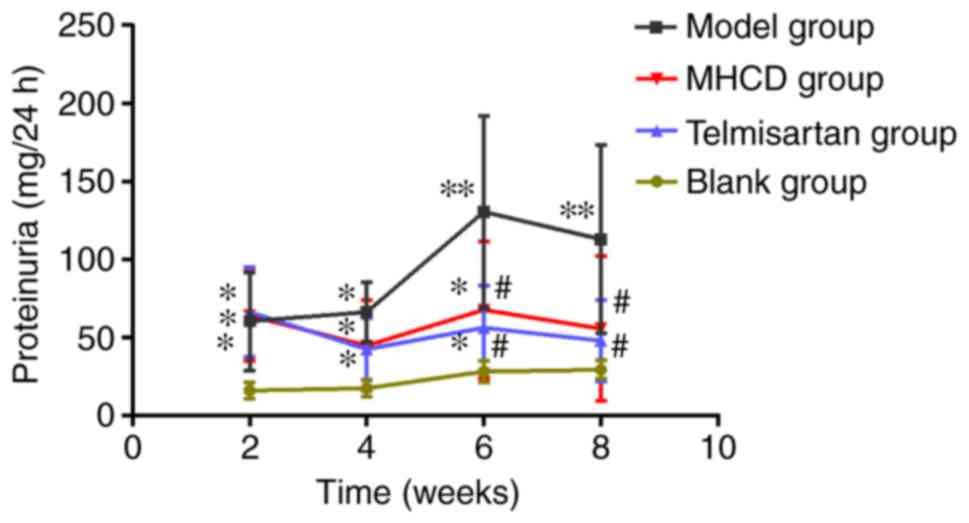
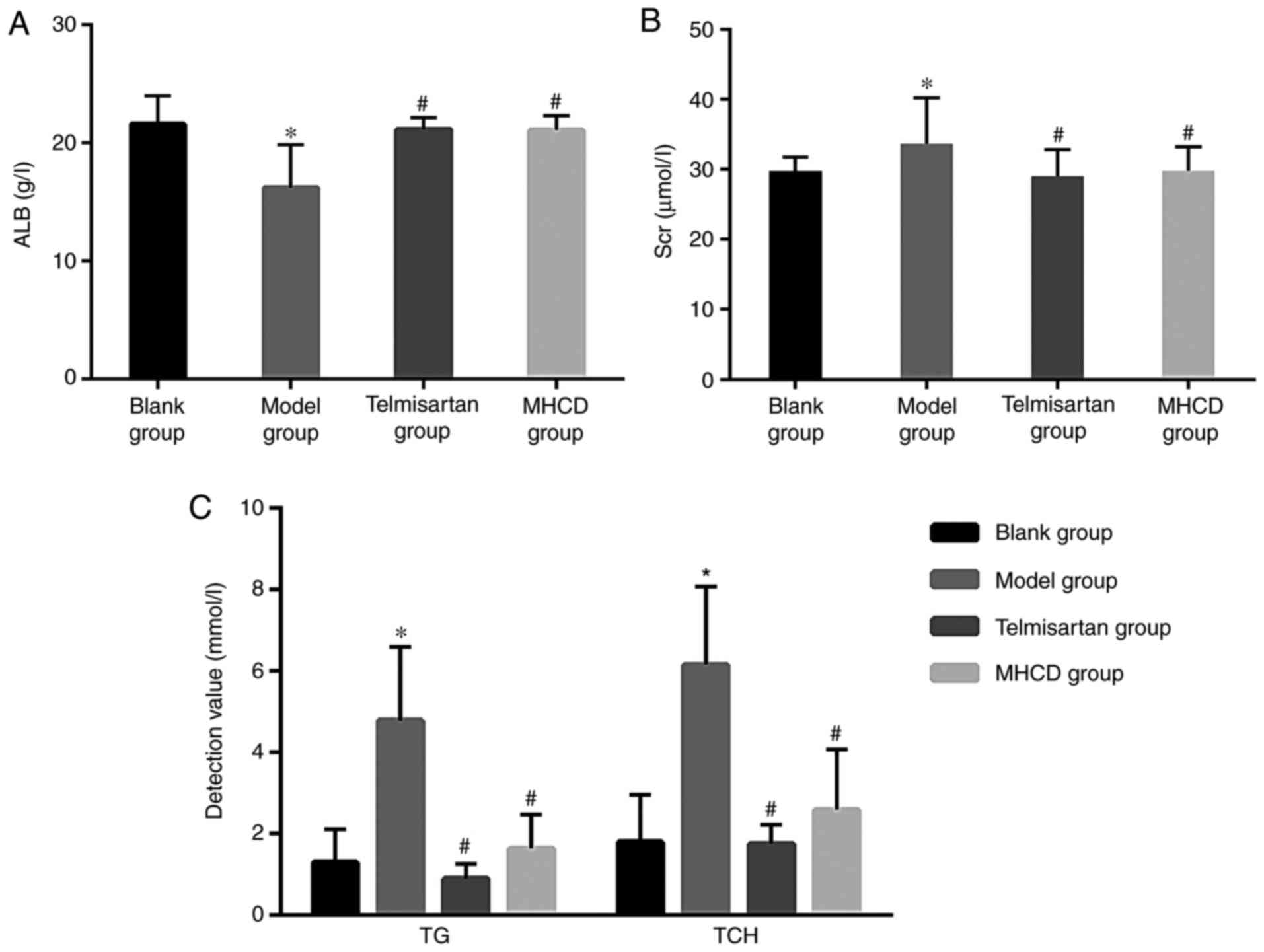
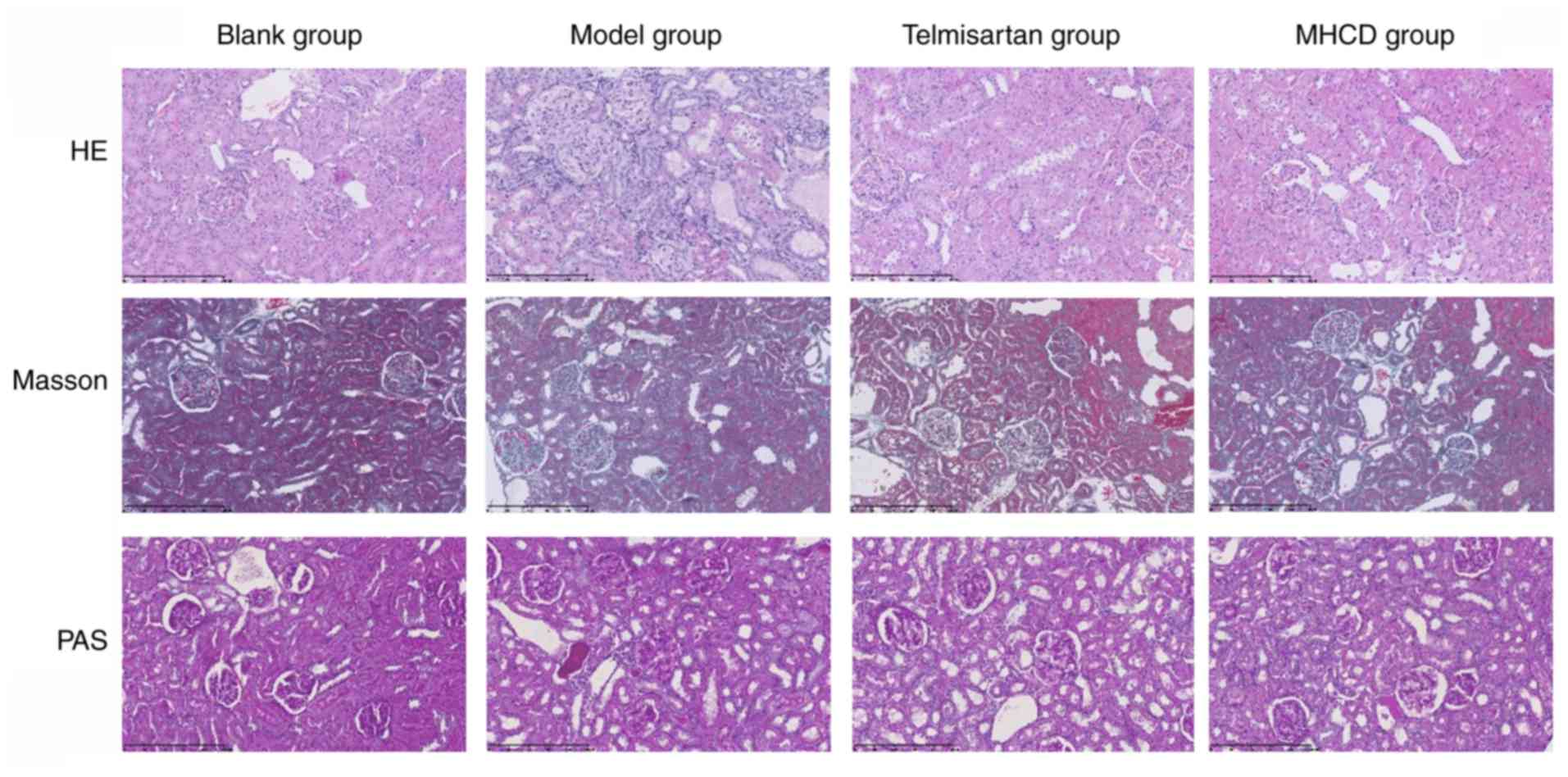
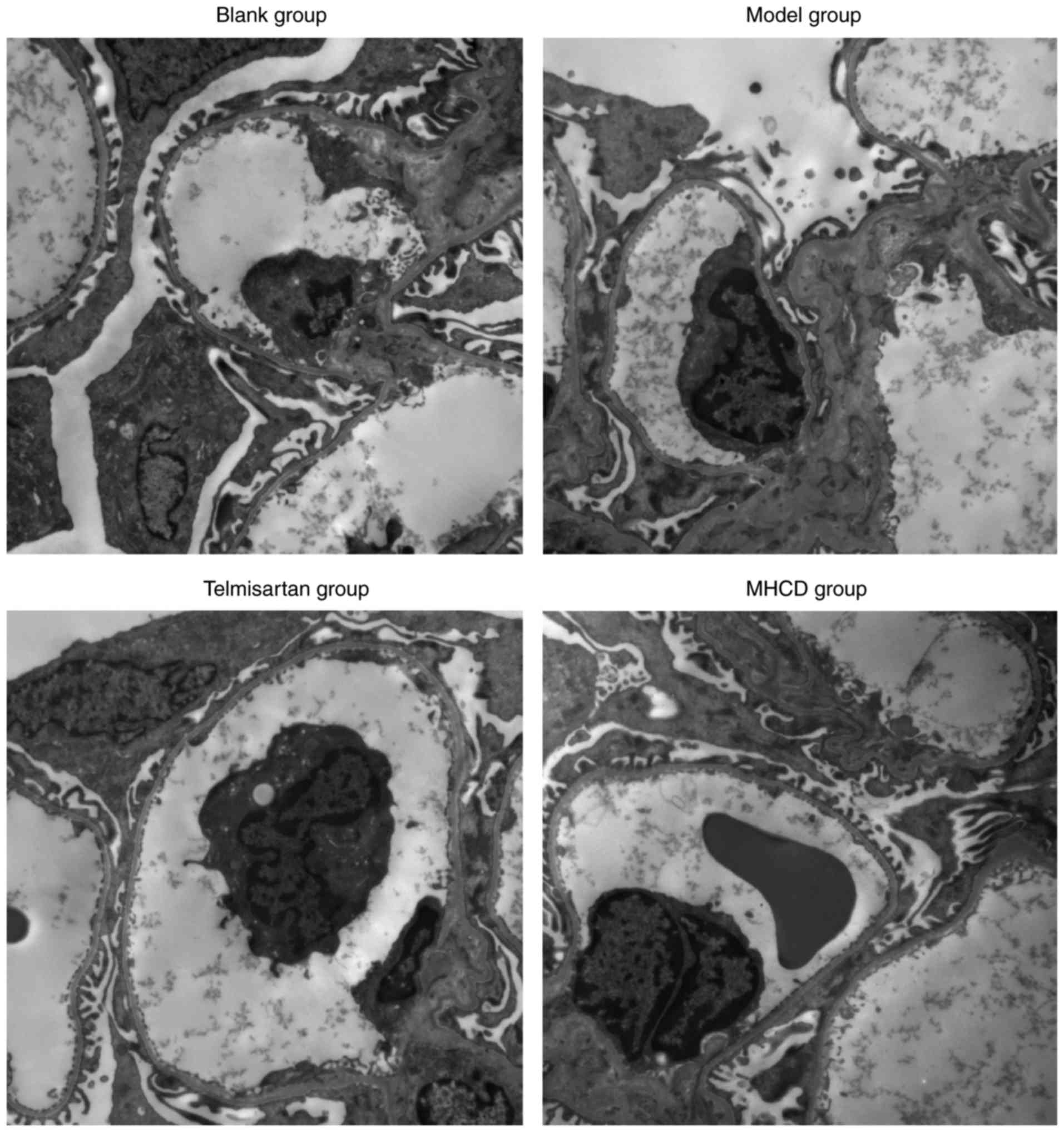
|
1
|
Kirsztajn GM, Filho NS, Draibe SA, Netto
MV, Thomé FS, Souza E and Bastos MG: Fast reading of the KDIGO
2012: Guidelines for evaluation and management of chronic
kidneydisease in clinical practice. J Bras Nefrol. 36:63–73.
2014.(In Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mills KT, Xu Y, Zhang W, Bundy JD, Chen
CS, Kelly TN, Chen J and He J: A systematic analysis of worldwide
population-based data on the global burden of chronic kidney
