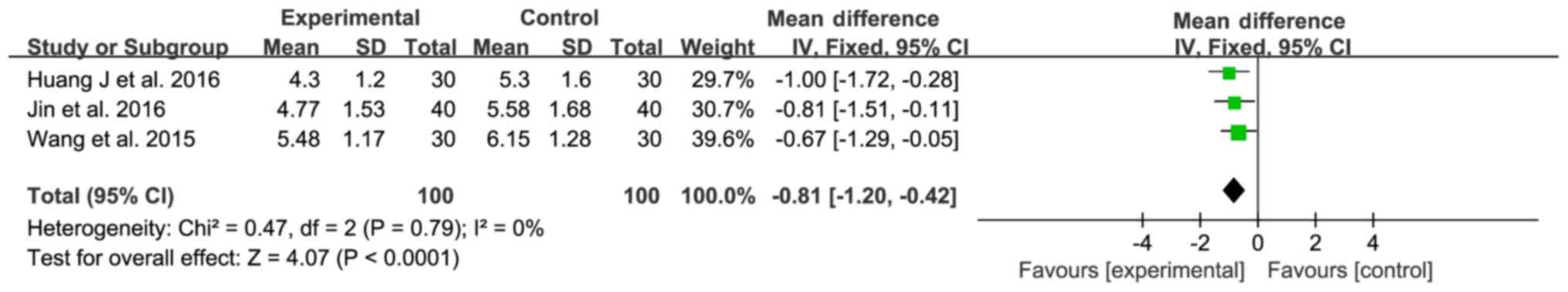
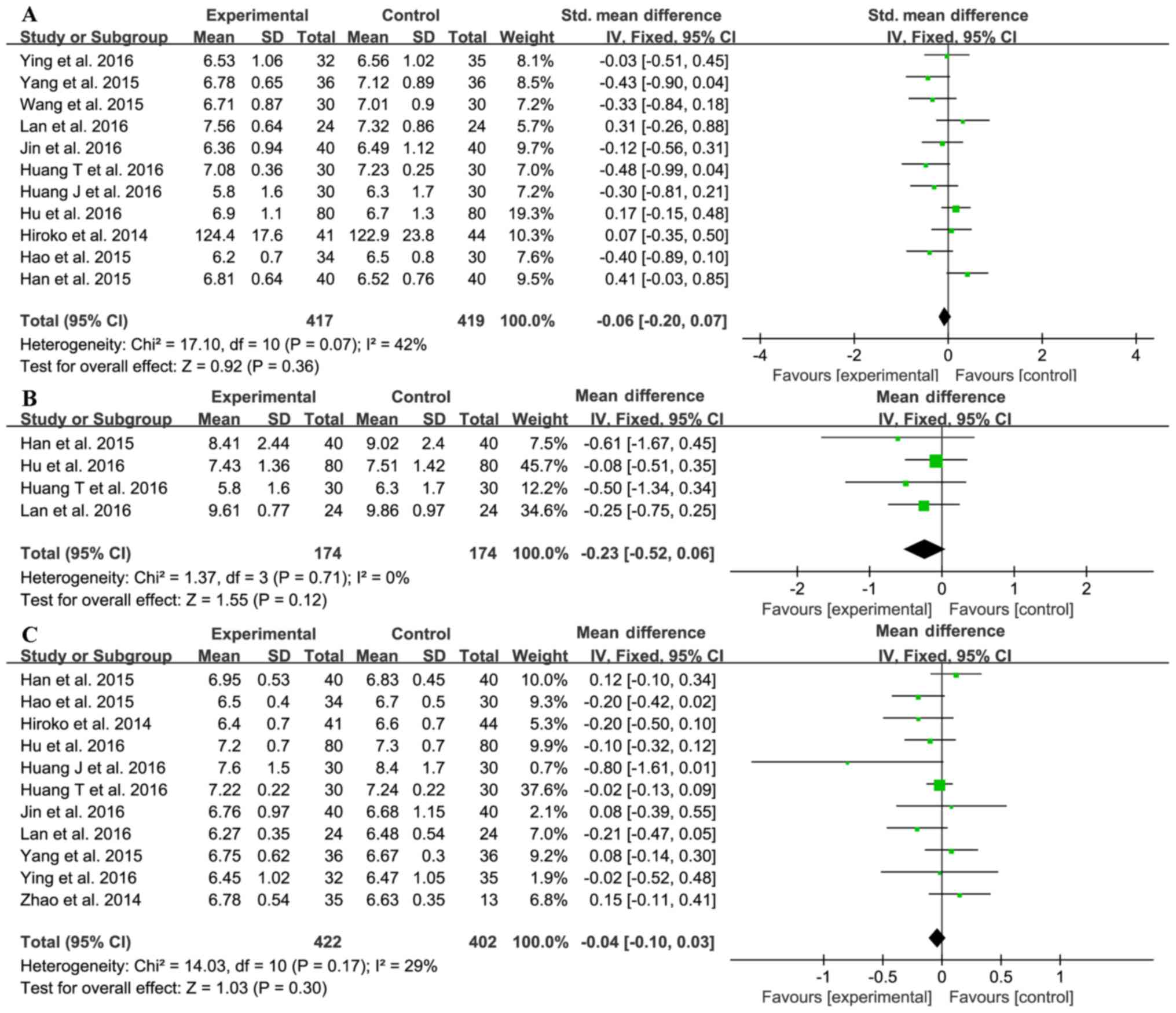
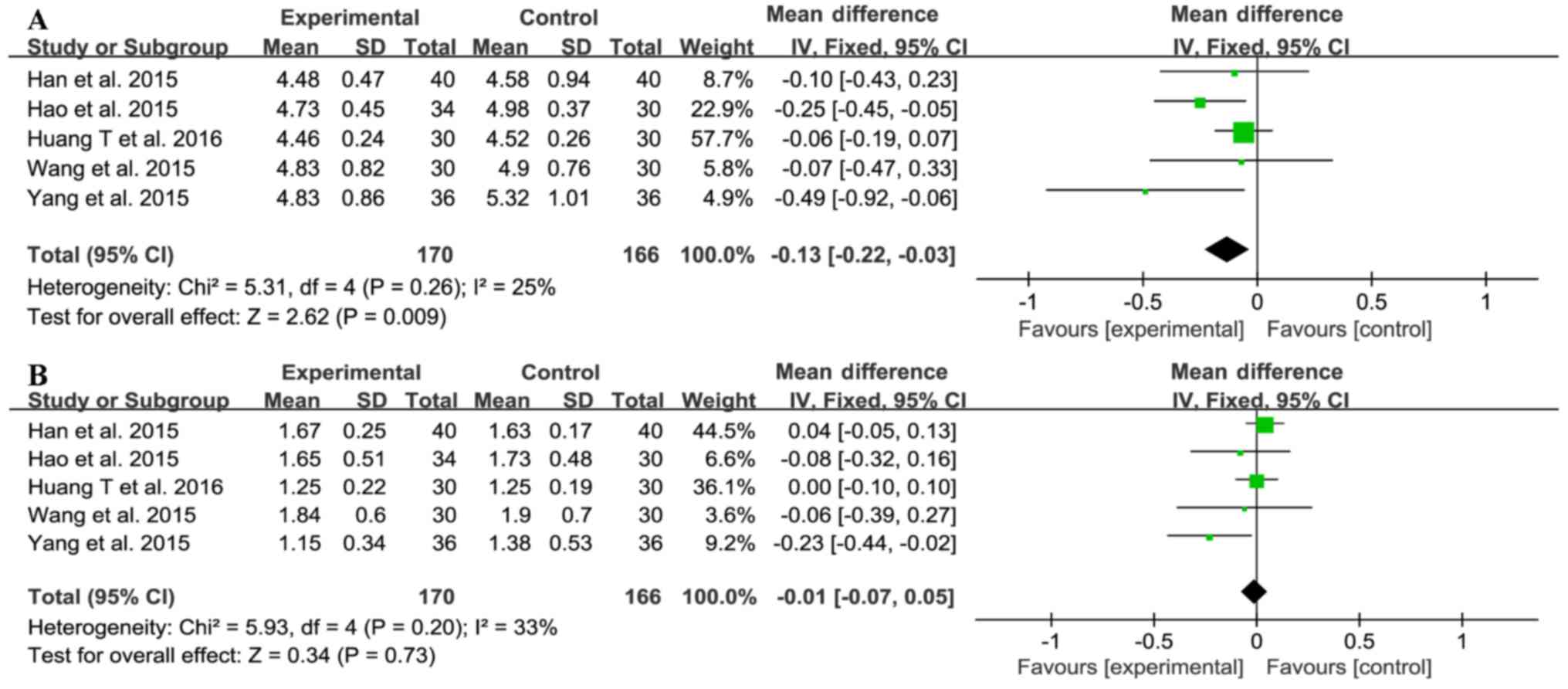
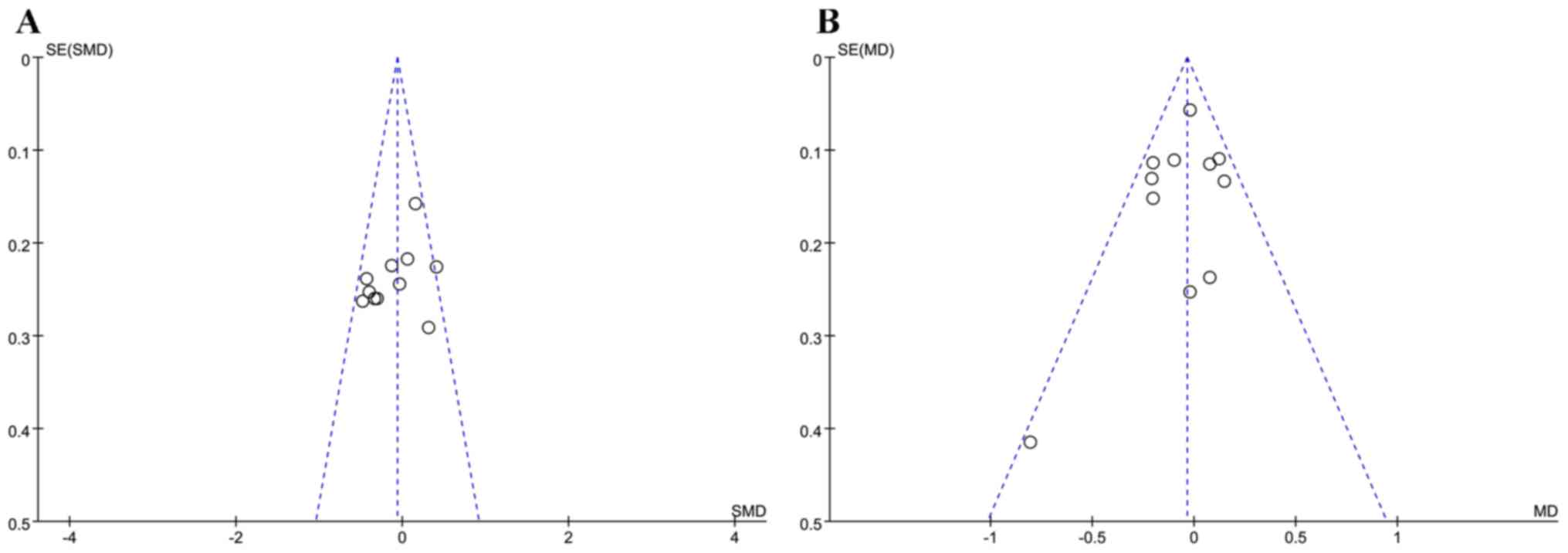
|
1
|
Unger RH and Orci L: The essential role of
glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1:14–16.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang
JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J, Hirsch IB, Kalantar-Zadeh K,
Narva AS, Navaneethan SD, et al: Diabetic kidney disease: A report
from an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care. 37:2864–2883.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahn JH, Yu JH, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim DJ, Kim
JH, Kim CS, Song KH, Won JC, Lim S, et al: Prevalence and
determinants of diabetic nephropathy in Korea: Korea national
health and nutrition examination survey. Diabetes Metab J.
38:109–119. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Venkatachalam MA, Weinberg JM, Kriz W and
