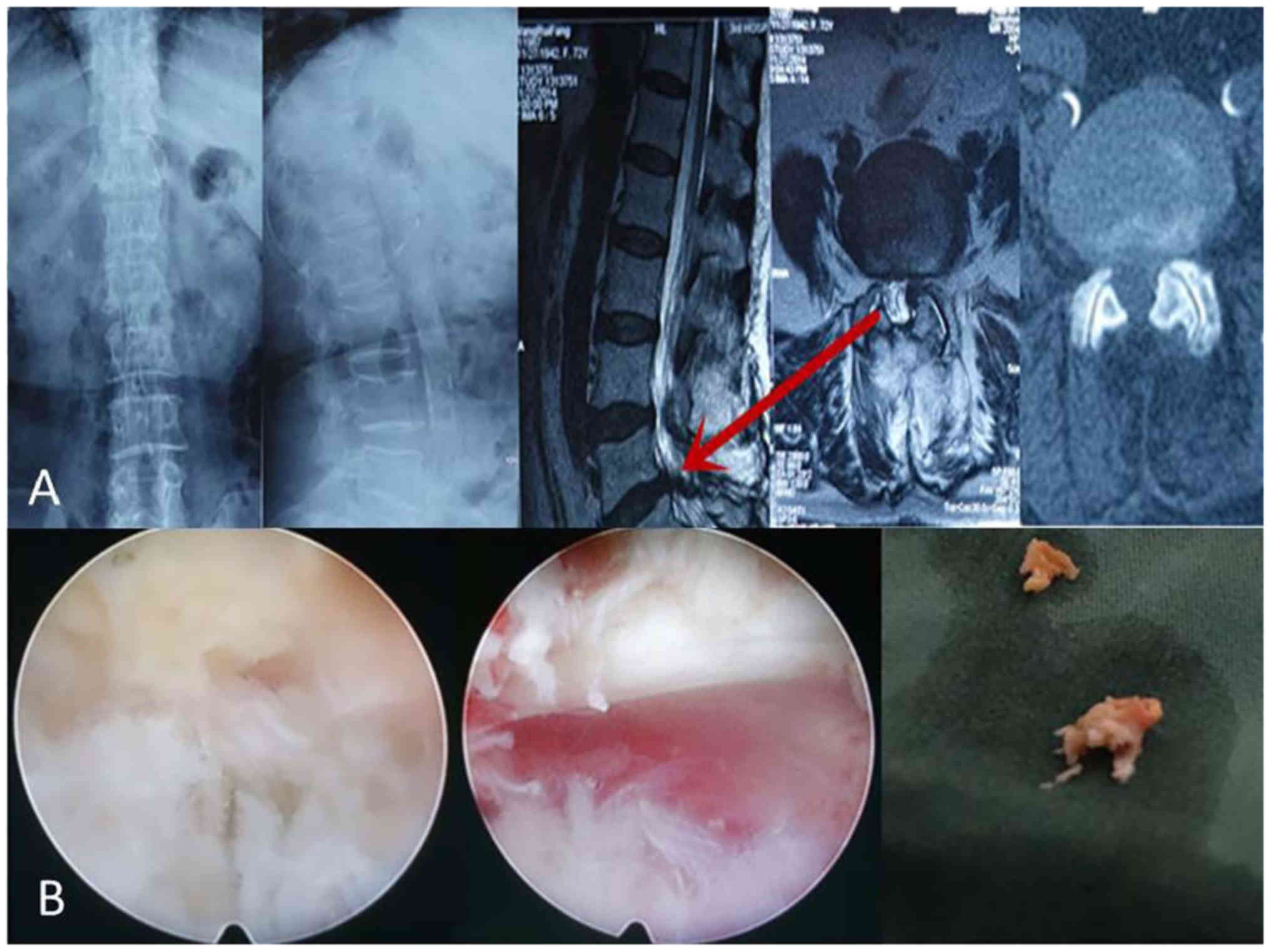
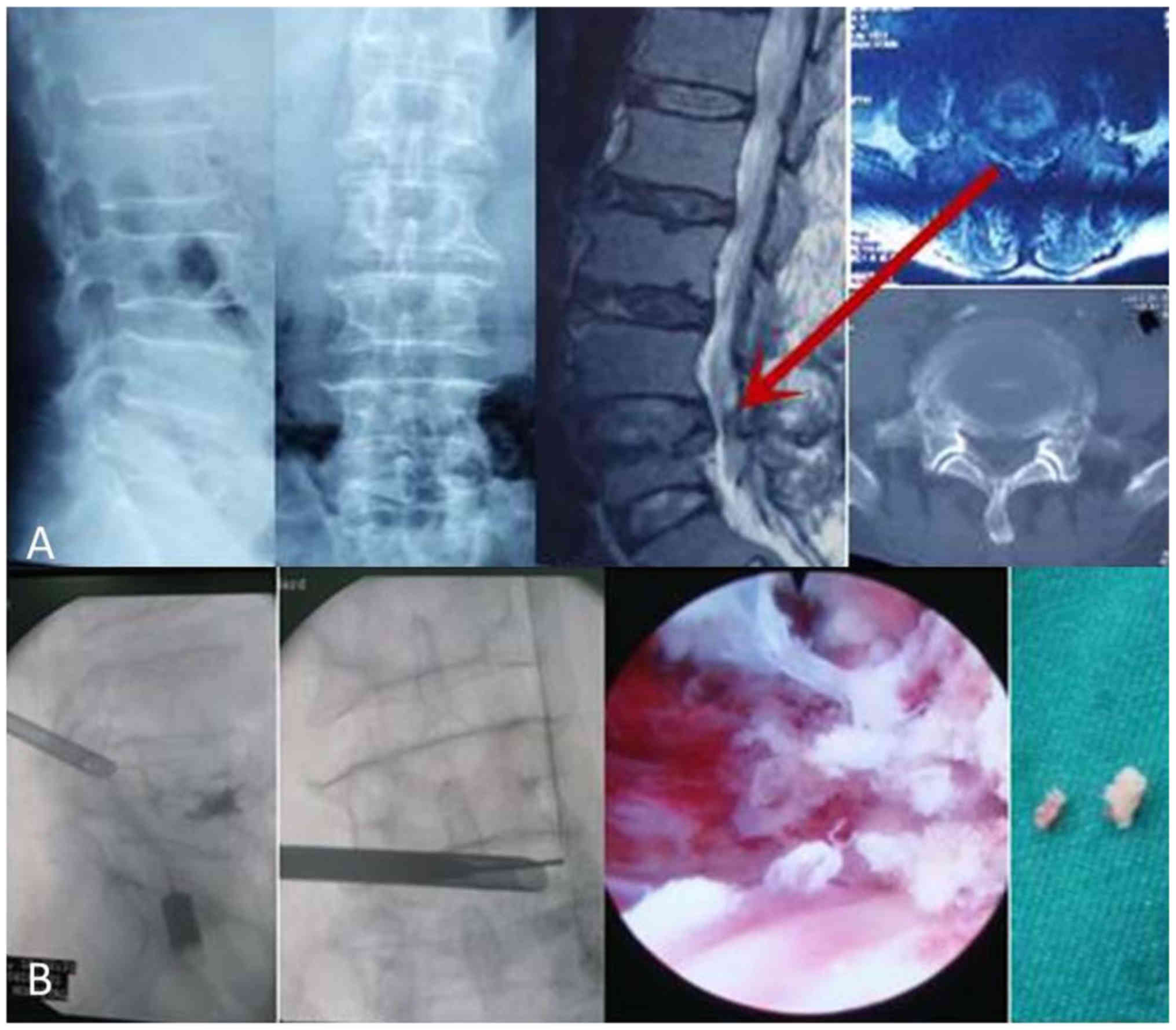
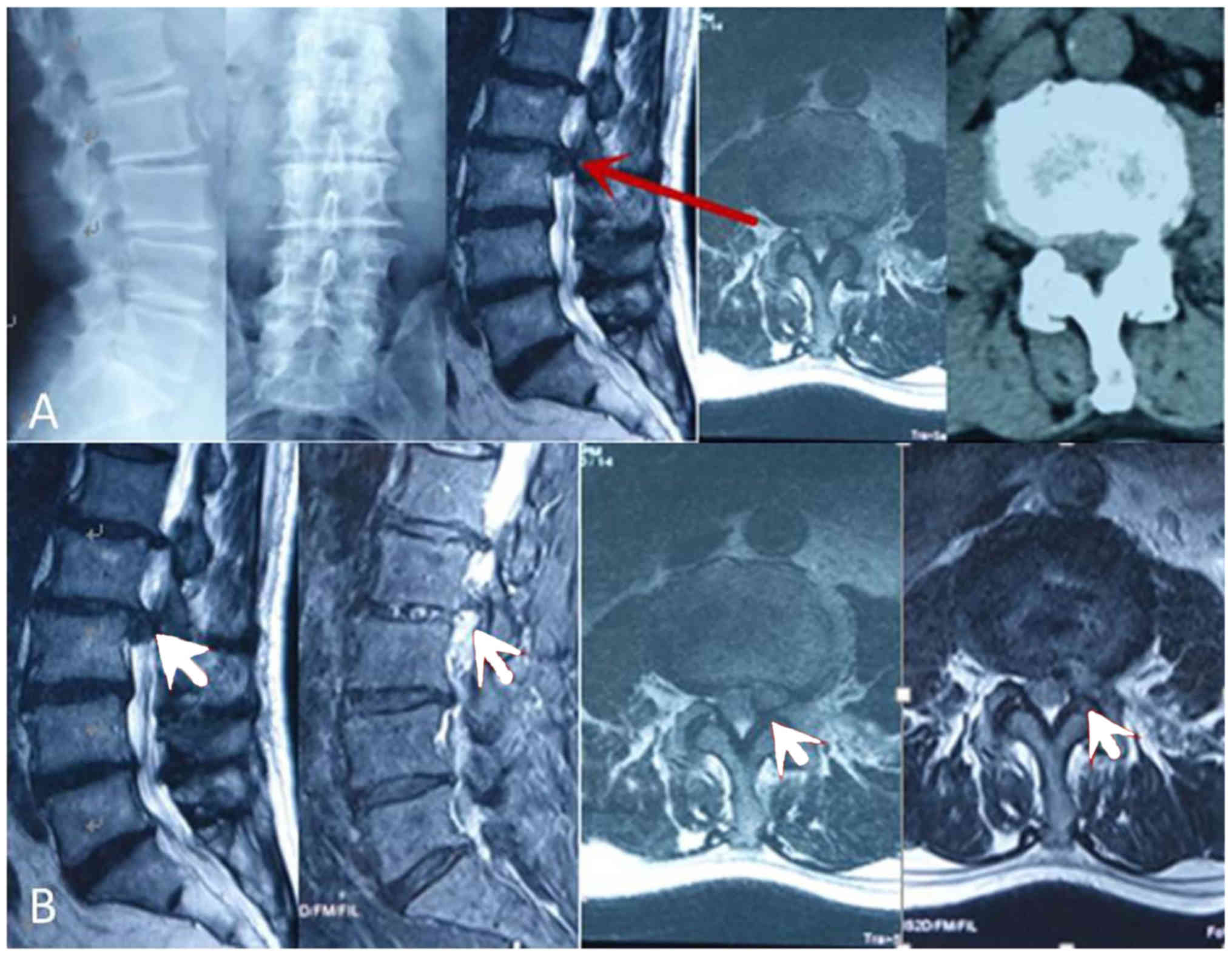
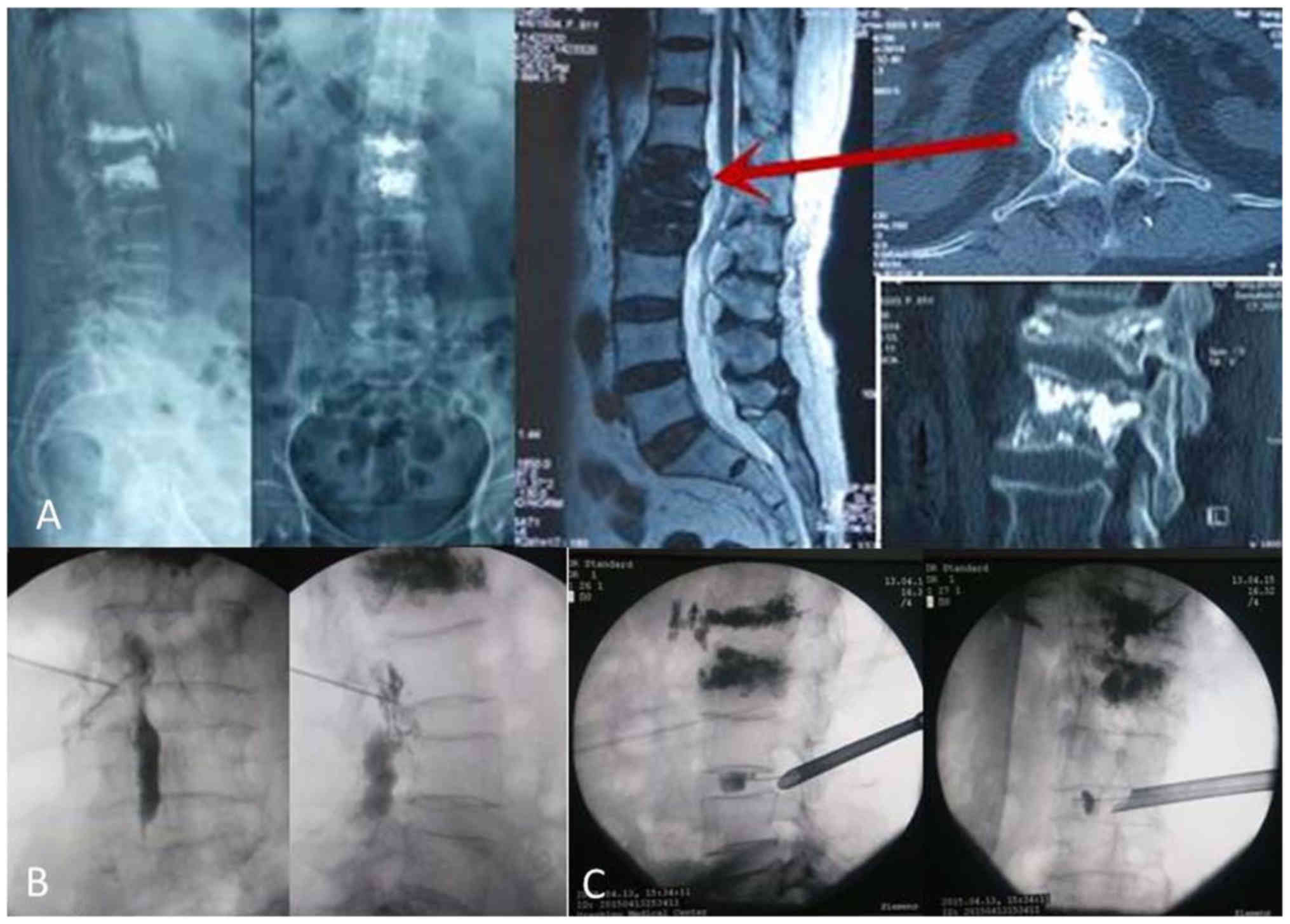
|
1
|
Siebert E, Prüss H, Klingebiel R, Failli
V, Einhäupl KM and Schwab JM: Lumbar spinal stenosis: Syndrome,
diagnostics and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 5:392–403. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aliabadi H and Isaacs R: Lumbar spinal
stenosis: A brief review. Neurosurg Quart. 19:200–206. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bresnahan L, Ogden AT, Natarajan RN and
Fessler RG: A biomechanical evaluation of graded posterior element
removal for treatment of lumbar stenosis: Comparison of a minimally
invasive approach with two standard laminectomy techniques. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 34:17–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kambin P: Arthroscopic microdiskectomy. Mt
