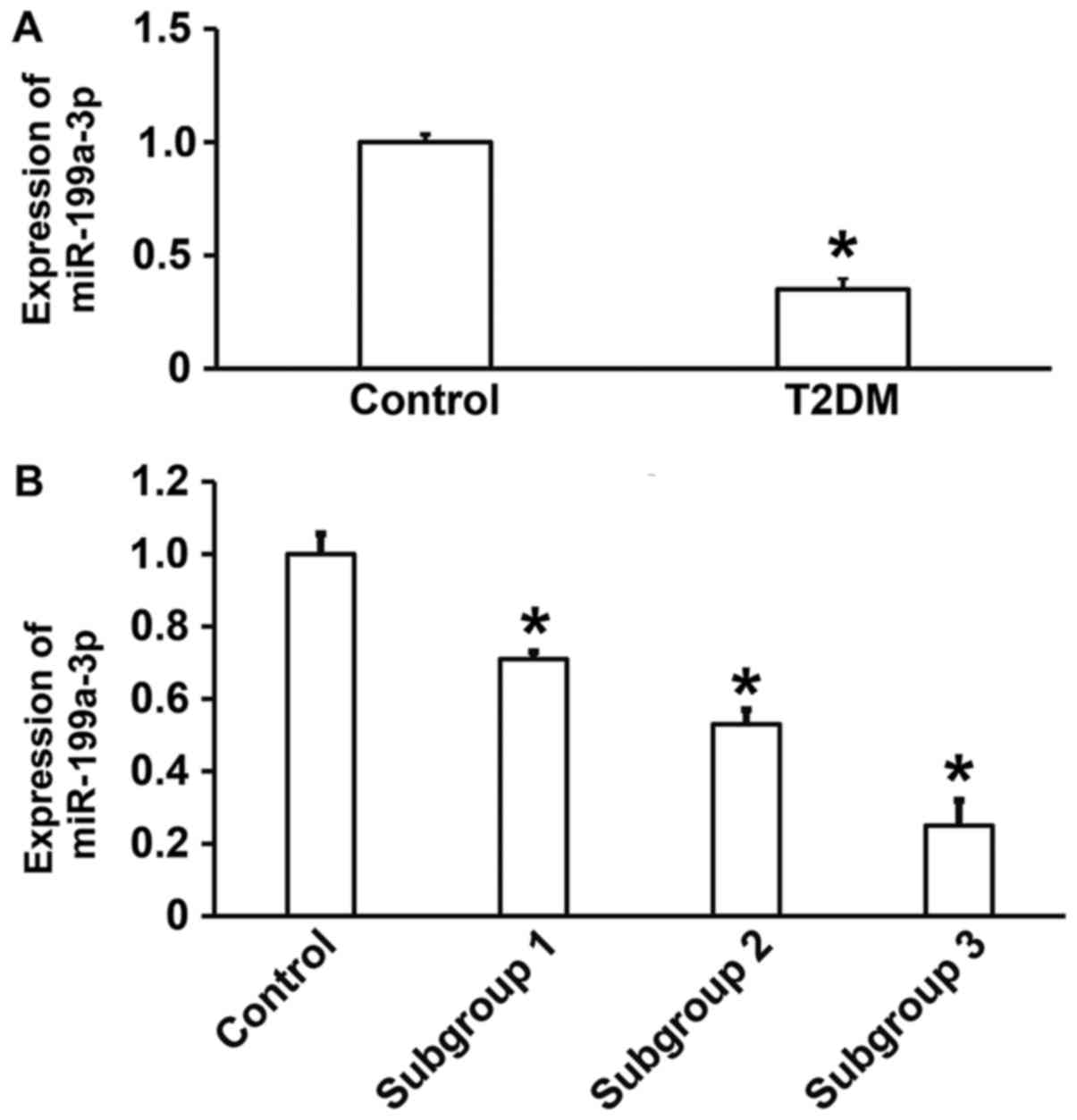
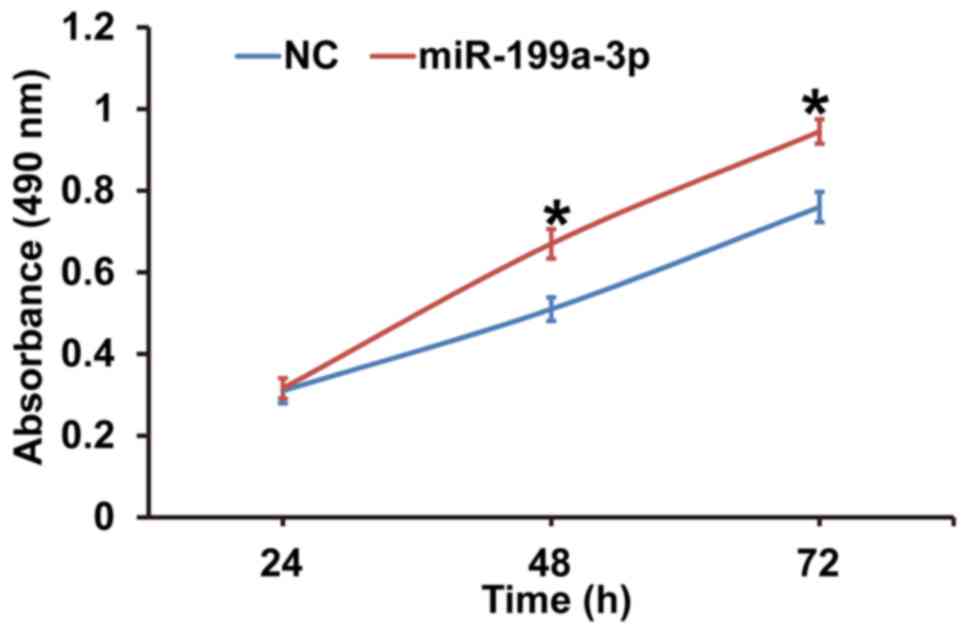
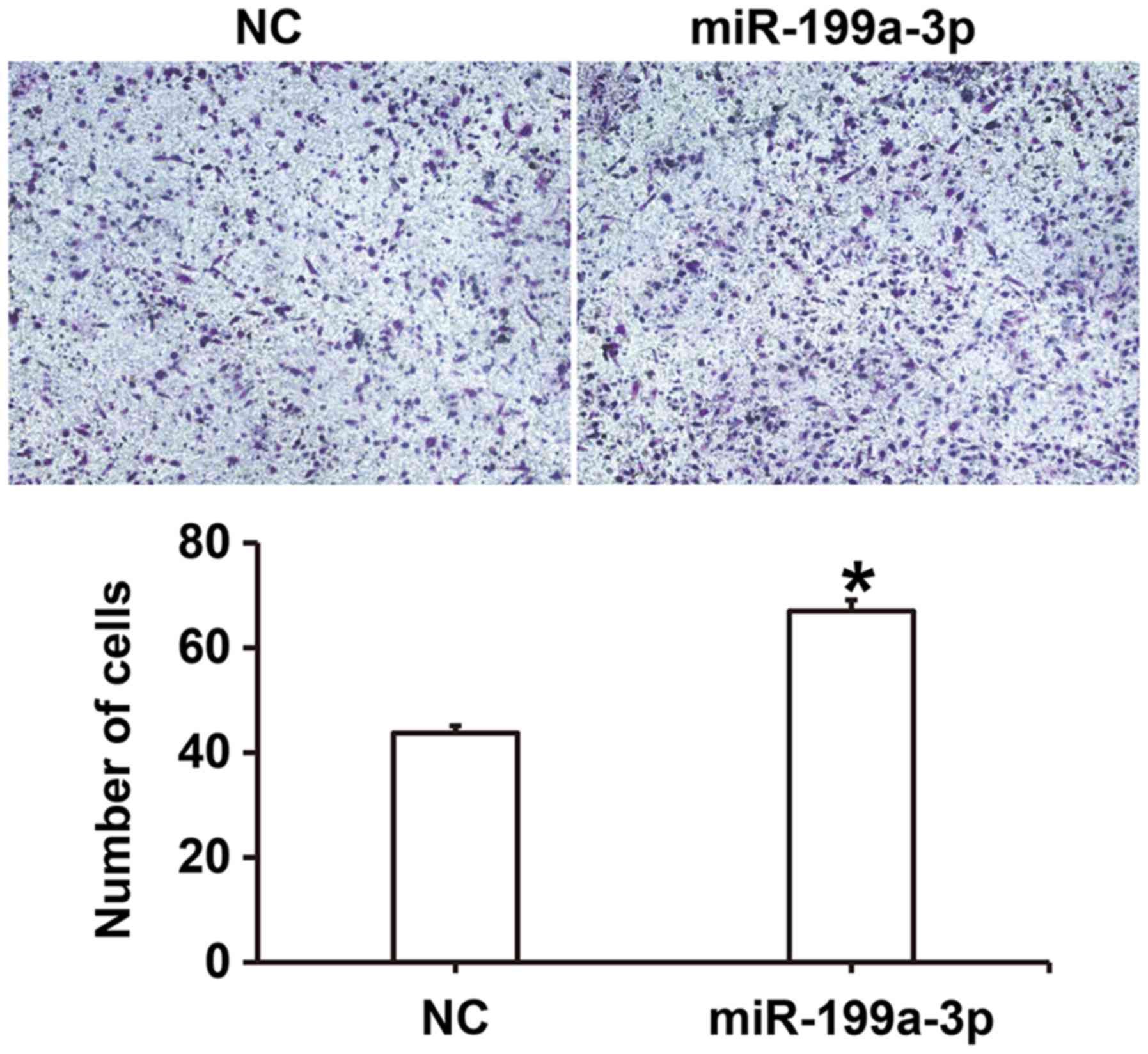
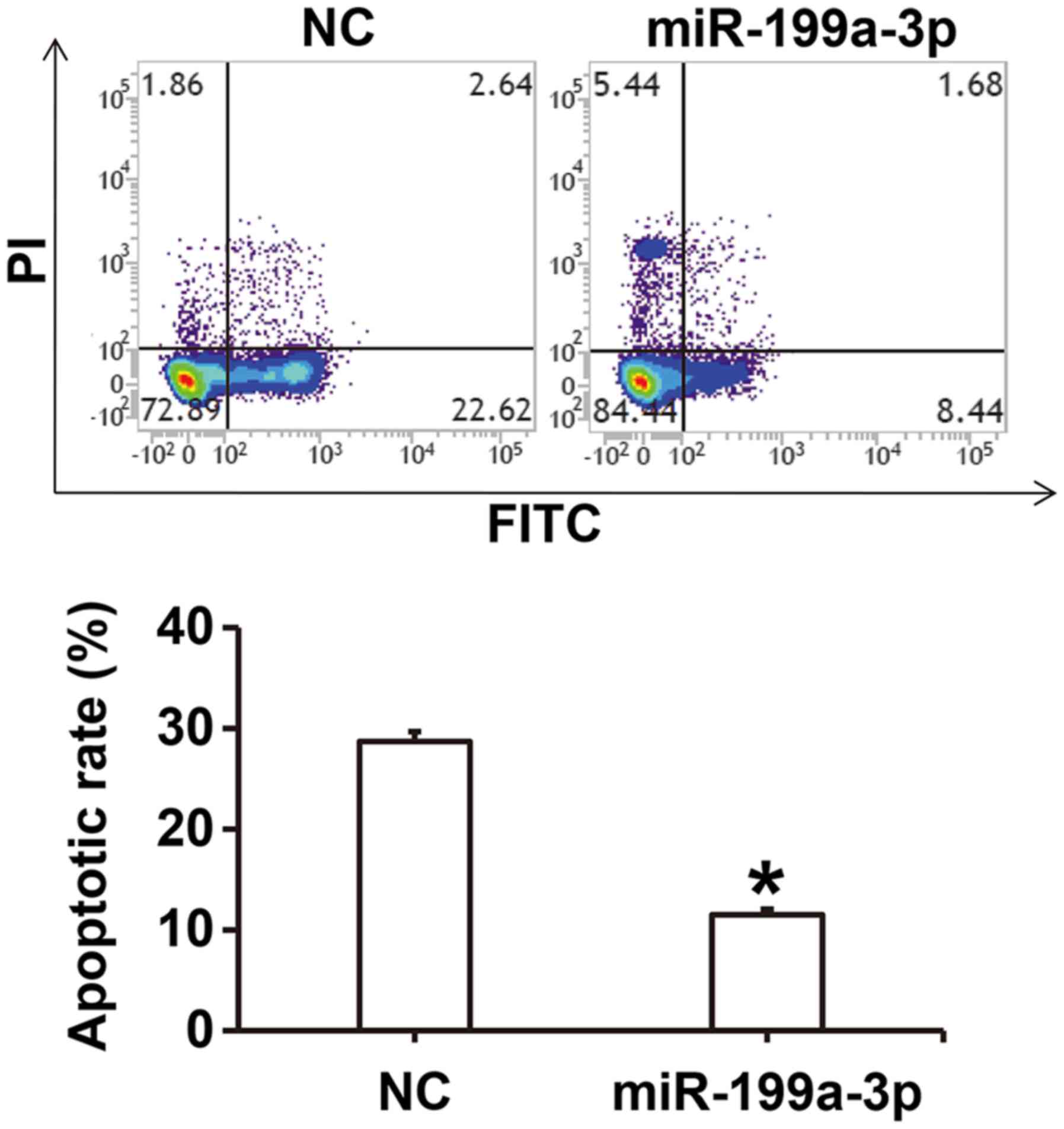
|
1
|
Buraczynska M, Buraczynska K, Zukowski P
and Ksiazek A: Interleukin-4 gene intron 3 VNTR polymorphism in
type 2 diabetes patients with peripheral neuropathy. Immunol
Invest. 47:146–153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vernstrom L, Funck KL, Grove EL, Laugesen
E, Baier JM, Hvas AM and Poulsen PL: Antiplatelet effect of aspirin
during 24h in patients with type 2 diabetes without cardiovascular
disease. Thromb Res. 161:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou ZW, Ju HX, Sun MZ, Chen HM, Fu QP and
Jiang DM: Serum fetuin-A levels in obese and non-obese subjects