Bidanai AK: Failed tubule recovery, AKI-CKD transition, and kidney
disease progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:1765–1776. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T and Susztak
K: Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest.
124:2333–2340. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee M and Rhee MK: Sitagliptin for type 2
diabetes: A 2015 update. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 13:597–610.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujita H, Taniai H, Murayama H, Ohshiro H,
Hayashi H, Sato S, Kikuchi N, Komatsu T, Komatsu K, Komatsu K, et
al: DPP-4 inhibition with alogliptin on top of angiotensin II type
1 receptor blockade ameliorates albuminuria via up-regulation of
SDF-1α in type 2 diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy.
Endocr J. 61:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hattori S: Sitagliptin reduces albuminuria
in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr J. 58:69–73. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kawasaki I, Hiura Y, Tamai A, Yoshida Y,
Yakusiji Y, Ikuno Y, Okada M, Ueno H, Tanaka N, Yamagami K, et al:
Sitagliptin reduces the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio in type 2
diabetes through decreasing both blood pressure and estimated
glomerular filtration rate. J Diabetes. 7:41–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mistry GC, Maes AL, Lasseter KC, Davies
MJ, Gottesdiener KM, Wagner JA and Herman GA: Effect of
sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, on blood pressure
in nondiabetic patients with mild to moderate hypertension. J Clin
Pharmacol. 48:592–598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogawa S, Ishiki M, Nako K, Okamura M,
Senda M, Mori T and Ito S: Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4
inhibitor, decreases systolic blood pressure in Japanese
hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Tohoku J Exp Med.
