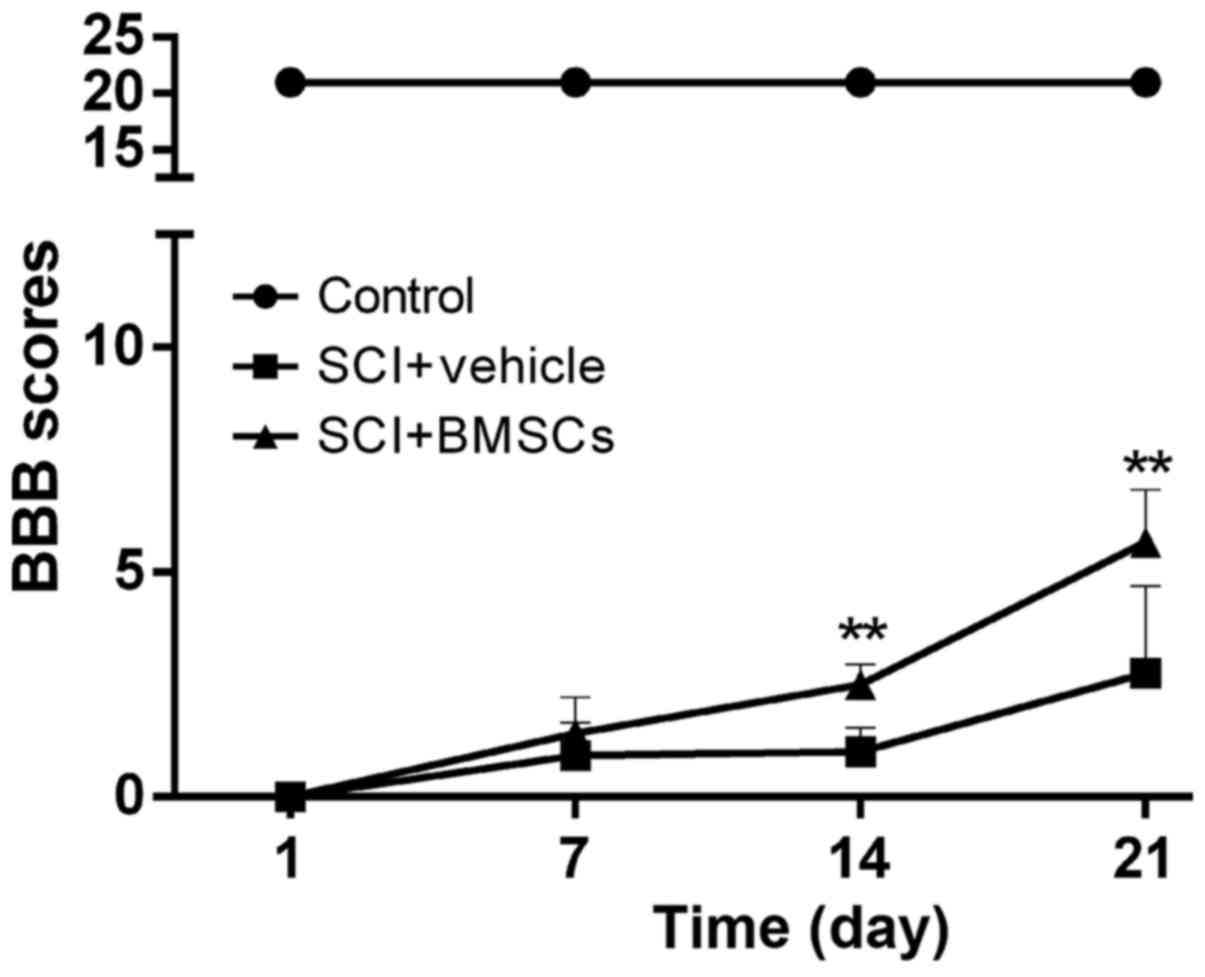
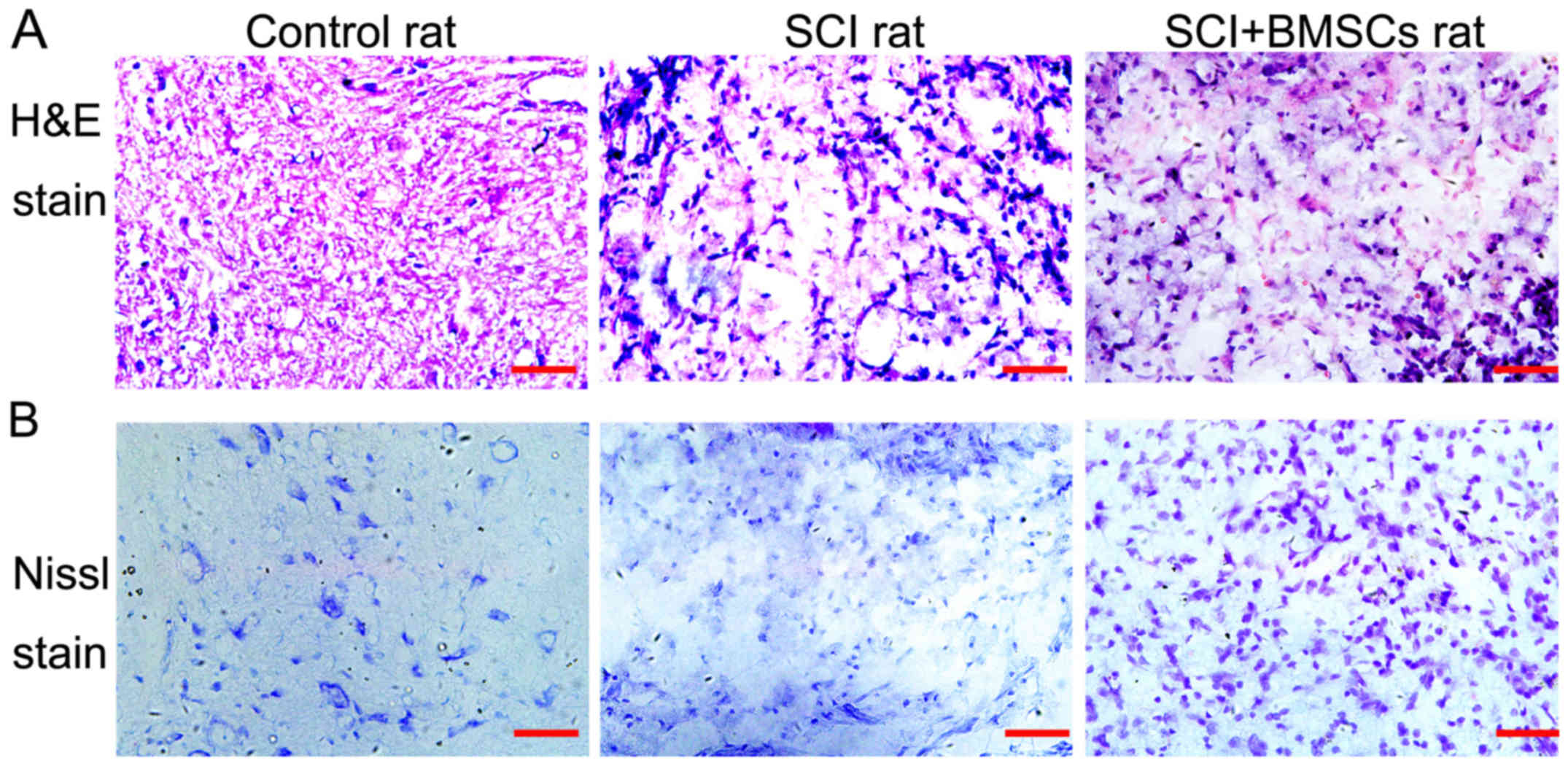
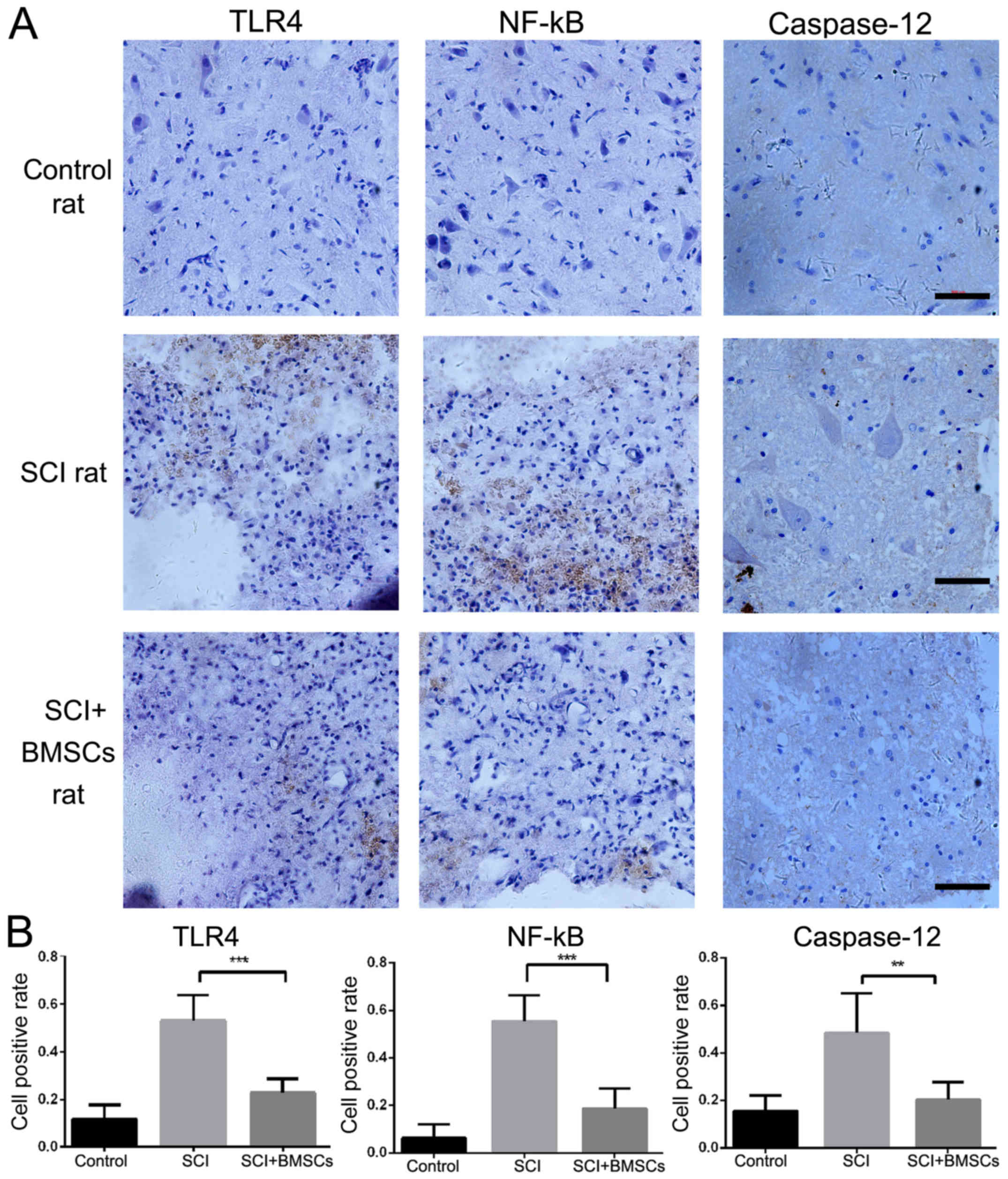
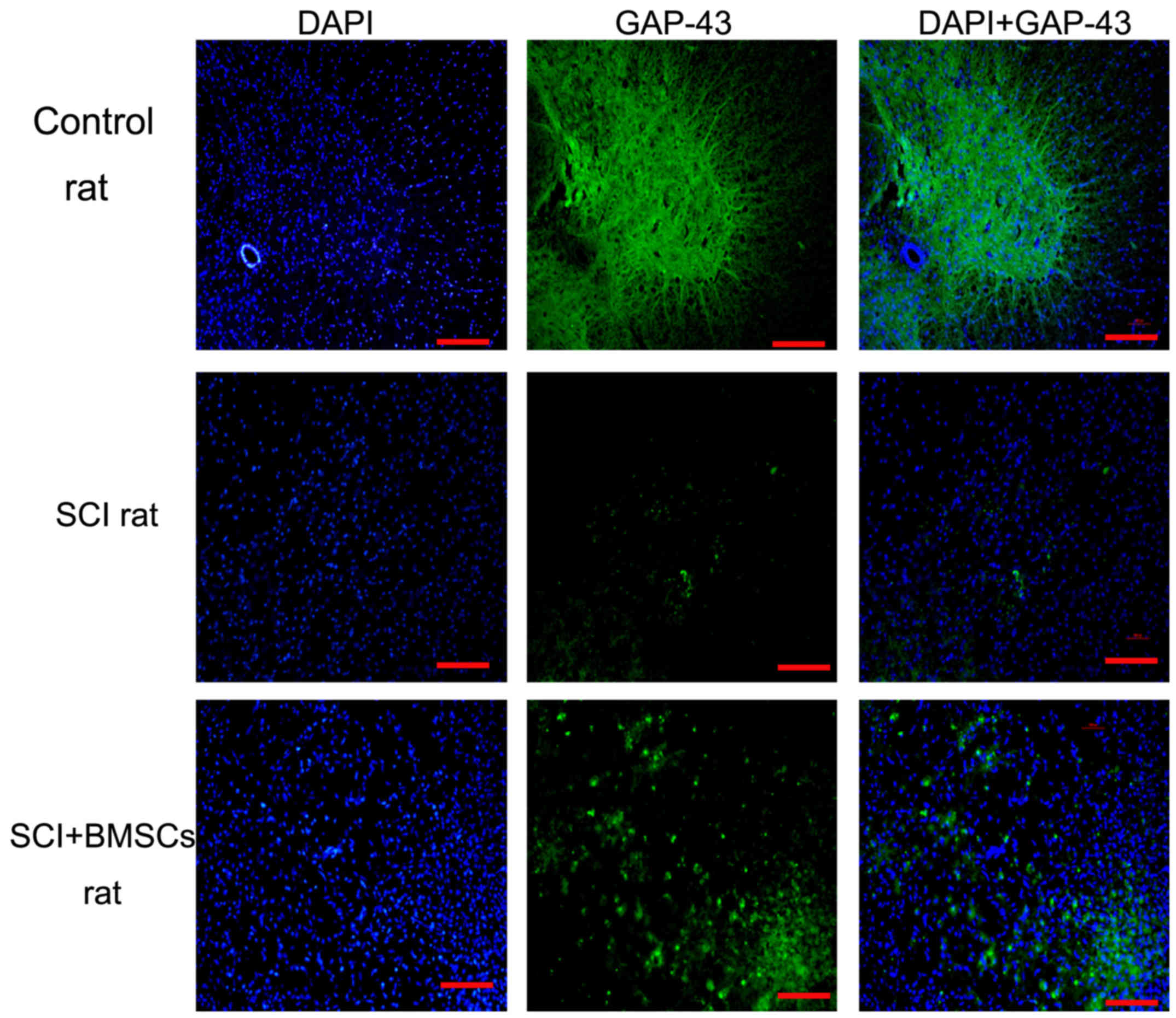
|
1
|
Rubiano AM, Carney N, Chesnut R and Puyana
JC: Global neurotrauma research challenges and opportunities.
Nature. 527:S193–S197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allison DJ and Ditor DS: Immune
dysfunction and chronic inflammation following spinal cord injury.
Spinal Cord. 53:14–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Orr MB, Simkin J, Bailey WM, Kadambi NS,
