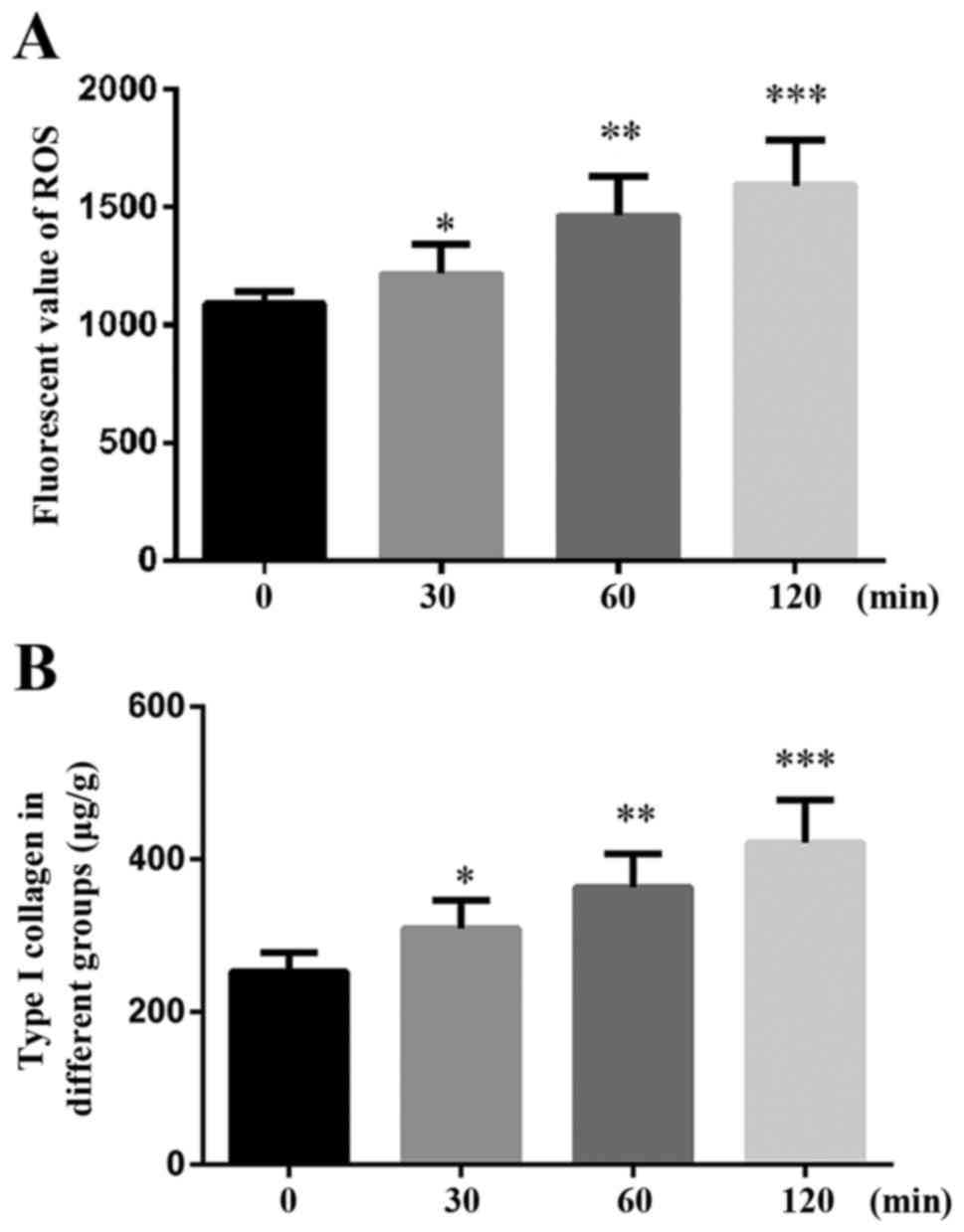
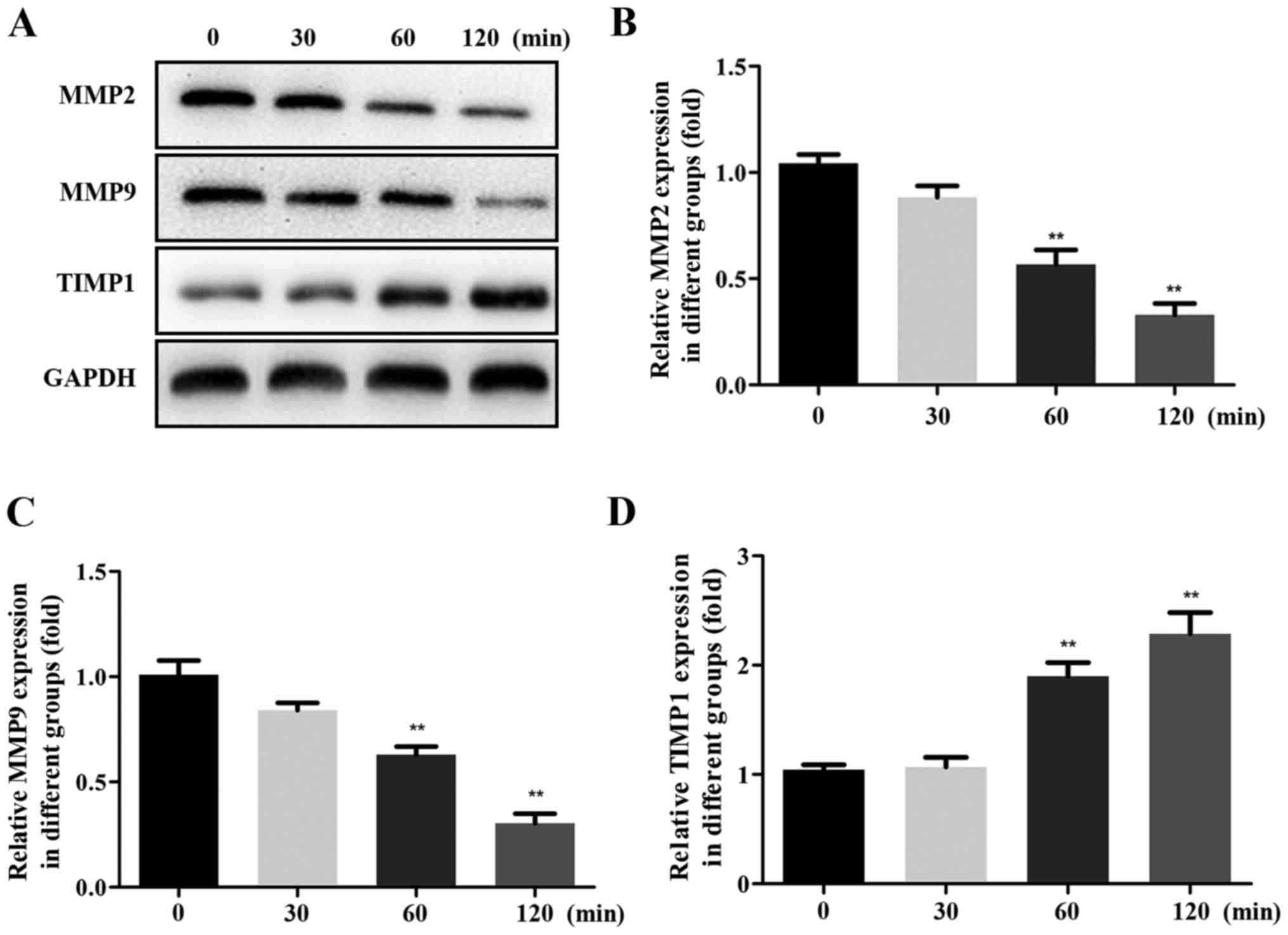
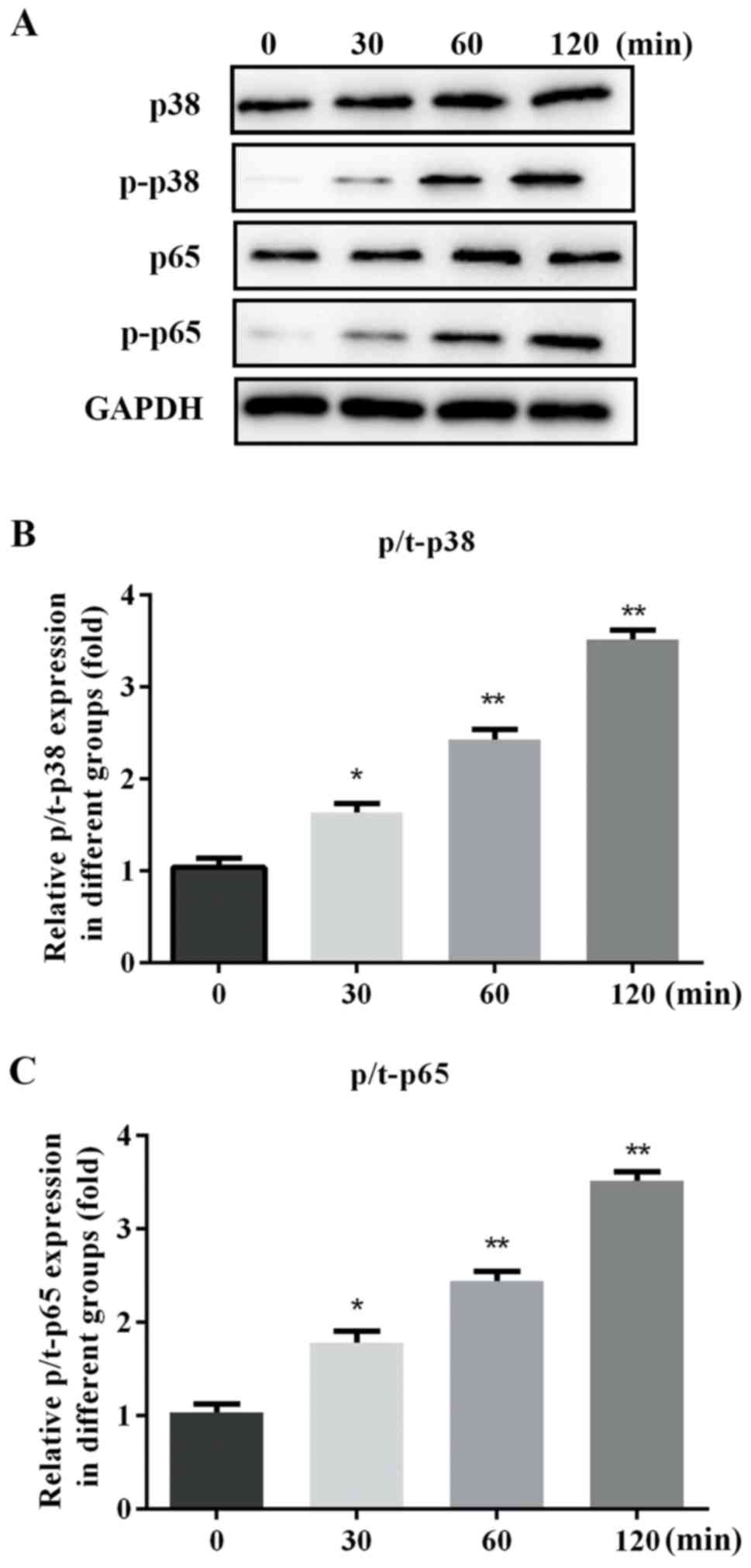
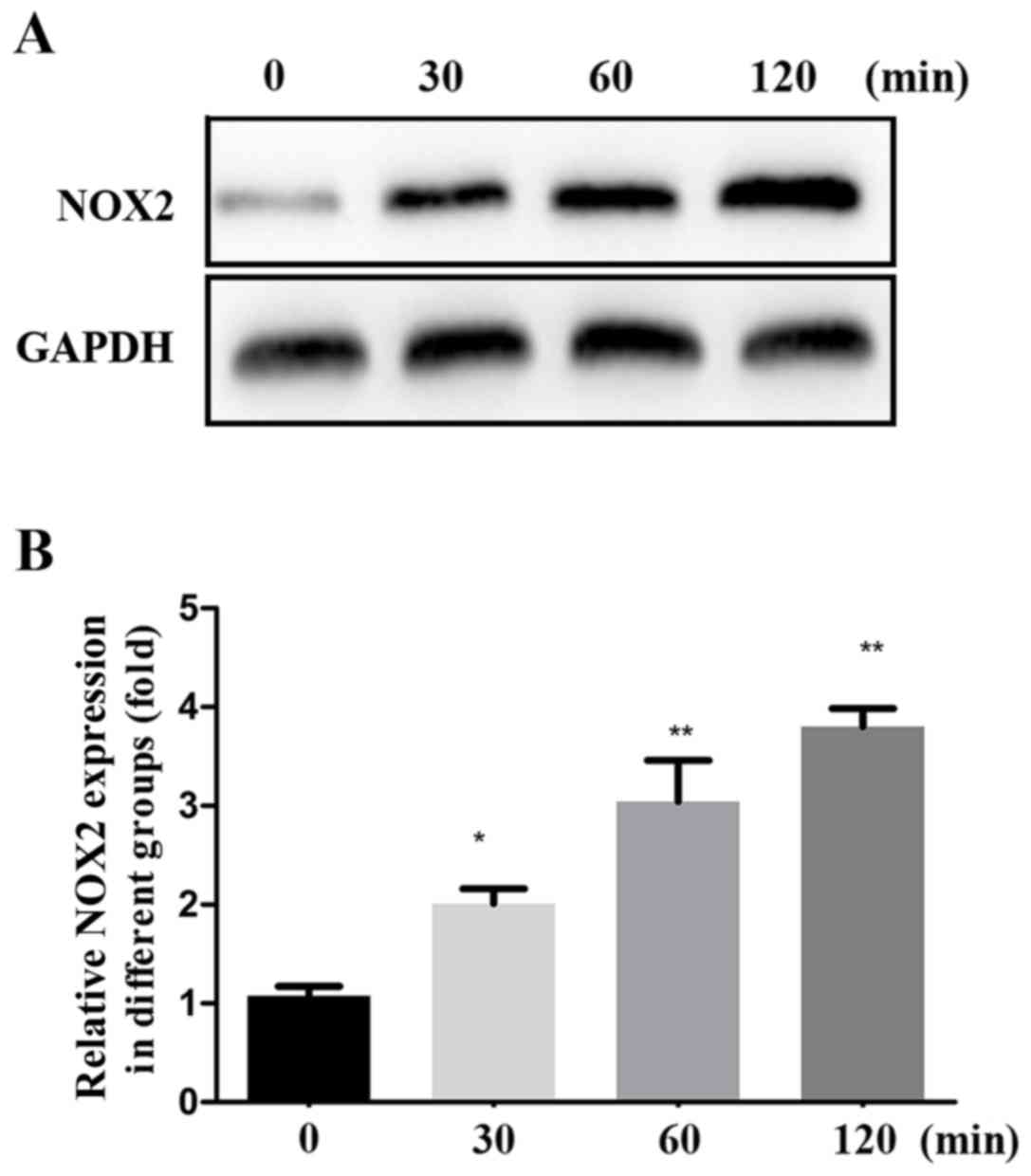
|
1
|
Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S and Piette J:
NF-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species: Fifteen years
later. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1493–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Samukawa T, Hamada T, Uto H, Yanagi M,
Tsukuya G, Nosaki T, Maeda M, Hirano T, Tsubouchi H and Inoue H:
The elevation of serum napsin A in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis,
compared with KL-6, surfactant protein-A and surfactant protein-D.
BMC Pulm Med. 12:552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takahashi H, Fujishima T, Koba H, Murakami
S, Kurokawa K, Shibuya Y, Shiratori M, Kuroki Y and Abe S: Serum
surfactant proteins A and D as prognostic factors in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis and their relationship to disease extent. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 162:1109–1114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mccormack FX: Structure, processing and