223:133–135. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gutzwiller JP, Tschopp S, Bock A, Zehnder
CE, Huber AR, Kreyenbuehl M, Gutmann H, Drewe J, Henzen C, Goeke B
and Beglinger C: Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces natriuresis in
healthy subjects and in insulin-resistant obese men. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 89:3055–3061. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Higgins JPT and Green S: Cochrane handbook
for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.2 [updated
March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011, http://handbook.cochrane.org/April
8–2018
|
|
14
|
Mori H, Okada Y, Arao T and Tanaka Y:
Sitagliptin improves albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 5:313–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang K, Ren Q, Wu T and Du J: Effects of
sitagliptin used alone or combined with irbesartan on changes of
interlukin-18 in early diabetic nephropathy patients. Med J Air
Force. 1:56–58. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Hu S, Bai X, Li X, Li S and Lv S: Effect
of sitagliptin on microalbuminuria of patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Prog Mod Biomed. 16:5324–5326. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Huang J, Xu H, Lin Y, Lin B, Wei Y, Yuan B
and Chen X: Effect of sitagliptin in combination with atorvastatin
on urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in type 2 diabetic patients
with early nephropathy. Acad J Guangzhou Med Univ. 44:51–53.
2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Jin J, Sun H, Xu Z, Lin Z and Tao K:
Sitagliptin influence on clinical indicators in elderly patients
with diabetic nephropathy. Chin J Gerontol. 36:79–81. 2016.(In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Lan L and Yan Z: Protective effects of
DPP-4 inhibitors on kidney in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin
Foreig Med Res. 14:1–3. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Yang T, Li D, Zhao J, Liu L and Hu L:
Effects of sitagliptin on renal function in patients with early
type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Prog Mod Biomed. 19:3690–3693.
2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Ying J, Zhang X, Chen J and Chen G:
Effects of sitagliptin on renal function and
gamma-glutamyltransferase in diabetes combined with kidney injury.
Chin J New Drugs Clin Rem. 35:273–276. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Zhao C, Guo H, Dai H, Tian J and Zhao Y:
Curative effects of sitagliptin with valsartan on incipient type 2
diabetic nephropathy. Pract Pharm Remed. 11:1420–1423. 2014.(In
Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Huang T: The effects of urine PCX
excretion for type 2 diabetic patients with early nephropathy with
treatment of sitagliptin. Shanxi Med Univ. 7-10:2016.(In
Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhang R, Shi M,
Lyu S and Gao P: Effects of sitagliptin on serum chemerin in early
diabetic patients with nephropathy. Acta Acad Med Xuzhou.
35:825–828. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Han H: Sitagliptin for type 2 diabetes
early kidney disease curative effect observation. Shanxi Med Univ.
5-9:2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Hao Q, Liu Y and Fei D: The effect of
sitagliptin on type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with early
diabetic kidney disease patients. J Taishan Med Coll. 36:989–991.
2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Aschner P, Chan J, Owens DR, Picard S,
Wang E, Dain MP, Pilorget V, Echtay A and Fonseca V; EASIE
investigators, : Insulin glargine versus sitagliptin in
insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus uncontrolled
on metformin (EASIE): A multicentre, randomised open-label trial.
Lancet. 379:2262–2269. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Katsuno T, Ikeda H, Ida K, Miyagawa J and
Namba M: Add-on therapy with the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin
improves glycemic control in insulin-treated Japanese patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J. 60:733–742. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lopez-Giacoman S and Madero M: Biomarkers
in chronic kidney disease, from kidney function to kidney damage.
World J Nephrol. 4:57–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Javanmardi M, Azadi NA, Amini S and Abdi
M: Diagnostic value of cystatin C for diagnosis of early renal
damages in type 2 diabetic mellitus patients: The first experience
in Iran. J Res Med Sci. 20:571–576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang D, Zhang G, Chen X, Wei T, Liu C,
Chen C, Gong Y and Wei Q: Sitagliptin ameliorates diabetic
nephropathy by blocking TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 41:2784–2792. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tsurutani Y, Omura M, Matsuzawa Y, Saito
J, Higa M, Taniyama M and Nishikawa T; SINGLE-Y investigation
group, : Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4
inhibitor sitagliptin on atherosclerosis, β-cell function, and
glycemic control in Japanese patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus
who are treatment naïve or poorly responsive to antidiabetes
agents: A multicenter, prospective observational, uncontrolled
study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 84:26–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arjona Ferreira JC, Marre M, Barzilai N,
Guo H, Golm GT, Sisk CM, Kaufman KD and Goldstein BJ: Efficacy and
safety of sitagliptin versus glipizide in patients with type 2
diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic renal insufficiency.
Diabetes Care. 36:1067–1073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|