with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta.
476:98–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iciek R, Brazert M, Wender-Ozegowska E,
Pietryga M and Brazert J: Low placental visfatin expression is
related to impaired glycaemic control and fetal macrosmia in
pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol.
69:61–66. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Plessas A, Robertson DP and Hodge PJ:
Radiographic bone loss in a Scottish non-smoking Type 1 Diabetes
mellitus population; a Bitewing Radiographic Study. J Periodontol.
May 15–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cottam A, Cottam D, Zaveri H, Cottam S,
Surve A, Medlin W and Richards C: An analysis of mid-term
complications, weight loss, and type 2 diabetes resolution of
stomach intestinal pylorus-sparing surgery (SIPS) versus Roux-En-Y
gastric bypass (RYGB) with three-year follow-up. Obes Surg. May
22–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Del Prato S and Chilton R: Practical
strategies for improving outcomes in T2DM: The potential role of
pioglitazone and DPP4 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes Metab. 20:786–799.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suchkova OV, Gurfinkel YI and Sasonko ML:
Microcirculatory parameters in compensated and decompensated type 2
diabetes mellitus. Ter Arkh. 89:28–35. 2017.(In Russian; Abstract
available in Russian from the publisher). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakamura H, Kato M, Nakaya T, Kono M,
Tanimura S, Sato T, Fujieda Y, Oku K, Ohira H, Bohgaki T, et al:
Decreased haptoglobin levels inversely correlated with pulmonary
artery pressure in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A
cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e83492017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blanco PJ, Muller LO and Spence JD: Blood
pressure gradients in cerebral arteries: A clue to pathogenesis of
cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2:108–117. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Hou J, Du J, Feng J, Yang Y, Shen Y,
Chen S, Feng J, Yang D, Pei H, et al: Potential protective
mechanism in the cardiac microvascular injury. Hypertension.