properties of surfactant protein A. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1408:109–131. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gardai SJ, Xiao Y, Dickinson M, Nick JA,
Voelker DR, Greene KE and Henson PM: By binding SIRPalpha or
calreticulin/CD91, lung collectins act as dual function
surveillance molecules to suppress or enhance inflammation. Cell.
115:13–23. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Wu G, Tate CG, Lookene A and
Olivecrona G: Calreticulin promotes folding/dimerization of human
lipoprotein lipase expressed in insect cells (Sf21). J Biol Chem.
278:29344–29351. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Liu L, Jin L, Yi X, Dang E, Yang
Y, Li C and Gao T: Oxidative stress-induced calreticulin expression
and translocation: New insights into the destruction of
melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 134:183–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ihara Y, Urata Y, Goto S and Kondo T: Role
of calreticulin in the sensitivity of myocardiac H9c2 cells to
oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 290:C208–C221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ihara Y, Kageyama K and Kondo T:
Overexpression of calreticulin sensitizes SERCA2a to oxidative
stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 329:1343–1349. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian S, Li C, Ran R and Chen SY:
Surfactant protein A deficiency exacerbates renal interstitial
fibrosis following obstructive injury in mice. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1863:509–517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Allen MJ, Voelker DR and Mason RJ:
Interactions of surfactant proteins A and D with Saccharomyces
cerevisiae and Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 69:2037–2044.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boor P, Ostendorf T and Floege J: Renal
fibrosis: Novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 6:643–656. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Farris AB and Colvin RB: Renal
interstitial fibrosis: Mechanisms and evaluation. Curr Opin Nephrol
Hypertens. 21:289–300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lawson J, Elliott J, Wheeler-Jones C, Syme
H and Jepson R: Renal fibrosis in feline chronic kidney disease:
Known mediators and mechanisms of injury. Vet J. 203:18–26. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hemmann S, Graf J, Roderfeld M and Roeb E:
Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis-a systematic review
with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. J Hepatol.
46:955–975. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pei Z, Meng R, Li G, Yan G, Xu C, Zhuang
Z, Ren J and Wu Z: Angiotensin-(1–7) ameliorates myocardial
remodeling and interstitial fibrosis in spontaneous hypertension:
Role of MMPs/TIMPs. Toxicol Lett. 199:173–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Manoury B, Nénan S, Guénon I, Lagente V
and Boichot E: Influence of early neutrophil depletion on
MMPs/TIMP-1 balance in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 7:900–911. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jian KL, Zhang C, Shang ZC, Yang L and
Kong LY: Eucalrobusone C suppresses cell proliferation and induces
ROS-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis via the p38 MAPK pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine. 25:71–82. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|