disease in 2010. Kidney Int. 88:950–957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carney EF: Epidemiology: Global burden of
disease study 2013 reports that disability caused by CKD is
increasing worldwide. Nat Rev Nephrol. 11:4462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barnett AH, Bain SC, Bouter P, Karlberg B,
Madsbad S, Jervell J and Mustonen J; Diabetics Exposed to
Telmisartan and Enalapril Study Group, : Angiotensin-receptor
blockade versus converting-enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetes and
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 351:1952–1961. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gong XZ, Zhou LF, Wang Q, Tang XC, Qian
YR, Wang YR, Lu L and Zhou JJ: Effect of Chuanhuang No.1 recipe on
renal function and micro-inflammation in phase 3 chronic kidney
disease patients. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 35:137–141.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong F, Cheng J, Lin S, Hu Z, Chen G and
He L: The clinical research on serum cystatin-C alteration on stage
II chronic kidney disease with gubenquduyishen decoction treatment.
J Ethnopharmacol. 131:581–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Yu: Clinical observation on 50 cases
of chronic nephritis proteinuria treated with modified Huangqi
Chifeng Decoction. Chin Med Guides. 36:137–138. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Clark SL Jr: Cellular differentiation in
the kidneys of newborn mice studied with the electron microscope. J
Biophys Biochem Cytol. 3:349–362. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Berkenstam A, Ahlberg J and Glaumann H:
Isolation and characterization of autophagic vacuoles from rat
kidney cortex. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol.
