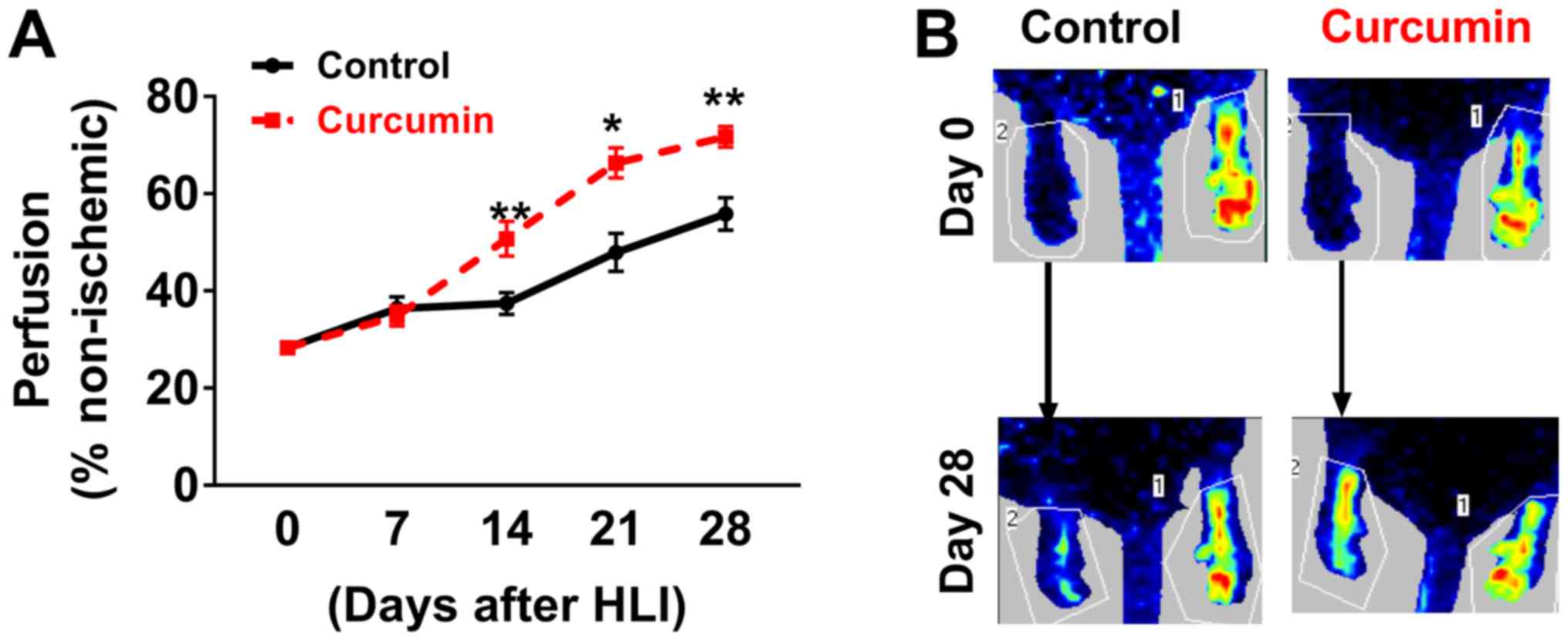
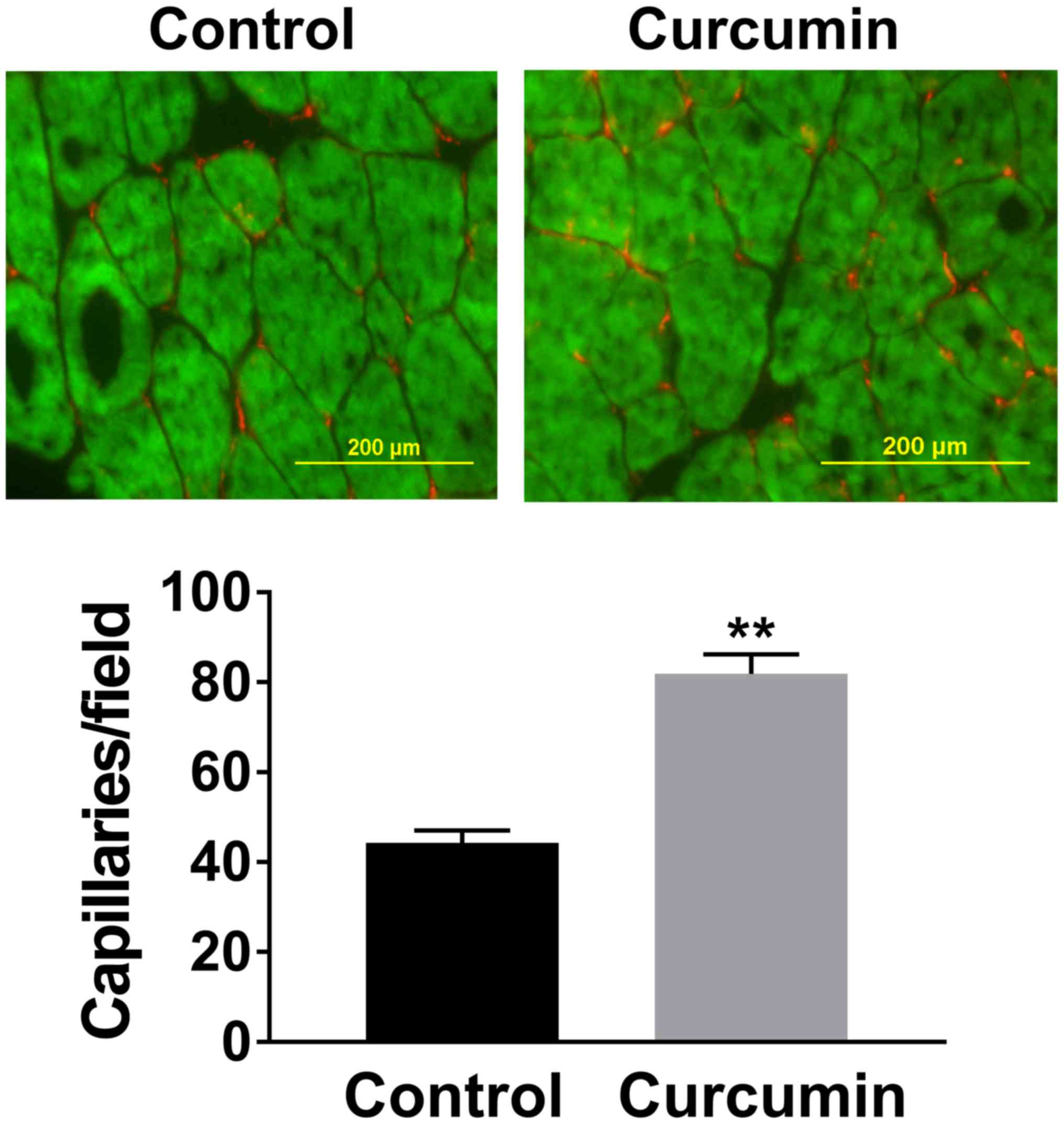
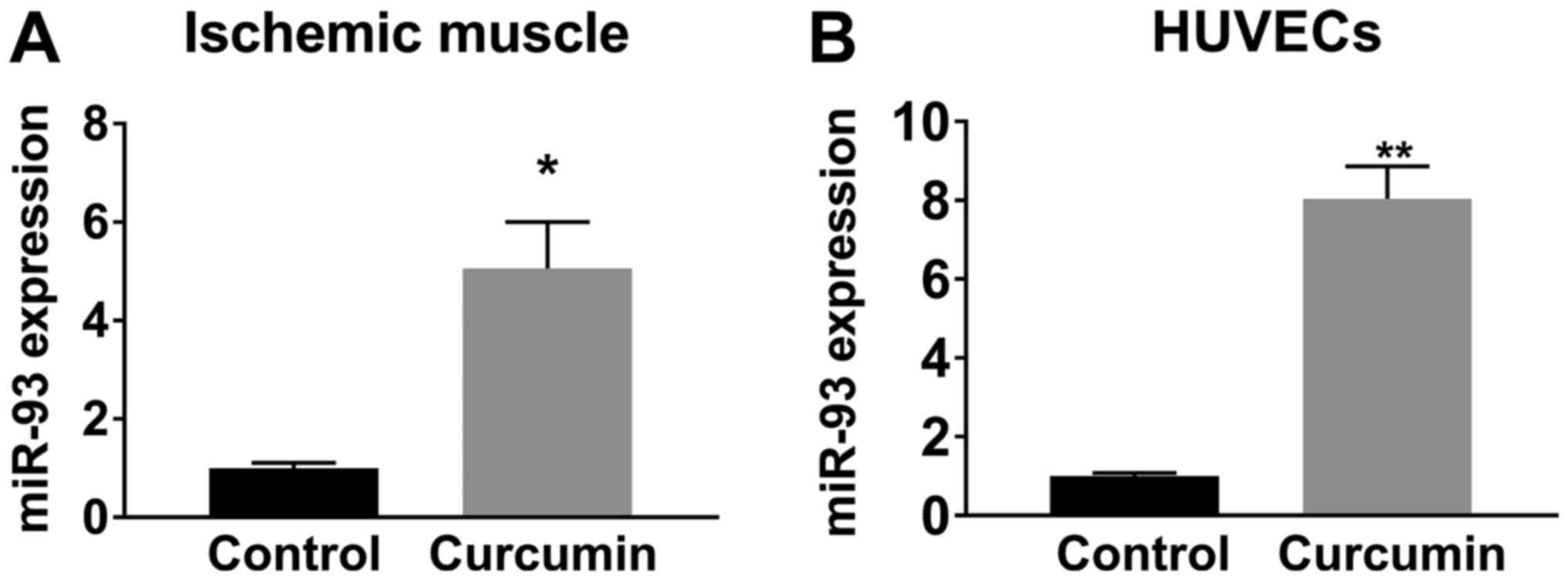
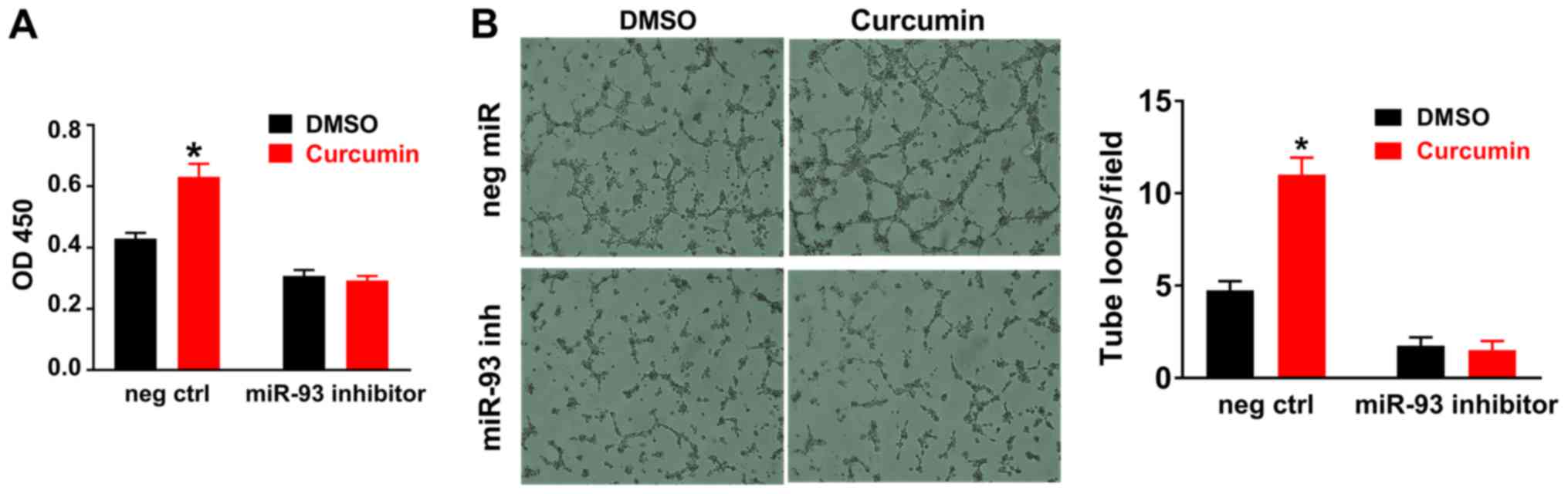
|
1
|
Guerchet M, Aboyans V, Mbelesso P, Mouanga
AM, Salazar J, Bandzouzi B, Tabo A, Clément JP, Preux PM and
Lacroix P: Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease in elder
general population of two cities of Central Africa: Bangui and
Brazzaville. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 44:164–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Criqui MH and Aboyans V: Epidemiology of
peripheral artery disease. Circ Res. 116:1509–1526. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fowkes FG, Aboyans V, Fowkes FJ, McDermott
MM, Sampson UK and Criqui MH: Peripheral artery disease:
Epidemiology and global perspectives. Nat Rev Cardiol. 14:156–170.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Espinola-Klein C and Savvidis S:
Peripheral arterial disease. Epidemiology, symptoms and diagnosis.