McVicar AL, Veldhorst AK and Gensel JC: Compression Decreases
Anatomical and Functional Recovery and Alters Inflammation after
Contusive Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 34:2342–2352. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Okada S: The pathophysiological role of
acute inflammation after spinal cord injury. Inflamm Regen.
36:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin L, Lin H, Bai S, Zheng L and Zhang X:
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) improved functional
recovery of spinal cord injury partly by promoting axonal
regeneration. Neurochem Int. 115:80–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pu Y, Meng K, Gu C, Wang L and Zhang X:
Thrombospondin-1 modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
(BMSCs) promote neurite outgrowth and functional recovery in rats
with spinal cord injury. Oncotarget. 8:96276–96289. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gu C, Li H, Wang C, Song X, Ding Y, Zheng
M, Liu W, Chen Y, Zhang X and Wang L: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells decrease CHOP expression and neuronal apoptosis after spinal
cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 636:282–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang X, Chen F, Lin Q, You Y, Ke J and
Zhao S: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repair the hippocampal
neurons and increase the expression of IGF-1 after cardiac arrest
in rats. Exp Ther Med. 14:4312–4320. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Chen J, Chai W, Ni M, Sun X and
Tian D: Glycitin regulates osteoblasts through TGF-β or AKT
signaling pathways in bone marrow stem cells. Exp Ther Med.
