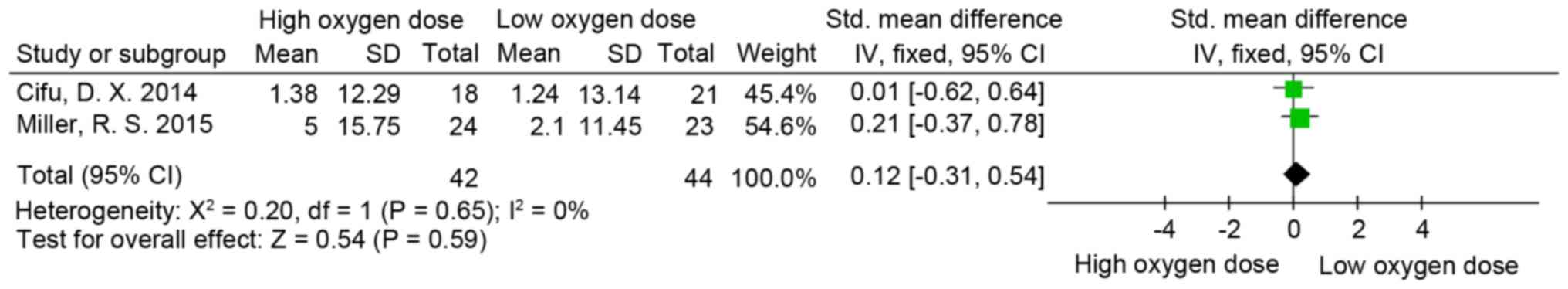
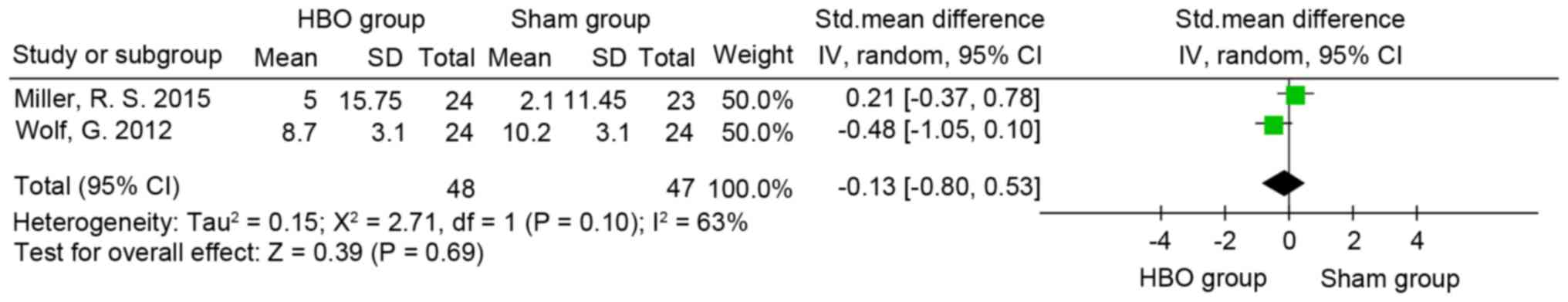
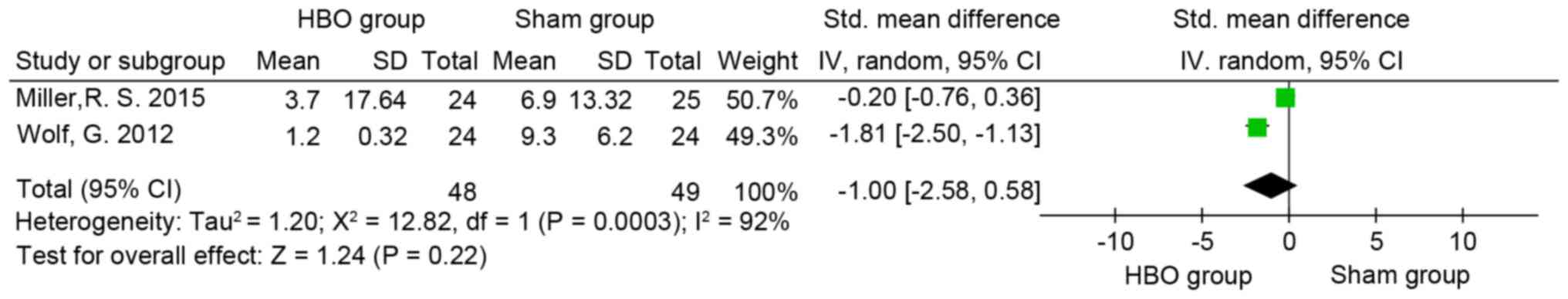
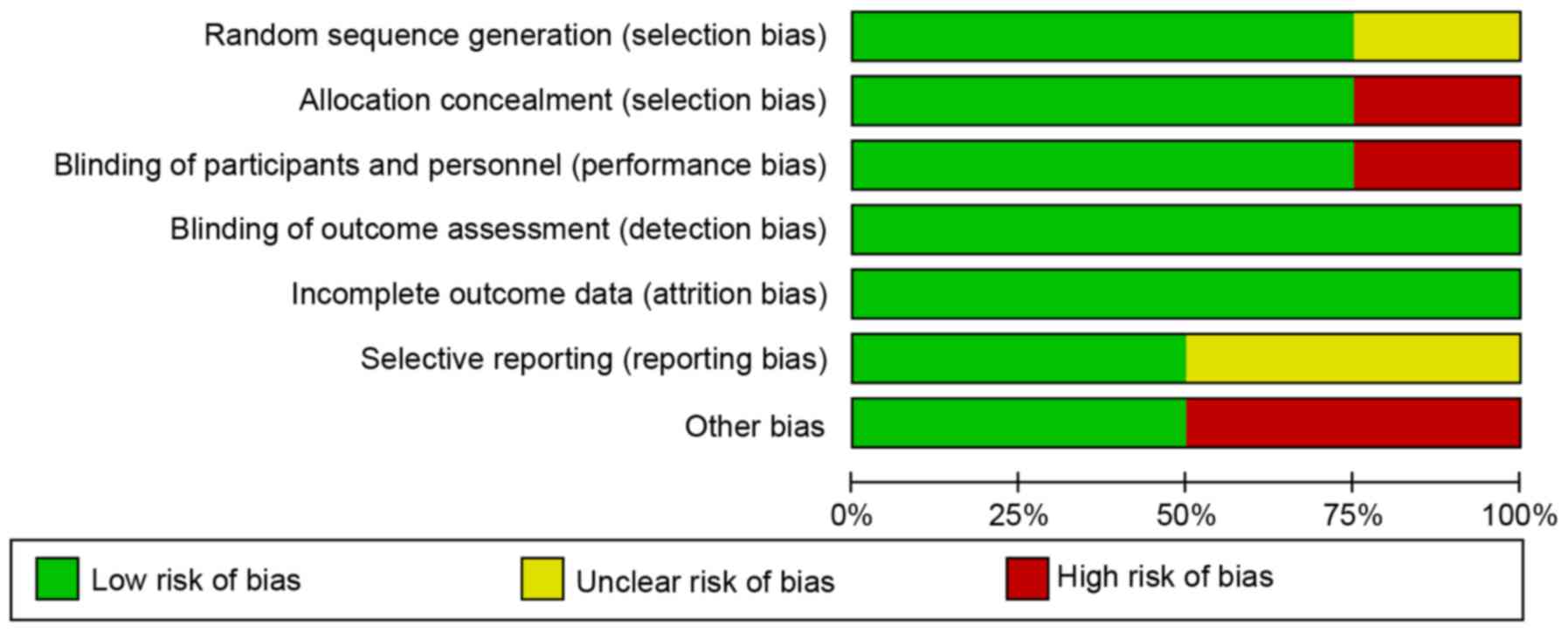
|
1
|
Hyder AA, Wunderlich CA, Puvanachandra P,
Gururaj G and Kobusingye OC: The impact of traumatic brain
injuries: A global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation. 22:341–353.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weaver LK, Cifu D, Hart B, Wolf G and
Miller S: Hyperbaric oxygen for post-concussion syndrome: Design of
department of defense clinical trials. Undersea Hyperb Med.
