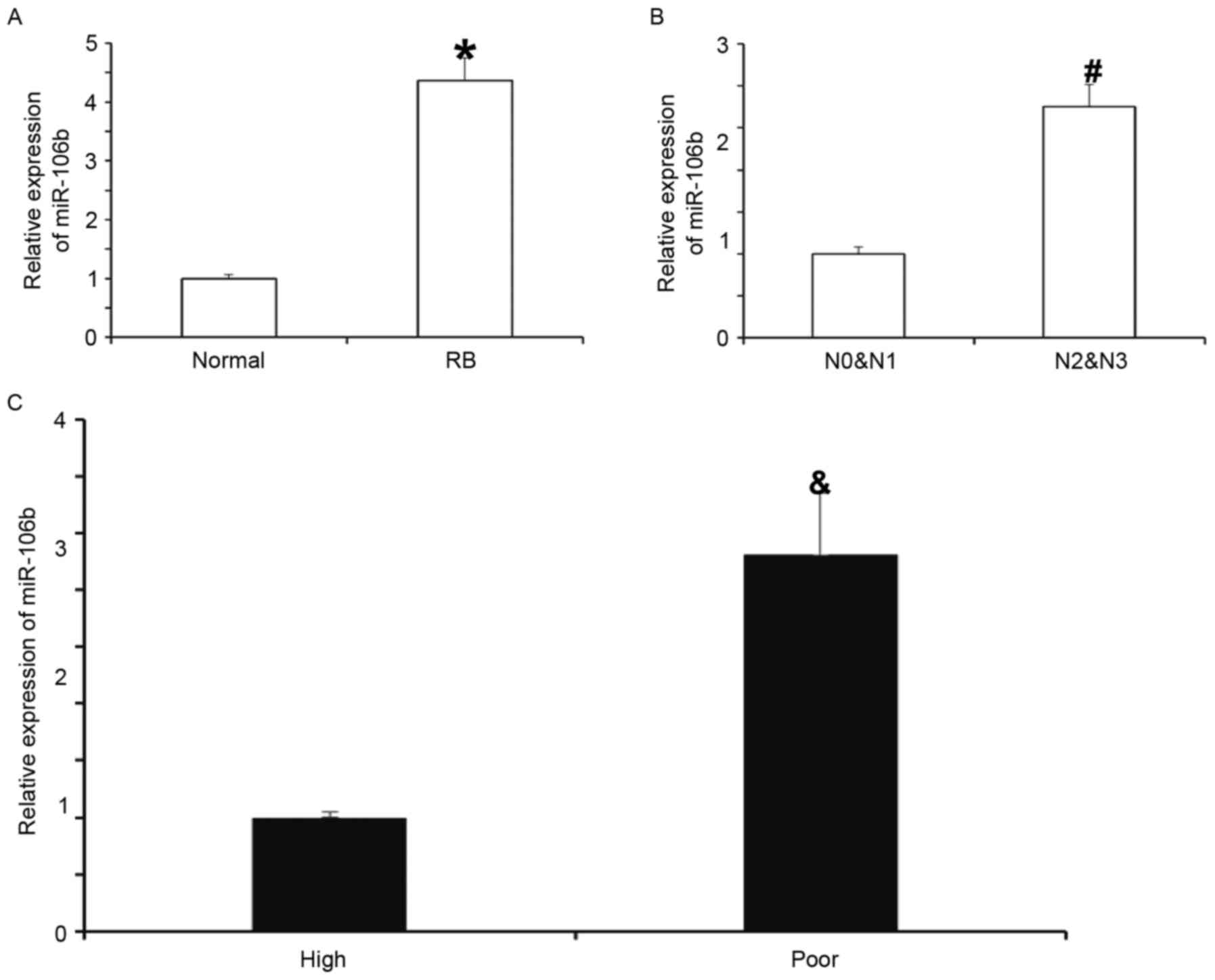
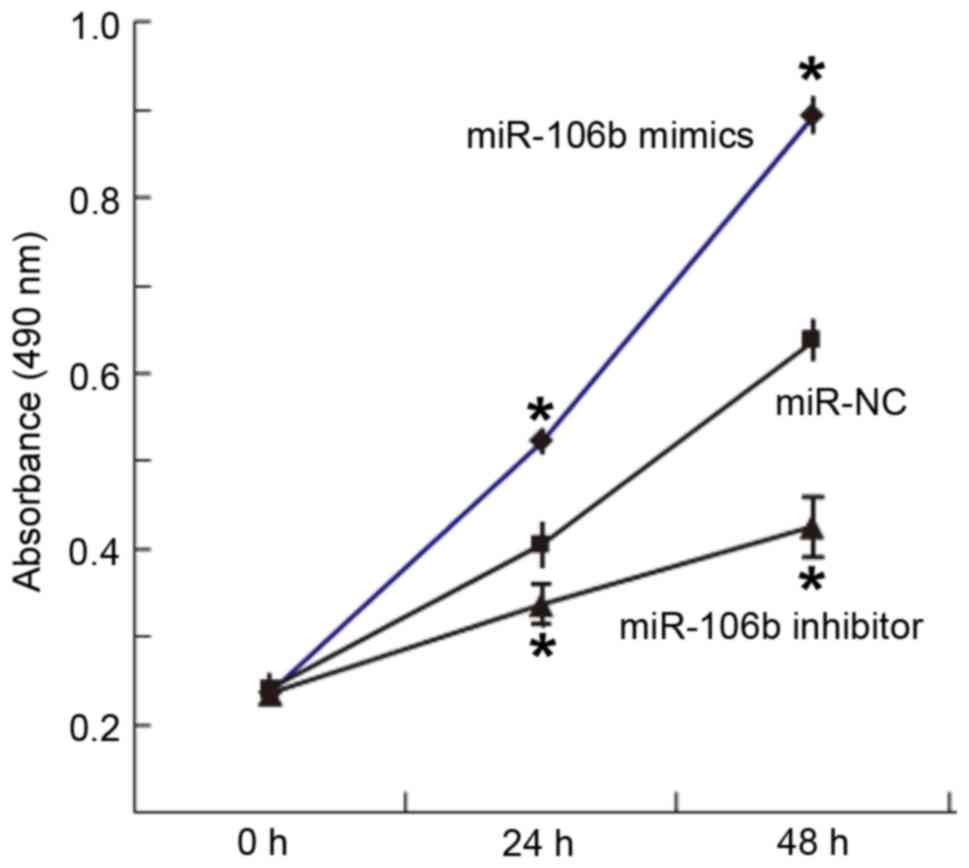