44:275–286. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Asanuma K, Tanida I, Shirato I, Ueno T,
Takahara H, Nishitani T, Kominami E and Tomino Y: MAP-LC3, a
promising autophagosomal marker, is processed during the
differentiation and recovery of podocytes from PAN nephrosis. FASEB
J. 17:1165–1167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M,
Yoshimori T and Ohsumi Y: In vivo analysis of autophagy in response
to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a
fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell. 15:1101–1104.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hartleben B, Gödel M, Meyer-Schwesinger C,
Liu S, Ulrich T, Köbler S, Wiech T, Grahammer F, Arnold SJ,
Lindenmeyer MT, et al: Autophagy influences glomerular disease
susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice. J
Clin Invest. 120:1084–1096. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeng C, Fan Y, Wu J, Shi S, Chen Z, Zhong
Y, Zhang C, Zen K and Liu Z: Podocyte autophagic activity plays a
protective role in renal injury and delays the progression of
podocytopathies. J Pathol. 234:203–213. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Z, Yang B and Zhang Y: Protective
effect of modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction on Doxorubicin
Nephrosis (AN) rats kidney and its regulated effect on its
autophagy level. Zhongguo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi.
23:477–479+563. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Faleiros CM, Francescato HD, Papoti M,
Chaves L, Silva CG, Costa RS and Coimbra TM: Effects of previous
physical training on adriamycin nephropathy and its relationship
with endothelial lesions and angiogenesis in the renal cortex. Life
Sci. 169:43–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee VW and Harris DC: Adriamycin
nephropathy: A model of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Nephrology (Carlton). 16:30–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rahman M, Yang W, Akkina S, Alper A,
Anderson AH, Appel LJ, He J, Raj DS, Schelling J, Strauss L, et al:
Relation of serum lipids and lipoproteins with progression of CKD:
The CRIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:1190–1198. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu N, Xu L, Shi Y and Zhuang S: Podocyte
autophagy: A potential therapeutic target to prevent the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res.
2017:35602382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mijaljica D, Prescott M and Devenish RJ:
The intriguing life of autophagosomes. Int J Mol Sci. 13:3618–3635.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stern ST, Adiseshaiah PP and Crist RM:
Autophagy and lysosomal dysfunction as emerging mechanisms of
nanomaterial toxicity. Part Fibre Toxicol. 9:202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guan H, Piao H, Qian Z, Zhou X, Sun Y, Gao
C, Li S and Piao F: 2,5-Hexanedione induces autophagic death of
VSC4.1 cells via a PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol Biosyst.
13:1993–2005. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Wang ZG and Liu Z: Changes of
glomerular fixed anionic charge sites in adriamycin nephrosis in
rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 104:128–131. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bertani T, Poggi A, Pozzoni R, Delaini F,
Sacchi G, Thoua Y, Mecca G, Remuzzi G and Donati MB:
Adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome in rats: Sequence of
pathologic events. Lab Invest. 46:16–23. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang YL, Zhang Y, Wang HX and Hao W:
Impact of jiaweihuangqichifeng decoction on proteinuria, renal
cortex SOD and renal cortex MDA in nephrotic rats induced by
adriamycin. Chin J Basic Med Trad Chin Med. 17:505–507. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Costas MA and Rubio MF: Autophagy: A
strategy for cell survival. Medicina (B Aires). 77:314–320.