39:807–814. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
King NS: Post-concussion syndrome: Clarity
amid the controversy? Br J Psychiatry. 183:276–278. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolf G, Cifu D, Baugh L, Carne W and
Profenna L: The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on symptoms after mild
traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 29:2606–2612. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harch PG, Fogarty EF, Staab PK and Van
Meter K: Low pressure hyperbaric oxygen therapy and SPECT brain
imaging in the treatment of blast-induced chronic traumatic brain
injury (post-concussion syndrome) and post traumatic stress
disorder: A case report. Cases J. 2:65382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harch PG, Andrews SR, Fogarty EF, Amen D,
Pezzullo JC, Lucarini J, Aubrey C, Taylor DV, Staab PK and Van
Meter KW: A phase I study of low-pressure hyperbaric oxygen therapy
for blast-induced post-concussion syndrome and post-traumatic
stress disorder. J Neurotrauma. 29:168–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Walker WC, Franke LM, Cifu DX and Hart BB:
Randomized, Sham-Controlled, feasibility trial of hyperbaric oxygen
for service members with postconcussion syndrome: Cognitive and
psychomotor outcomes 1 week postintervention. Neurorehabil Neural
Repair. 28:420–432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miller RS, Weaver LK, Bahraini N,
Churchill S, Price RC, Skiba V, Caviness J, Mooney S, Hetzell B,
Liu J, et al: Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on symptoms and quality
of life among service members with persistent postconcussion
symptoms: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 175:43–52.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loane DJ, Stoica BA and Faden AI:
Neuroprotection for traumatic brain injury. Handb Clin Neurol.
127:343–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fiskum G: Mitochondrial participation in
ischemic and traumatic neural cell death. J Neurotrauma.
17:843–855. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roth TL, Nayak D, Atanasijevic T, Koretsky
AP, Latour LL and McGavern DB: Transcranial amelioration of
inflammation and cell death after brain injury. Nature.
505:223–228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Warriner RA III and Hopf HW: The effect of
hyperbaric oxygen in the enhancement of healing in selected problem
wounds. Undersea Hyperb Med. 39:923–935. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Palzur E, Vlodavsky E, Mulla H, Arieli R,
Feinsod M and Soustiel JF: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for reduction
of secondary brain damage in head injury: An animal model of brain
contusion. J Neurotrauma. 21:41–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harch PG, Kriedt C, Van Meter KW and
Sutherland RJ: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves spatial learning
and memory in a rat model of chronic traumatic brain injury. Brain
Res. 1174:120–129. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vlodavsky E, Palzur E and Soustiel JF:
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces neuroinflammation and expression
of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the rat model of traumatic brain
injury. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 32:40–50. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Palzur E, Zaaroor M, Vlodavsky E, Milman F
and Soustiel JF: Neuroprotective effect of hyperbaric oxygen
therapy in brain injury is mediated by preservation of
mitochondrial membrane properties. Brain Res. 1221:126–133. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Teasdale G and Jennett B: Assessment of
coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet.
2:81–84. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bennett MH, Trytko B and Jonker B:
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the adjunctive treatment of traumatic
brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
12:CD0046092012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tal S, Hadanny A, Berkovitz N, Sasson E,
Ben-Jacob E and Efrati S: Hyperbaric oxygen may induce angiogenesis
in patients suffering from prolonged post-concussion syndromedue to
traumatic brain injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 33:943–951.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group, : Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int J Surg.
8:336–341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Higgins JP and Green S: Cochrane Handbook
for Systematic Reviews of Interventions: Cochrane Book Series. John
Wiley and Sons, Ltd.; Chichester, UK: 2008,
doi:10.1002/9780470712184.ch1. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bennett M: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy no
better than sham in improving post-concussion symptoms following
mild traumatic brain injury. Diving Hyperb Med.
43:1732013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Efrati S and Ben-Jacob E: Reflections on
the neurotherapeutic effects of hyperbaric oxygen. Expert Rev
Neurother. 14:233–236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Davis MC, Shoja MM, Tubbs SR and
Griessenauer CJ: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for chronic
post-concussive syndrome. Med Gas Res. 4:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harch PG: Hyperbaric oxygen in chronic
traumatic brain injury: Oxygen, pressure, and gene therapy. Med Gas
Res. 5:92015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hoge C and Jonas WB: The ritual of
hyperbaric oxygen and lessons for the treatment of persistent
postconcussion symptoms in military personnel. JAMA Intern Med.