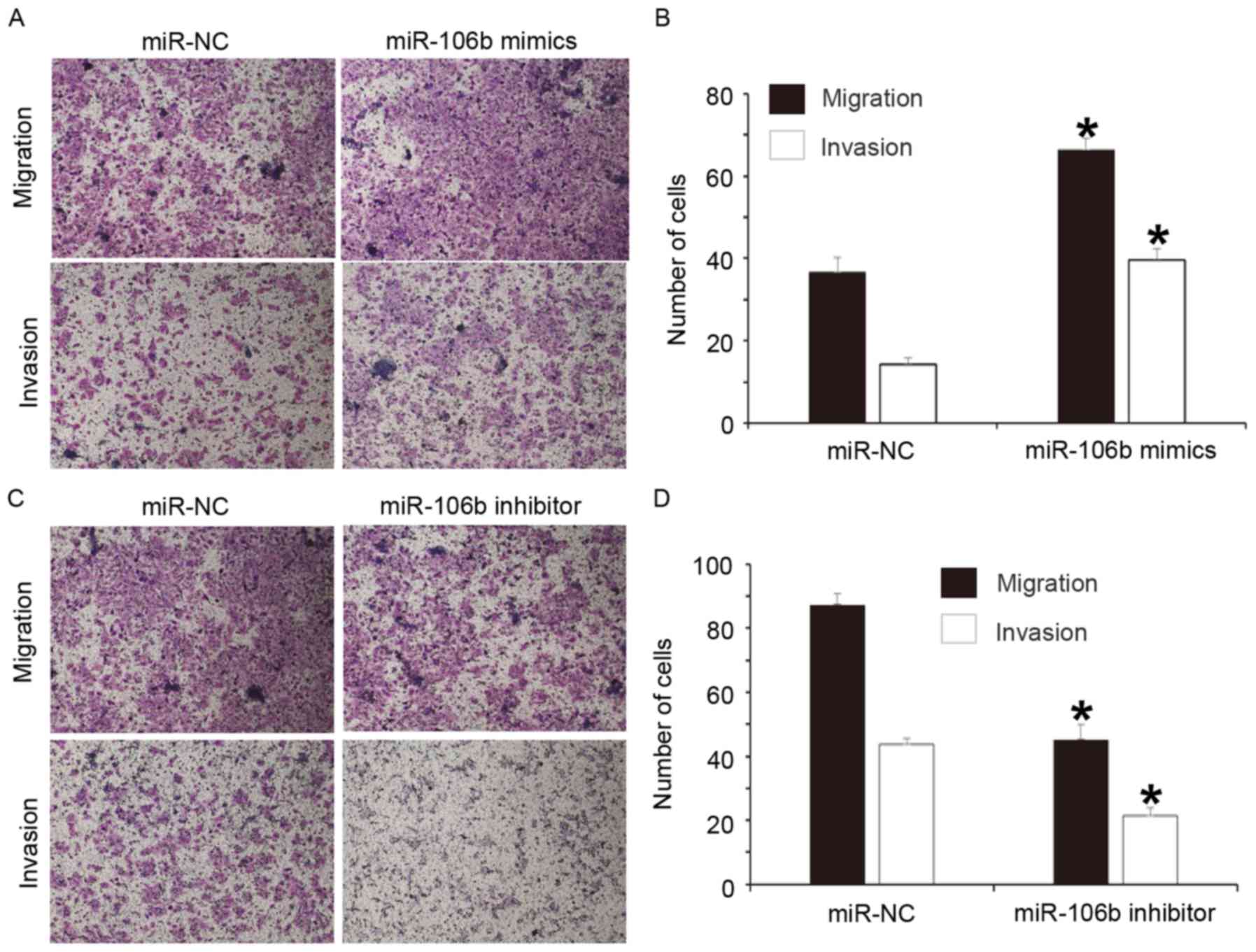
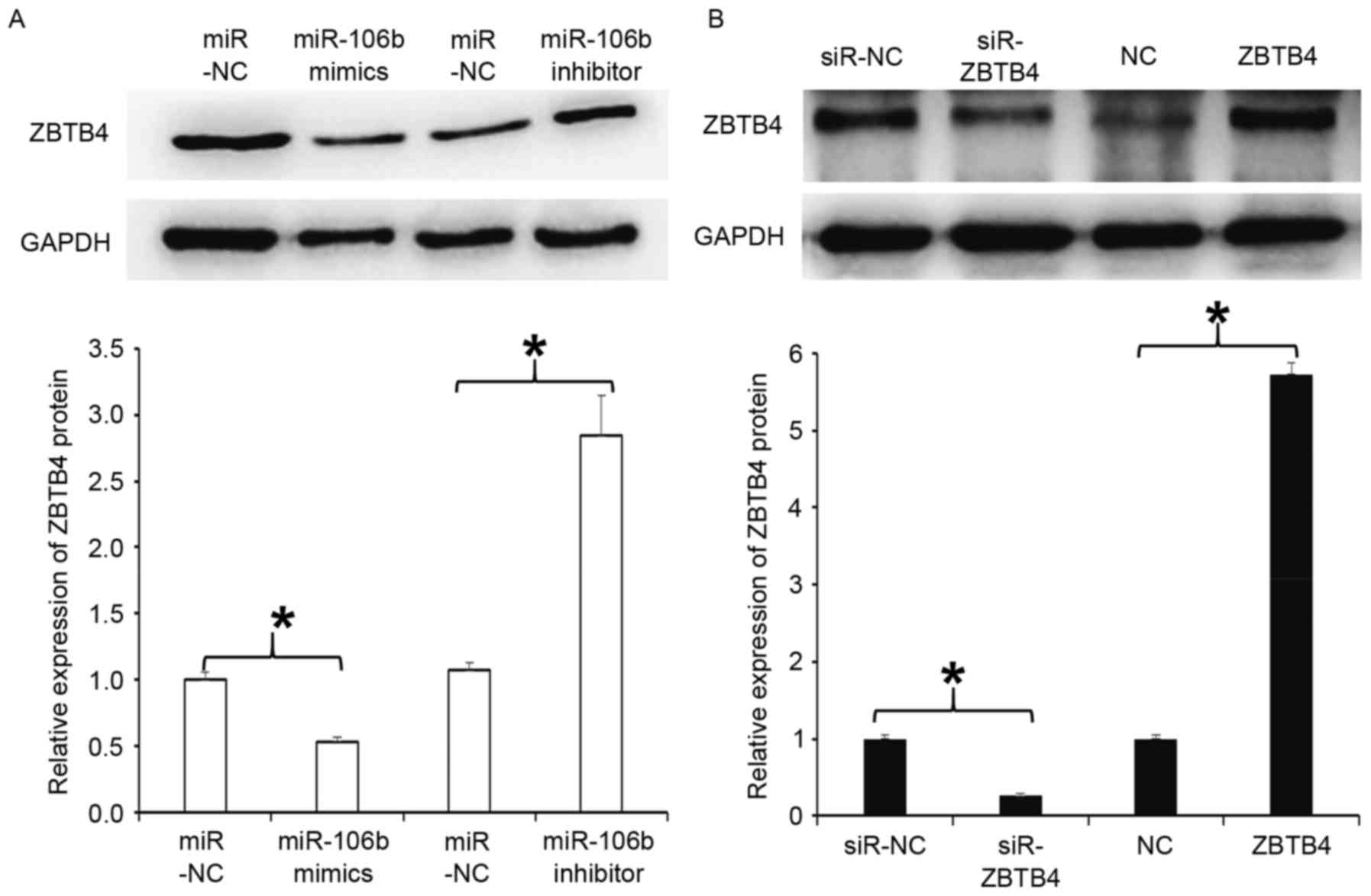