Sinai J Med. 58:159–164. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piñera AR, Duran C, Lopez B, Saez I,
Correia E and Alvarez L: Instrumented lumbar arthrodesis in elderly
patients: Prospective study using cannulated cemented pedicle screw
instrumentation. Eur Spine J. 20 Suppl 3:S408–S414. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li G, Patil CG, Lad SP, Ho C, Tian W and
Boakye M: Effects of age and comorbidities on complication rates
and adverse outcomes after lumbar laminectomy in elderly patients.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:1250–1255. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yeung AT: The evolution of percutaneous
spinal endoscopy and discectomy: State of the art. Mt Sinai J Med.
67:327–332. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yeung AT and Tsou PM: Posterolateral
endoscopic excision for lumbar disc herniation: Surgical technique,
outcome, and complications in 307 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 27:722–731. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yeung AT and Yeung CA: Minimally invasive
techniques for the management of lumbar disc herniation. Orthop
Clin North Am. 38:363–372, abstract vi. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liao Z, Chen W and Wang CH: Transforaminal
percutaneous endoscopic surgery for far lateral lumbar
intervertebral disk herniation. Orthopedics. 37:e717–e727. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SH, Kang BU, Ahn Y, Choi G, Choi YG,
Ahn KU, Shin SW and Kang HY: Operative failure of percutaneous
endoscopic lumbar discectomy: A radiologic analysis of 55 cases.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:E285–E290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim CH, Chung CK, Choi Y, Shin S, Kim MJ,
Lee J and Park BJ: The selection of open or percutaneous endoscopic
lumbar discectomy according to an age cut-off point: Nationwide
cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:E1063–E1070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hoogland T, Schubert M, Miklitz B and
Ramirez A: Transforaminal posterolateral endoscopic discectomy with
or without the combination of a low-dose chymopapain: A prospective
randomized study in 280 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
31:E890–E897. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schlegel KF and Pon A: The biomechanics of
posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in spondylolisthesis. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 193:115–119. 1985.