2017.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao ST and Qin SC: The relationship of
autophagy with endoplasmic reticulum stress and its role in
pathogenesis, prevention and therapy of atherosclerosis. Sheng Li
Xue Bao. 69:515–521. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Davis S, Wang J and Ferro-Novick S:
Crosstalk between the secretory and autophagy pathways regulates
autophagosome formation. Dev Cell. 41:23–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3 and
autophagy. Methods Mol Biol. 445:77–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shibata M, Yoshimura K, Tamura H, Ueno T,
Nishimura T, Inoue T, Sasaki M, Koike M, Arai H, Kominami E and
Uchiyama Y: LC3, a microtubule-associated protein1A/B light chain3,
is involved in cytoplasmic lipid droplet formation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 393:274–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3
conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2503–2518. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Glover K, Li Y, Mukhopadhyay S, Leuthner
Z, Chakravarthy S, Colbert CL and Sinha SC: Structural transitions
in conserved, ordered Beclin 1 domains essential to regulating
autophagy. J Biol Chem. 292:16235–16248. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mei Y, Glover K, Su M and Sinha SC:
Conformational flexibility of BECN1: Essential to its key role in
autophagy and beyond. Protein Sci. 25:1767–1785. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yin Z, Pascual C and Klionsky DJ:
Autophagy: Machinery and regulation. Microb Cell. 3:588–596. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter
M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M,
Korolchuk VI, Lichtenberg M, Luo S, et al: Regulation of mammalian
autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.
90:1383–1435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Martinet W, Agostinis P, Vanhoecke B,
Dewaele M and De Meyer GR: Autophagy in disease: A double-edged
sword with therapeutic potential. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:697–712.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kroemer G and Jäättelä M: Lysosomes and
autophagy in cell death control. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:886–897. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Johnson-Lyles DN, Peifley K, Lockett S,
Neun BW, Hansen M, Clogston J, Stern ST and McNeil SE: Fullerenol
cytotoxicity in kidney cells is associated with cytoskeleton
disruption, autophagic vacuole accumulation, and mitochondrial
dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 248:249–258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy: From phenomenology
to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 11:931–937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Peng Y, Qiu L, Xu D, Zhang L, Yu H, Ding
Y, Deng L and Lin J: M4IDP, a zoledronic acid derivative, induces
G1 arrest, apoptosis and autophagy in HCT116 colon carcinoma cells
via blocking PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Life Sci. 185:63–72. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang S, Li J, Du Y, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhang Z,
Xu Z, Zeng Y, Mao X and Cao B: The class I PI3K inhibitor S14161
induces autophagy in malignant blood cells by modulating the Beclin
1/Vps34 complex. J Pharmacol Sci. 134:197–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
De Santis MC, Sala V, Martini M, Ferrero
GB and Hirsch E: PI3K signaling in tissue hyper-proliferation: From
overgrowth syndromes to kidney cysts. Cancers (Basel). 9(pii):
E302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Reilly R, Mroz MS, Dempsey E, Wynne K,
Keely SJ, McKone EF, Hiebel C, Behl C and Coppinger JA: Targeting
the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway in cystic fibrosis. Sci Rep.
7:76422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luo T, Liu G, Ma H, Lu B, Xu H, Wang Y, Wu
J, Ge P and Liang J: Inhibition of autophagy via activation of
PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to the protection of ginsenoside Rb1
against neuronal death caused by ischemic insults. Int J Mol Sci.
15:15426–15442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oh I, Cho H and Lee Y, Cheon M, Park D and
Lee Y: Blockage of autophagy rescues the dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor
BEZ235-induced growth inhibition of colorectal cancer cells. Dev
Reprod. 20:1–10. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Echeverry N, Ziltener G, Barbone D, Weder
W, Stahel RA, Broaddus VC and Felley-Bosco E: Inhibition of
autophagy sensitizes malignant pleural mesothelioma cells to dual
PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Y, Wang W, Li D, Li M, Wang P, Wen J,
Liang M, Su B and Yin Y: IGF-1 alleviates NMDA-induced
excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons against autophagy
via the NR2B/PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. J Cell Physiol. 229:1618–1629.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xing Y, Liu YX, Liu X, Wang SL, Li P, Lin
XH, Sui CL, Xu C, Qi B and Tong Q: Effects of Gui Zhu Yi Kun
formula on the P53/AMPK pathway of autophagy in granulosa cells of
rats with polycystic ovary syndrome. Exp Ther Med. 13:3567–3573.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li S: The effect of MHCD on proteinuria
and its cellular molecular mechanism [D]. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da
Xue. 2016.(In Chinese).
|