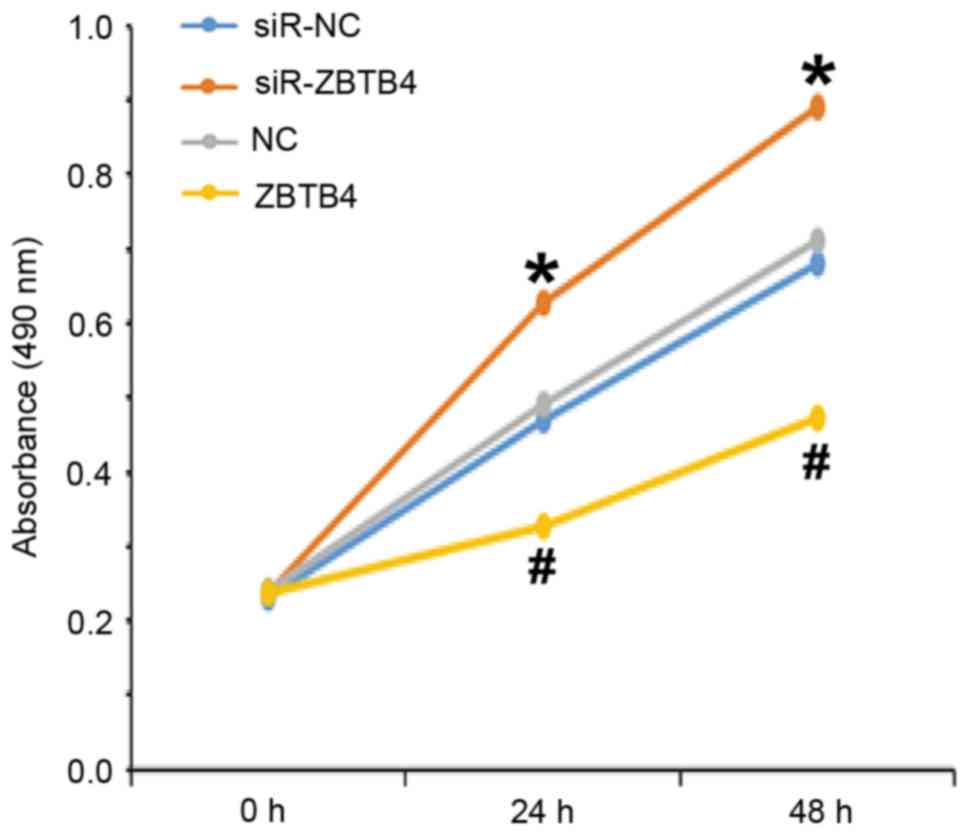
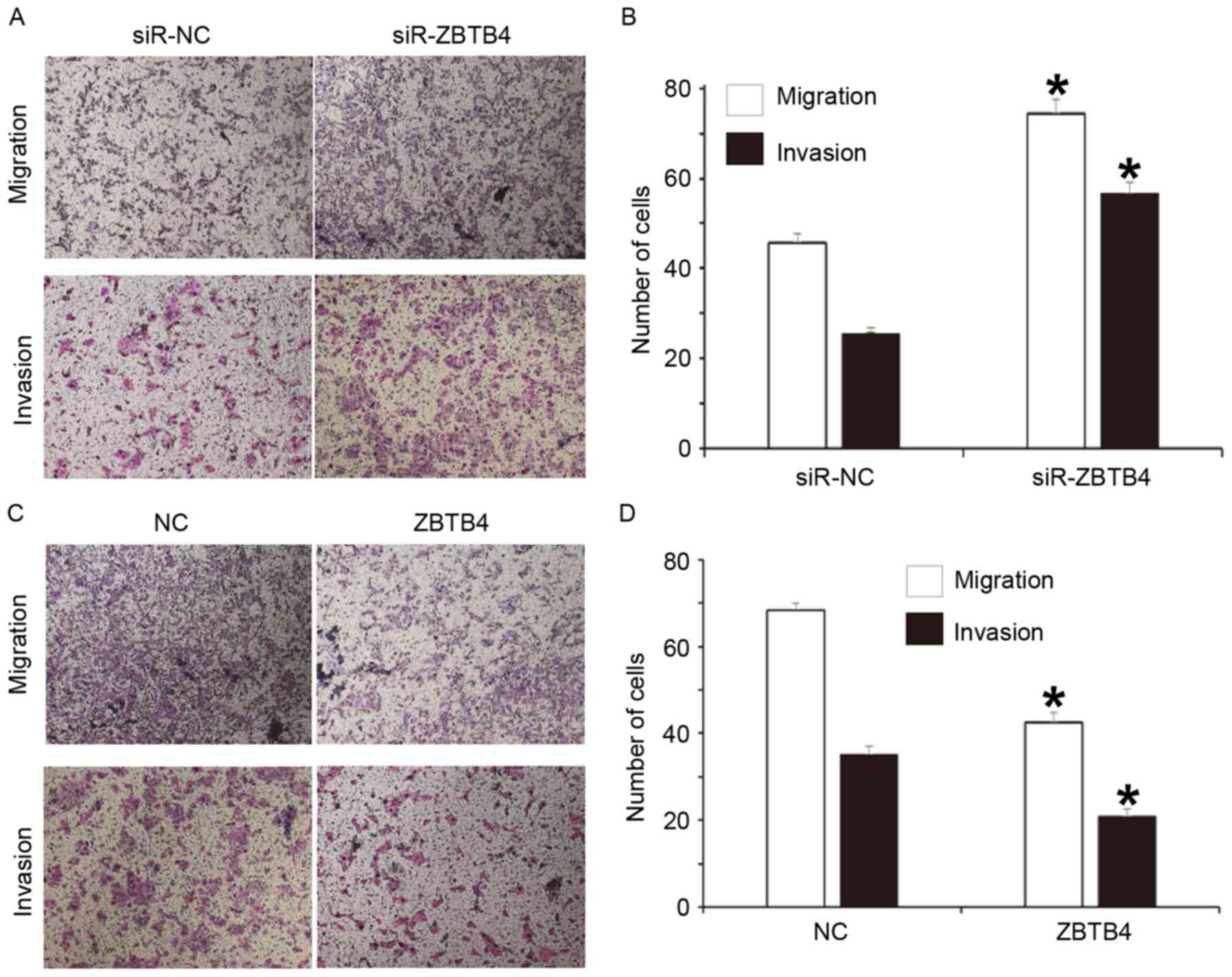