|
|
15
|
Suri P, Miyakoshi A, Hunter DJ, Jarvik JG,
Rainville J, Guermazi A, Li L and Katz JN: Does lumbar spinal
degeneration begin with the anterior structures? A study of the
observed epidemiology in a community-based population. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 12:2022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang X, Tao L, Cui Z, Du Y and Yin H:
Application of rehabilitation nursing on spinal surgery. J
Changchun Univ Trad Chin Med. 23:130–132. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Kato S, Oshima Y, Oka H, Chikuda H,
Takeshita Y, Miyoshi K, Kawamura N, Masuda K, Kunogi J, Okazaki R,
et al: Comparison of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA)
Score and Modified JOA (mJOA) score for the assessment of cervical
myelopathy: A multicenter observational study. PLoS One.
10:e01230222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zanoli G, Strömqvist B and Jönsson B:
Visual analog scales for interpretation of back and leg pain
intensity in patients operated for degenerative lumbar spine
disorders. Spine. 26:(Phila Pa 1976). 2375–2380. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Galbusera F, van Rijsbergen M, Ito K,
Huyghe JM, Brayda-Bruno M and Wilke HJ: Ageing and degenerative
changes of the intervertebral disc and their impact on spinal
flexibility. Eur Spine J. 23 Suppl 3:S324–S332. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao F, Pollintine P, Hole BD, Dolan P and
Adams MA: Discogenic origins of spinal instability. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 30:2621–2630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeong SH, Kim HS and Kim SW: Mini-open
PLIF for moderate to high grade spondylolisthesis: Technique to
achieve spontaneous reduction. Korean J Spine. 12:251–255. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song D, Chen Z, Song D and Li Z:
Comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) with
autogenous bone chips and PLIF with cage for treatment of
double-level isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.
138:111–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bai J, Zhang W, Zhang X, Sun Y, Ding W and
Shen Y: A clinical investigation of contralateral neurological
symptom after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF). Med
Sci Monit. 21:1831–1838. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian Y and Liu X: Clinical outcomes of two
minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF)
for lumbar degenerative diseases. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.
26:745–751. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee DY and Lee SH: Learning curve for
percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).
48:383–389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tanaka N, An HS, Lim TH, Fujiwara A, Jeon
CH and Haughton VM: The relationship between disc degeneration and
flexibility of the lumbar spine. Spine J. 1:47–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schaffer JL and Kambin P: Percutaneous
posterolateral lumbar discectomy and decompression with a
6.9-millimeter cannula. Analysis of operative failures and
complications. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 73:822–831. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schreiber A, Suezawa Y and Leu H: Does
percutaneous nucleotomy with discoscopy replace conventional
discectomy? Eight years of experience and results in treatment of
herniated lumbar disc. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 35–42. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choy DS: Percutaneous laser disc
decompression (PLDD): A first line treatment for herniated discs. J
Clin Laser Med Surg. 19:1–2. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ozgur BM, Aryan HE, Pimenta L and Taylor
WR: Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion (XLIF): A novel surgical
technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 6:435–443.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mummaneni PV and Rodts GE Jr: The
mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurgery. 57
Suppl 4:S256–S261. 2005.
|
|
32
|
Ozgur BM, Hughes SA, Baird LC and Taylor
WR: Minimally disruptive decompression and transforaminal lumbar
interbody fusion. Spine J. 6:27–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jasper GP, Francisco GM and Telfeian AE: A
retrospective evaluation of the clinical success of transforaminal
endoscopic discectomy with foraminotomy in geriatric patients. Pain
Physician. 16:225–229. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hoogland T, van den Brekel-Dijkstra K,
Schubert M and Miklitz B: Endoscopic transforaminal discectomy for
recurrent lumbar disc herniation: A prospective, cohort evaluation
of 262 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:973–978. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nicol M, Sun Y, Craig N and Wardlaw D:
Incidence of thromboembolic complications in lumbar spinal surgery
in 1,111 patients. Eur Spine J. 18:1548–1552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|