175:53–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mychaskiw G: Known knowns, known unknowns
and unknown unknowns: The science and the passion of HBO2 therapy
and traumatic brain injury: An editorial perspective. Undersea
Hyperb Med. 40:371–372. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brkic P, Sanja P, Danijela K and Jovanović
T: Hyperbaric oxygenation as an adjuvant therapy for traumatic
brain injury: A review of literature. Periodicum Biologorum.
116:29–36. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Figueroa XA and Wright JK: Clinical
results in brain injury trials using HBO2 therapy: Another
perspective. Undersea Hyperb Med. 42:333–351. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guedes VA, Song S, Provenzano M and
Borlongan CV: Understanding the pathology and treatment of
traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder: A
therapeutic role for hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Expert Rev
Neurother. 16:61–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu Q, Manaenko A, Guo Z, Huang L, Tang J
and Zhang JH: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for post concussion
symptoms: Issues may affect the results. Med Gas Res. 5:102015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McCrary BF, Weaver L, Marrs K, Miller RS,
Dicks C, Deru K, Close N and DeJong M: Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) for
post-concussive syndrome/chronic TBI product summary. Undersea
Hyperb Med. 40:443–467. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mitchell SJ and Bennett MH: Unestablished
indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Diving Hyperb Med.
44:228–234. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies
in Health (CADTH), : Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Adults with
Mental Illness: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness. CADTH Rapid
Response Reports. CADTH; Ottawa, ON, Canada: 2014
|
|
35
|
Armistead-Jehle P and Lee D: Response to
the Harch Group's ‘A phase I study of low-pressure hyperbaric
oxygen therapy for blast-induced post-concussion syndrome and
post-traumatic stress disorder’. J Neurotrauma. 29:2513–2515. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Harch PG, Andrews SR, Fogarty EF, Amen D,
Pezzullo JC, Lucarini J, Aubrey C, Taylor DV, Staab PK, Van Meter
KW; Response to the letter to the editor by Armistead-Jehle and Lee
on Harch, ; et al: A Phase I Study of Low-Pressure Hyperbaric
Oxygen Therapy for Blast-Induced Post-Concussion Syndrome and
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. J Neurotrauma. 29:2516–2519. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harch PG: Department of defense trials for
hyperbaric oxygen and TBI: Issues of study design and questionable
conclusions. Undersea Hyperb Med. 40:469–470. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hoge CW and Jonas WB: Hyperbaric oxygen
treatment for persistent postconcussion symptoms-reply. JAMA Intern
Med. 175:12412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marois P, Mukherjee A and Ballaz L:
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for persistent postconcussion
symptoms-A Placebo effect? JAMA Intern Med. 175:1239–1240. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Miller RS, Weaver LK and Brenner LA:
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for persistent postconcussion
symptoms-reply. JAMA Intern Med. 175:1240–1241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weaver LK, Cifu D, Hart B, Wolf G and
Miller RS: Reply: Department of Defense trials for hyperbaric
oxygen and TBI: Issues of study design and questionable
conclusions. Undersea Hyperb Med. 40:471–472. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wolf EG, Baugh LM, Kabban CM, Richards MF
and Prye J: Cognitive function in a traumatic brain injury
hyperbaric oxygen randomized trial. Undersea Hyperb Med.
42:313–332. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wortzel HS, Arciniegas DB, Anderson CA,
Vanderploeg RD and Brenner LA: A phase I study of low-pressure
hyperbaric oxygen therapy for blast-induced post-concussion
syndrome and post-traumatic stress disorder: A neuropsychiatric
perspective. J Neurotrauma. 29:2421–2424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miller RS, Brenner L, Churchill S, et al:
A phase II, randomized, sham-controlled trial hyperbaric oxygen for
post-concussion syndrome: Impact of intervention on symptoms and
well being. J Neurotrauma. 30:A562013.
|
|
45
|
Walker W, Cifu D, West S, Sima A, Graham
C, Hart B, Franke LM and Carne W: Hyperbaric oxygen for blast
related post-concussion syndrome: 3-month outcomes. Brain Injury.
