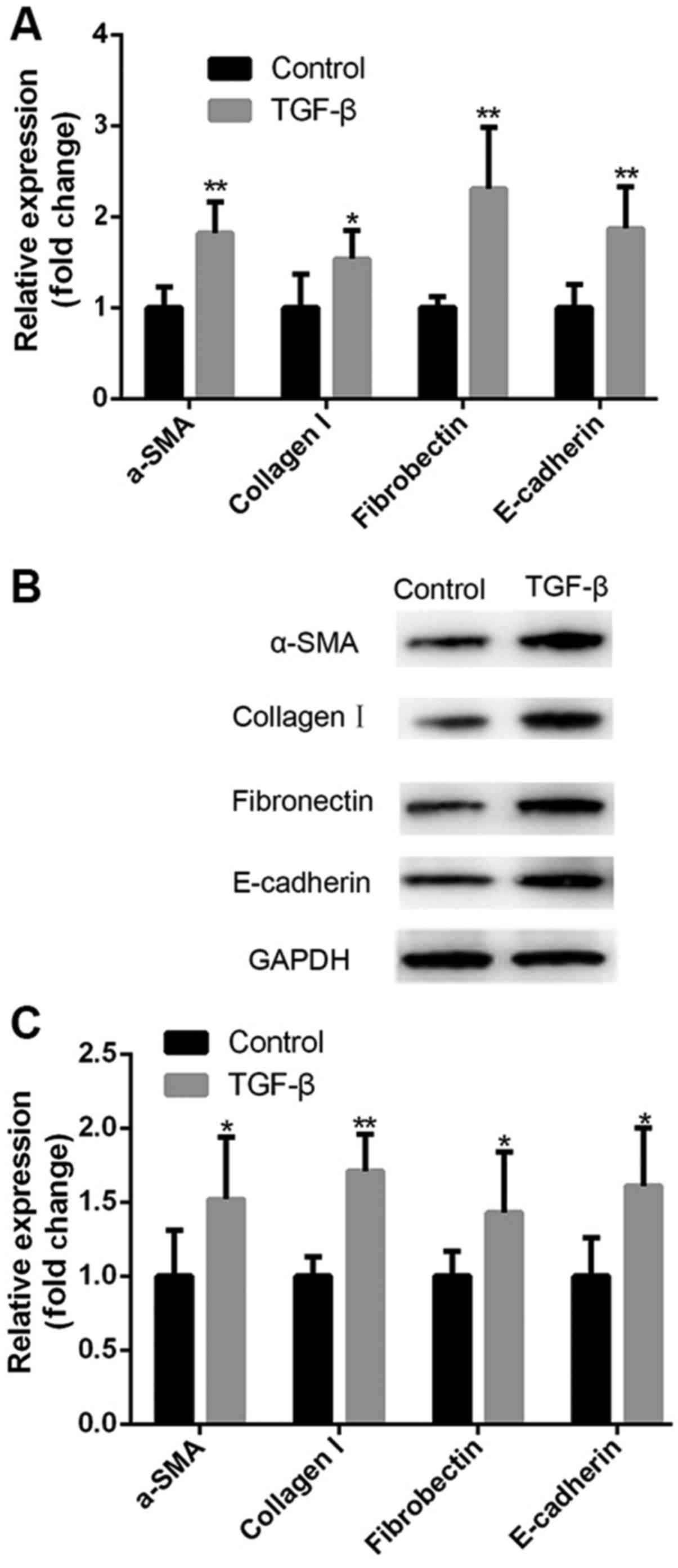
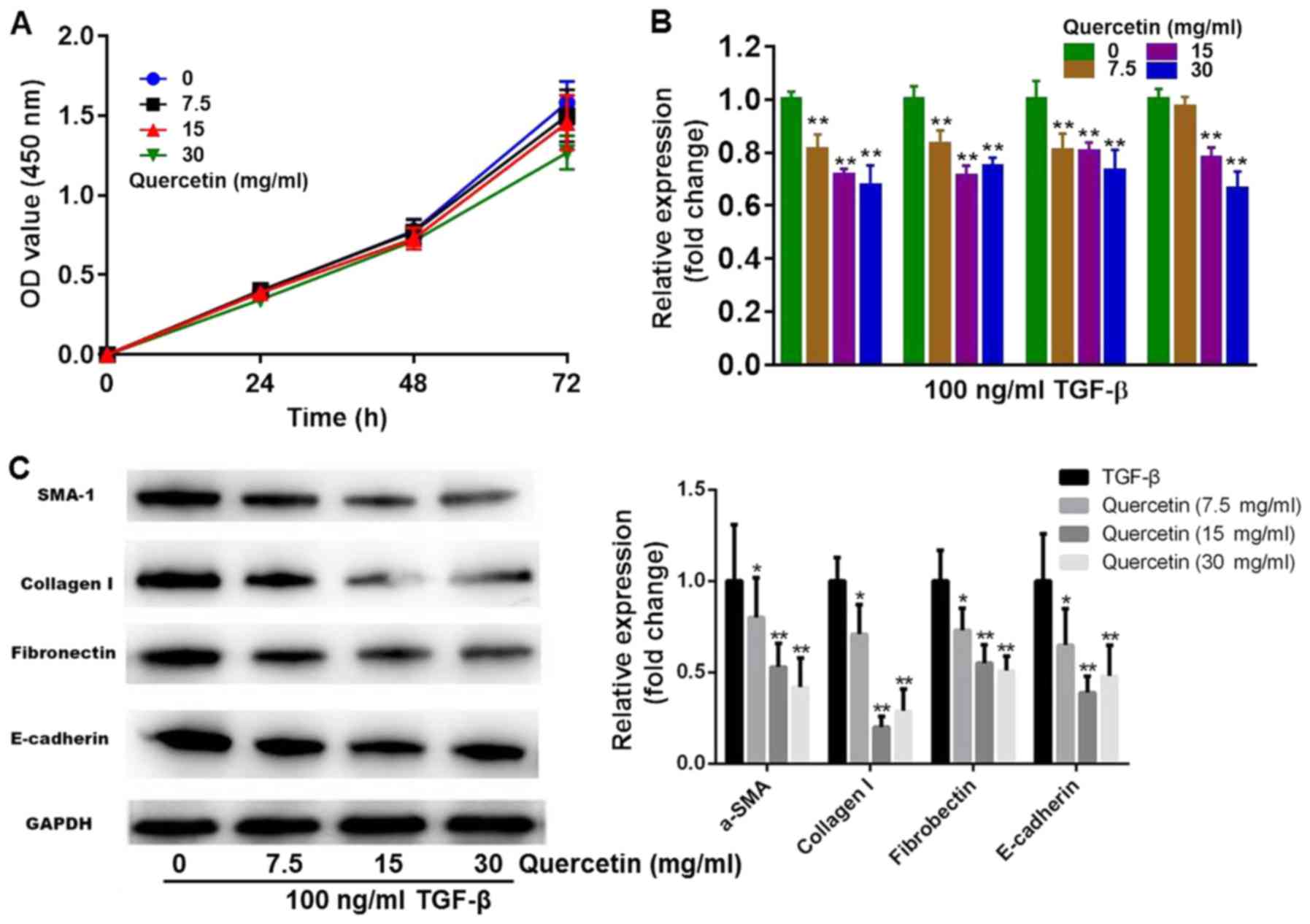
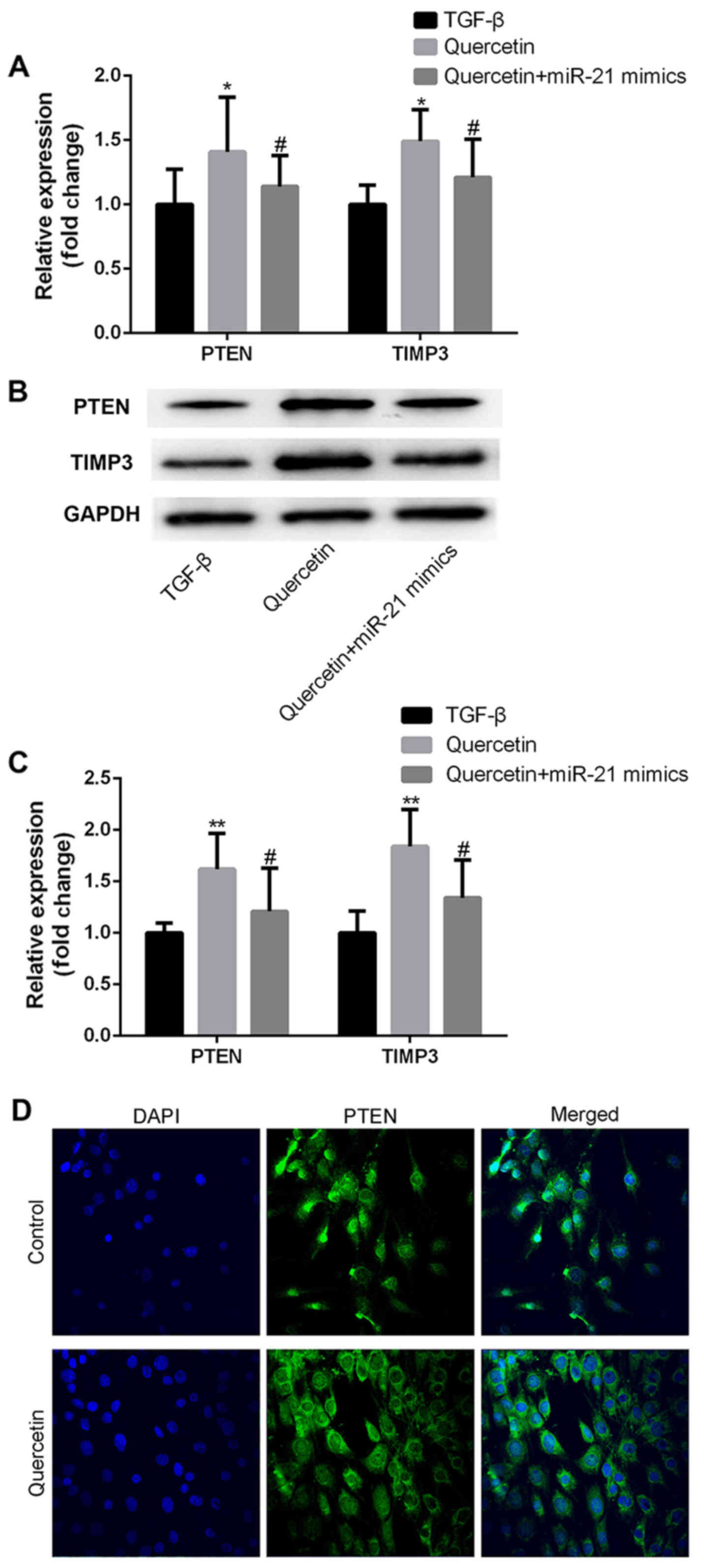
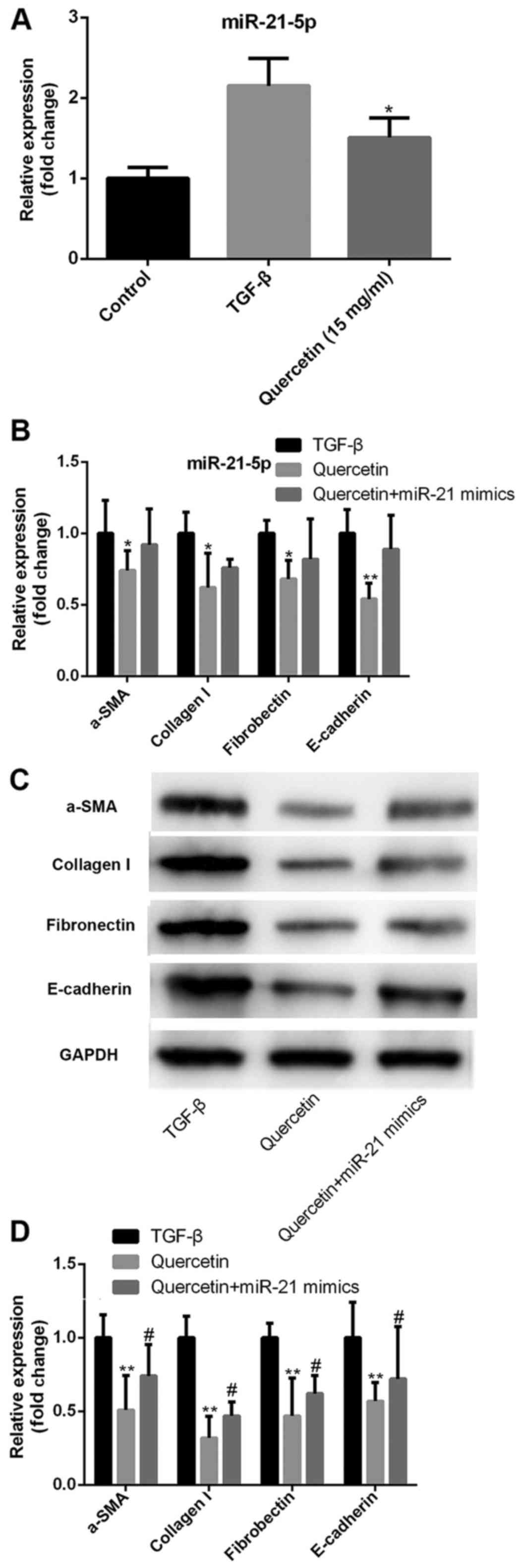
|
1
|
Zhou D, Fu H, Zhang L, Zhang K, Min Y,
Xiao L, Lin L, Bastacky SI and Liu Y: Tubule-derived wnts are
required for fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 28:2322–2336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Omata M, Doke Y, Yamada C, Kawashima K,
Sho R, Enomoto K, Furuya M and Inomata N: Hepatocyte nuclear
factor-1β induces redifferentiation of dedifferentiated tubular
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 11:e01549122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu H, Chen B, Hong W, Liang Y and Bai Y:
transforming growth factor-β1 stimulates hedgehog signaling to
promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition after kidney injury. FEBS
