collections in critically ill patients:
Correlation with C-reactive protein values. Clin Imaging.
30:114–119. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zerem E: Reply to: Draining sterile fluid
collections in acute pancreatitis? Primum non nocere! Surg Endosc.
25:979–980. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|