28:6682014.
|
|
46
|
Hu Q, Liang X, Chen D, Chen Y, Doycheva D,
Tang J, Tang J and Zhang JH: Delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy
promotes neurogenesis through reactive oxygen
species/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/β-catenin pathway in middle
cerebral artery occlusion rats. Stroke. 45:1807–1814. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wolf EG, Prye J, Michaelson R, Brower G,
Profenna L and Boneta O: Hyperbaric side effects in a traumatic
brain injury randomized clinical trial. Undersea Hyperb Med.
39:1075–1082. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Deng J, Lei C, Chen Y, Fang Z, Yang Q,
Zhang H, Cai M, Shi L, Dong H and Xiong L: Neuroprotective
gases-fantasy or reality for clinical use? Prog Neurobiol.
115:210–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Eovaldi B and Zanetti C: Hyperbaric oxygen
ameliorates worsening signs and symptoms of post-traumatic stress
disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 6:785–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Morries LD, Cassano P and Henderson TA:
Treatments for traumatic brain injury with emphasis on transcranial
near-infrared laser phototherapy. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
11:2159–2175. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Raji CA, Tarzwell R, Pavel D, Schneider H,
Uszler M, Thornton J, van Lierop M, Cohen P, Amen DG and Henderson
T: Clinical utility of spect neuroimaging in the diagnosis and
treatment of traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. PLoS One.
9:e910882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wright JK, Zant E, Groom K, Schlegel RE
and Gilliland K: Case report: Treatment of mild traumatic brain
injury with hyperbaric oxygen. Undersea Hyperb Med. 36:391–399.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cifu DX, Walker WC, West SL, Hart BB,
Franke LM, Sima A, Graham CW and Carne W: Hyperbaric oxygen for
blast-related postconcussion syndrome: Three-month outcomes. Ann
Neurol. 75:277–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cifu DX, Hoke KW, Wetzel PA, Wares JR,
Gitchel G and Carne W: Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on eye tracking
abnormalities in males after mild traumatic brain injury. J Rehabil
Res Dev. 51:1047–1056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cifu DX, Hart BB, West SL, Walker W and
Carne W: The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on persistent
postconcussion symptoms. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 29:11–20. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Boussi-Gross R, Golan H, Fishlev G, Bechor
Y, Volkov O, Bergan J, Friedman M, Hoofien D, Shlamkovitch N,
Ben-Jacob E and Efrati S: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can improve
post concussion syndrome years after mild traumatic brain
injury-randomized prospective trial. PLoS One. 8:e799952013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Harch PG: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for
post-concussion syndrome: Contradictory conclusions from a study
mischaracterized as sham-controlled. J Neurotrauma. 30:1995–1999.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Eyres S, Carey A, Gilworth G, Neumann V
and Tennant A: Construct validity and reliability of the Rivermead
Post-Concussion symptoms questionnaire. Clin Rehabil. 19:878–887.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bliese PD, Wright KM, Adler AB, Cabrera O,
Castro CA and Hoge CW: Validating the primary care posttraumatic
stress disorder screen and the posttraumatic stress disorder
checklist with soldiers returning from combat. J Consult Clin
Psychol. 76:272–281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rice VJ, Overby C, Boykin G, Jeter A and
Villarreal J: How do I handle my life now? Coping and the post
traumatic stress disorder checklist-military version. Proc Hum
Factors Ergonomics Soc Ann Meet. 58:1252–1256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gardner PJ, Knittel-Keren D and Gomez M:
The posttraumatic stress disorder checklist as a screening measure
for posttraumatic stressdisorder in rehabilitation after burn
injuries. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 93:623–628. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
King PR, Donnelly KT, Donnelly JP, Dunnam
M, Warner G, Kittleson CJ, Bradshaw CB, Alt M and Meier ST:
Psychometric study of the neurobehavioral symptom inventory. J
Rehabil Res Dev. 49:879–888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ibarra S: Immediate post-concussion
assessment and cognitive testing. Encyclopedia of Clinical
Neuropsychology. Kreutzer JS, DeLuca J and Caplan B: Springer; New
York: pp. 1297–1299. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Kashluba S, Paniak C, Blake T, Reynolds S,
Toller-Lobe G and Nagy J: A longitudinal, controlled study of
patient complaints following treated mild traumatic brain injury.
Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 19:805–816. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bohnen N, Jolles J and Twijnstra A:
Neuropsychological deficits in patients with persistent symptoms
six months after mild head injury. Neurosurgery. 30:692–696. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bazarian JJ, McClung J, Shah MN, Cheng YT,
Flesher W and Kraus J: Mild traumatic brain injury in the United
States, 1998-2000. Brain Inj. 19:85–91. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Al Sayegh A, Sandford D and Carson AJ:
Psychological approaches to treatment of postconcussion syndrome: A
systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 81:1128–1134.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mulkey DK, Henderson RA III, Putnam RW and
Dean JB: Pressure (< or=4 ATA) increases membrane conductance
and firing rate in the rat solitary complex. J Appl Physiol (1985).
95:922–930. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gabizon I, Shiyovich A, Novack V,
Khalameizer V, Yosefy C, Moses SW and Katz A: Impact of descent and
stay at a Dead sea resort (low altitude) on patients with systolic
congestive heart failure and an implantable cardioverter
defibrillator. Isr Med Assoc J. 13:402–407. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Goldbart AD, Cohen AD, Weitzman D and Tal
A: Effects of rehabilitation winter camps at the Dead Sea on
European cystic fibrosis patients. Isr Med Assoc J. 9:806–809.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Falk B, Nini A, Zigel L, Yahav Y, Aviram
M, Rivlin J, Bentur L, Avital A, Dotan R and Blau H: Effect of low
altitude at the Dead Sea on exercise capacity and cardiopulmonary
response to exercise in cystic fibrosis patients with moderate to
severe lung disease. Pediatr Pulmonol. 41:234–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Collet JP, Vanasse M, Marois P, Amar M,
Goldberg J, Lambert J, Lassonde M, Hardy P, Fortin J, Tremblay SD,
et al: Hyperbaric oxygen for children with cerebral palsy: A
randomised multicentre trial. HBO-CP Research Group. Lancet.
357:582–586. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sham. September 13–2013http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/sham
|
|
74
|
Potter S, Leigh E, Wade D and Fleminger S:
The rivermead post concussion symptoms questionnaire: A
confirmatory factor analysis. J Neurol. 253:1603–1614. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lin JW, Tsai JT, Lee LM, Lin CM, Hung CC,
Hung KS, Chen WY, Wei L, Ko CP, Su YK and Chiu WT: Effect of
hyperbaric oxygen on patients with traumatic brain injury. Acta
Neurochir Suppl. 101:145–149. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Mychaskiw G II and Stephens PL: Hyperbaric
oxygen, mild traumatic brain injury, and study design: An elusive
target. J Neurotrauma. 30:1681–1682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Peskind ER, Brody D, Cernak I, McKee A and
Ruff RL: Military- and sports-related mild traumatic brain injury:
Clinical presentation, management, and long-termconsequences. J
Clin Psychiatry. 74:180–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Liu XH, Zhao YL, Ma QM, Zhou XH and Wang
Y: Optimal therapeutic window of hyperbaric oxygenation in neonatal
rat with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi.
44:177–181. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liu XH, Yan H, Xu M, Zhao YL, Li LM, Zhou
XH, Wang MX and Ma L: Hyperbaric oxygenation reduces long term
brain injury and ameliorates behavioral function by suppression of
apoptosis in a rat model of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurochem
Int. 62:922–930. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhu M, Lu M, Li QJ, Zhang Z, Wu ZZ, Li J,
Qian L, Xu Y and Wang ZY: Hyperbaric oxygen suppresses
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in newborn rats. J Child Neurol.
30:75–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Scorza KA, McCarthy W, Miller RS, Carne W
and Wolf G: Hyperbaric oxygen effects on PTSD and mild TBI
symptoms: A subset analysis. Undersea Hyperb Med (UHMS Annual
Meeting abstracts). 5:1066–2936. 2013.http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/10677
|
|
82
|
Hooker JS: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy:
Using evidence-based medicine to heal injured brain tissue. N C Med
J. 77:69–70. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|