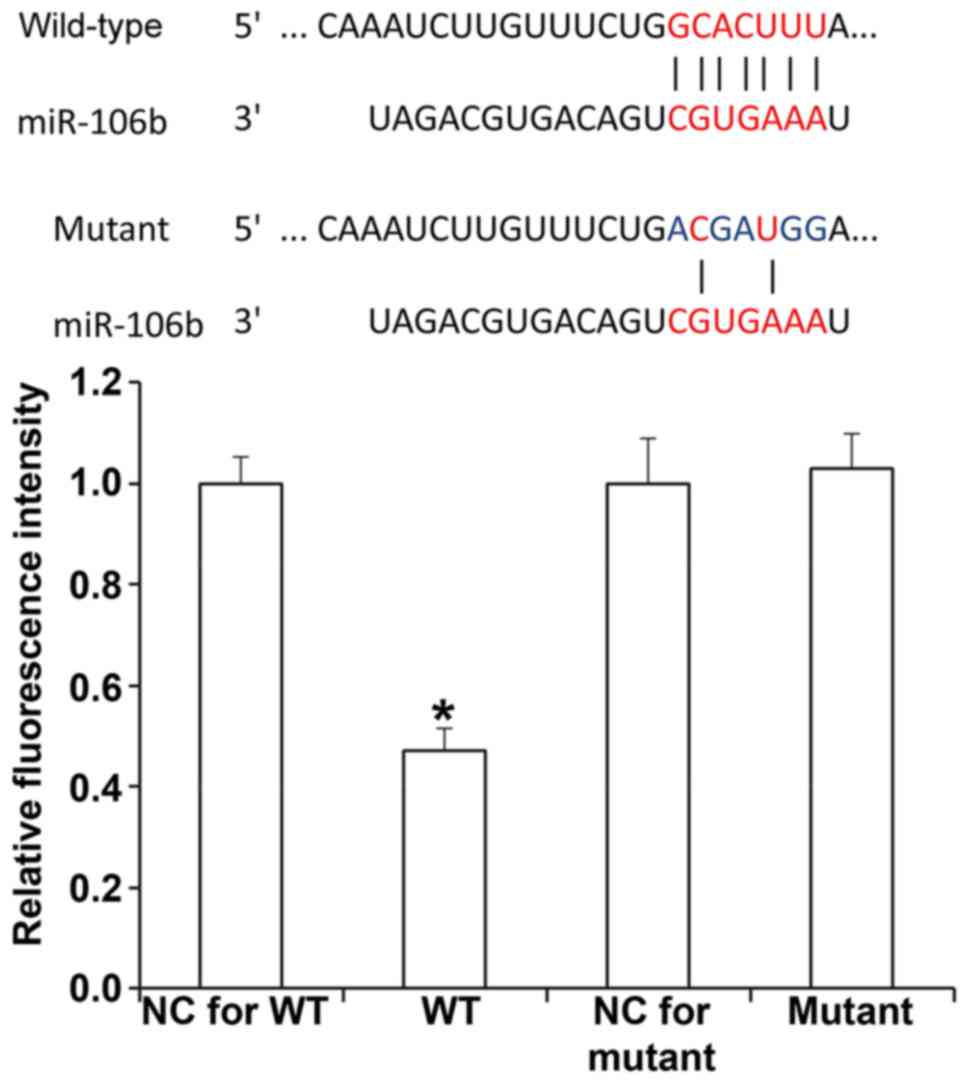
|
1
|
Soliman SE, Dimaras H, Khetan V, Gardiner
JA, Chan HS, Héon E and Gallie BL: Prenatal versus postnatal
screening for familial retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology.