J. 283:3771–3790. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen SJ, Wu P, Sun LJ, Zhou B, Niu W, Liu
S, Lin FJ and Jiang GR: miR-204 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by targeting SP1 in the tubular epithelial cells after
acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion. Oncol Rep.
37:1148–1158. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jara P, Calyeca J, Romero Y, Plácido L, Yu
G, Kaminski N, Maldonado V, Cisneros J, Selman M and Pardo A:
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-19-deficient fibroblasts display a
profibrotic phenotype. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
308:L511–L522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meng XM, Zhang Y, Huang XR, Ren GL, Li J
and Lan HY: Treatment of renal fibrosis by rebalancing TGF-β/Smad
signaling with the combination of asiatic acid and naringenin.
Oncotarget. 6:36984–36997. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muñoz-Félix JM, González-Núñez M,
Martínez-Salgado C and López-Novoa JM: TGF-U/BMP proteins as
therapeutic targets in renal fibrosis. Where have we arrived after
25 years of trials and tribulations? Pharmacol Ther. 156:44–58.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vega G, Alarcón S and San Martin R: The
cellular and signalling alterations conducted by TGF-β contributing
to renal fibrosis. Cytokine. 88:115–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Groce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han F, Konkalmatt P, Chen J, Gildea J,
Felder RA, Jose PA and Armando I: miR-217 mediates the protective
effects of the dopamine D2 receptor on fibrosis in human renal
proximal tubule cells. Hypertension. 65:1118–1125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He F, Peng F, Xia X, Zhao C, Luo Q, Guan
W, Li Z, Yu X and Huang F: miR-135a promotes renal fibrosis in
diabetic nephropathy by regulating TRPC1. Diabetologia.
57:1726–1736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu D, Zhang N, Zhang J, Zhao H and Wang
X: miR-410 suppresses the expression of interleukin-6 as well as
renal fibrosis in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 43:616–625. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han M, Song Y and Zhang X: Quercetin
suppresses the migration and invasion in human colon cancer caco-2
cells through regulating toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa
B pathway. Pharmacogn Mag. 12 Suppl 2:S237–S244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chan CY, Lien CH, Lee MF and Huang CY:
Quercetin suppresses cellular migration and invasion in human head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Biomedicine (Taipei).