72:116–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu X, Cao L, Zhang Y, Lian H, Sun Z and
Cui Y: MicroRNA-1246 inhibits cell invasion and epithelial
mesenchymal transition process by targeting CXCR4 in lung cancer
cells. Cancer Biomark. 21:251–260. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tesfaye D, Gebremedhn S, Salilew-Wondim D,
Hailay T, Hoelker M, Grosse-Brinkhaus C and Schellander K:
MicroRNAs: Tiny molecules with significant role in mammalian
follicular and oocyte development. Reproduction. 155:R121–R135.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, He X, Li Y and Wang T:
Cerebrospinal fluid CD4+ T lymphocyte-derived miRNA-let-7b can
enhances the diagnostic performance of Alzheimer's disease
biomarkers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:1144–1150. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lv G, Zhu H, Li C, Wang J, Zhao D, Li S,
Ma L, Sun G, Li F, Zhao Y and Gao Y: Inhibition of IL-8-mediated
endothelial adhesion, VSMCs proliferation and migration by
siRNA-TMEM98 suggests TMEM98's emerging role in atherosclerosis.
Oncotarget. 8:88043–88058. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang HH, Sun PF, Chen WK, Zhong J, Shi QQ,
Weng ML, Ma D and Miao CH: High glucose stimulates expression of
MFHAS1 to mitigate inflammation via Akt/HO-1 pathway in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Inflammation. 41:400–408. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bartoszewski R, Serocki M,
Janaszak-Jasiecka A, Bartoszewska S, Kochan-Jamrozy K, Piotrowski
A, Króliczewski J and Collawn JF: miR-200b downregulates Kruppel
Like Factor 2 (KLF2) during acute hypoxia in human endothelial
cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 96:758–766. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang HW, Li H, Yan H and Liu BL:
MicroRNA-142 promotes the expression of eNOS in human peripheral
blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells in vitro. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 20:4167–4175. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Varshney A, Panda JJ, Singh AK, Yadav N,
Bihari C, Biswas S, Sarin SK and Chauhan VS: Targeted delivery of
microRNA-199a-3p using self-assembled dipeptide nanoparticles
efficiently reduces hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology.
67:1392–1407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qu F, Zheng J, Gan W, Lian H, He H, Li W,
Yuan T, Yang Y, Li X, Ji C, et al: MiR-199a-3p suppresses
proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by targeting
Smad1. Oncotarget. 8:52465–52473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park KM, Teoh JP, Wang Y, Broskova Z,
Bayoumi AS, Tang Y, Su H, Weintraub NL and Kim IM:
Carvedilol-responsive microRNAs, miR-199a-3p and −214 protect
cardiomyocytes from simulated ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 311:H371–H383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu H and Leung SW: Identification of
microRNA biomarkers in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of
controlled profiling studies. Diabetologia. 58:900–911. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mathews E, Thomas E, Absetz P, D'Esposito
F, Aziz Z, Balachandran S, Daivadanam M, Thankappan KR and
Oldenburg B: Cultural adaptation of a peer-led lifestyle
intervention program for diabetes prevention in India: The Kerala
diabetes prevention program (K-DPP). BMC Public Health. 17:9742018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coelho SC, Berillo O, Caillon A, Ouerd S,
Fraulob-Aquino JC, Barhoumi T, Offermanns S, Paradis P and
Schiffrin EL: Three-month endothelial human endothelin-1
overexpression causes blood pressure elevation and vascular and
kidney injury. Hypertension. 71:208–216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lai TS, Lindberg RA, Zhou HL, Haroon ZA,
Dewhirst MW, Hausladen A, Juang YL, Stamler JS and Greenberg CS:
Endothelial cell-surface tissue transglutaminase inhibits
neutrophil adhesion by binding and releasing nitric oxide. Sci Rep.