12:3063–3067. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng YH, Deng YY, Lai W, Zheng SY, Bian
HN, Liu ZA, Huang ZF, Sun CW, Li HH, Luo HM, et al: Effect of bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the polarization of macrophages.
Mol Med Rep. 17:4449–4459. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ock SA, Baregundi Subbarao R, Lee YM, Lee
JH, Jeon RH, Lee SL, Park JK, Hwang SC and Rho GJ: Comparison of
Immunomodulation Properties of Porcine Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem
Cells Derived from the Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue, and Dermal Skin
Tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2016:95813502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ide C, Nakai Y, Nakano N, Seo TB, Yamada
Y, Endo K, Noda T, Saito F, Suzuki Y, Fukushima M, et al: Bone
marrow stromal cell transplantation for treatment of sub-acute
spinal cord injury in the rat. Brain Res. 1332:32–47. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hawryluk GW, Mothe A, Wang J, Wang S,
Tator C and Fehlings MG: An in vivo characterization of trophic
factor production following neural precursor cell or bone marrow
stromal cell transplantation for spinal cord injury. Stem Cells
Dev. 21:2222–2238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang W, Yang Y, Yang JY, Liang M and Song
J: Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with
plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative
stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the Nrf2
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:1075–1082. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho SR, Kim YR, Kang HS, Yim SH, Park CI,
Min YH, Lee BH, Shin JC and Lim JB: Functional Recovery after the
Transplantation of Neurally Differentiated Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Derived from Bone Marrow in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell
Transplant. 25:14232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lester SN and Li K: Toll-like receptors in
antiviral innate immunity. J Mol Biol. 426:1246–1264. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kigerl KA and Popovich PG: Toll-like
receptors in spinal cord injury. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
336:121–136. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heiman A, Pallottie A, Heary RF and
Elkabes S: Toll-like receptors in central nervous system injury and
disease: A focus on the spinal cord. Brain Behav Immun. 42:232–245.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ntoufa S, Vilia MG, Stamatopoulos K, Ghia
P and Muzio M: Toll-like receptors signaling: A complex network for
NF-κB activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Semin Cancer
Biol. 39:15–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Wang Y and Ouyang X: Beyond
toll-like receptors: Porphyromonas gingivalis induces IL-6, IL-8,
and VCAM-1 expression through NOD-mediated NF-κB and ERK signaling
pathways in periodontal fibroblasts. Inflammation. 37:522–533.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou R, Alvarado L, Ogilvie R, Chong SL,
Shaw O and Mushahwar VK: Non-gait-specific intervention for the
rehabilitation of walking after SCI: Role of the arms. J
Neurophysiol. 119:2194–2211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kong X and Gao J: Macrophage polarization:
A key event in the secondary phase of acute spinal cord injury. J
Cell Mol Med. 21:941–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou Z, Liu C, Chen S, Zhao H, Zhou K,
Wang W, Yuan Y, Li Z, Guo Y, Shen Z, et al: Activation of the
Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway by probucol contributes to inhibiting
inflammation and neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury.
Oncotarget. 8:52078–52093. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu Q, Li C and Yu L: Gambogic acid
inhibits spinal cord injury and inflammation through suppressing
the p38 and Akt signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 17:2026–2032.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yuan B, Liu D and Liu X: Spinal cord
stimulation exerts analgesia effects in chronic constriction injury
rats via suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Neurosci Lett.
581:63–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He Z, Zhou Y, Lin L, Wang Q, Khor S, Mao
Y, Li J, Zhen Z, Chen J, Gao Z, et al: Dl-3-n-butylphthalide
attenuates acute inflammatory activation in rats with spinal cord
injury by inhibiting microglial TLR4/NF-κB signalling. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:3010–3022. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Chen X, Huang X, Qin C, Fang Y,
Liu Y, Zhang G, Pan D, Wang W and Xie M: Soluble epoxide hydrolase
inhibition provides multi-target therapeutic effects in rats after
spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 53:1565–1578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|