123:2610–2617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Natalino RJ, Antoneli CB, Ribeiro KC,
Campos AH and Soares FA: Immunohistochemistry of apoptosis-related
proteins in retinoblastoma. Pathol Res Pract. 212:1144–1150. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta AK, Jones M, Prelog K, Bui J, Zhu J,
Ng A and Dalla-Pozza L: Pineal cysts-A benign association with
familial retinoblastoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 33:408–414. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tian T, Ji XD, Zhang Q, Peng J and Zhao
PQ: A delayed diagnosis of unsuspected retinoblastoma in an in
vitro fertilisation infant with retinopathy of prematurity. Int J
Ophthalmol. 9:1361–1363. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Silva BB, Sapienza L, Castro DG, Ferreira
DDV, Leão CR, Neves DFGDS, Silva B, Aiza A, Scintini AC, Pellizzon
C and Regalin M: eye plaque brachytherapy for retinoblastoma-A
uni-institutional retrospective analysis of 40 eyes in 38 patients
treated from 2001 to 2014. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
96:E5542016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Assayag F, Nicolas A, Vacher S, Dehainault
C, Bieche I, Meseure D, Aerts I, Cassoux N, Houdayer C, Doz F and
Decaudin D: Combination of carboplatin and bevacizumab is an
efficient therapeutic approach in retinoblastoma patient-derived
xenografts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:4916–4926. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shehata HH, Ghalia Abou AH, Elsayed EK,
Said Ahmed AM and Mahmoud SS: Clinical significance of high levels
of survivin and transforming growth factor beta-1 proteins in
aqueous humor and serum of retinoblastoma patients. J AAPOS.
20:444.e441–444.e449. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Singh U, Malik MA, Goswami S, Shukla S and
Kaur J: Epigenetic regulation of human retinoblastoma. Tumour Biol.
37:14427–14441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malorni L, Piazza S, Ciani Y, Guarducci C,
Bonechi M, Biagioni C, Hart CD, Verardo R, Di Leo A and Migliaccio
I: A gene expression signature of Retinoblastoma loss-of-function
is a predictive biomarker of resistance to palbociclib in breast
cancer cell lines and is prognostic in patients with ER positive
early breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:68012–68022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin D and Lee H: Prioritizing
cancer-related microRNAs by integrating microRNA and mRNA datasets.
Sci Rep. 6:353502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lima TI, Araujo HN, Menezes ES, Sponton
CH, Araújo MB, Bomfim LH, Queiroz AL, Passos MA, Sousa E TA,
Hirabara SM, et al: Role of microRNAs on the regulation of
mitochondrial biogenesis and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle.
J Cell Physiol. 232:958–966. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Carvalho IN, de Freitas RM and Vargas
FR: Translating microRNAs into biomarkers: What is new for
pediatric cancer? Med Oncol. 33:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gui F, Hong Z, You Z, Wu H and Zhang Y:
MiR-21 inhibitor suppressed the progression of retinoblastoma via
the modulation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Biol Int.
40:1294–1302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bai S, Tian B, Li A, Yao Q, Zhang G and Li
F: MicroRNA-125b promotes tumor growth and suppresses apoptosis by
targeting DRAM2 in retinoblastoma. Eye (Lond). 30:1630–1638. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Xue C, Zhu X, Zhu X, Xian H and
Huang Z: Suppression of microRNA-125a-5p upregulates the TAZ-EGFR
signaling pathway and promotes retinoblastoma proliferation. Cell
Signal. 28:850–860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng Q, Jin C, Chen W, Xia F, Wang Q, Fan
F, Du J, Guo Y, Lin C, Yang K, et al: Downregulation of serum
miR-17 and miR-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric
diseases. Chin J Cancer Res. 26:711–716. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu X, Liu Z, Wang J, Ling Q, Xie H, Guo H,
Wei X, Zhou L and Zheng S: miRNA profiles in livers with different
mass deficits after partial hepatectomy and miR-106b~25 cluster
accelerating hepatocyte proliferation in rats. Sci Rep.