6:152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song NR, Chung MY, Kang NJ, Seo SG, Jang
TS, Lee HJ and Lee KW: Quercetin suppresses invasion and migration
of H-Ras-transformed MCF10A human epithelial cells by inhibiting
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Food Chem. 142:66–71. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen BL, Wang LT, Huang KH, Wang CC,
Chiang CK and Liu SH: Quercetin attenuates renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury via an activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase-regulated autophagy pathway. J Nutr Biochem.
25:1226–1234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Erboga M, Aktas C, Erboga ZF, Donmez YB
and Gurel A: Quercetin ameliorates methotrexate-induced renal
damage, apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats. Ren Fail.
37:1492–1497. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kou B, Liu W, Tang X and Kou Q: HMGA2
facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell
carcinoma by regulating the TGF-β/Smad2 signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 39:101–108. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kinashi H, Falke LL, Nguyen TQ, Bovenschen
N, Aten J, Leask A, Ito Y and Goldschmeding R: Connective tissue
growth factor regulates fibrosis-associated renal
lymphangiogenesis. Kidney Int. 92:850–863. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma J, Zhang L, Hao J, Li N, Tang J and Hao
L: Up-regulation of microRNA-93 inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT and
renal fibrogenesis by down-regulation of Orai1. J Pharmacol Sci.
136:218–227. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi B, Wang Y, Zhao R, Long X, Deng W and
Wang Z: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21
protects C-kit+ cardiac stem cells from oxidative injury through
the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis. PLoS One. 13:e01916162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gutsaeva DR, Thounaojam M, Rajpurohit S,
Powell FL, Martin PM, Goei S, Duncan M and Bartoli M:
STAT3-mediated activation of miR-21 is involved in down-regulation
of TIMP3 and neovascularization in the ischemic retina. Oncotarget.
8:103568–103580. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gelen V, Şengül E, Gedikli S, Gür C and
Özkanlar S: Therapeutic effect of quercetin on renal function and
tissue damage in the obesity induced rats. Biomed Pharmacother.
89:524–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuksel Y, Yuksel R, Yagmurca M, Haltas H,
Erdamar H, Toktas M and Ozcan O: Effects of quercetin on
methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. Mar
22–2016.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elbe H, Dogan Z, Taslidere E, Cetin A and
Turkoz Y: Beneficial effects of quercetin on renal injury and
oxidative stress caused by ciprofloxacin in rats: A histological
and biochemical study. Hum Exp Toxicol. 35:276–281. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hennino MF, Buob D, Van der Hauwaert C,
Gnemmi V, Jomaa Z, Pottier N, Savary G, Drumez E, Noël C, Cauffiez
C and Glowacki F: miR-21-5p renal expression is associated with
fibrosis and renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Sci
Rep. 6:272092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu XJ, Hong Q, Wang Z, Yu YY, Zou X and
Xu LH: MicroRNA21 promotes interstitial fibrosis via targeting
DDAH1: A potential role in renal fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem.
411:181–189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang J, Gao Y, Ma M, Li M, Zou D, Yang J,
Zhu Z and Zhao X: Effect of miR-21 on renal fibrosis by regulating
MMP-9 and TIMP1 in kk-ay diabetic nephropathy mice. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 67:537–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lan R, Geng H, Polichnowski AJ, Singha PK,
Saikumar P, McEwen DG, Griffin KA, Koesters R, Weinberg JM, Bidani
AK, et al: PTEN loss defines a TGF-β-induced tubule phenotype of
failed differentiation and JNK signaling during renal fibrosis. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F1210–F1223. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kassiri Z, Oudit GY, Kandalam V, Awad A,
Wang X, Ziou X, Maeda N, Herzenberg AM and Scholey JW: Loss of
TIMP3 enhances interstitial nephritis and fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 20:1223–1235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McClelland AD, Herman-Edelstein M, Komers
R, Jha JC, Winbanks CE, Hagiwara S, Gregorevic P, Kantharidis P and
Cooper ME: miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy
by targeting PTEN and SMAD7. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:1237–1249. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang N, Zhang CQ, He JH, Duan XF, Wang YY,
Ji X, Zang WQ, Li M, Ma YY, Wang T and Zhao GQ: miR-21
down-regulation suppresses cell growth, invasion and induces cell
apoptosis by targeting FASL, TIMP3, and RECK genes in esophageal
carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 58:1863–1870. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|