Internist (Berl). 50:919–926. 2009.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grundmann S, Piek JJ, Pasterkamp G and
Hoefer IE: Arteriogenesis: Basic mechanisms and therapeutic
stimulation. Eur J Clin Invest. 37:755–766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hirsch AT: Treatment of peripheral
arterial disease-extending ‘intervention’ to ‘therapeutic choice’.
N Engl J Med. 354:1944–1947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Joh JH, Joo SH and Park HC: Simultaneous
hybrid revascularization for symptomatic lower extremity arterial
occlusive disease. Exp Ther Med. 7:804–810. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aviles RJ, Annex BH and Lederman RJ:
Testing clinical therapeutic angiogenesis using basic fibroblast
growth factor (FGF-2). Brit J Pharmacol. 140:637–646. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Owens CD and Conte MS: Medical management
of peripheral arterial disease: Bridging the ‘Gap’? Circulation.
126:1319–1321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Annex BH: Therapeutic angiogenesis for
critical limb ischaemia. Nat Rev Cardiol. 10:387–396. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Allegra A, Innao V, Russo S, Gerace D,
Alonci A and Musolino C: Anticancer activity of curcumin and its
analogues: Preclinical and clinical studies. Cancer Invest.
35:1–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goozee KG, Shah TM, Sohrabi HR,
Rainey-Smith SR, Brown B, Verdile G and Martins RN: Examining the
potential clinical value of curcumin in the prevention and
diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Br J Nutr. 115:449–465. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiménez-Osorio AS, Monroy A and Alavez S:
Curcumin and insulin resistance-Molecular targets and clinical
evidences. Biofactors. 42:561–580. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
You J, Sun J, Ma T, Yang Z, Wang X, Zhang
Z, Li J, Wang L, Ii M, Yang J and Shen Z: Curcumin induces
therapeutic angiogenesis in a diabetic mouse hindlimb ischemia
model via modulating the function of endothelial progenitor cells.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:1822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barrett PM, Wall CAM and Stack AG:
Peripheral artery disease prevalence and mortality trends of United
States dialysis population: 1995–2005. Irish J Med Sci.
179:S409–S410. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Waters RE, Terjung RL, Peters KG and Annex
BH: Preclinical models of human peripheral arterial occlusive
disease: Implications for investigation of therapeutic agents. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 97:773–780. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Albadawi H, Oklu R, Cormier NR, O'Keefe
RM, Heaton JT, Kobler JB, Austen WG and Watkins MT: Hind limb
ischemia-reperfusion injury in diet-induced obese mice. J Surg Res.
190:683–691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baudin B, Bruneel A, Bosselut N and
Vaubourdolle M: A protocol for isolation and culture of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Nat Protoc. 2:481–485. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hazarika S, Farber CR, Dokun AO,
Pitsillides AN, Wang T, Lye RJ and Annex BH: MicroRNA-93 controls
perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia by modulating expression
of multiple genes in the cell cycle pathway. Circulation.
127:1818–1828. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elavarasu S, Suthanthiran T, Thangavelu A,
Alex S, Palanisamy VK and Kumar TS: Evaluation of superoxide
dismutase levels in local drug delivery system containing 0.2%
curcumin strip as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in chronic
periodontitis: A clinical and biochemical study. J Pharm Bioallied
Sci. 8 Suppl 1:S48–S52. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang F, Yao Y, Wu J, Liu Q, Zhang J, Pu
X, Zhang Q and Xia L: Curcumin inhibits gastric cancer-derived
mesenchymal stem cells mediated angiogenesis by regulating
NF-kB/VEGF signaling. Am J Transl Res. 9:5538–5547. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
González-Duarte RJ, Cázares-Ordoñez V and
Ávila-Chávez E: The microRNA biogenesis machinery: Regulation by
steroid hormones and alterations in cancer. Rev Invest Clin.
66:460–464. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jonas S and Izaurralde E: Towards a
molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat
Rev Genet. 16:421–433. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou X, Yuan P and He Y: Role of microRNAs
in peripheral artery disease (review). Mol Med Rep. 6:695–700.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ganta VC, Choi MH, Kutateladze A, Fox TE,
Farber CR and Annex BH: A MicroRNA93-interferon regulatory
factor-9-immunoresponsive gene-1-itaconic acid pathway
modulatesM2-like macrophage polarization to revascularize ischemic
muscle. Circulation. 135:2403–2425. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|