7:161632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pang LP, Li Y, Zou QY, Zhou C, Lei W,
Zheng J and Huang SA: ITE inhibits growth of human pulmonary artery
endothelial cells. Exp Lung Res. 43:283–292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang X, He XQ, Li GD and Xu YQ:
AntagomiR-451 inhibits oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced
HUVEC necrosis via activating AMPK signaling. PLoS One.
12:e01755072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Howe GA, Kazda K and Addison CL:
MicroRNA-30b controls endothelial cell capillary morphogenesis
through regulation of transforming growth factor beta 2. PLoS One.
12:e01856192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Z, Wang M, He Q, Li Z, Zhao Y, Wang
W, Ma J, Li Y and Chang G: MicroRNA-98 rescues proliferation and
alleviates ox-LDL-induced apoptosis in HUVECs by targeting LOX-1.
Exp Ther Med. 13:1702–1710. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun JY, Zhao ZW, Li WM, Yang G, Jing PY,
Li P, Dang HZ, Chen Z, Zhou YA and Li XF: Knockdown of MALAT1
expression inhibits HUVEC proliferation by upregulation of miR-320a
and downregulation of FOXM1 expression. Oncotarget. 8:61499–61509.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin SY, Hsieh SY, Fan YT, Wei WC, Hsiao
PW, Tsai DH, Wu TS and Yang NS: Necroptosis promotes
autophagy-dependent upregulation of DAMP and results in
immunosurveillance. Autophagy. 14:778–795. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan Y, Li X and Li M: Overexpression of
miR-17-5p protects against high glucose-induced endothelial cell
injury by targeting E2F1-mediated suppression of autophagy and
promotion of apoptosis. Int J Mol Med. May 21–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chao CH, Chen HR, Chuang YC and Yeh TM:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor-induced autophagy
contributes to thrombin-triggered endothelial hyperpermeability in
sepsis. Shock. 50:103–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Sun J, Yu X, Shi L, Du W, Hu L,
Liu C and Cao Y: SIRT1 regulates accumulation of oxidized LDL in
HUVEC via the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. Prostaglandins Other
Lipid Mediat. 122:37–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fan H, Ma X, Lin P, Kang Q, Zhao Z, Wang
L, Sun D, Cheng J and Li Y: Scutellarin prevents nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease (NAFLD) and hyperlipidemia via PI3K/AKT-dependent
activation of nuclear factor (Erythroid-Derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) in
rats. Med Sci Monit. 23:5599–5612. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu LT, Liang L, Wang W, Yan CQ, Zhang J,
Xiao YC, Ye L, Zhao MX, Huang QS, Bian JJ, et al:
Isolariciresinol-9′-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside protects against
hydrogen peroxideinduced apoptosis of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells via a PI3K/Akt/Bad-dependent pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 17:488–494. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xing Y, Lai J, Liu X, Zhang N, Ming J, Liu
H and Zhang X: Netrin-1 restores cell injury and impaired
angiogenesis in vascular endothelial cells upon high glucose by
PI3K/AKT-eNOS. J Mol Endocrinol. 58:167–177. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chu P, Han G, Ahsan A, Sun Z, Liu S, Zhang
Z, Sun B, Song Y, Lin Y, Peng J and Tang Z: Phosphocreatine
protects endothelial cells from methylglyoxal induced oxidative
stress and apoptosis via the regulation of PI3K/Akt/eNOS and NF-κB
pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 91:26–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|