6:312672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu D, Shin HS, Lee YS and Lee YC: miR-106b
modulates cancer stem cell characteristics through TGF-β/Smad
signaling in CD44-positive gastric cancer cells. Lab Invest.
94:1370–1381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai F, Liu T, Zheng S, Liu Q, Yang C, Zhou
J, Chen Y, Sheyhidin I and Lu X: MiR-106b promotes migration and
invasion through enhancing EMT via downregulation of Smad 7 in
Kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:14595–14604. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li N, Liu Y, Miao Y, Zhao L, Zhou H and
Jia L: MicroRNA-106b targets FUT6 to promote cell migration,
invasion, and proliferation in human breast cancer. IUBMB Life.
68:764–775. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ishaq SM, Kehar SI, Zafar S and Hasan SF:
Correlation of CD24 expression with histological grading and TNM
staging of retinoblastoma. Pak J Med Sci. 32:160–164.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang R, Wang W, Li F, Zhang H and Liu J:
MicroRNA-106b~25 expressions in tumor tissues and plasma of
patients with gastric cancers. Med Oncol. 31:2432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Verboon LJ, Obulkasim A, de Rooij JD,
Katsman-Kuipers JE, Sonneveld E, Baruchel A, Trka J, Reinhardt D,
Pieters R, Cloos J, et al: MicroRNA-106b~25 cluster is upregulated
in relapsed MLL-rearranged pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncotarget. 7:48412–48422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng L, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhou M, Lu Y,
Yuan L, Zhang C, Hong M, Wang S and Li X: MiR-106b induces cell
radioresistance via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathways and p21 in
colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 13:2522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim K, Chadalapaka G, Pathi SS, Jin UH,
Lee JS, Park YY, Cho SG, Chintharlapalli S and Safe S: Induction of
the transcriptional repressor ZBTB4 in prostate cancer cells by
drug-induced targeting of microRNA-17-92/106b-25 clusters. Mol
Cancer Ther. 11:1852–1862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang WS, Chadalapaka G, Cho SG, Lee SO,
Jin UH, Jutooru I, Choi K, Leung YK, Ho SM, Safe S and Kim K: The
transcriptional repressor ZBTB4 regulates EZH2 through a
MicroRNA-ZBTB4-specificity protein signaling axis. Neoplasia.
16:1059–1069. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim K, Chadalapaka G, Lee SO, Yamada D,
Sastre-Garau X, Defossez PA, Park YY, Lee JS and Safe S:
Identification of oncogenic microRNA-17-92/ZBTB4/specificity
protein axis in breast cancer. Oncogene. 31:1034–1044. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamada D, Pérez-Torrado R, Filion G, Caly
M, Jammart B, Devignot V, Sasai N, Ravassard P, Mallet J,
Sastre-Garau X, et al: The human protein kinase HIPK2
phosphorylates and downregulates the methyl-binding transcription
factor ZBTB4. Oncogene. 28:2535–2544. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guarnieri AL, Towers CG, Drasin DJ,
Oliphant MUJ, Andrysik Z, Hotz TJ, Vartuli RL, Linklater ES, Pandey
A, Khanal S, et al: The miR-106b-25 cluster mediates breast tumor
initiation through activation of NOTCH1 via direct repression of
NEDD4L. Oncogene. Apr 17–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gruszka R and Zakrzewska M: The oncogenic
relevance of miR-17-92 cluster and its paralogous miR-106b-25 and
miR-106a-363 clusters in brain tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 19:pii:
E8792018. View Article : Google Scholar
|